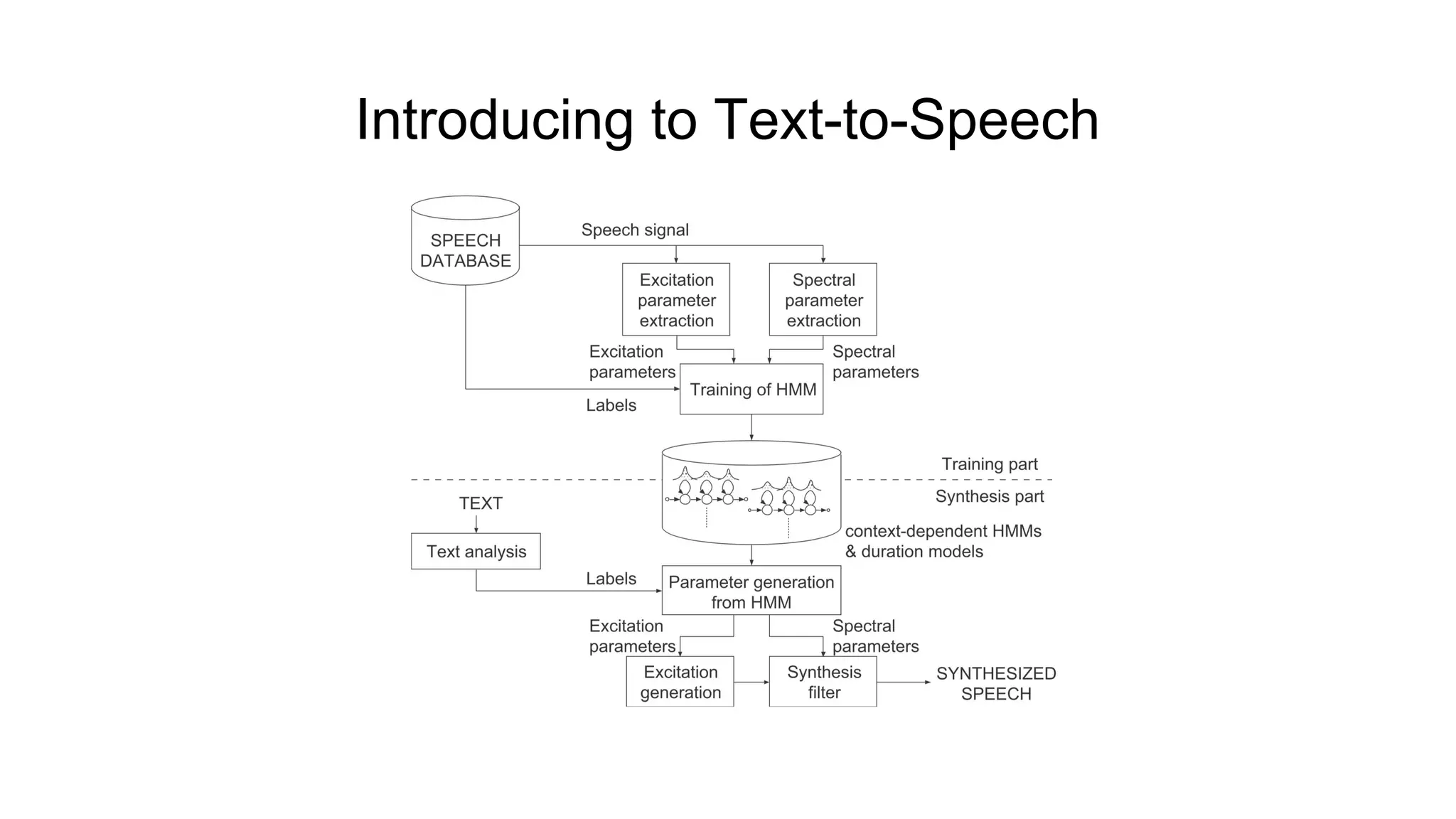
The document is a comprehensive review of modern text-to-speech (TTS) systems, detailing advancements from various models such as WaveNet, Deep Voice, and Tacotron, along with their evaluation metrics like the Mean Opinion Score (MOS). It covers technical architectures, training methods, and speech synthesis quality improvements over time, emphasizing recent innovations such as transformers and unsupervised style modeling. Additionally, it introduces the Ruslan corpus, a significant resource