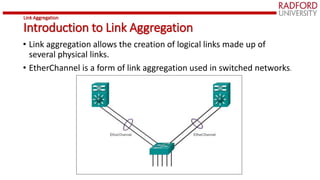
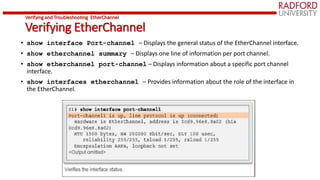
The document provides an overview of link aggregation, specifically focusing on EtherChannel, which allows multiple physical links to be combined into a single logical link for improved redundancy and load balancing. It covers the advantages of EtherChannel, configuration guidelines, and the protocols involved like PAgP and LACP. Additionally, it explains how to verify and troubleshoot EtherChannel setups using specific CLI commands.