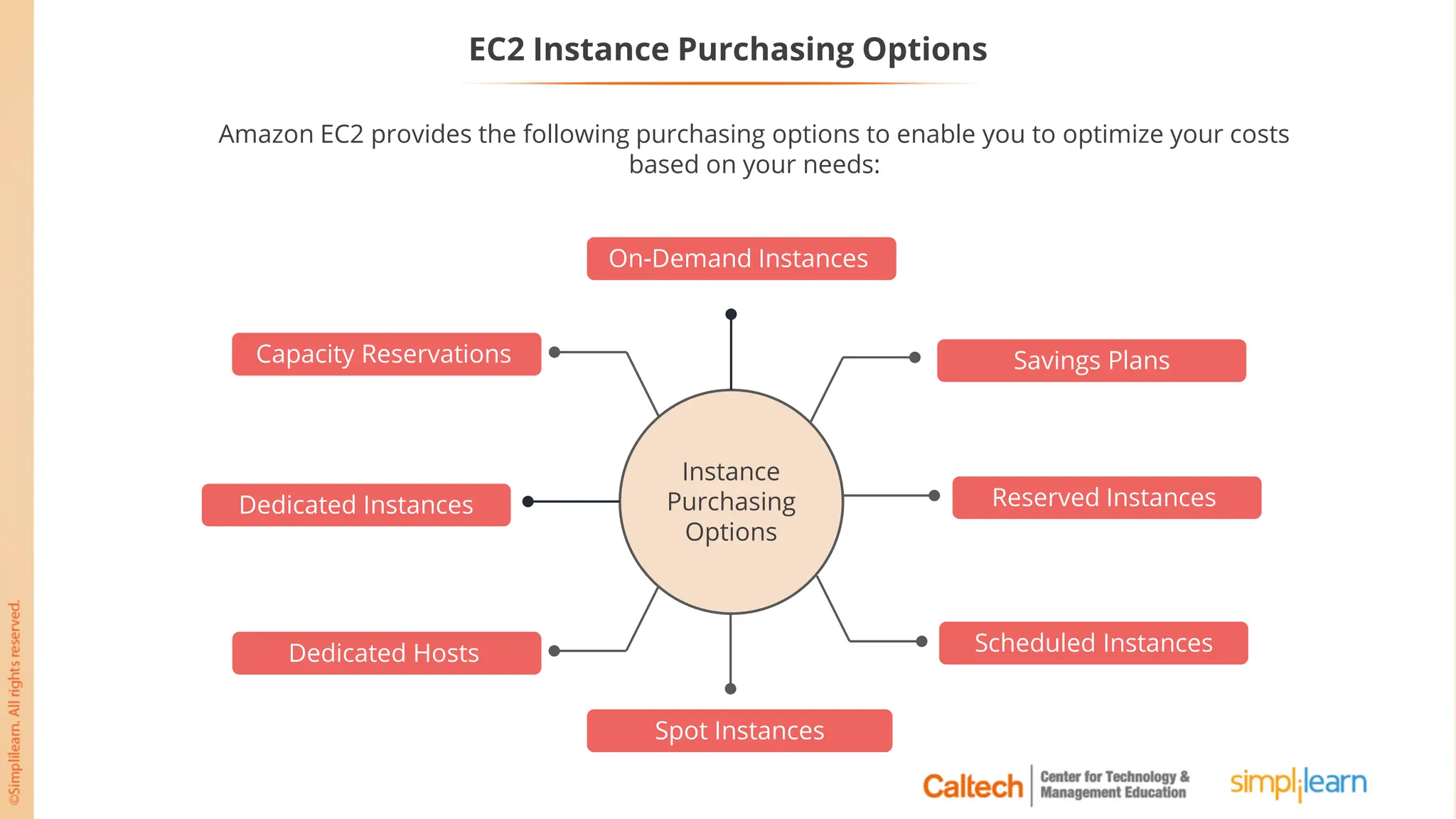
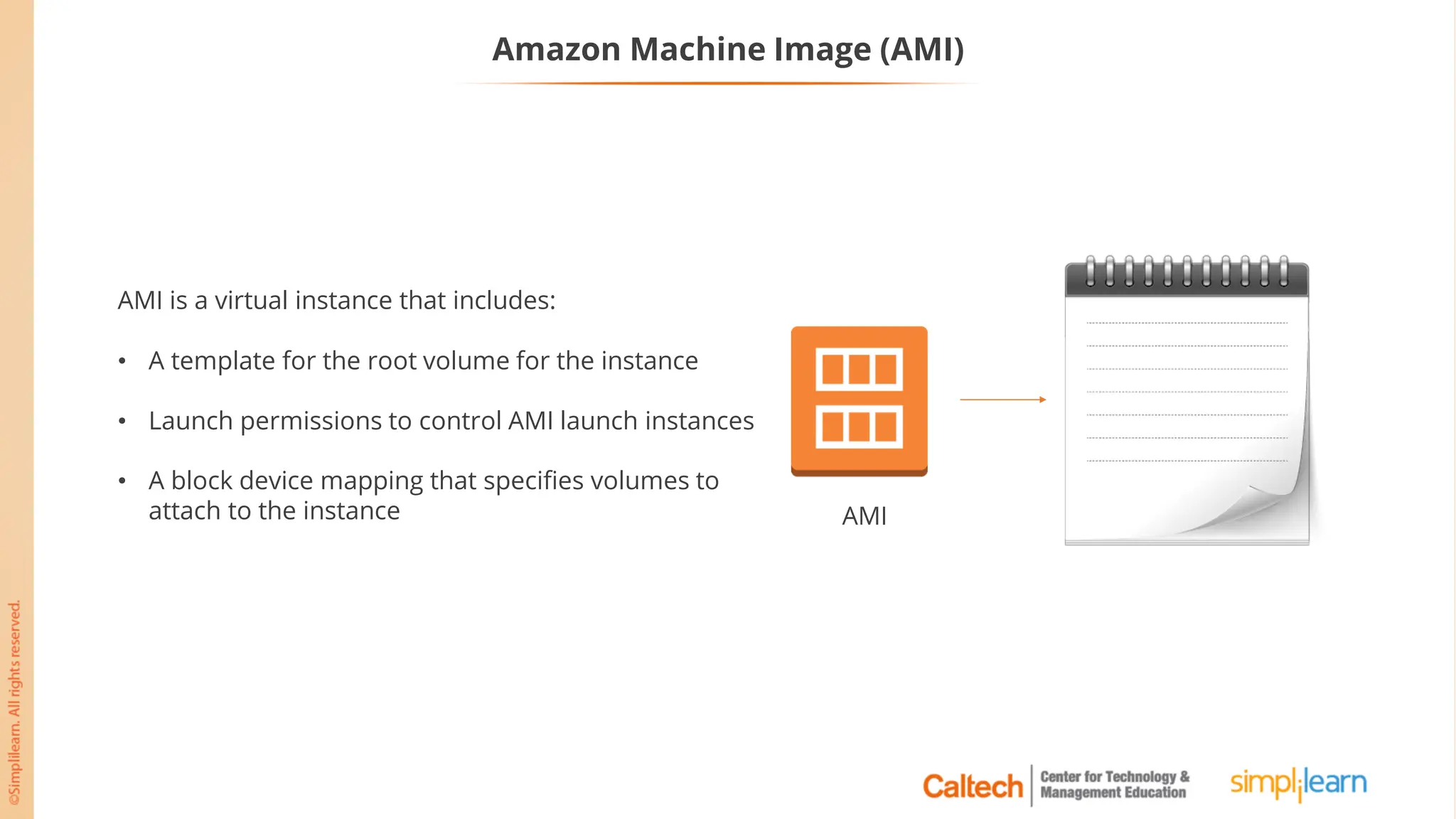
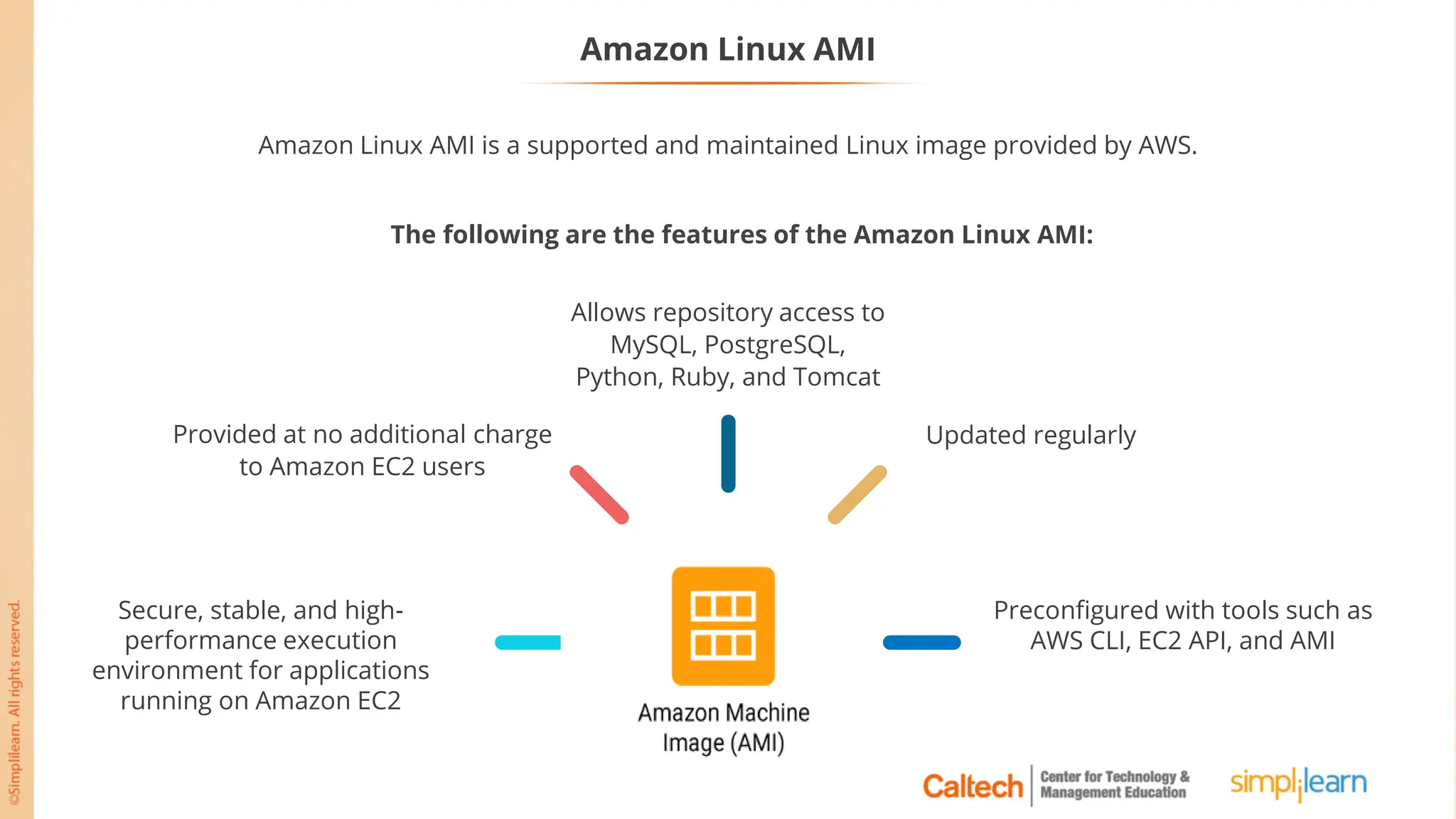
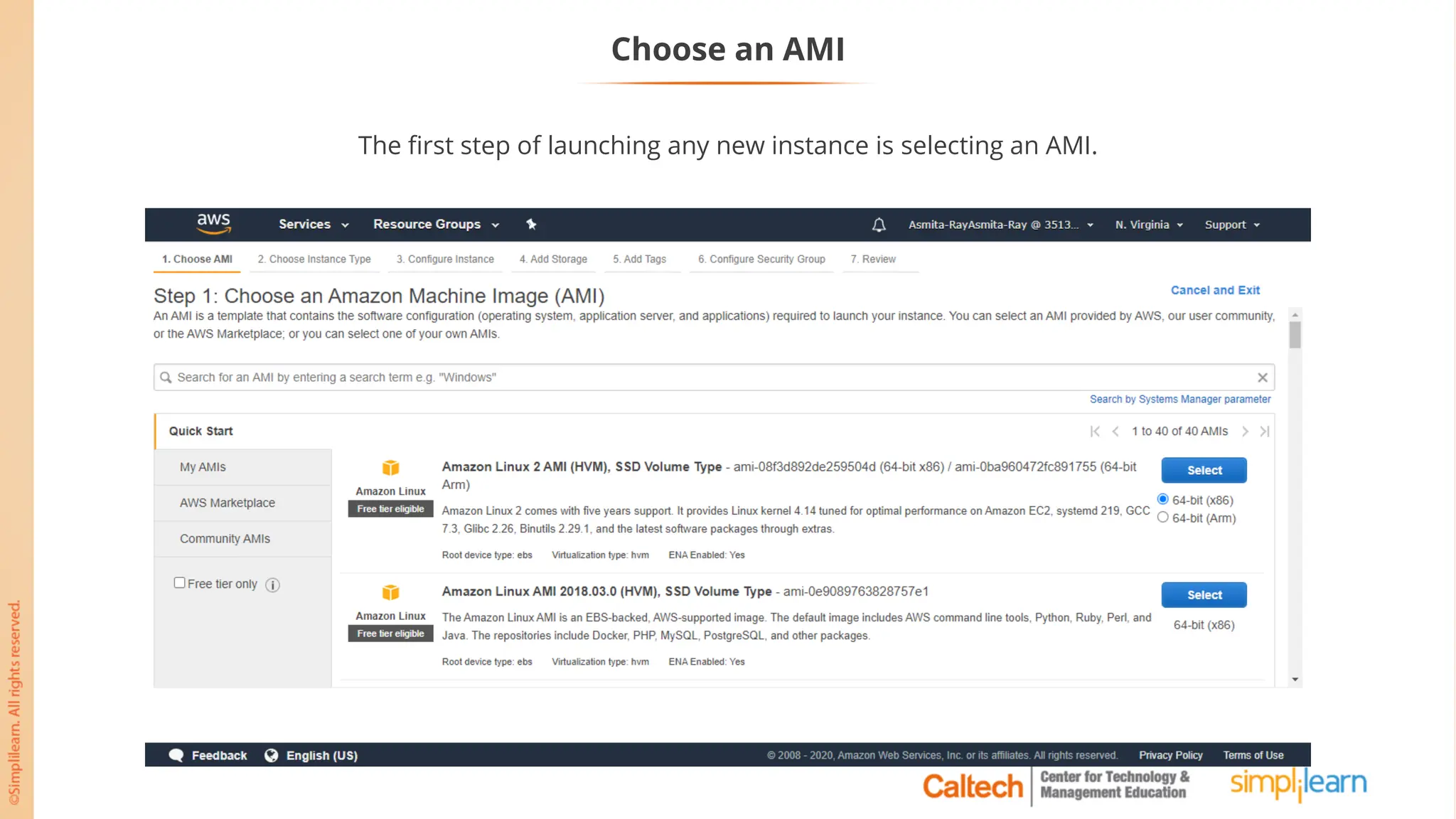
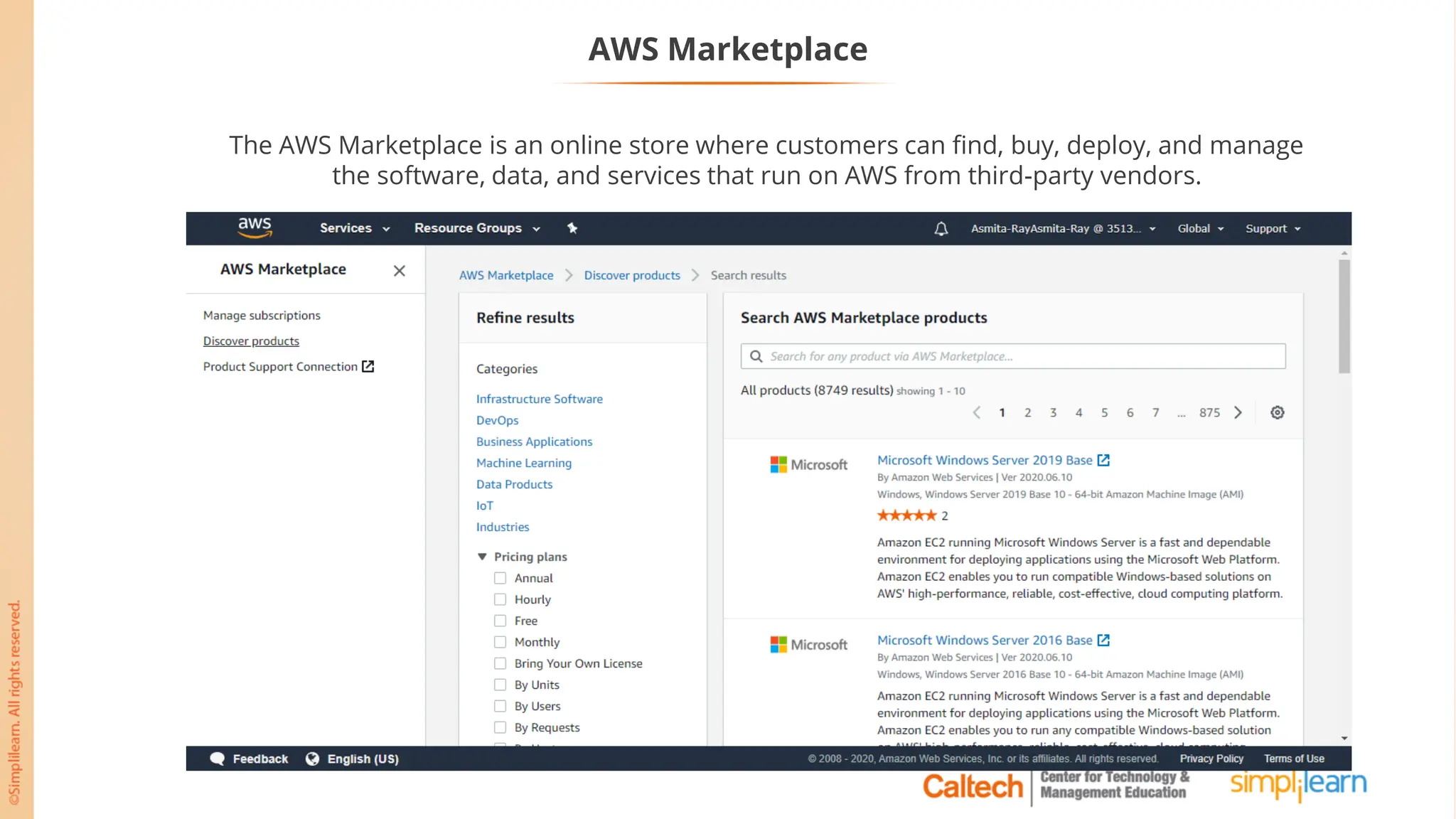