for Russian speech synthesis, providing insights into the evolution of TTS technologies.





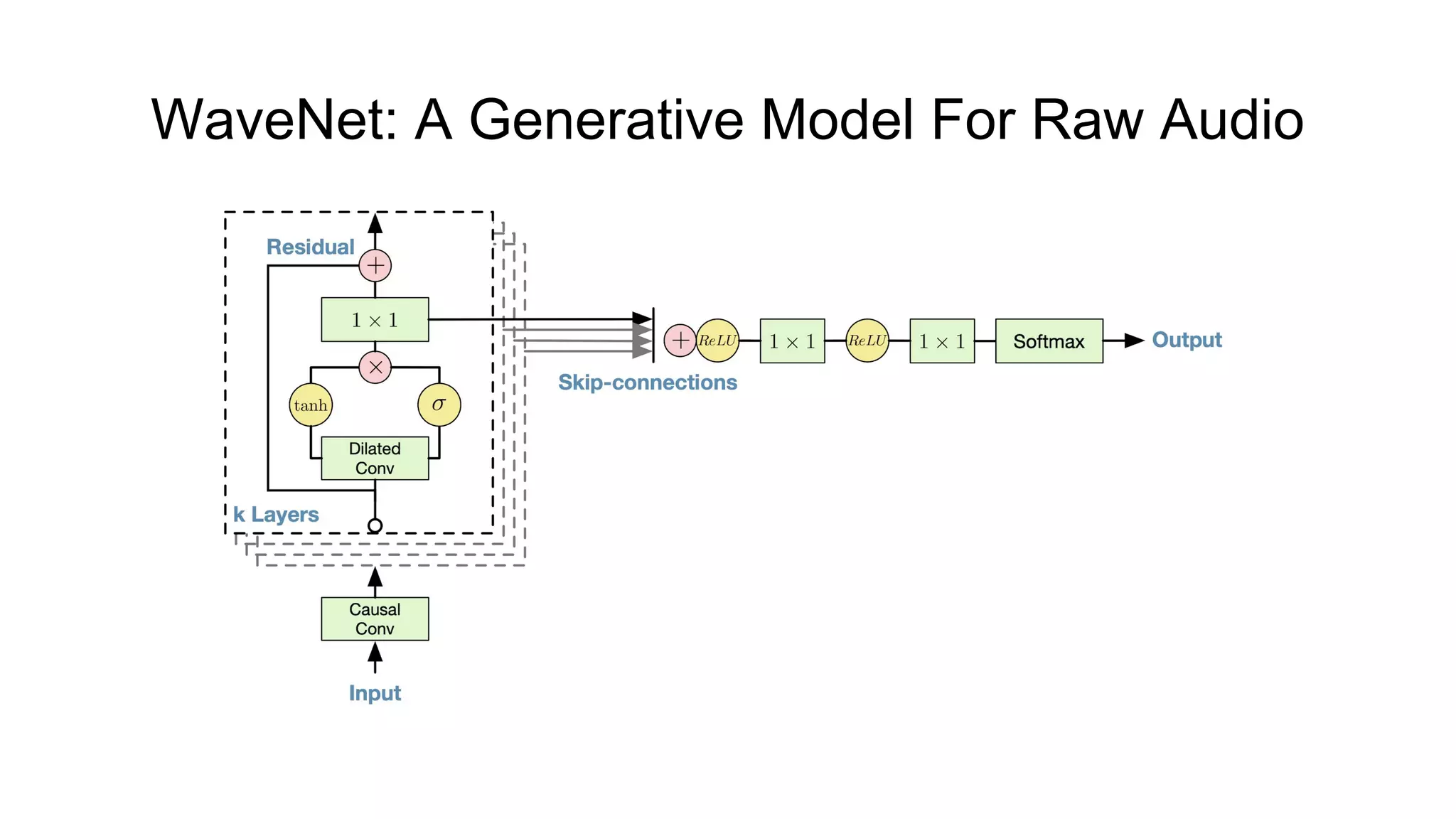
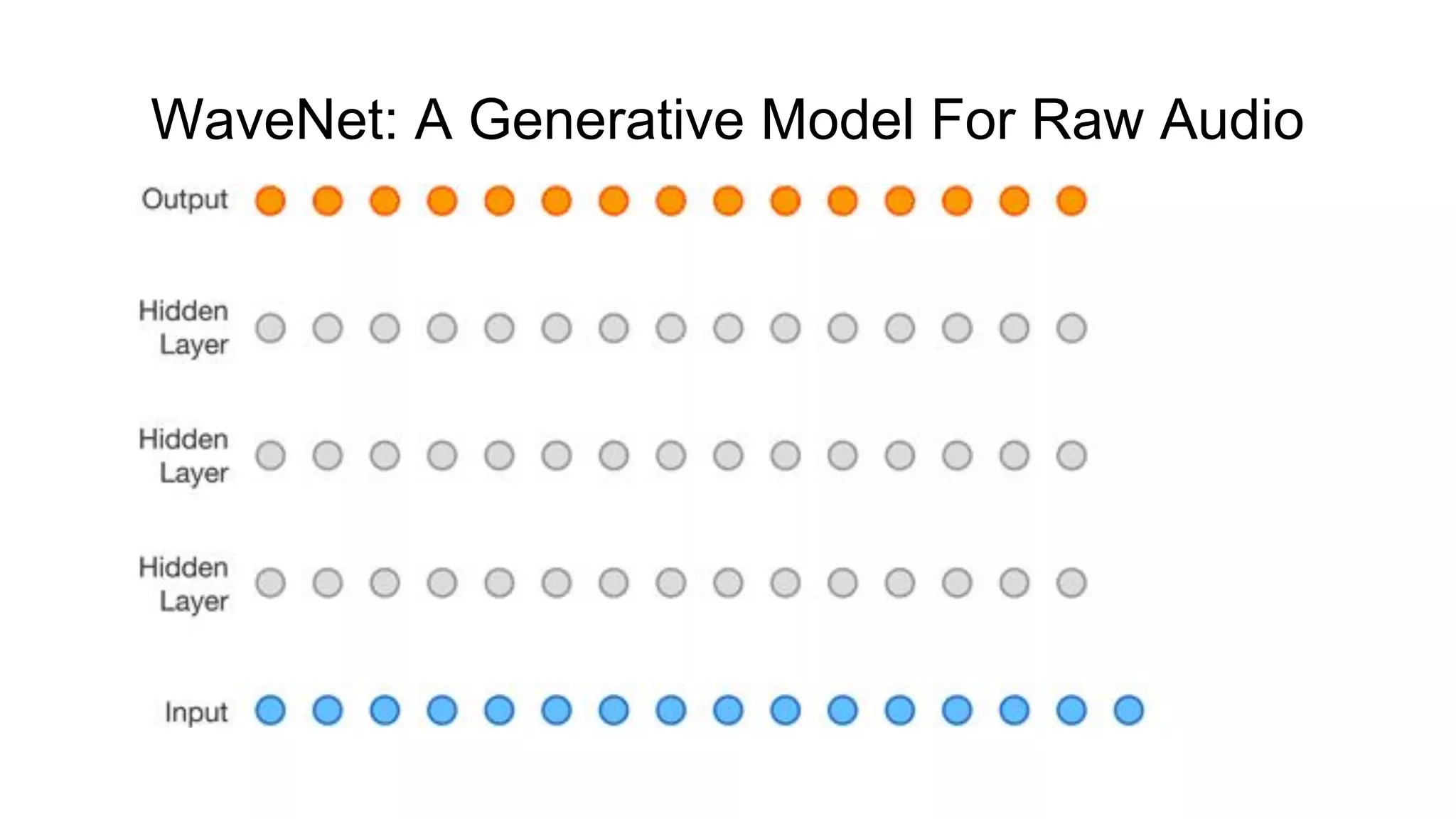
![WaveNet: A Generative Model For Raw Audio [1]
● Not truly end-to-end system yet;
● Generates raw audio waveforms (≥ 16k samples per second!);
● Fully convolutional neural network;
● Every new sample is conditioned on all previous samples;
● Softmax layer models conditional distributions over individual audio sample;
