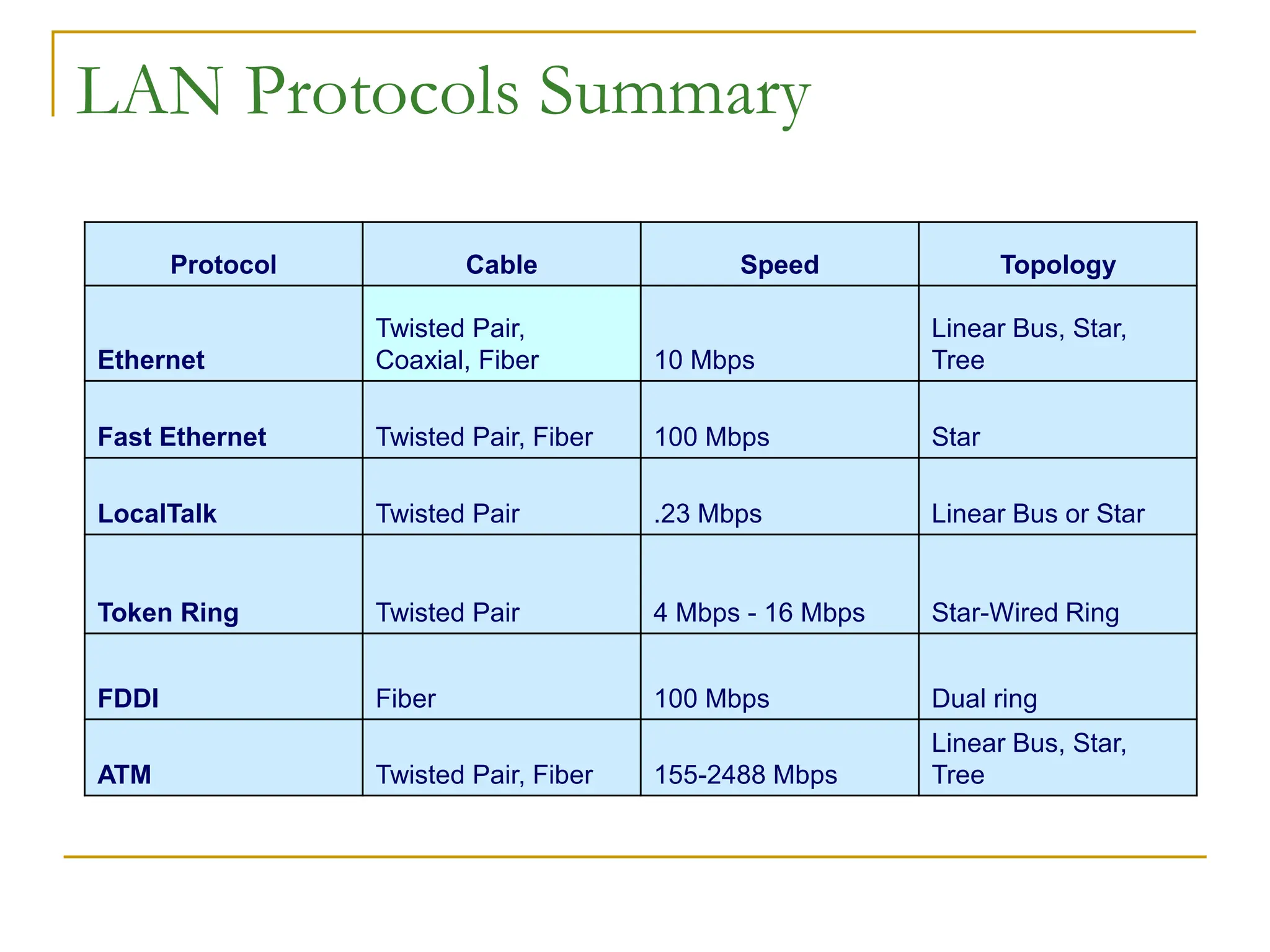
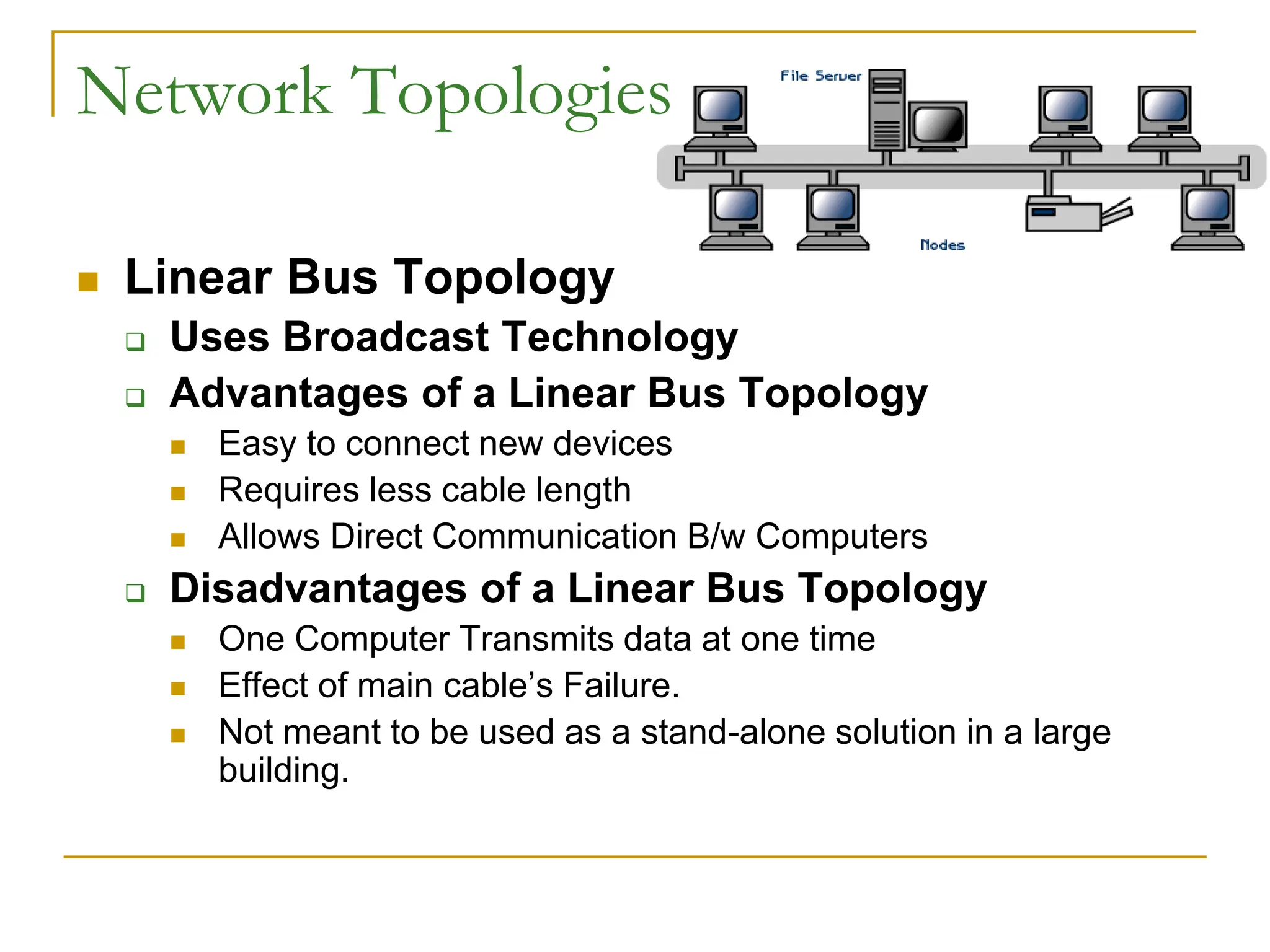
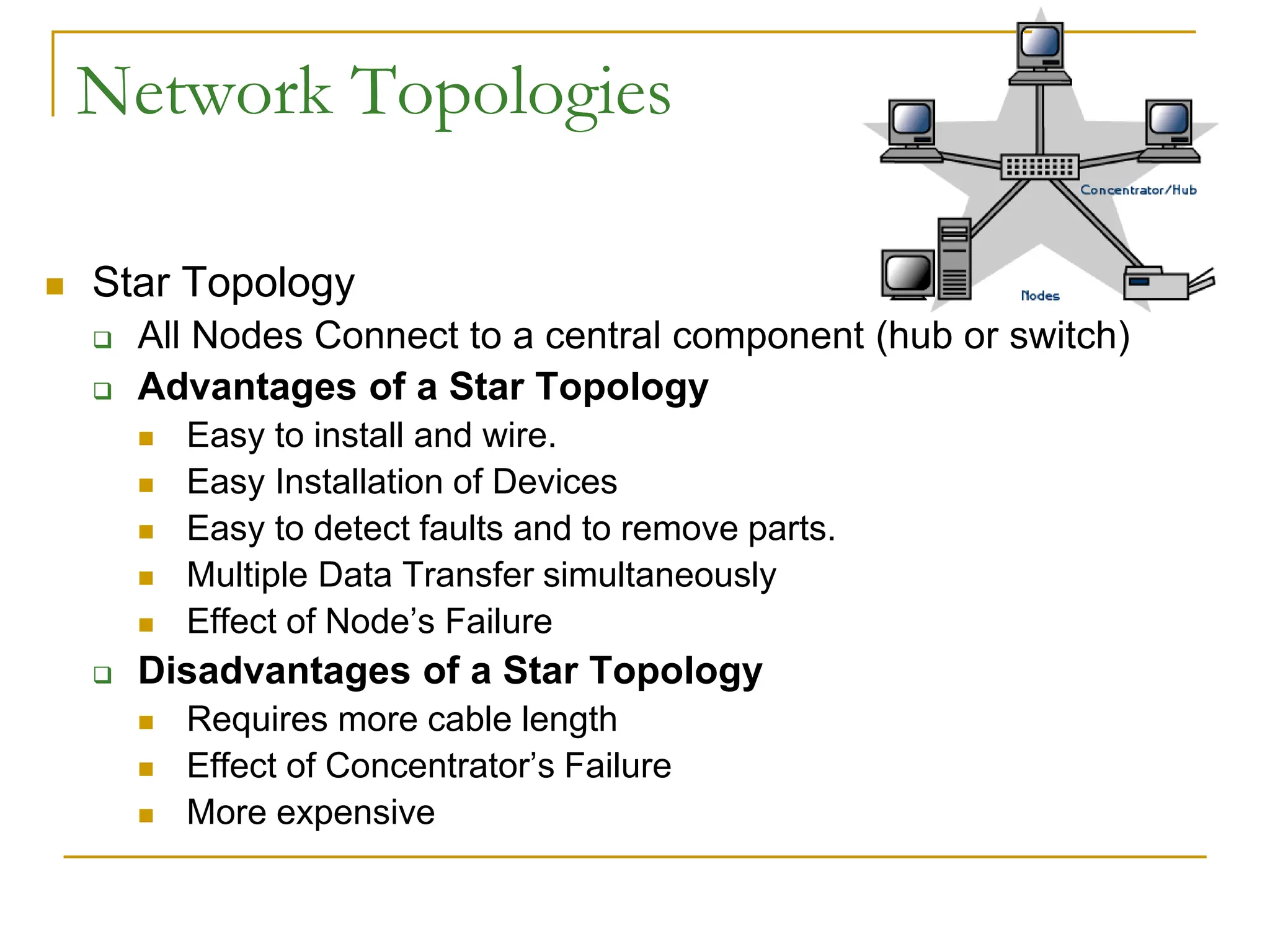