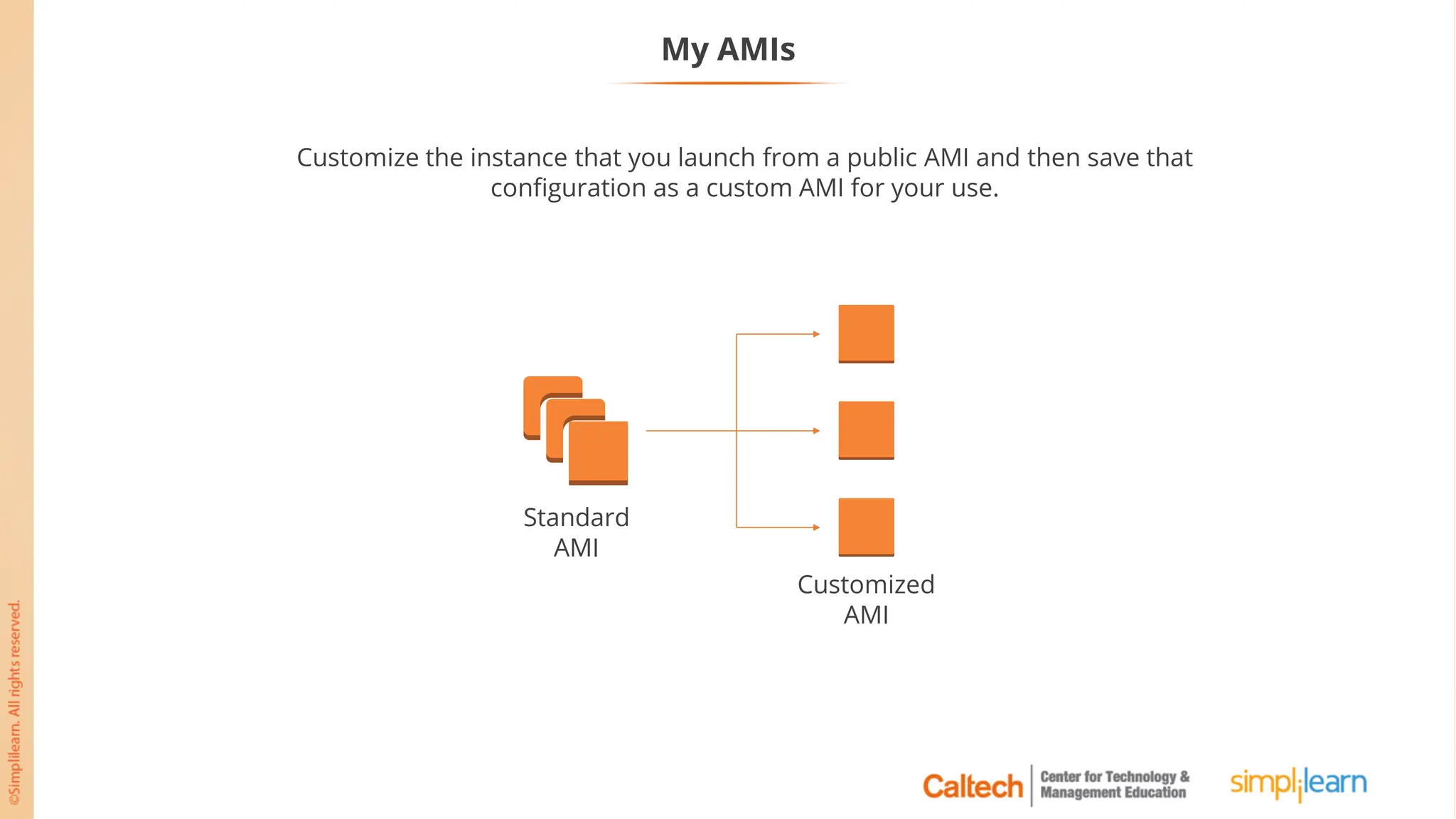
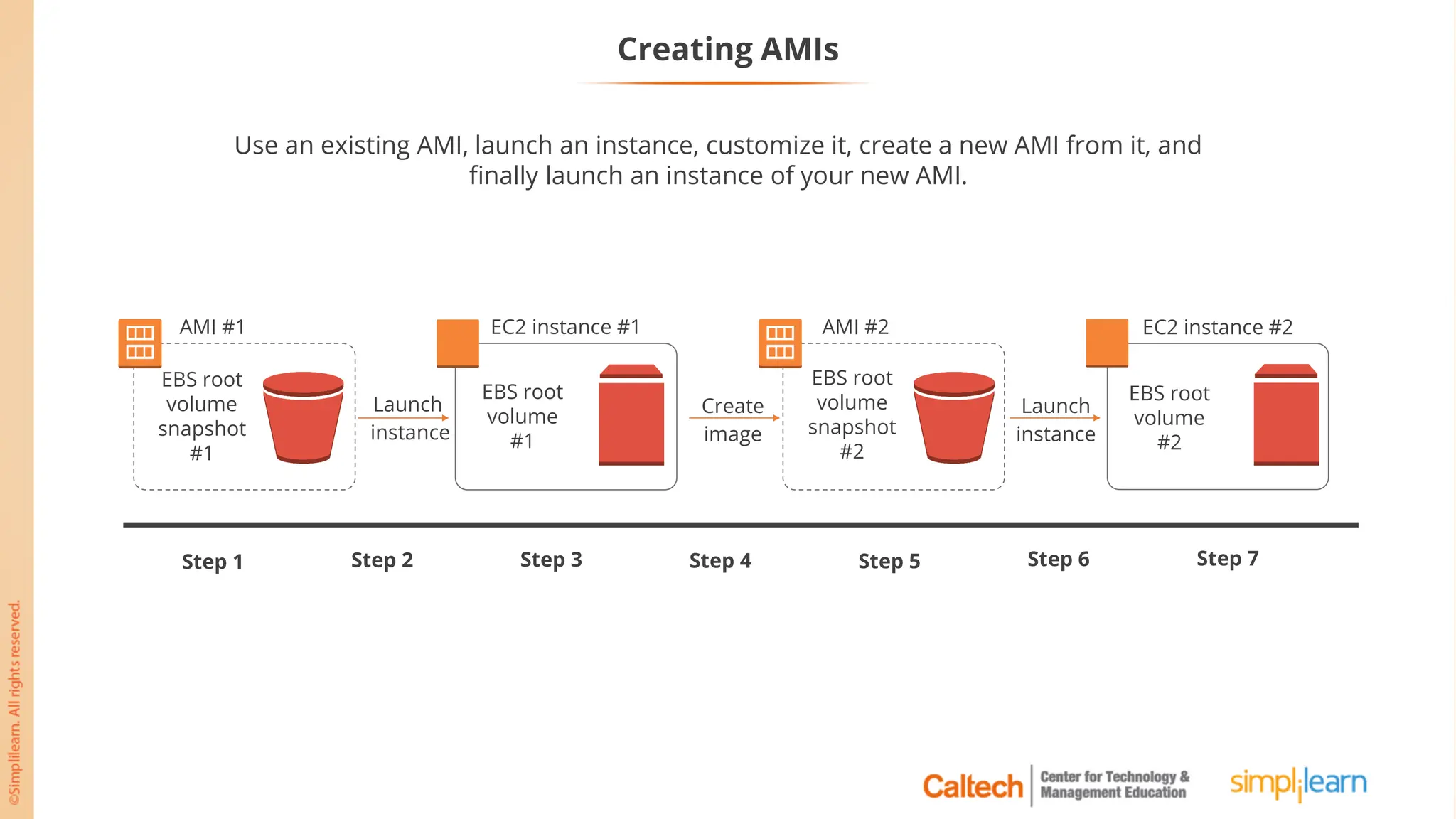
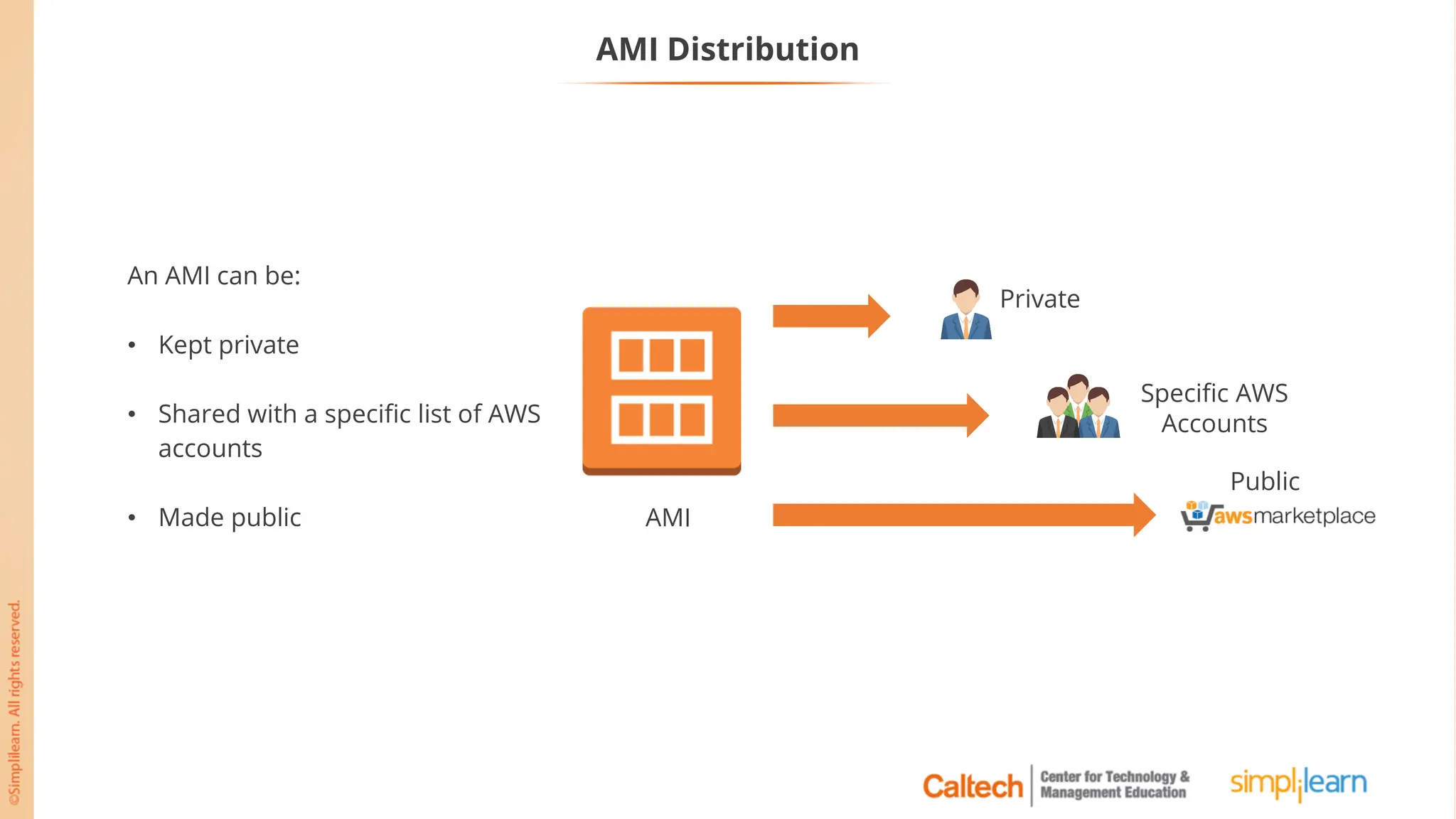
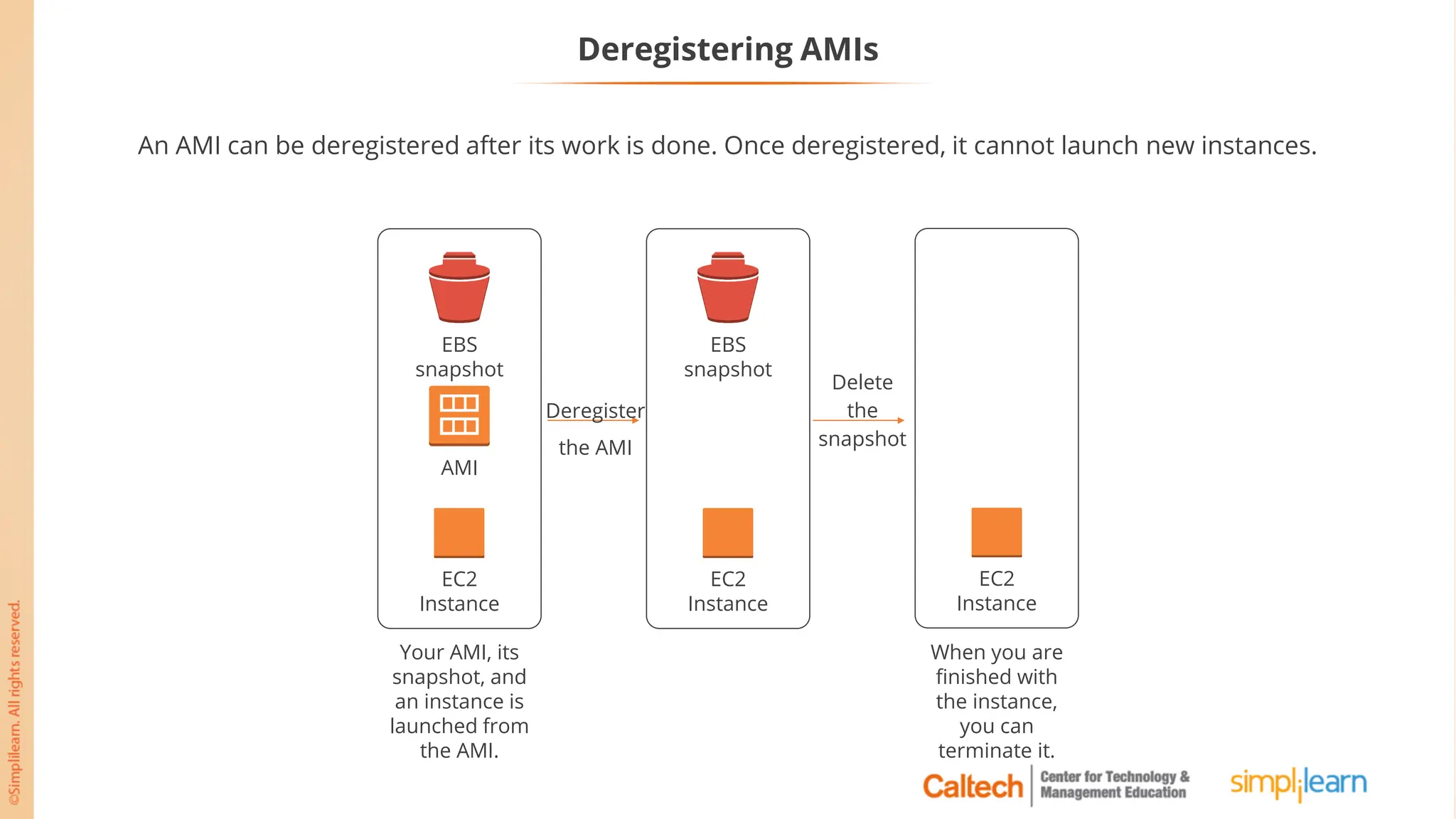
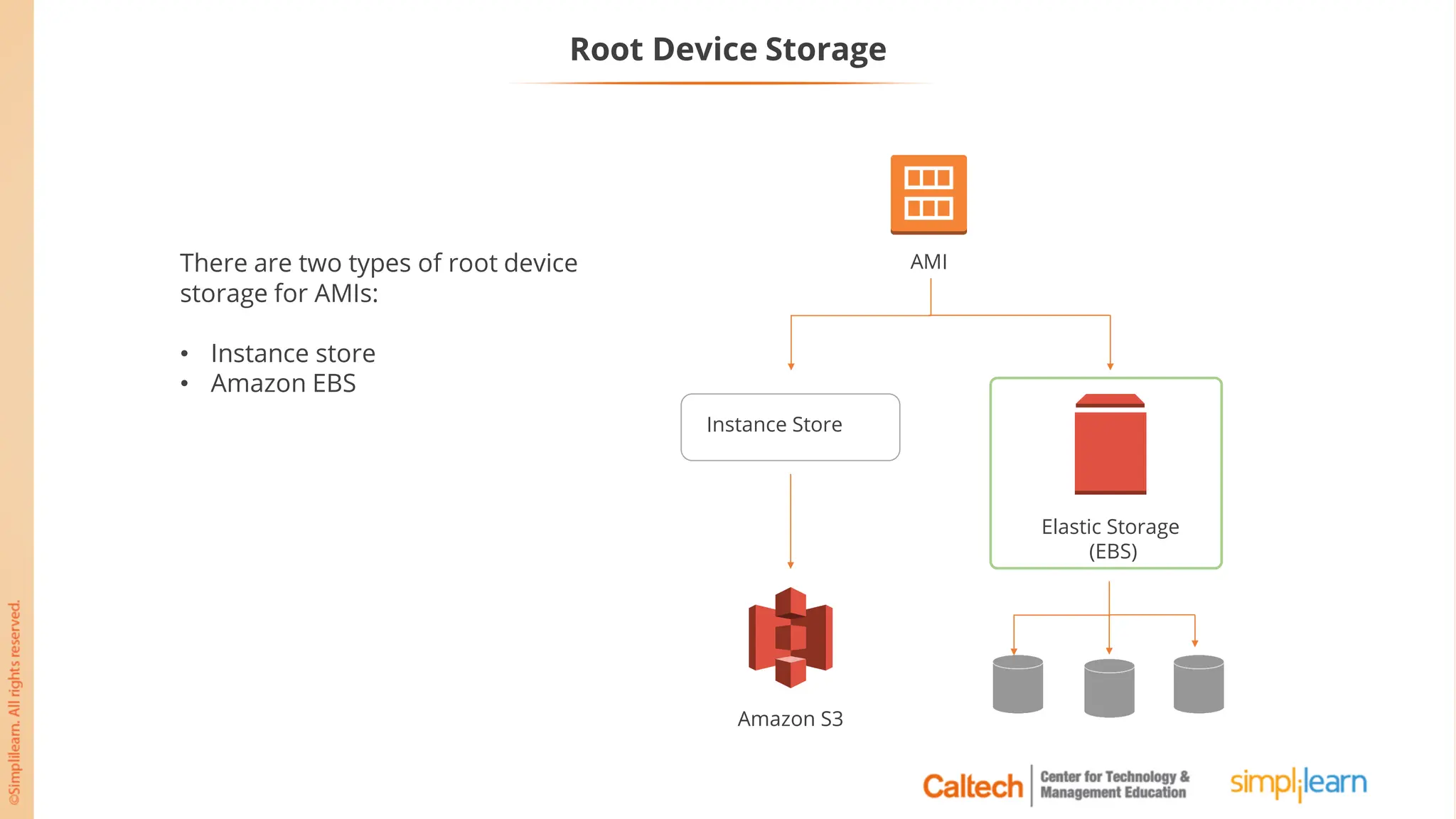