● Extra linguistic features (e.g. phone identities, syllable stress, fundamental
frequency F0
) required;
● Can be extended to multi-speaker TTS;
● Achieves a 4.21 ± 0.081 MOS on US English, a 4.08 ± 0.085 on Chinese;
● Computationally expensive.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-8-2048.jpg)

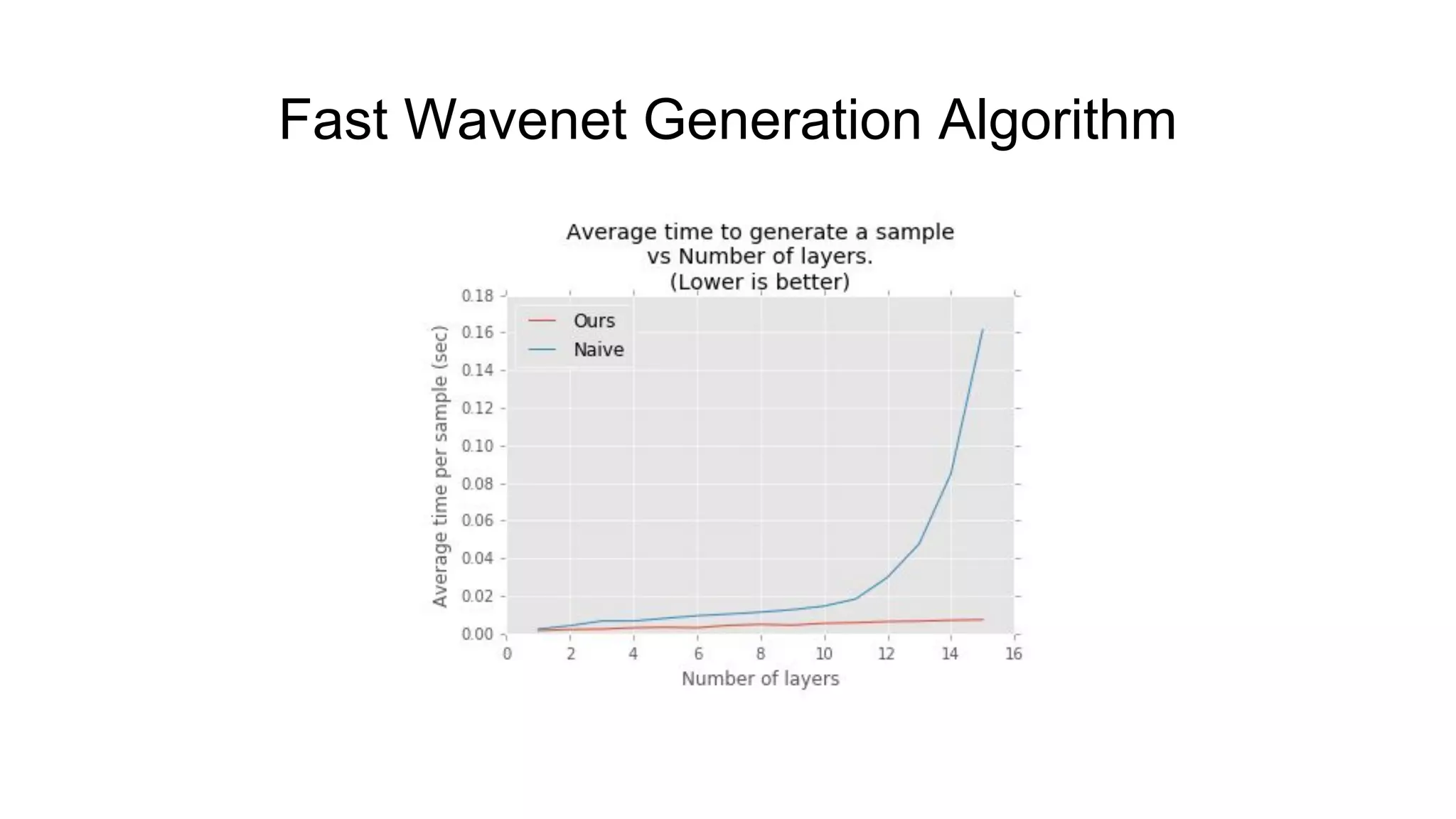
![Fast Wavenet Generation Algorithm [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-12-2048.jpg)
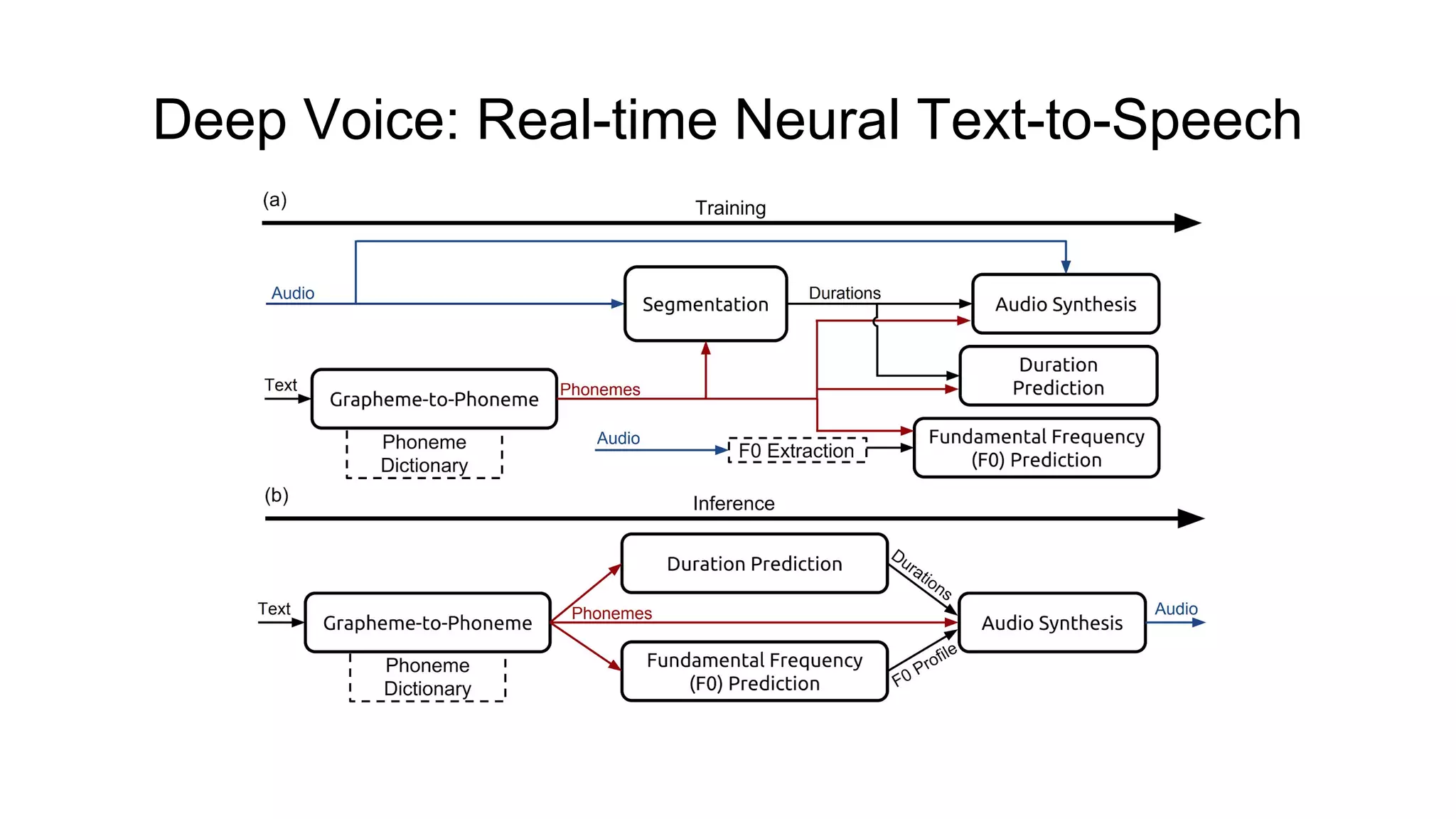
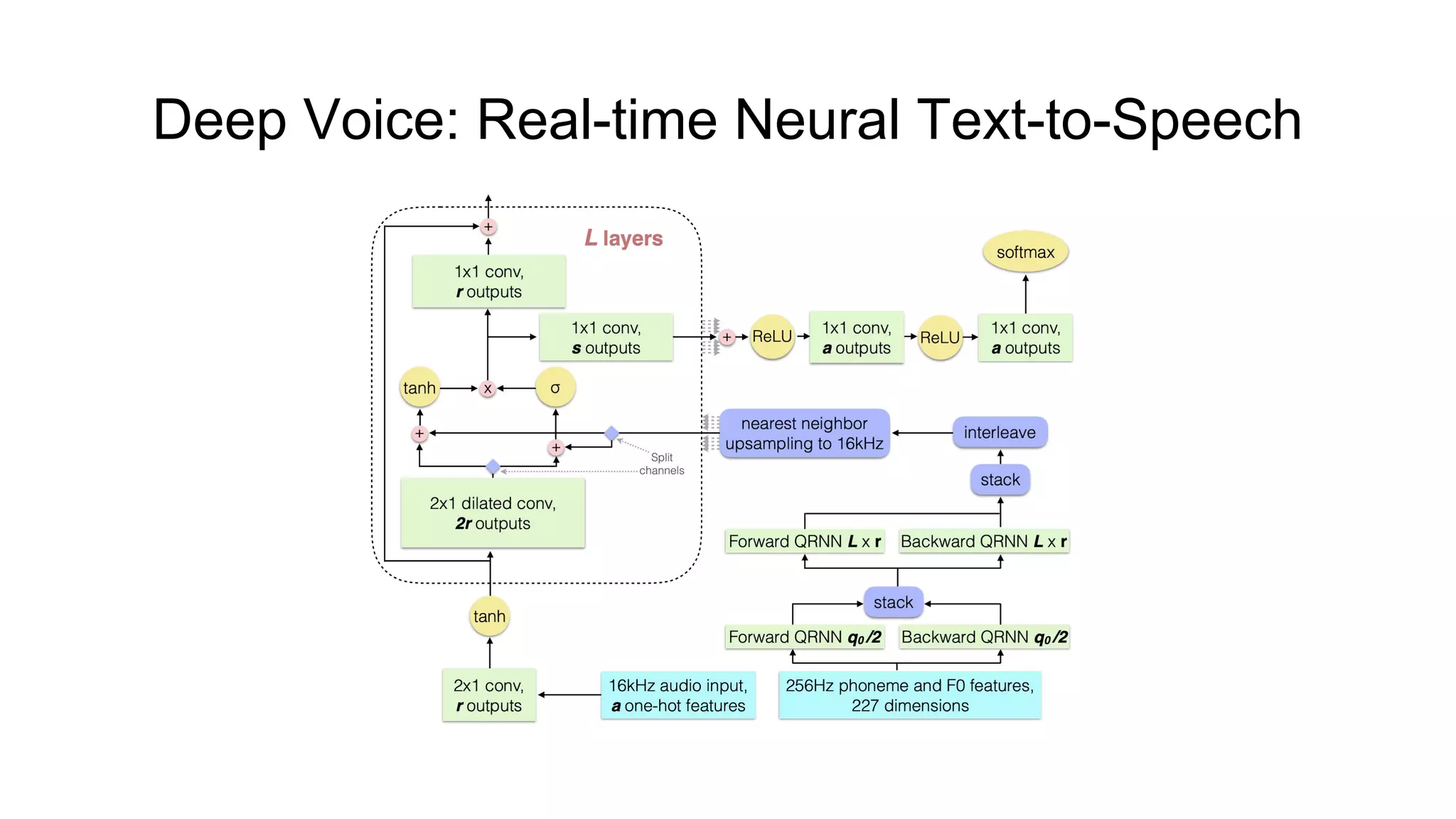
![Deep Voice: Real-time Neural Text-to-Speech [3]
● Not truly end-to-end system yet: “Deep Voice lays the groundwork for truly
end-to-end neural speech synthesis”;
● Consists of five blocks:
○ grapheme-to-phoneme conversion model (encoder - Bi-GRU with 1024 units x 3, decoder -
GRU with 1024 units x 3);
○ segmentation model for locating phoneme boundaries (Convs + GRU + Convs);
○ phoneme duration prediction model (FC-256 x 2, GRU with 128 units x 2, FC);
○ fundamental frequency prediction model (joint model with above);
○ audio synthesis model (variant of WaveNet).
