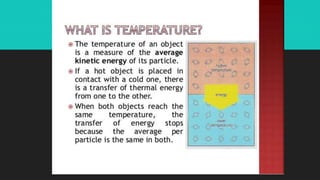
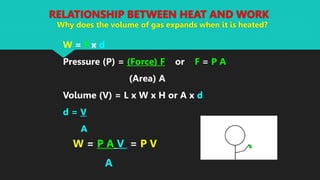
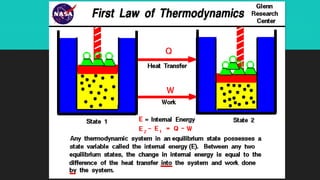
Heat refers to the hotness of an object, while temperature measures both hotness and coldness. The document discusses how heat can be converted into work through machines and engines, and how doing work releases heat. It defines key terms like heat, work, thermal equilibrium, and internal energy. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that the change in a system's internal energy equals the heat added minus any work done by the system. Sample problems demonstrate using this law to calculate internal energy changes.