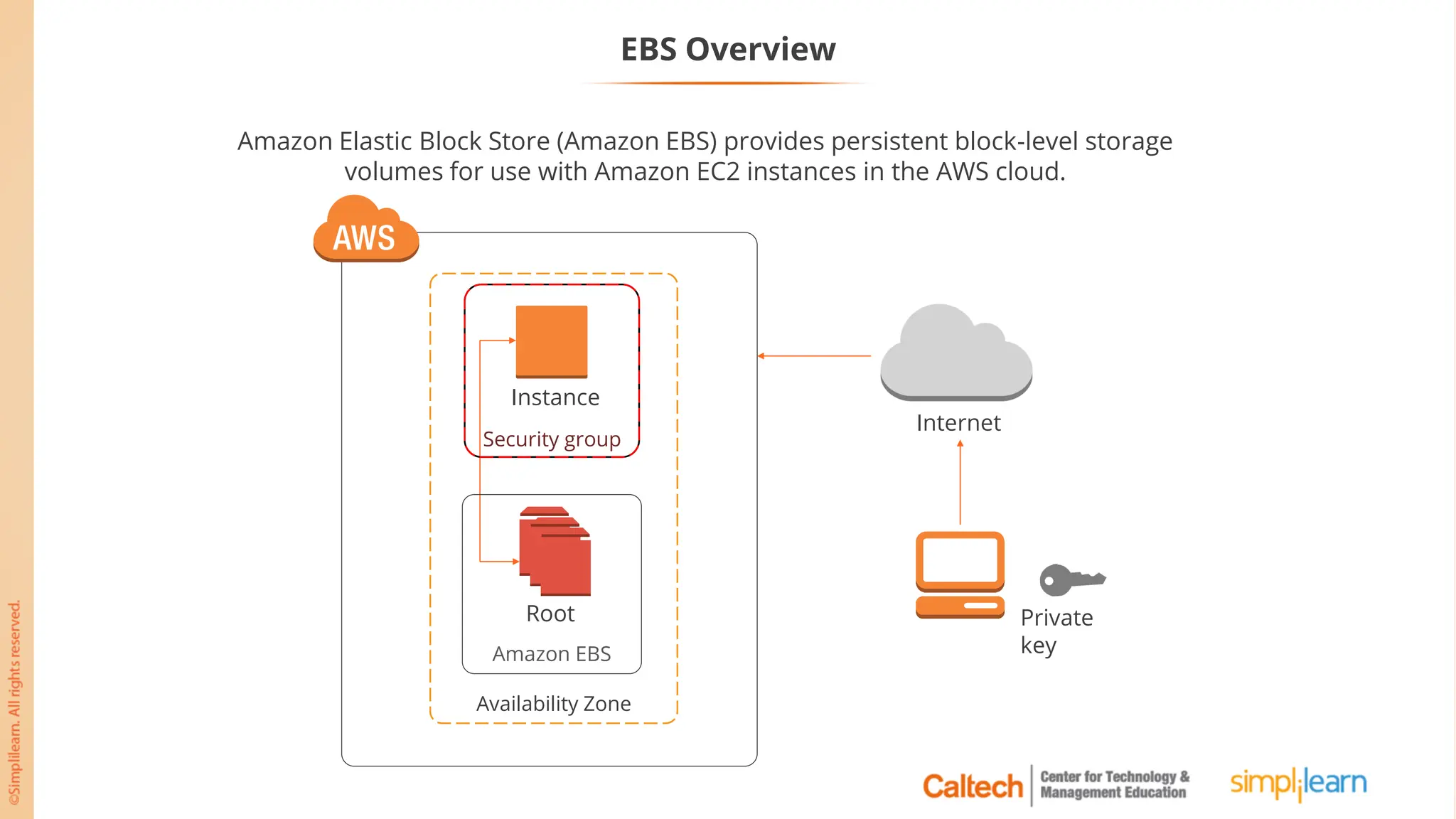
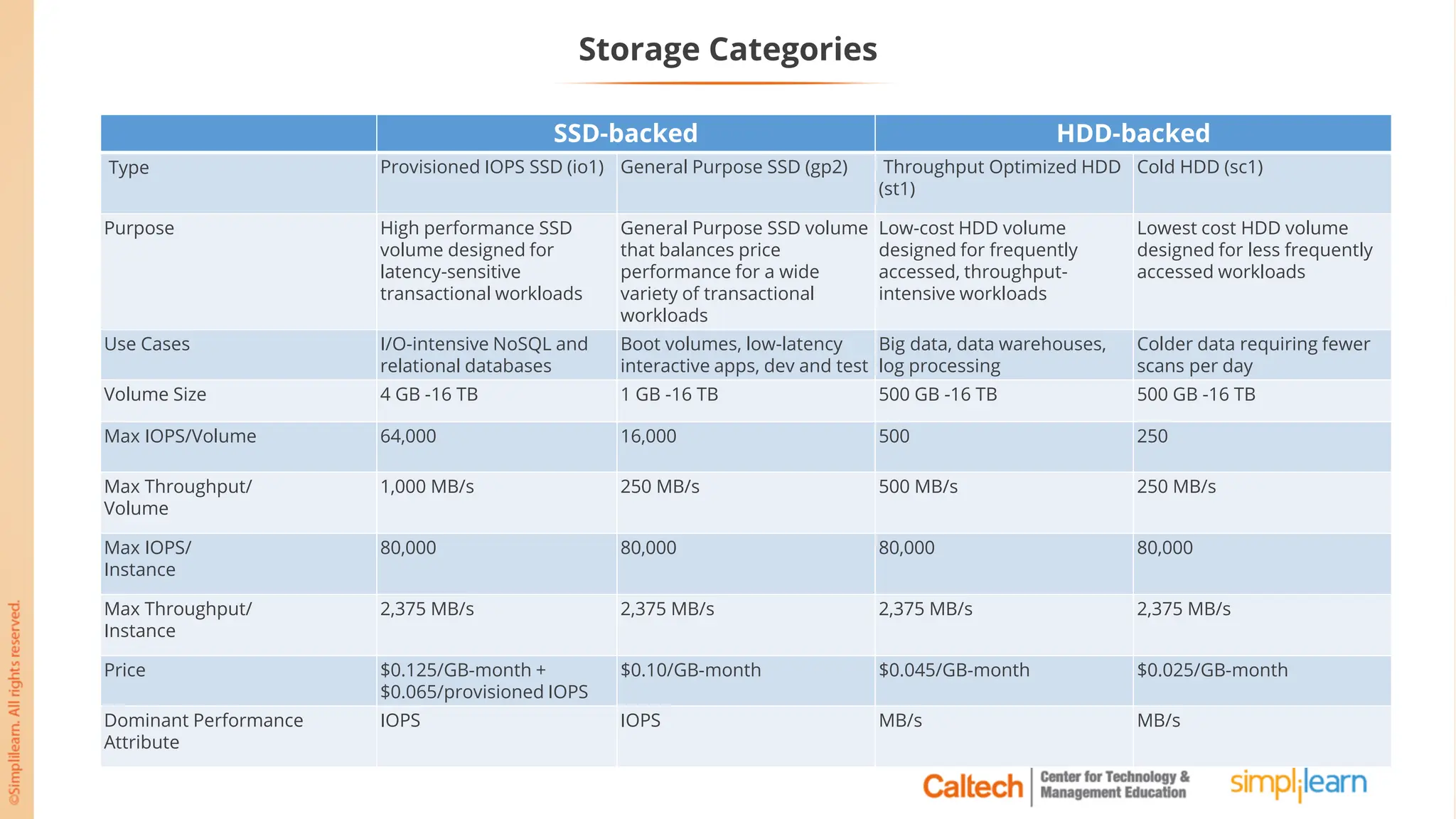
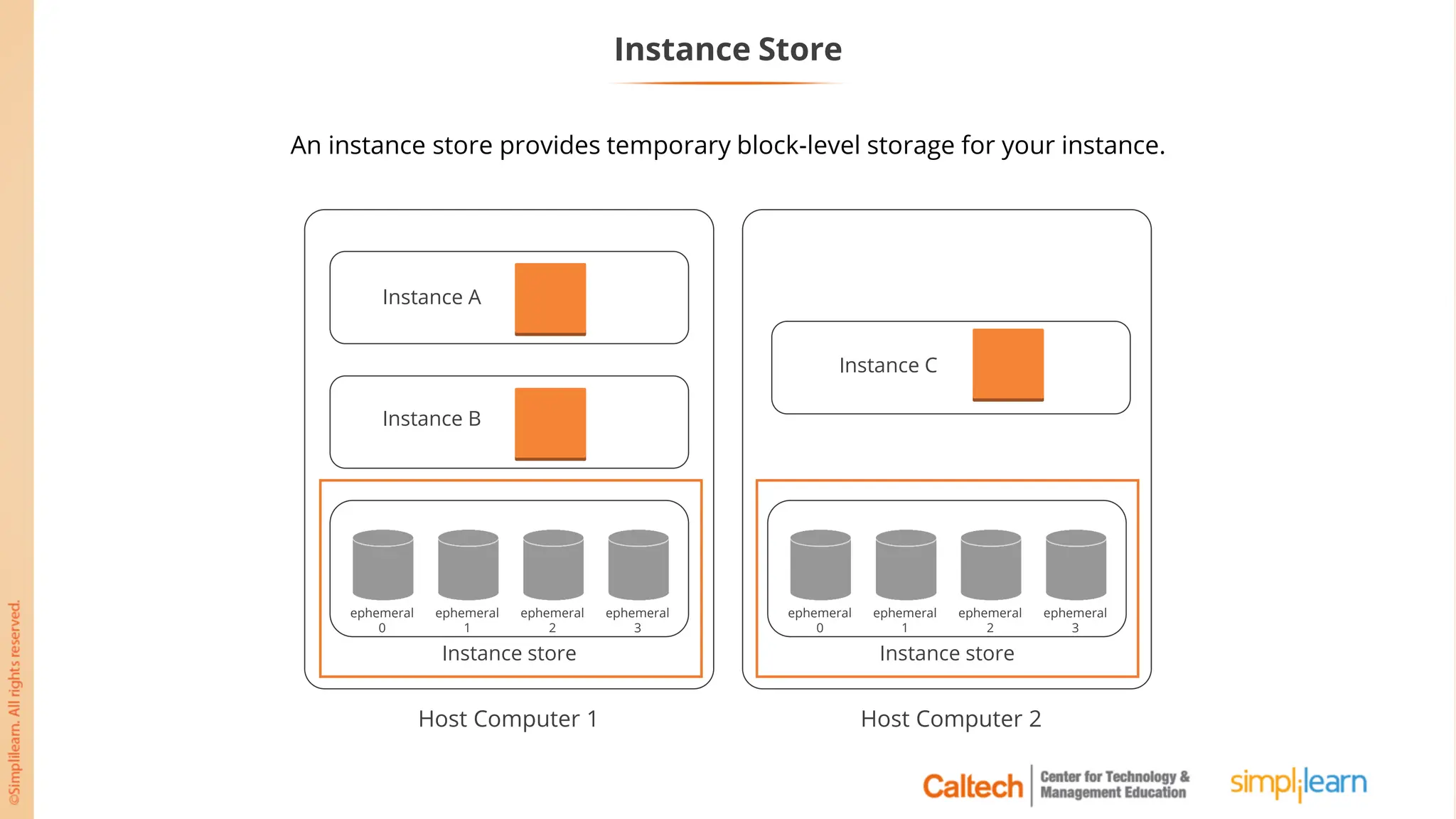
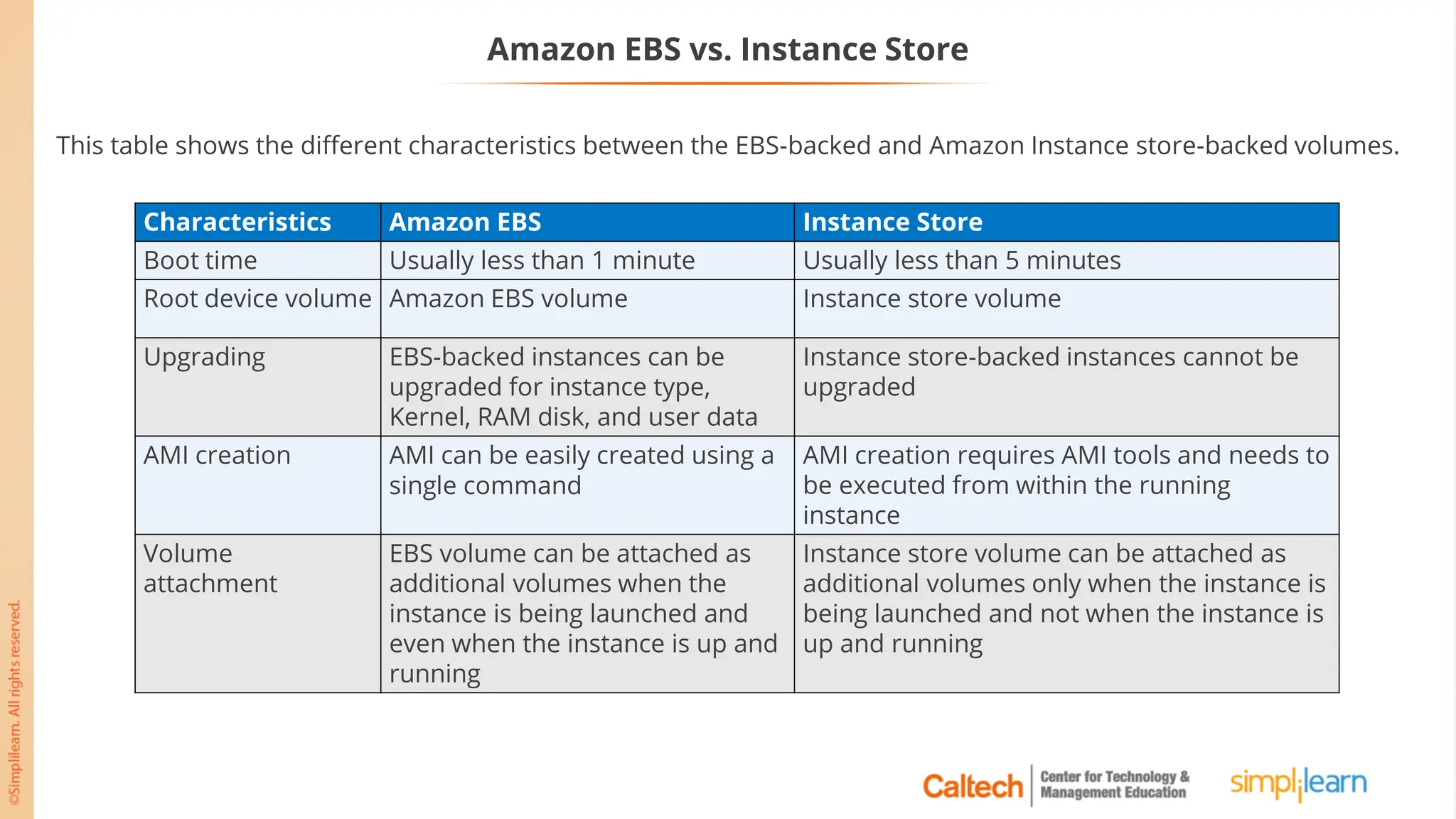
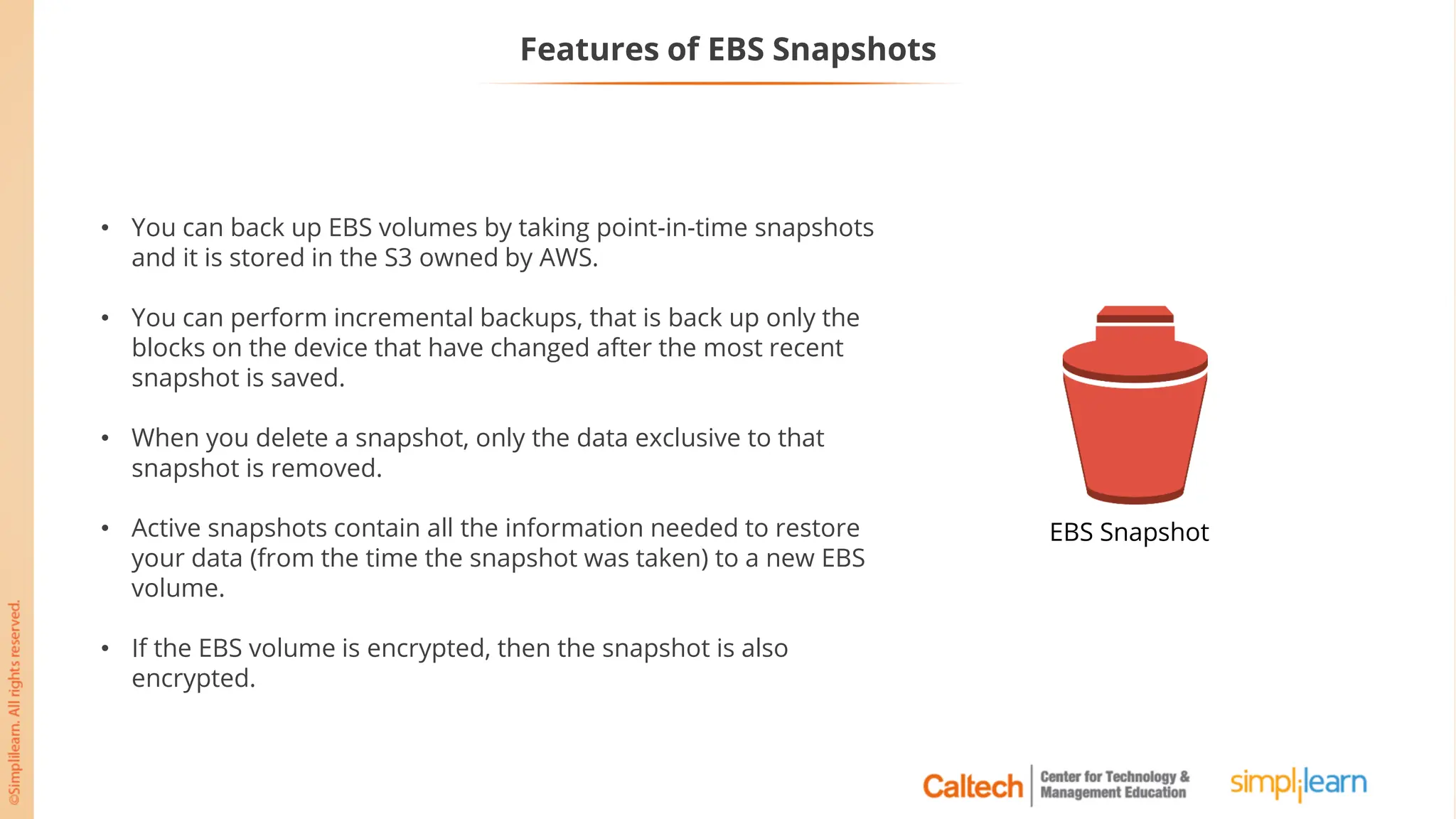