● Faster than real time inference (up to 400x faster on both CPU and GPU
compared to Fast WaveNet [2]);
● Achieves a 2.67± 0.37 MOS on US English;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-14-2048.jpg)
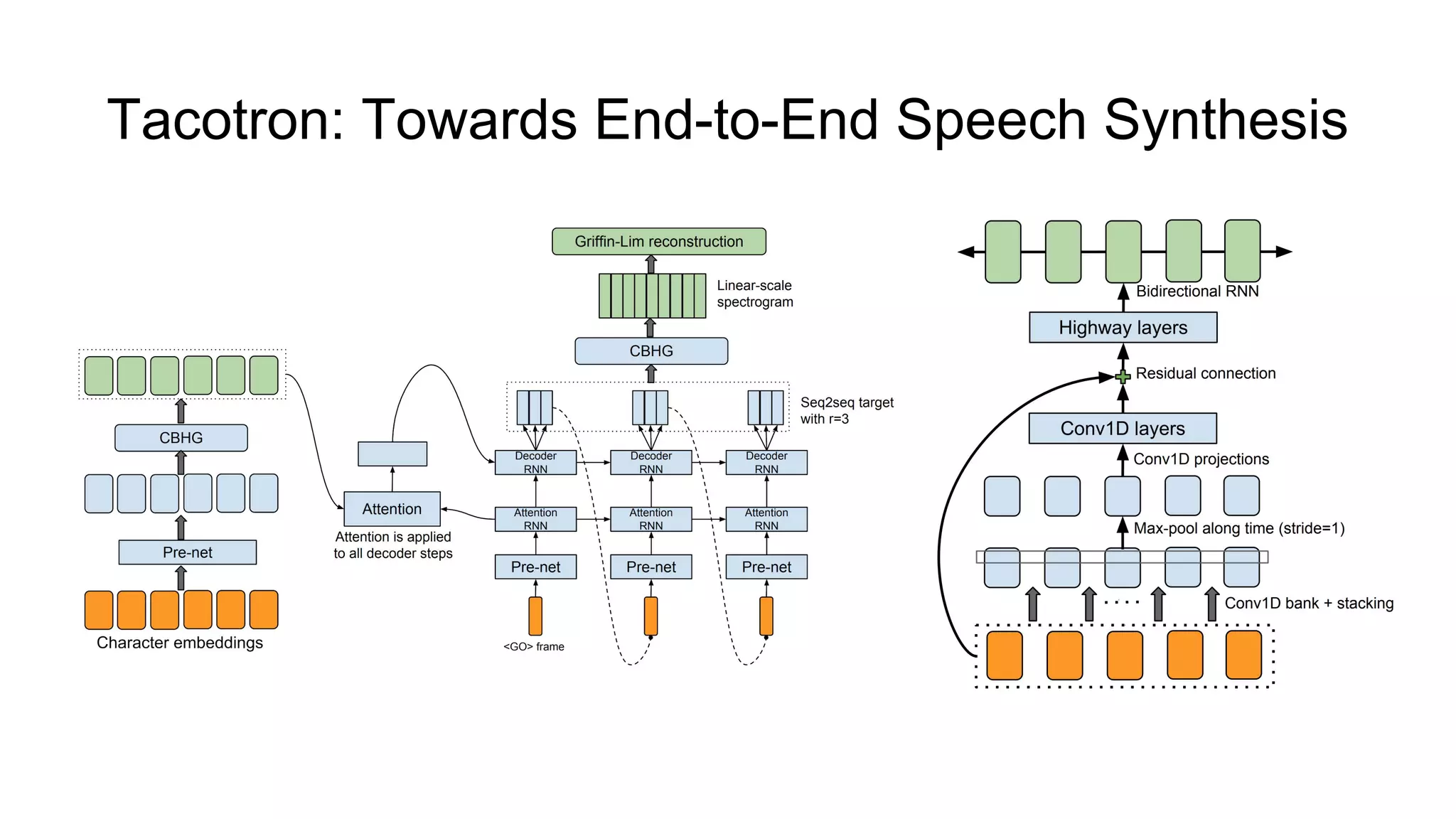
![Tacotron: Towards End-to-End Speech Synthesis [4]
● Fully end-to-end: given <text, audio> pairs, model can be trained completely
from scratch with random initialization;
● Predicts linear- and mel-scale spectrograms;
● Achieves a 3.82 MOS on US English.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-17-2048.jpg)

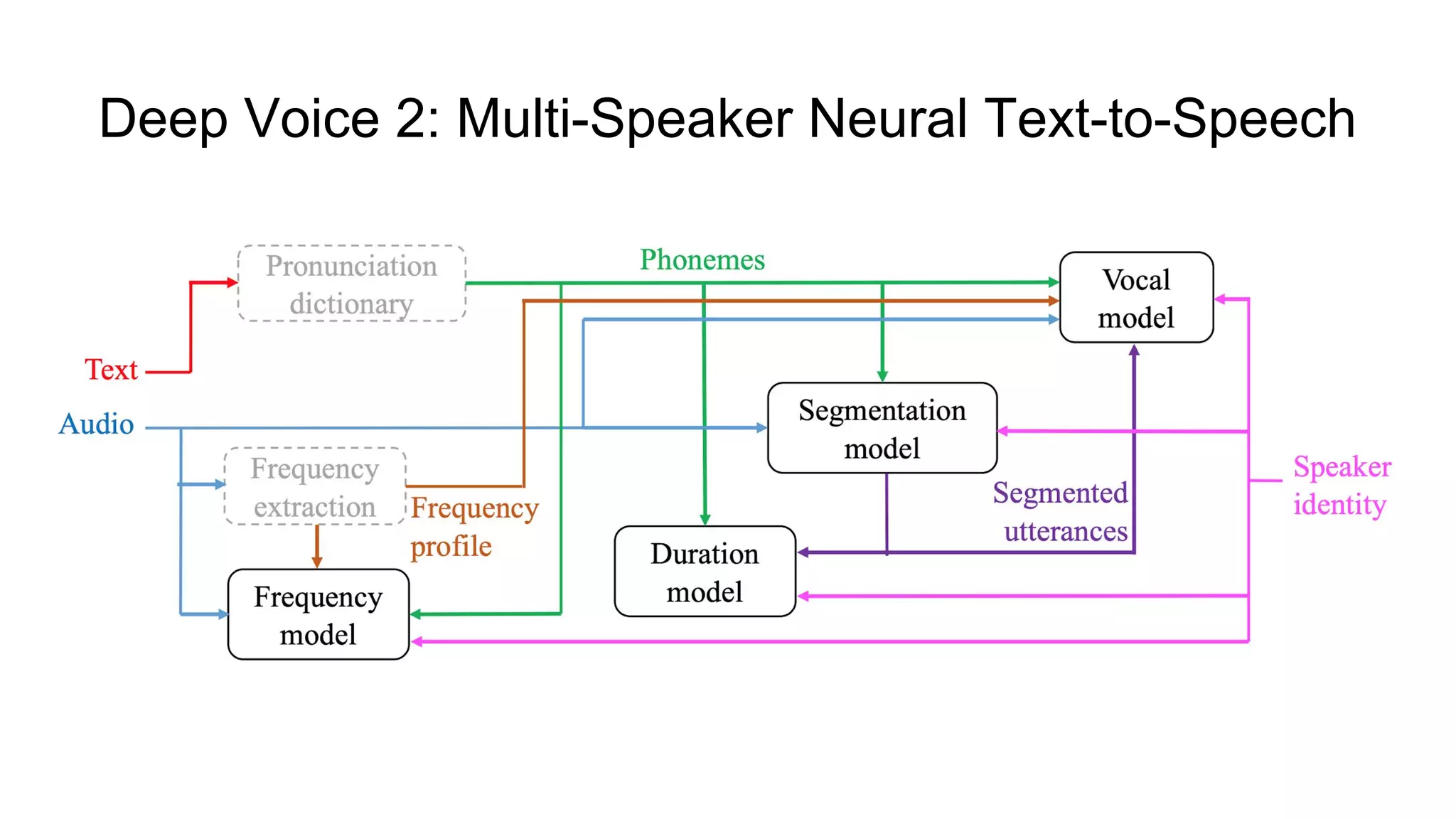
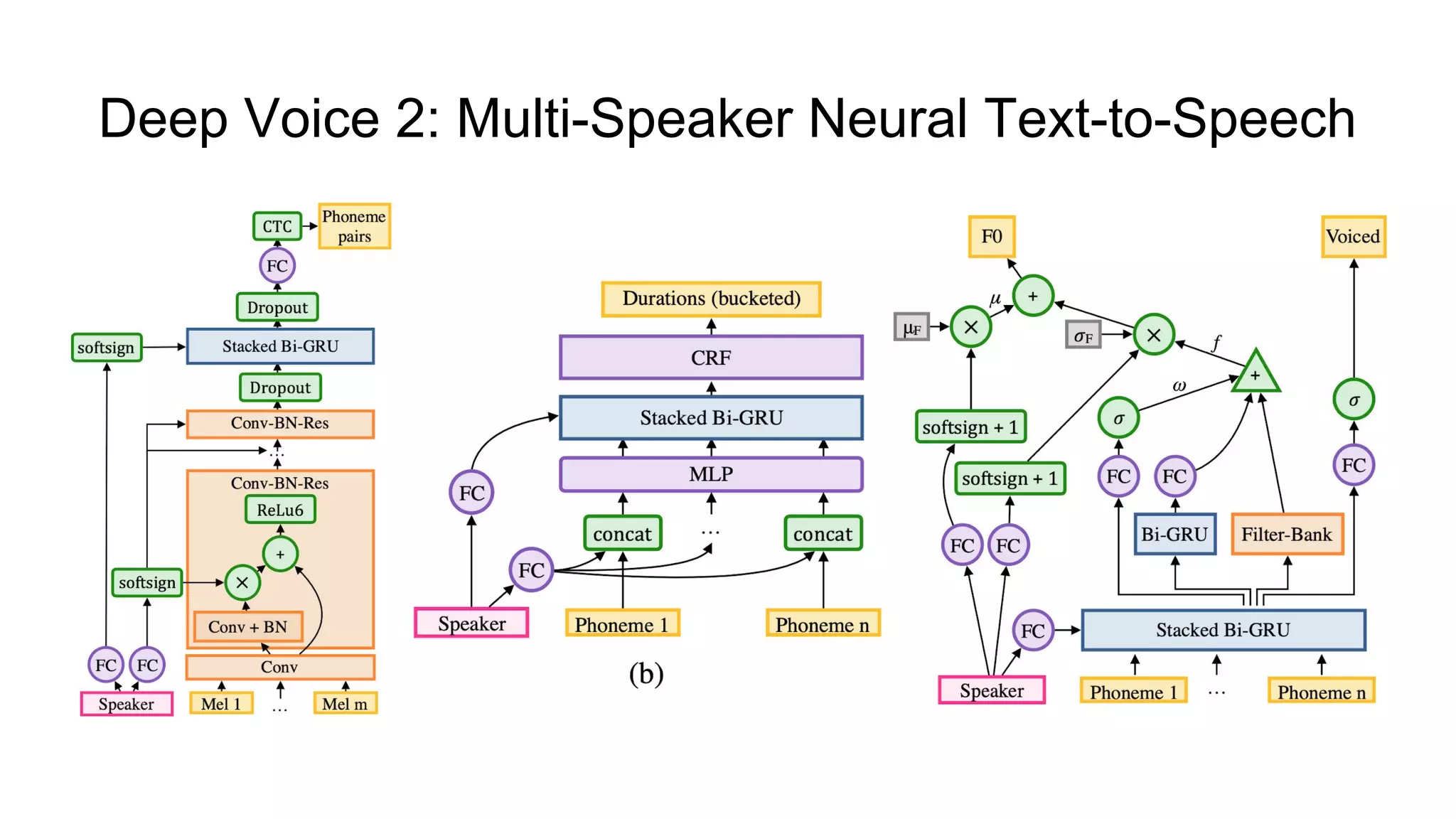
![Deep Voice 2: Multi-Speaker Neural Text-to-Speech
[5]
● Improved architecture based on Deep Voice [3];
● Can learn from hundreds of unique voices from less than half an hour of data
per speaker;
● Voice model based on WaveNet [1] architecture;
● Achieves a 3.53 ± 0.12 MOS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-20-2048.jpg)

![Listening while Speaking: Speech Chain by Deep
Learning [6]
● Two parts: TTS model and ASR model;
● Single- and multi-speaker;
● Jointly training:
○ Supervised step;
○ Unsupervised: unpaired text and speech.
● Both TTS and AST models are Tacotron-like [4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-24-2048.jpg)
![Listening while Speaking: Speech Chain by Deep
Learning [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-25-2048.jpg)
![Deep Voice 3: Scaling Text-to-Speech with
Convolutional Sequence Learning [7]
● Fully-convolutional sequence-to-sequence attention-based model;
● Converts input text to spectrograms (or other acoustic parameters);
● Suitable for both single and multi speaker;
● Needs 10x less training time and and converges after 500k iterations
(compared to Tacotron [4] that converges after 2m iterations);
● Novel attention mechanism to introduce monotonic alignment;
● MOS: 3.78 ± 0.30 (with WaveNet), same score for Tacotron [4] (with
Wavenet), 2.74 ± 0.35 for Deep Voice 2 [5] (with WaveNet).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-26-2048.jpg)
![Deep Voice 3: Scaling Text-to-Speech with
Convolutional Sequence Learning [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-27-2048.jpg)
![Deep Voice 3: Scaling Text-to-Speech with
Convolutional Sequence Learning [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-28-2048.jpg)
![Deep Voice 3: Scaling Text-to-Speech with
Convolutional Sequence Learning [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-29-2048.jpg)
![Deep Voice 3: Scaling Text-to-Speech with
