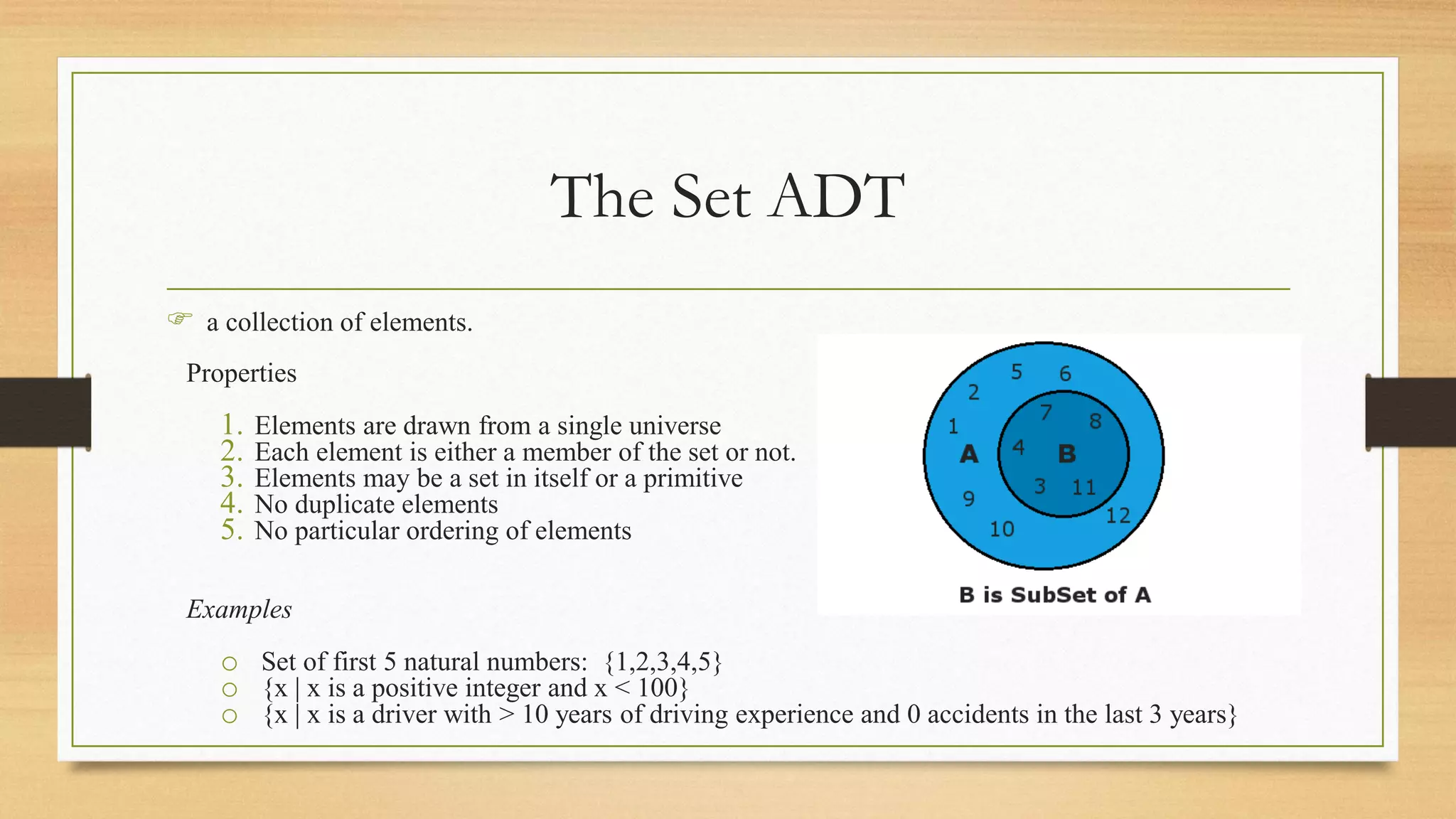
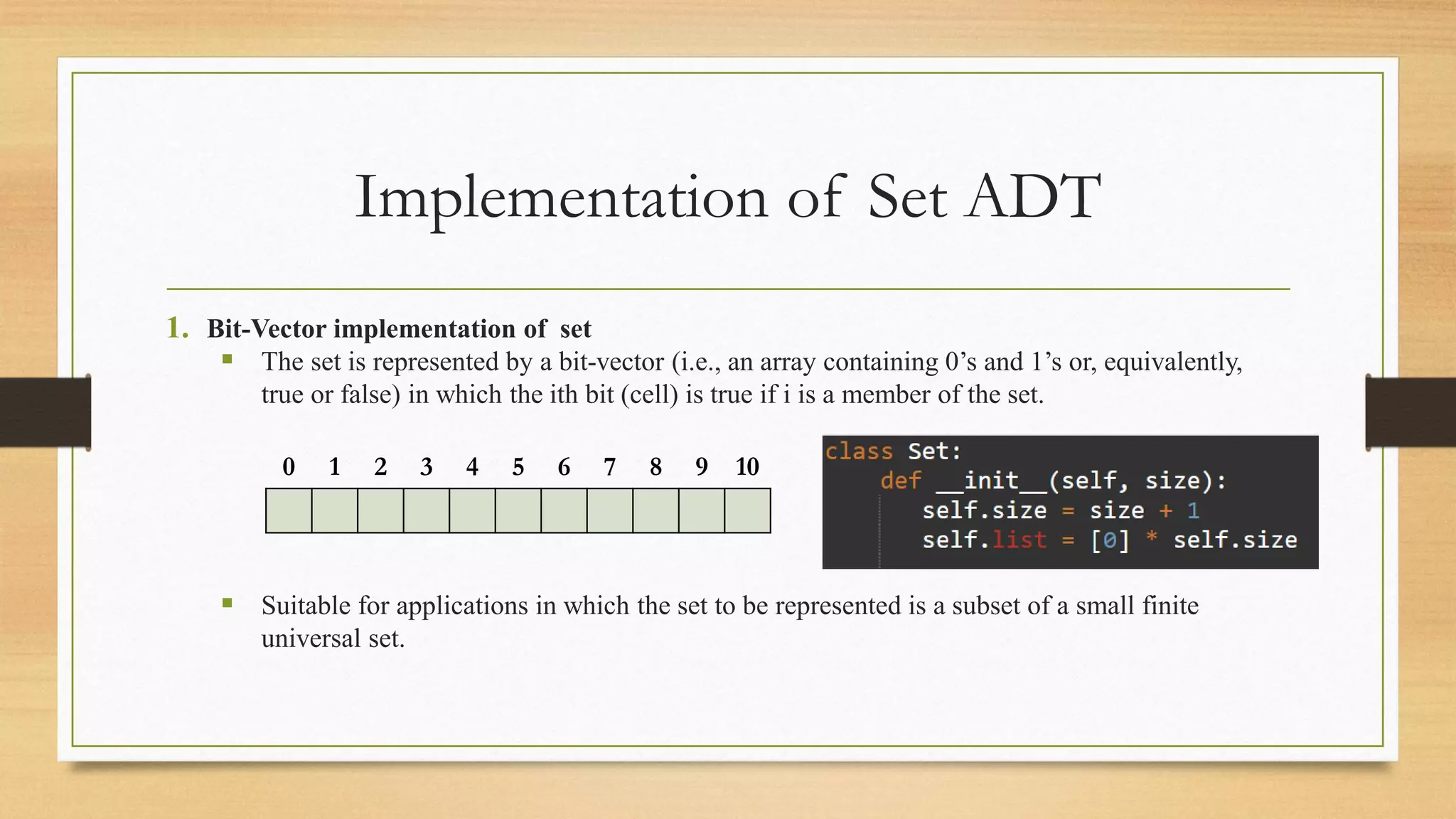
This document discusses the set abstract data type (ADT). It defines a set as a collection of elements drawn from a single universe with no duplicates and no ordering. The document outlines common set operations and provides examples of using sets to represent collections like articles or students. It then describes two common implementations of sets - using a bit vector for a finite set of elements, or linked lists for more flexible sets. Code snippets are provided for common set operations like insertion, deletion, union and intersection under both implementations.













![Implementation of Queue ADT
▪ Linked List implementation of Set [SLL]
▪ The entire set is represented by a linked list of nodes.
▪ Suitable for applications in which the set to be
represented does not necessarily have to be a subset of
some finite universal set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson5-setadt-230924224225-7254f2d0/75/Lesson-5-Set-ADT-pdf-16-2048.jpg)