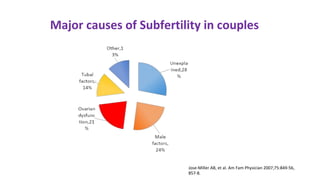
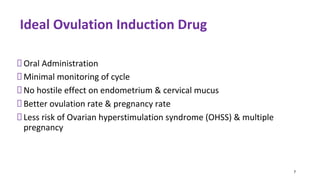
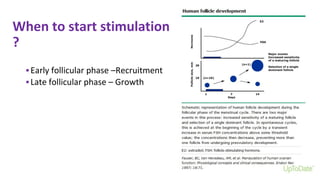
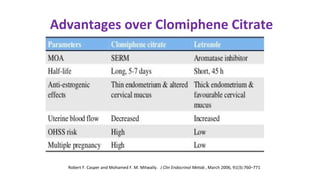
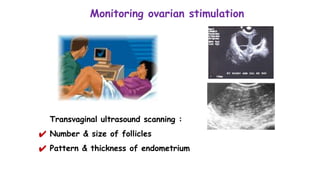
Dr. Laxmi Shrikhande is a prominent figure in obstetrics and gynecology, holding various leadership roles and receiving multiple awards for her contributions, particularly in women's health. The document discusses the clinical approach to ovulation induction, highlighting letrozole as the preferred treatment over clomiphene citrate for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Recommendations include monitoring ovarian stimulation and adjusting treatment based on individual patient needs and conditions.