Convolutional Sequence Learning [6]
Samples:
1. … (trained for single speaker - 20 hours total);
2. … (trained for 108 speakers - 44 hours total);
3. <same>;
4. … (trained for 2484 speakers - 820 hours of ASR data total);
5. <same>.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-30-2048.jpg)
![Natural TTS Synthesis by Conditioning WaveNet on
Mel Spectrogram Predictions [8]
● Uses simpler building blocks, in contrast to original Tacotron [4];
● Maps input characters to mel-scale spectrogram;
● Modified WaveNet [1] synthesizes audio waveforms from spectrograms
directly (no need for linguistic, phoneme duration and other features);
● However, this WaveNet is pretrained separately;
● Achieves a 4.526 ± 0.066 MOS on US English.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-31-2048.jpg)
![Natural TTS Synthesis by Conditioning WaveNet on
Mel Spectrogram Predictions [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-32-2048.jpg)
![Natural TTS Synthesis by Conditioning WaveNet on
Mel Spectrogram Predictions [7]
Samples:
1. “Generative adversarial network or variational auto-encoder.”;
2. “Don't desert me here in the desert!”;
3. “He thought it was time to present the present.”;
4. “The buses aren't the problem, they actually provide a solution.”;
5. “The buses aren't the PROBLEM, they actually provide a SOLUTION.”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-33-2048.jpg)
![Style Tokens: Unsupervised Style Modeling, Control
and Transfer in End-to-End Speech Synthesis [9]
● Based on Tacotron [4] with slight changes;
● Learn embeddings for 10 style tokens;
● Reference encoder: stack of 2D Convs, GRU with 128 units;
● Style token layer: Attention with 256-D token embeddings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-34-2048.jpg)
![Style Tokens: Unsupervised Style Modeling, Control
and Transfer in End-to-End Speech Synthesis [9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-35-2048.jpg)
![Style Tokens: Unsupervised Style Modeling, Control
and Transfer in End-to-End Speech Synthesis [9]
Samples:
1. “United Airlines five six three from Los Angeles to New Orleans has Landed”;
2. <same>;
3. <same>;
4. <same>;
5. <same>.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-36-2048.jpg)
![Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to
Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis [10]
● Consists of several independently trained components:
○ Speaker encoder network to generate speaker embedding vectors: LSTM with 768 units
followed by 256-D projection layer x 3;
○ Synthesis network - Tacotron 2 [8].