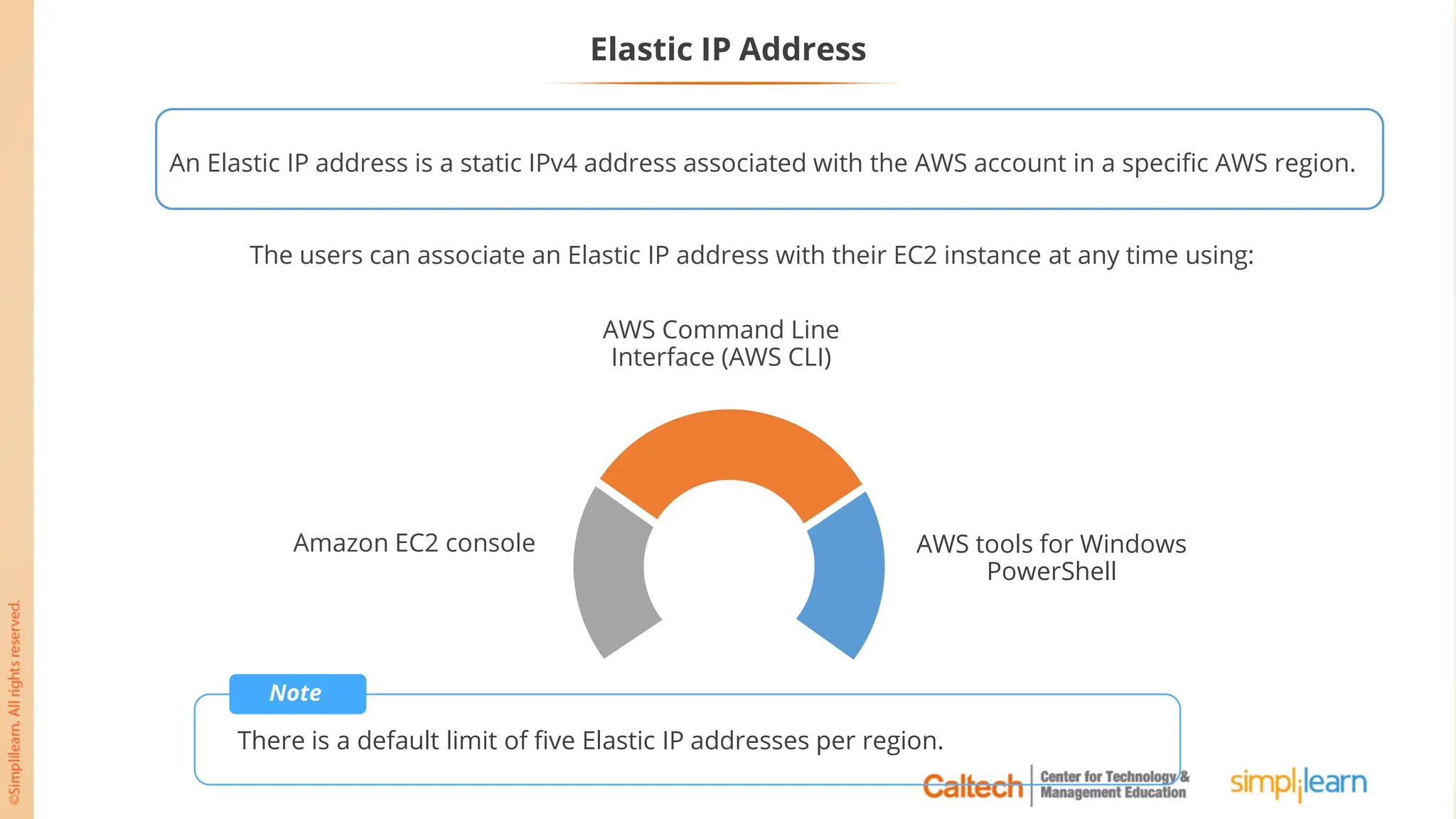
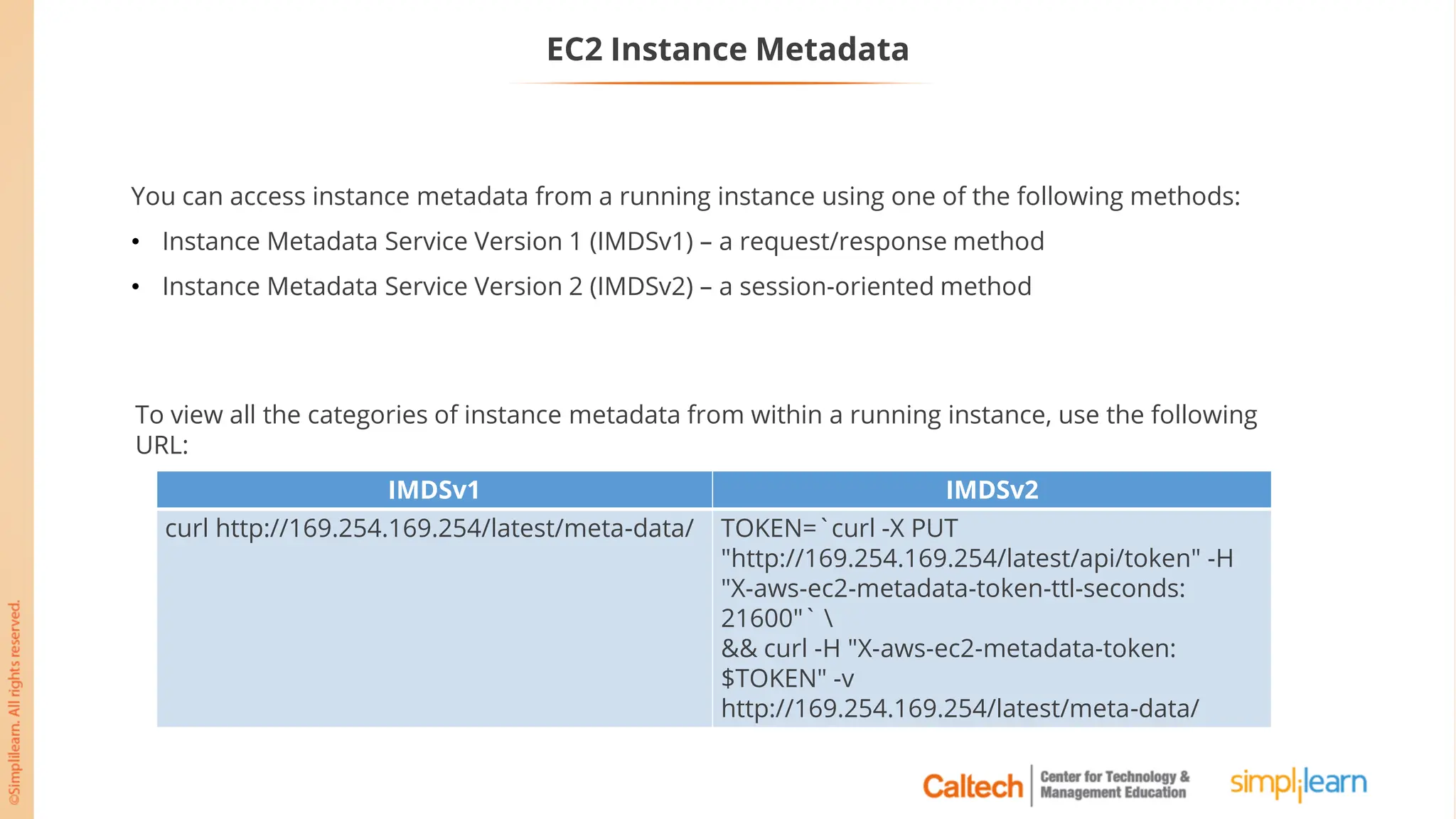
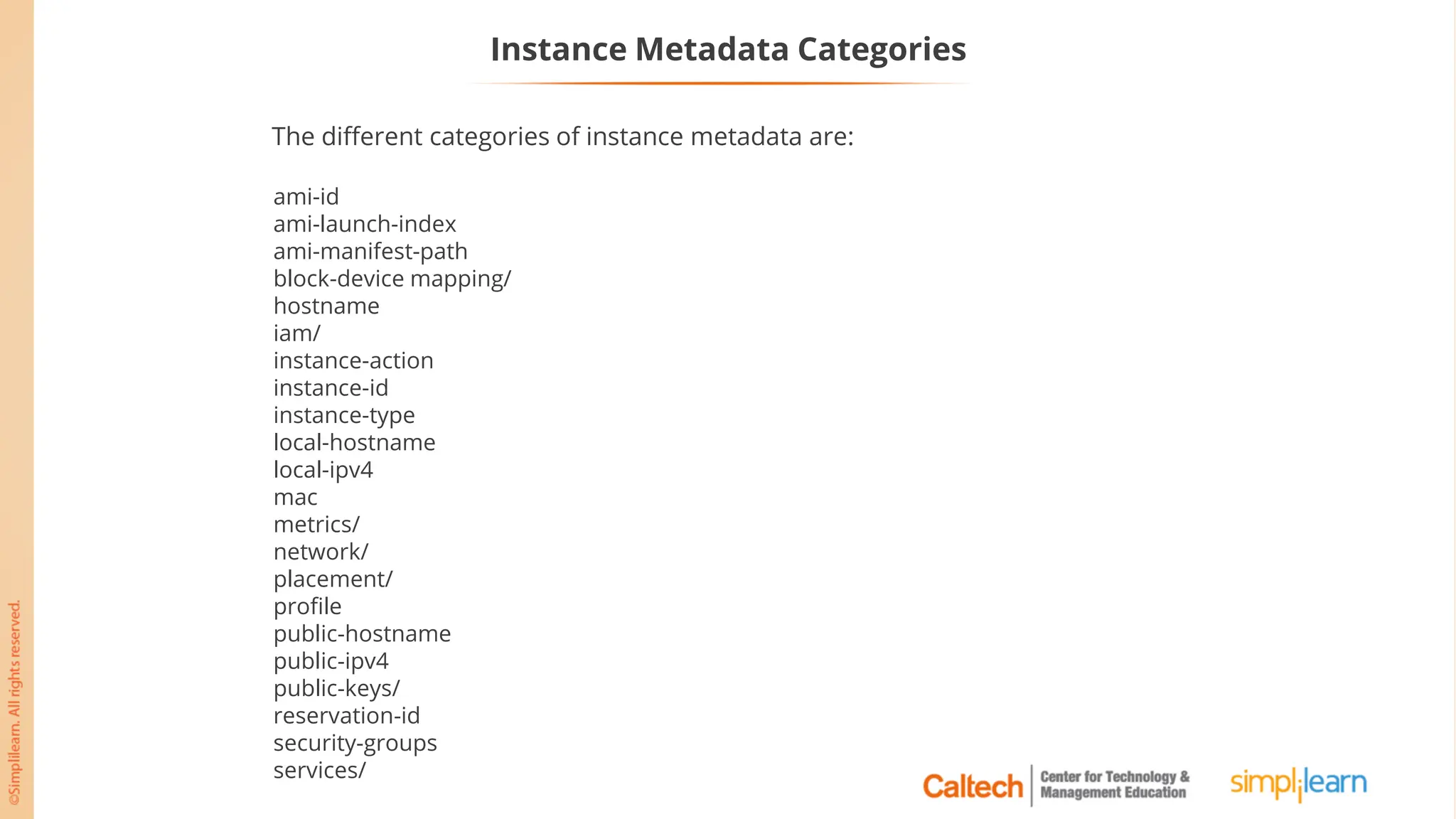
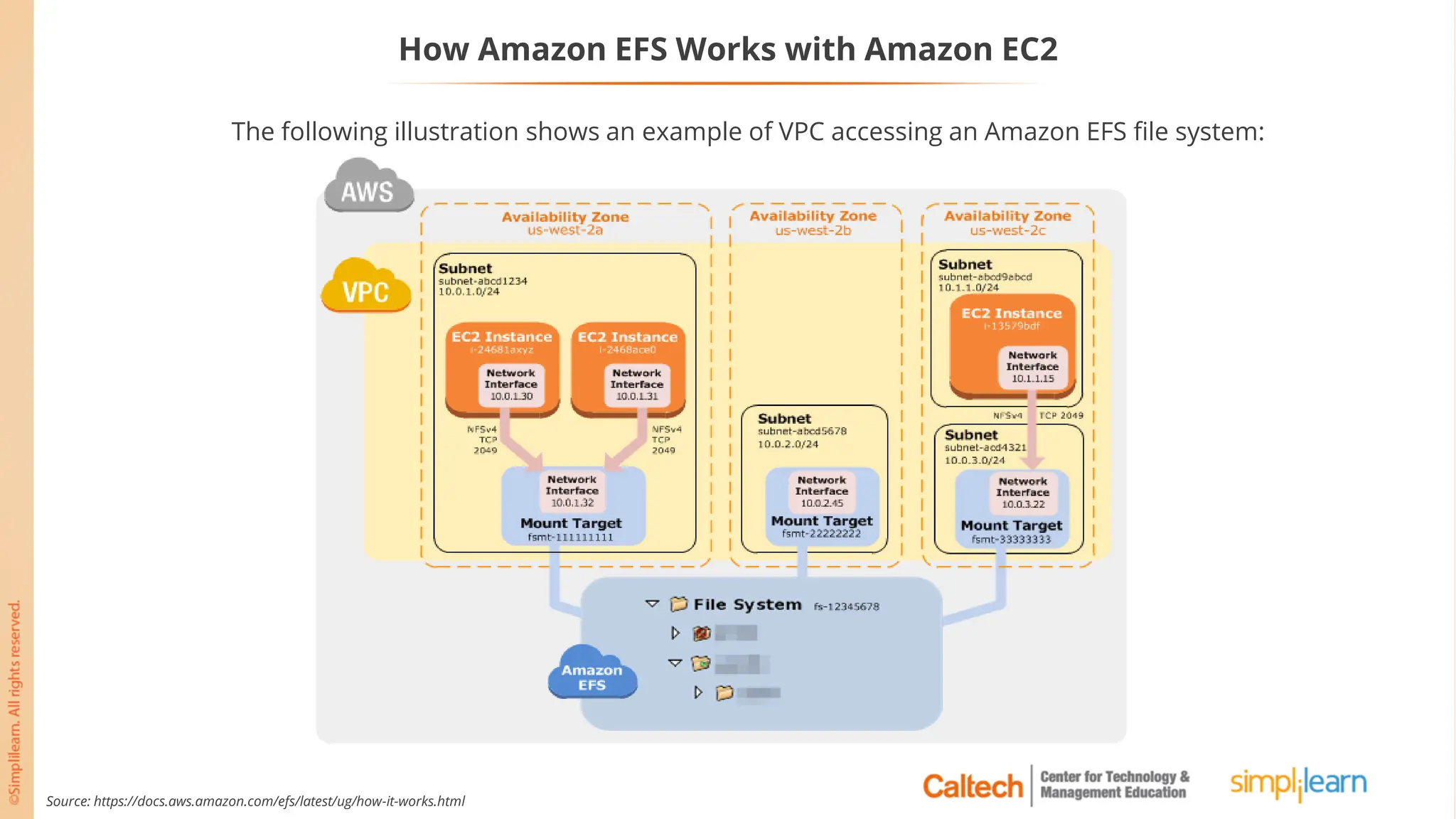
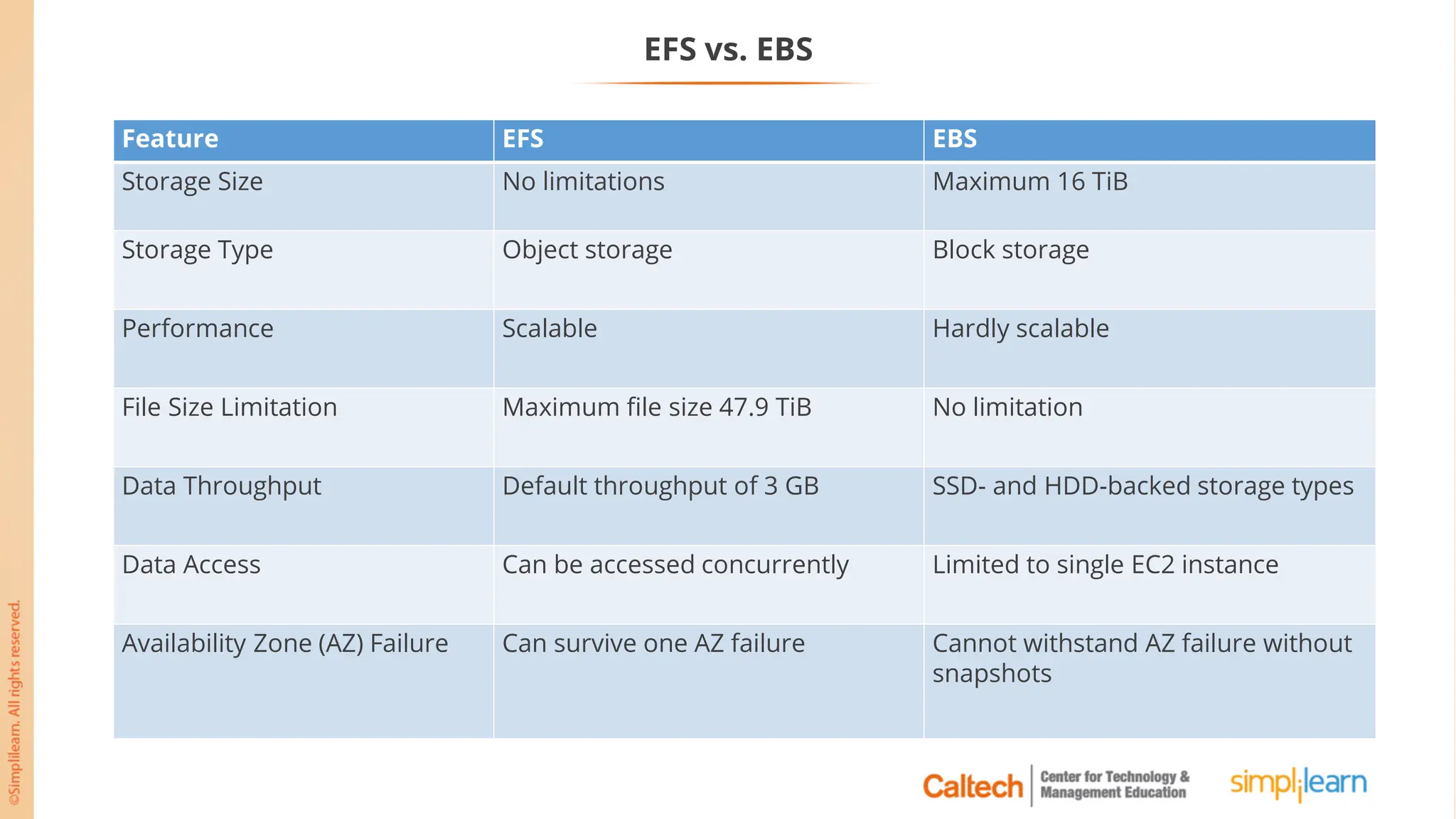