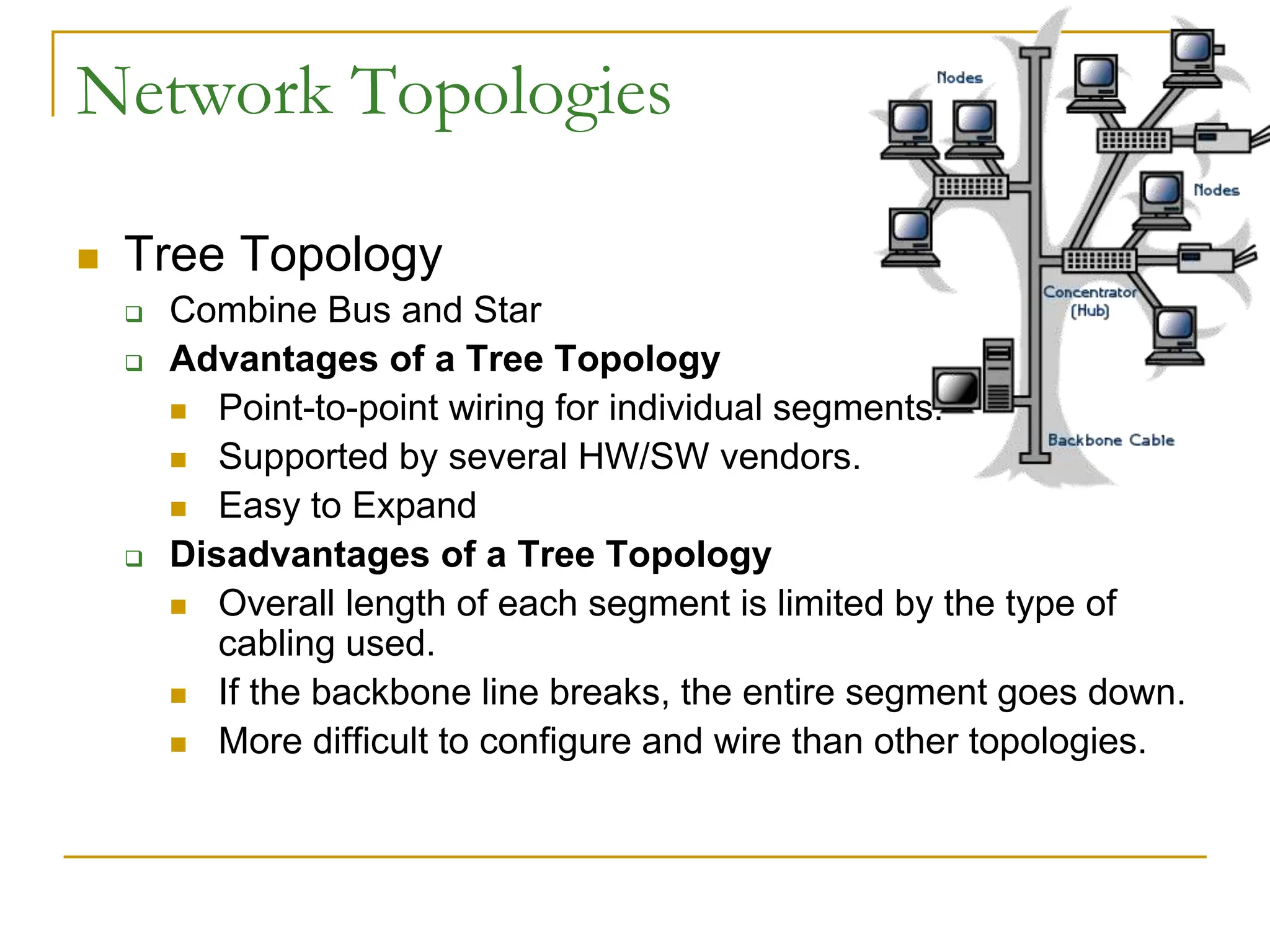
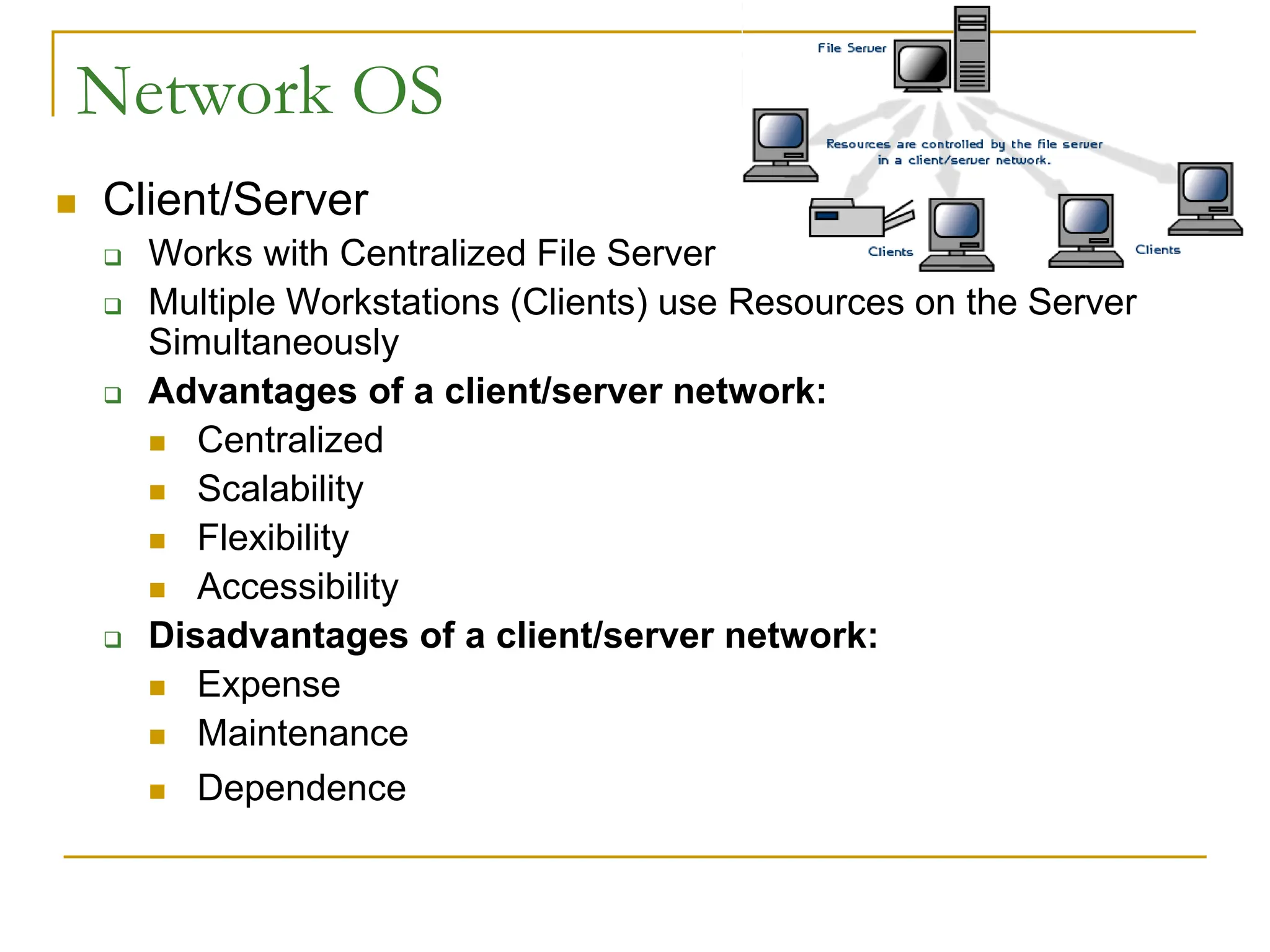
The document provides an overview of computer networks, focusing on wireless communication, LAN standards, protocols, and network topologies. It discusses the pros and cons of wireless communication, common LAN protocols like Ethernet and Token Ring, and various network topologies such as star and tree structures. Additionally, it touches on network operating systems, security measures, and addressing methods necessary for effective network management.