● MOS: 4.22 ± 0.06 and 3.28 ± 0.07 for seen and unseen speakers
respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-37-2048.jpg)
![Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to
Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis [10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-38-2048.jpg)
![Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to
Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis [10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-39-2048.jpg)
![Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to
Multispeaker Text-To-Speech Synthesis [10]
Samples:
1. … (reference audio, seen speaker);
2. … (synthesized audio, seen speaker);
3. … (ref., unseen);
4. … (synth., unseen);
5. … (ref., different language);
6. … (synth., different language).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-40-2048.jpg)
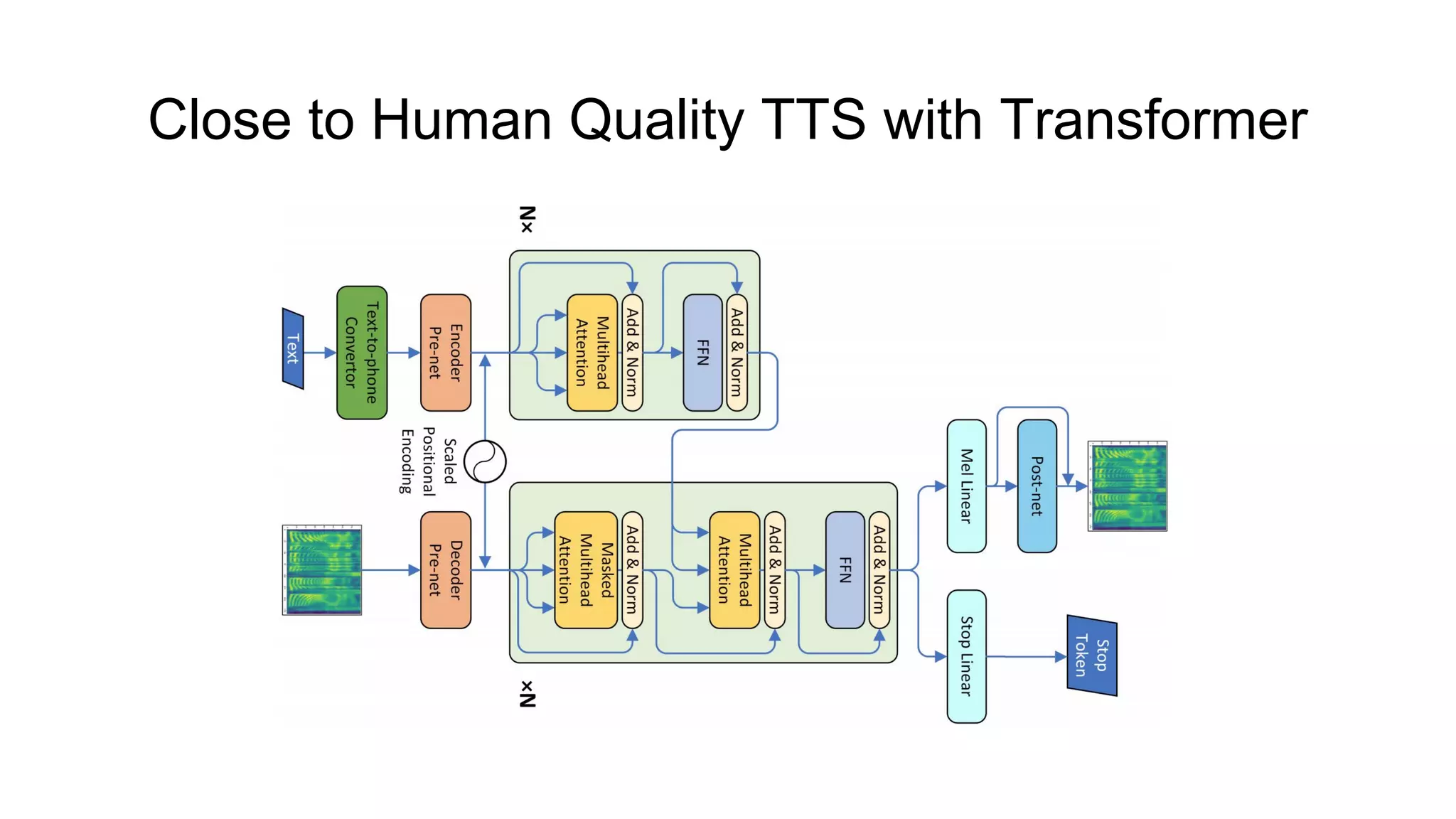
![Close to Human Quality TTS with Transformer [11]
● Based on state-of-the-art NMT model called “Transformer”;
● Based on Tacotron 2 [8] model, but all RNN layers are replaced with
Transformers;
● Using of Transformer allows to construct encoder and decoder hidden states
in parallel;
● Training about 4.25 times faster compared with Tacotron 2;
● Achieves state-of-the-art performance: 4.39 ± 0.05 (proposed model), 4.38 ±
0.05 (Tacotron 2), 4.44 ± 0.05 (ground truth).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-41-2048.jpg)


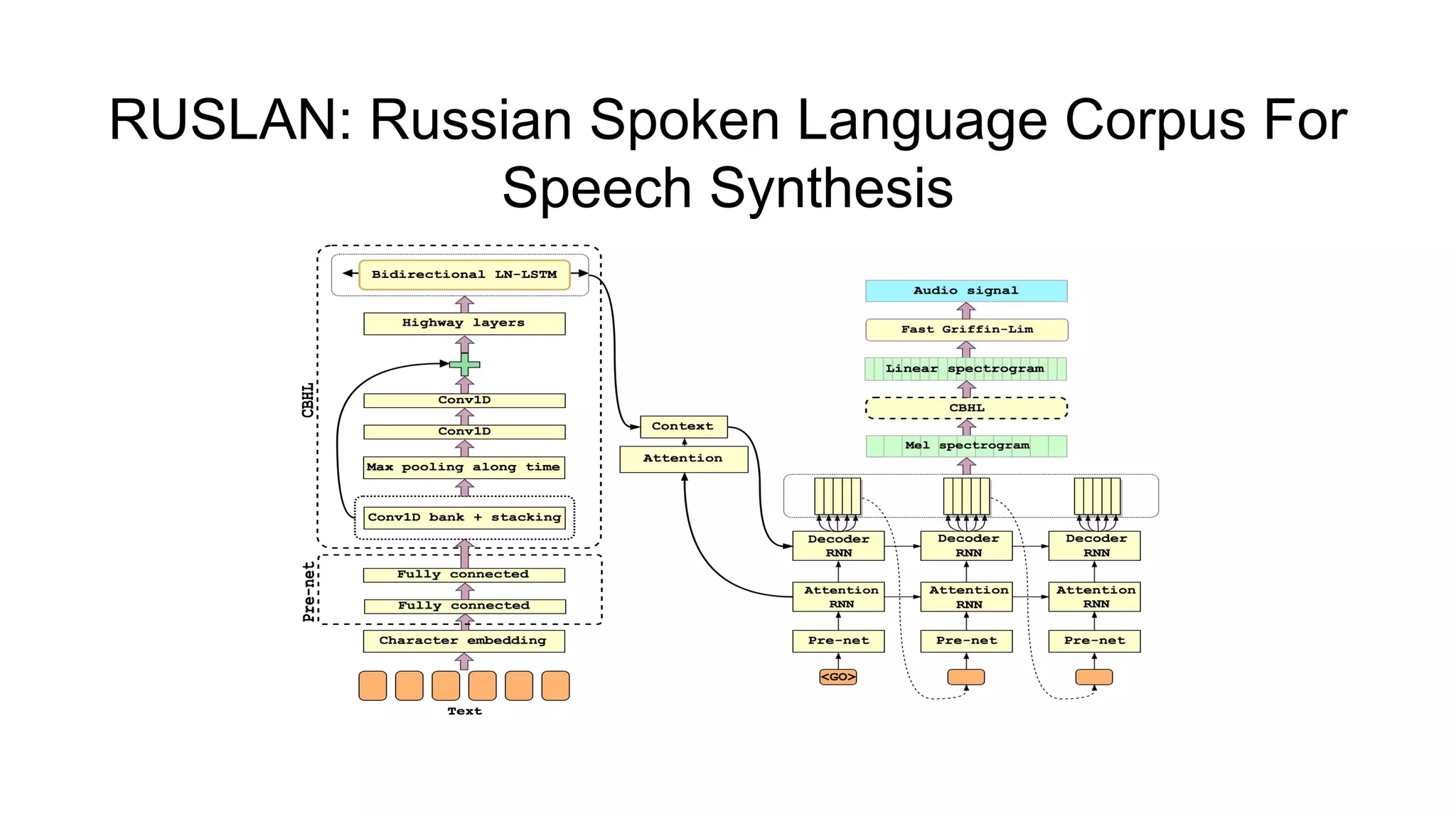
![RUSLAN: Russian Spoken Language Corpus For
Speech Synthesis
● Authors: Rustem Garaev, Evgenii Razinkov, Lenar Gabdrakhmanov;
● Largest annotated speech corpus in Russian for a single speaker - more than
31 hours of speech (<text, audio> pairs) - 22200 samples;
● Several improvements for Tacotron [4] were proposed:
○ All GRU layers replaced with Layer Normalized LSTM;
○ Fast Griffin-Lim algorithm used for waveform synthesizing from spectrogram.
● MOS: 4.05 for intelligibility and 3.78 for naturalness (vs 3.12 and 2.17 for
original model);
● Corpus site with recordings and synthesized speech:
https://ruslan-corpus.github.io/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-45-2048.jpg)


![References
[1] Van Den Oord, Aäron, Sander Dieleman, Heiga Zen, Karen Simonyan, Oriol
Vinyals, Alex Graves, Nal Kalchbrenner, Andrew W. Senior, and Koray
Kavukcuoglu. "WaveNet: A generative model for raw audio." In SSW, p. 125.
2016.
[2] Paine, Tom Le, Pooya Khorrami, Shiyu Chang, Yang Zhang, Prajit
Ramachandran, Mark A. Hasegawa-Johnson, and Thomas S. Huang. "Fast
