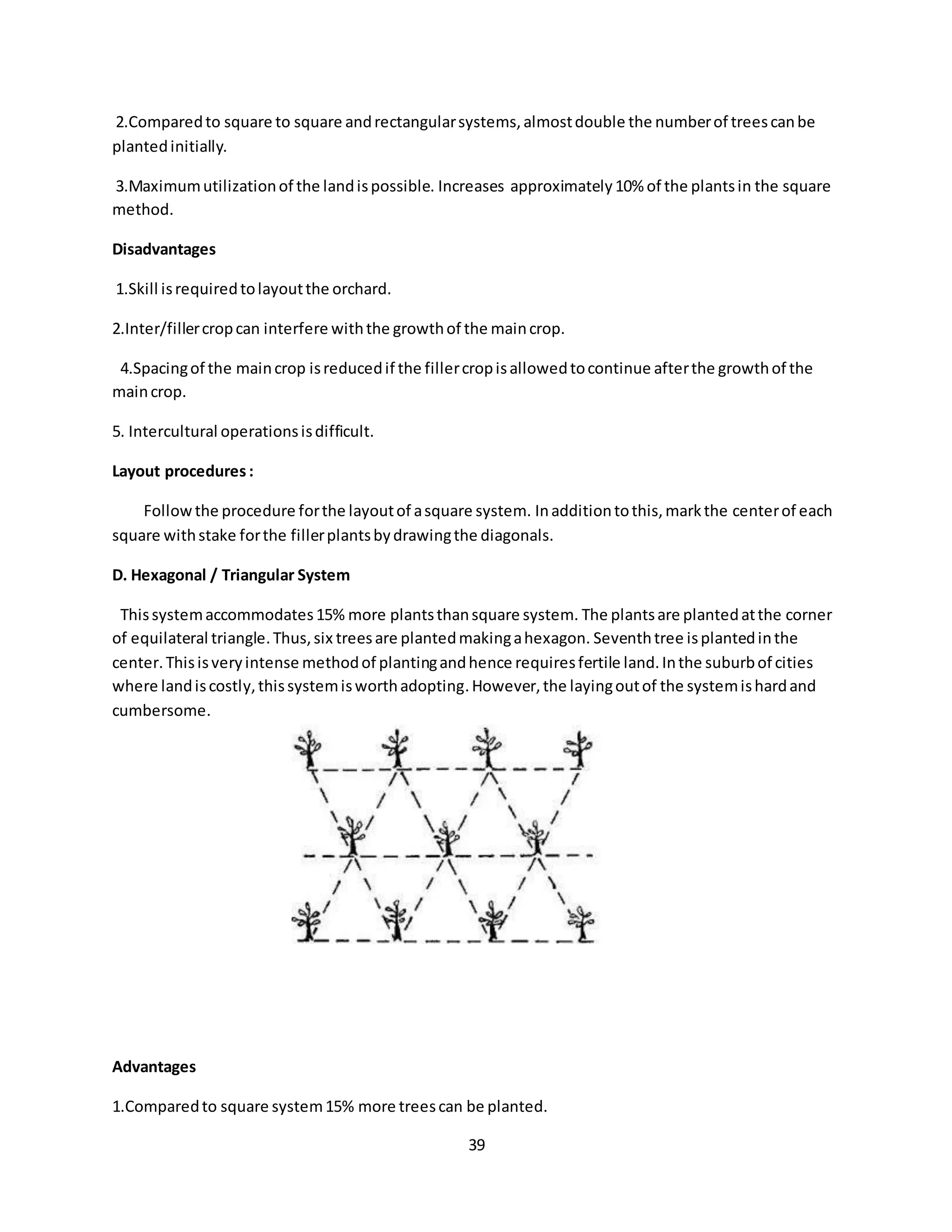
This document discusses elements to observe when planting trees and fruit-bearing trees. It identifies several key elements: proper care of plants and soil, including choosing the best place for planting and seeds suited to the season and soil; putting sufficient fertilizers in the soil; and preparing seeds for planting by soaking, removing the seed coat, and allowing for germination. It also notes the importance of conducting a survey to identify elements to observe in planting, market demands for fruits, sources of fruit-bearing trees, and famous orchard farms.