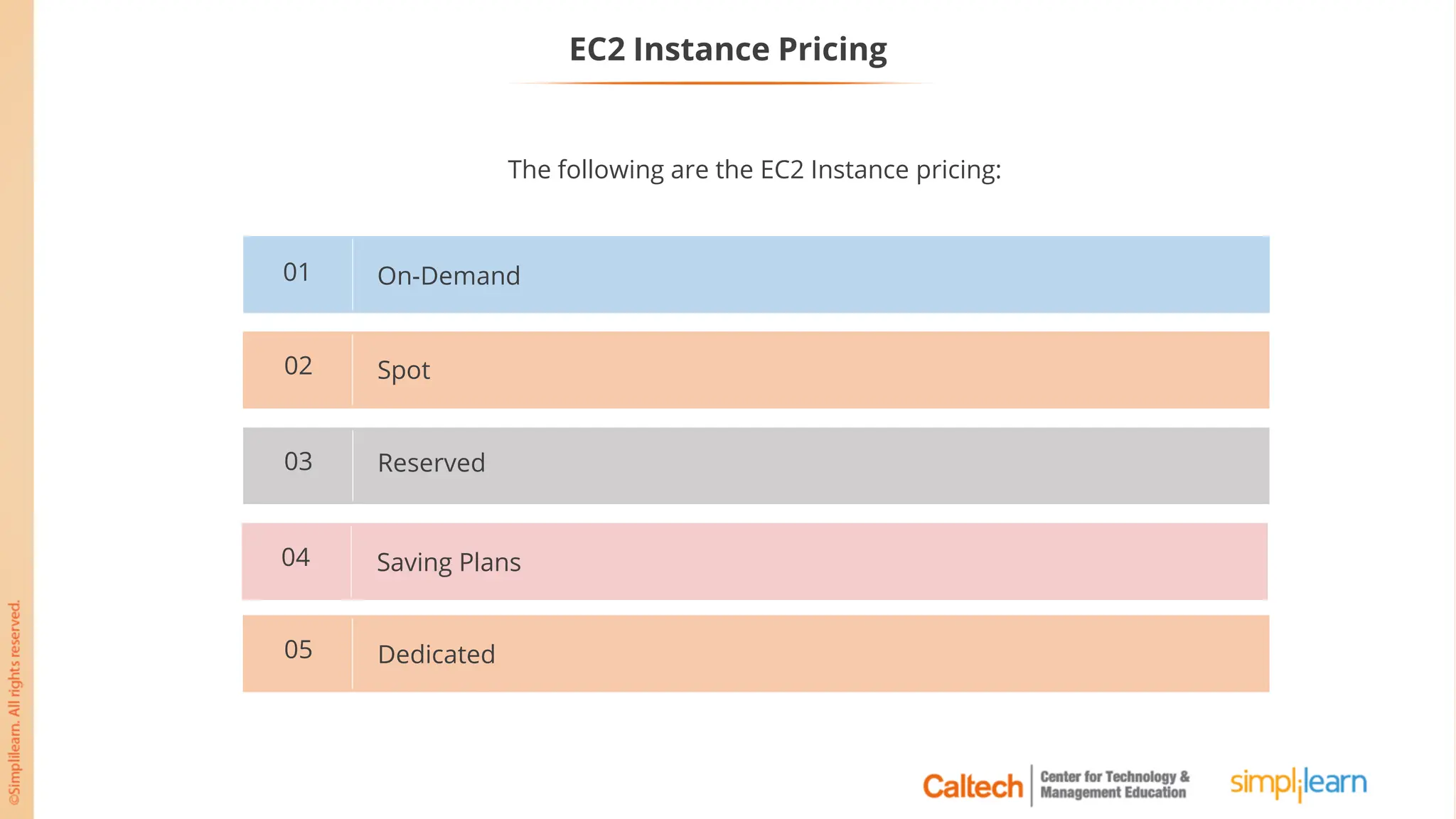
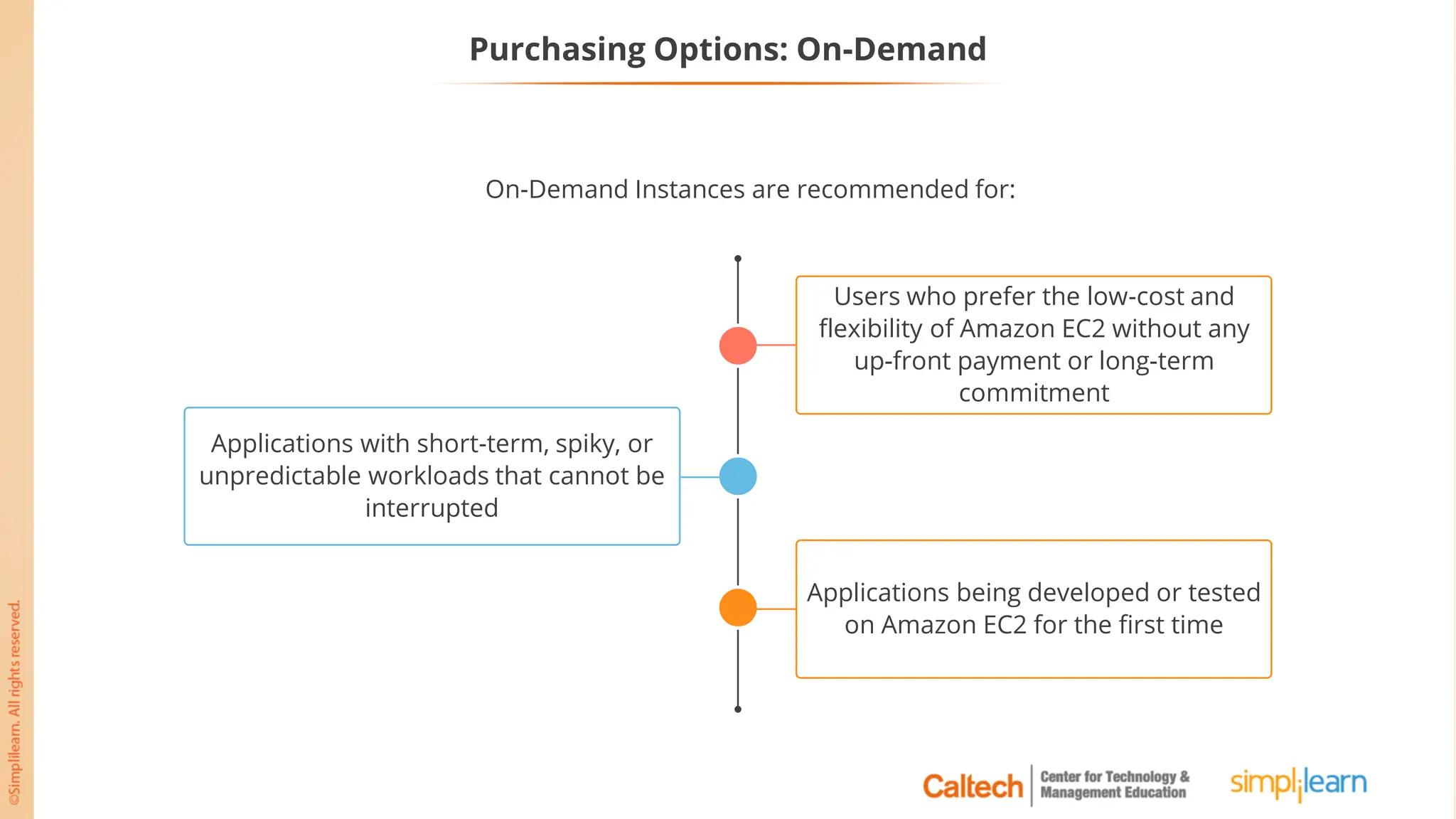
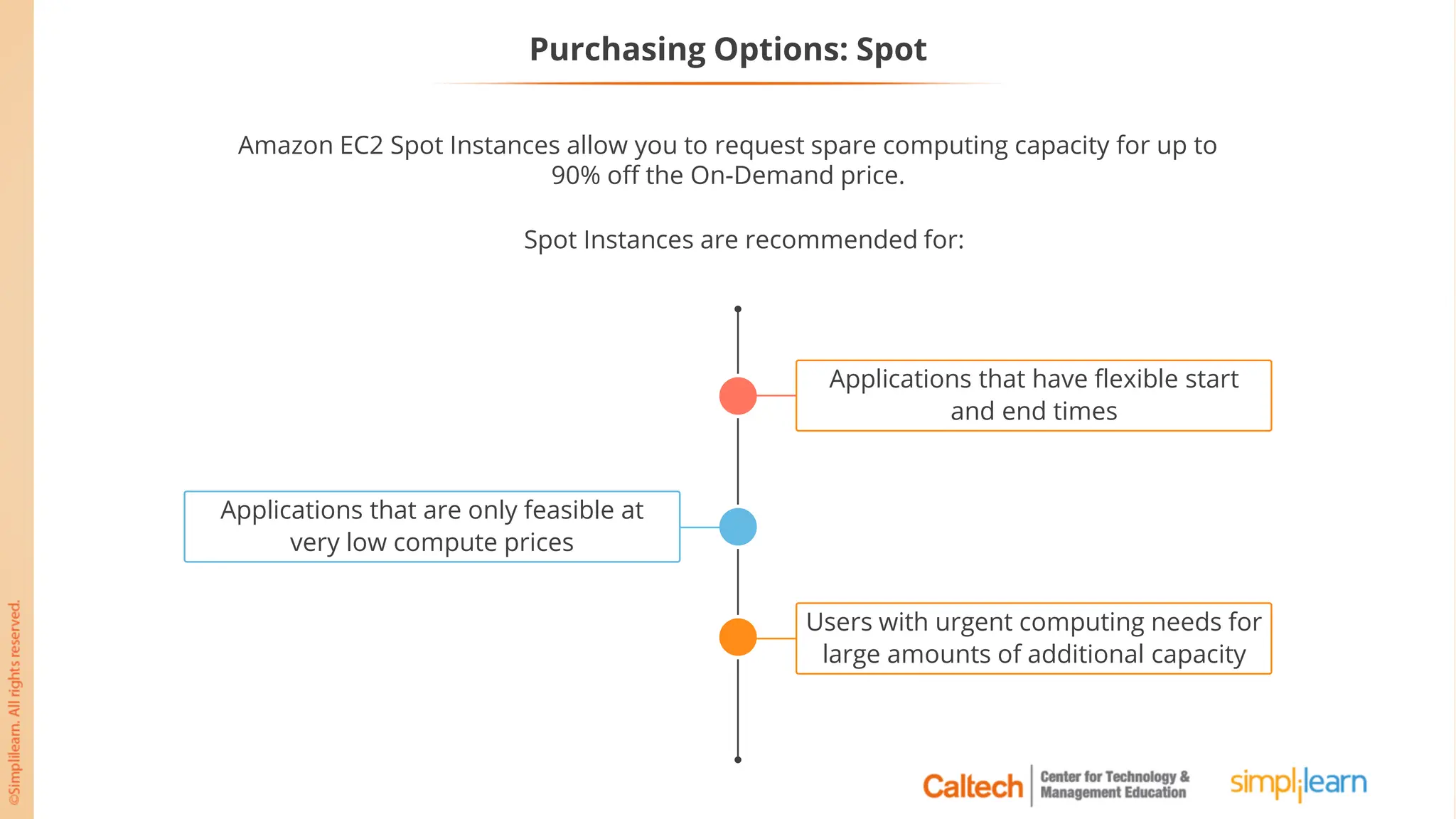
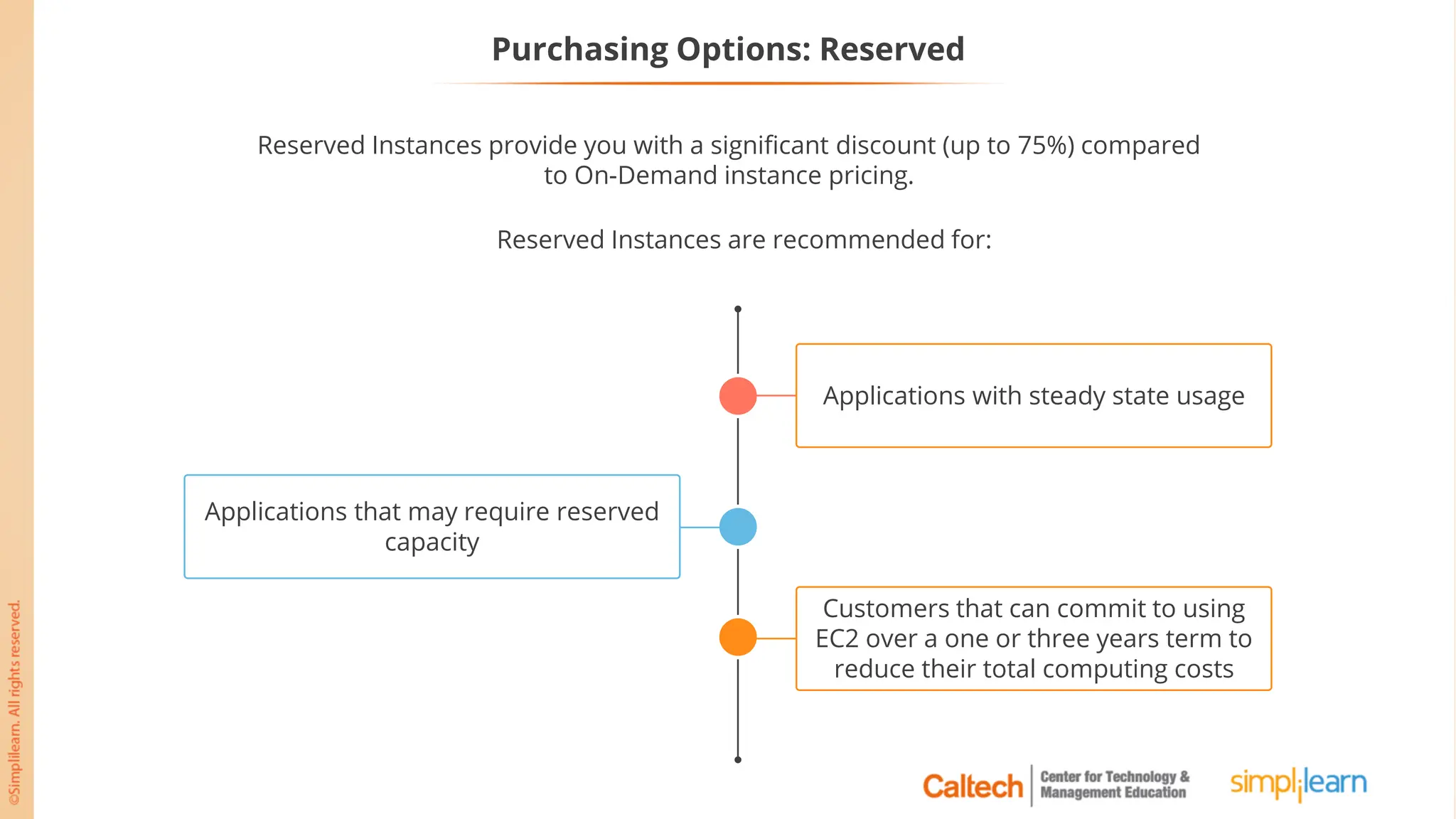
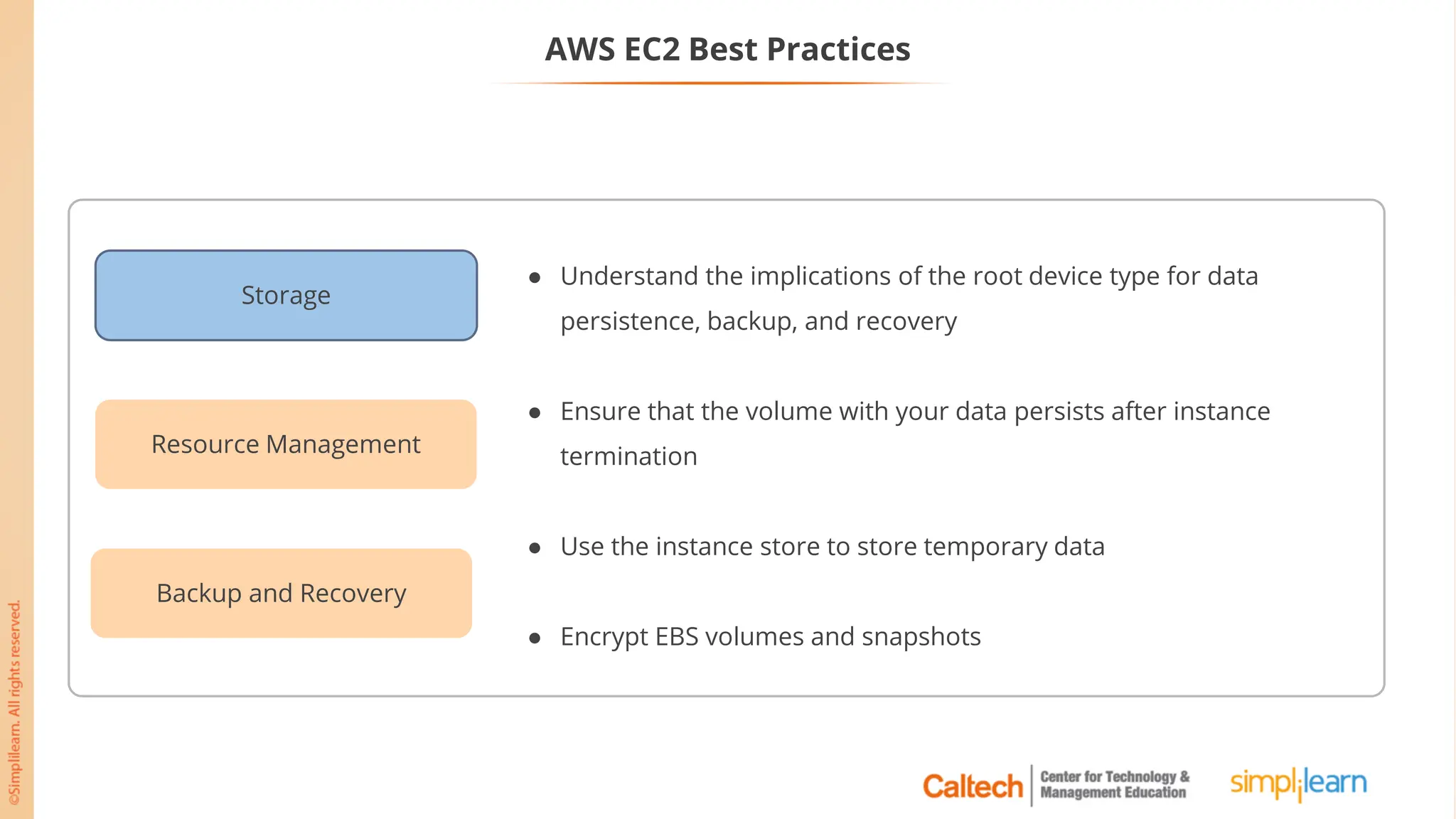