wavenet generation algorithm." arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.09482 (2016).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-49-2048.jpg)
![References (2)
[3] Arik, Sercan O., Mike Chrzanowski, Adam Coates, Gregory Diamos, Andrew
Gibiansky, Yongguo Kang, Xian Li et al. "Deep voice: Real-time neural
text-to-speech." arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.07825 (2017).
[4] Wang, Yuxuan, R. J. Skerry-Ryan, Daisy Stanton, Yonghui Wu, Ron J. Weiss,
Navdeep Jaitly, Zongheng Yang et al. "Tacotron: Towards end-to-end speech
synthesis." arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10135 (2017).
[5] Arik, Sercan, Gregory Diamos, Andrew Gibiansky, John Miller, Kainan Peng,
Wei Ping, Jonathan Raiman, and Yanqi Zhou. "Deep voice 2: Multi-speaker
neural text-to-speech." arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.08947 (2017).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-50-2048.jpg)
![References (3)
[6] Tjandra, Andros, Sakriani Sakti, and Satoshi Nakamura. "Listening while
speaking: Speech chain by deep learning." Automatic Speech Recognition
and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), 2017 IEEE. IEEE, 2017.
[7] Ping, Wei, Kainan Peng, Andrew Gibiansky, Sercan O. Arik, Ajay Kannan,
Sharan Narang, Jonathan Raiman, and John Miller. "Deep voice 3: Scaling
text-to-speech with convolutional sequence learning." (2018).
[8] Shen, Jonathan, Ruoming Pang, Ron J. Weiss, Mike Schuster, Navdeep
Jaitly, Zongheng Yang, Zhifeng Chen et al. "Natural tts synthesis by
conditioning wavenet on mel spectrogram predictions." In 2018 IEEE
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing
(ICASSP), pp. 4779-4783. IEEE, 2018.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-51-2048.jpg)
![References (4)
[9] Wang, Yuxuan, et al. "Style Tokens: Unsupervised Style Modeling, Control
and Transfer in End-to-End Speech Synthesis." arXiv preprint
arXiv:1803.09017 (2018).
[10] Jia, Ye, et al. "Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker
Text-To-Speech Synthesis." arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.04558 (2018).
[11] Li, N., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Zhao, S., Liu, M., & Zhou, M. (2018). Close to Human
Quality TTS with Transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.08895.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provectusmeetupmodernttssystemsreview-181210131924/75/Lenar-Gabdrakhmanov-Provectus-Speech-synthesis-52-2048.jpg)