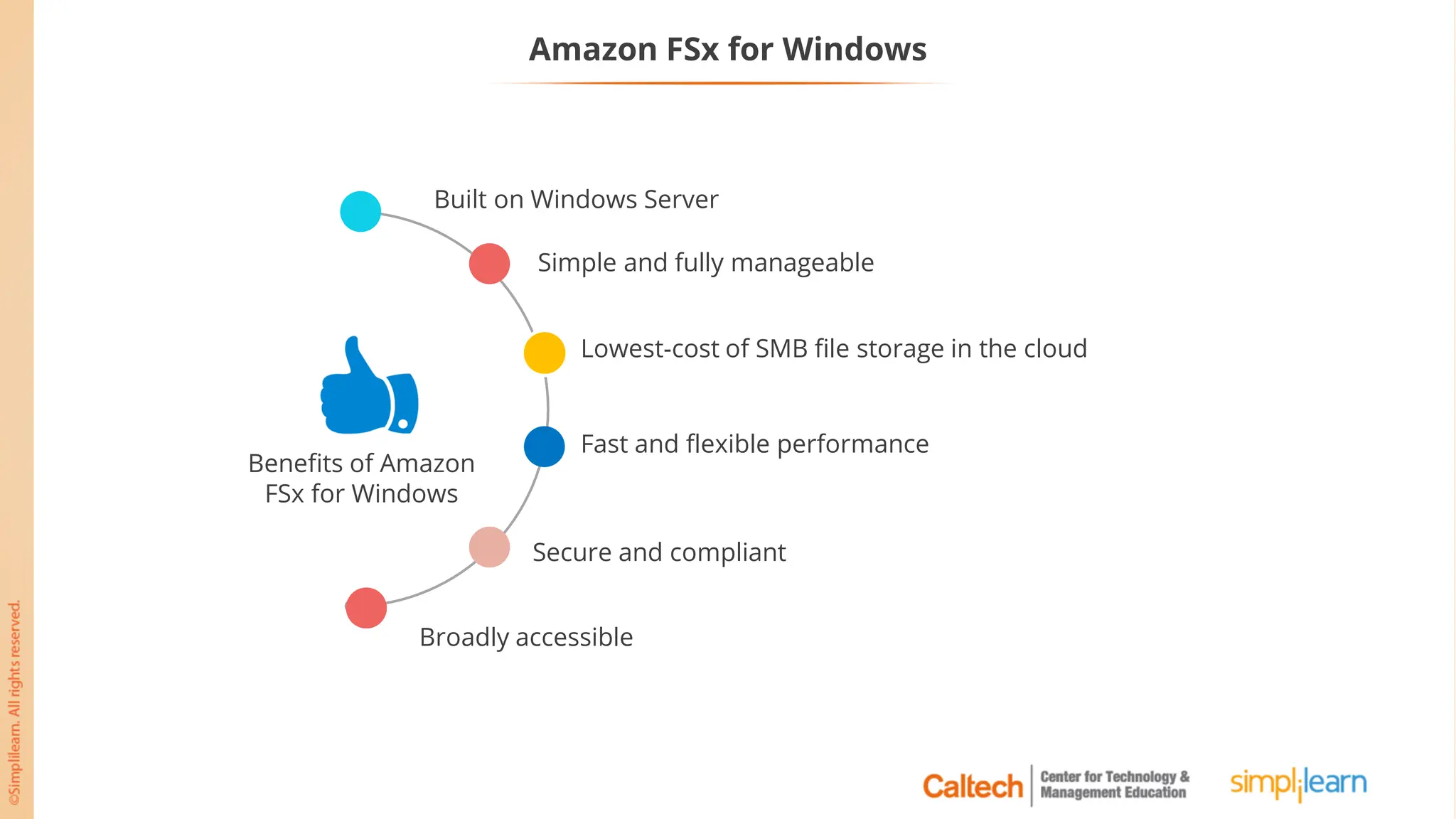
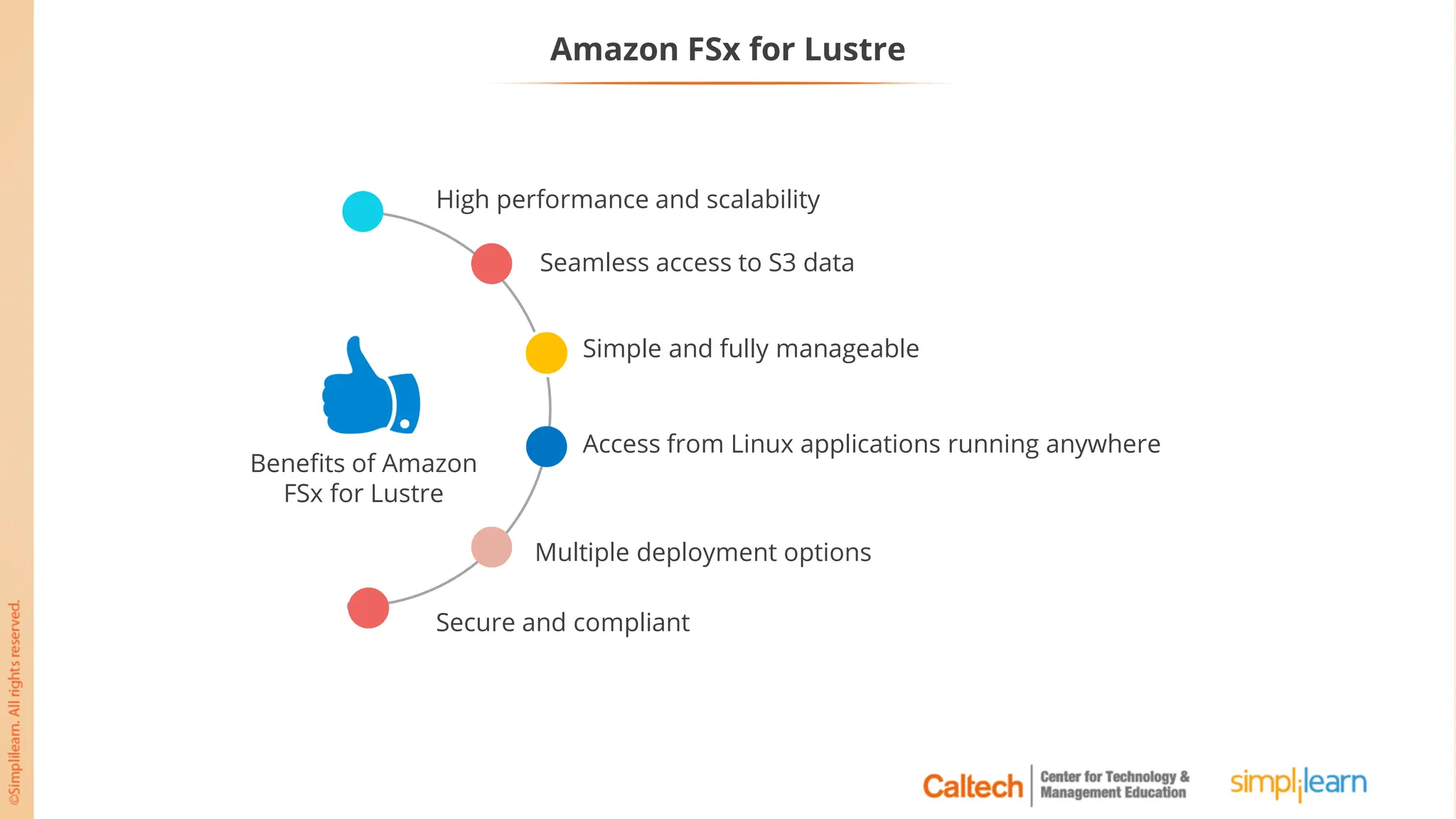
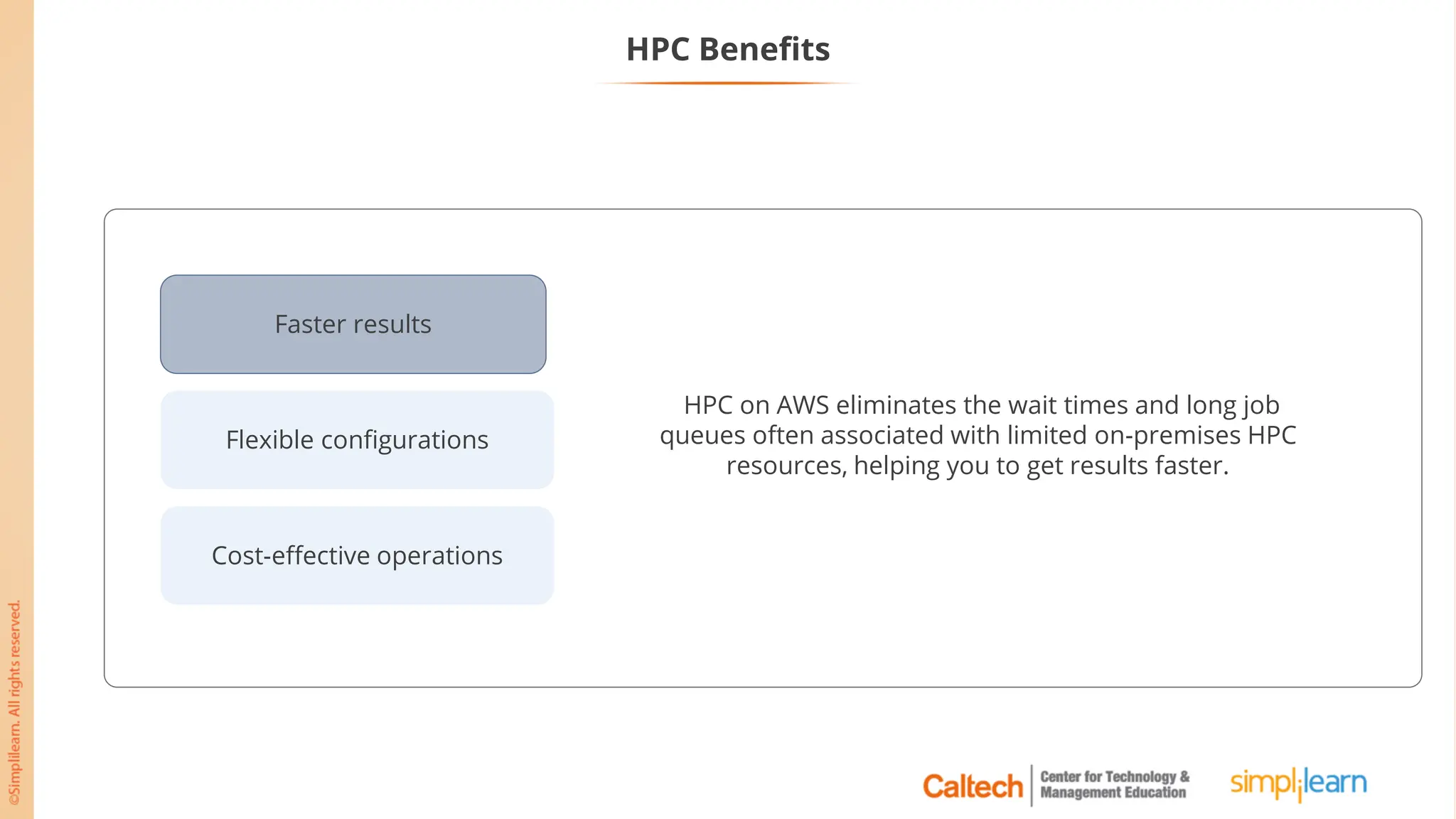
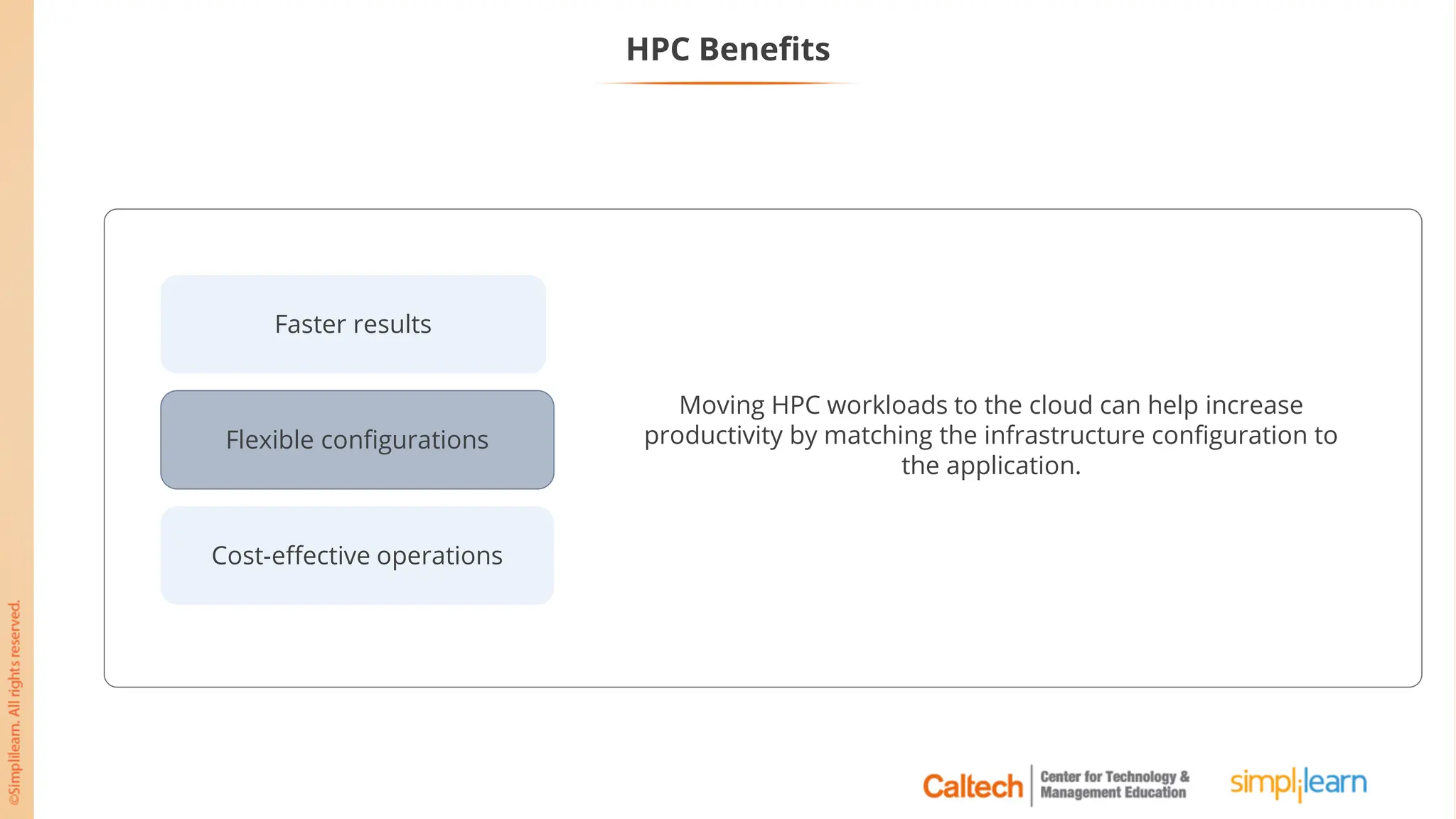
The document outlines a postgraduate program focused on AWS Cloud Solutions Architecture, specifically Amazon EC2 and its functionalities. It covers learning objectives, benefits of EC2, different instance types, and the use of Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) and Elastic Block Store (EBS). Additionally, it provides guidance on practical exercises, pricing options, and best practices for using AWS resources effectively.