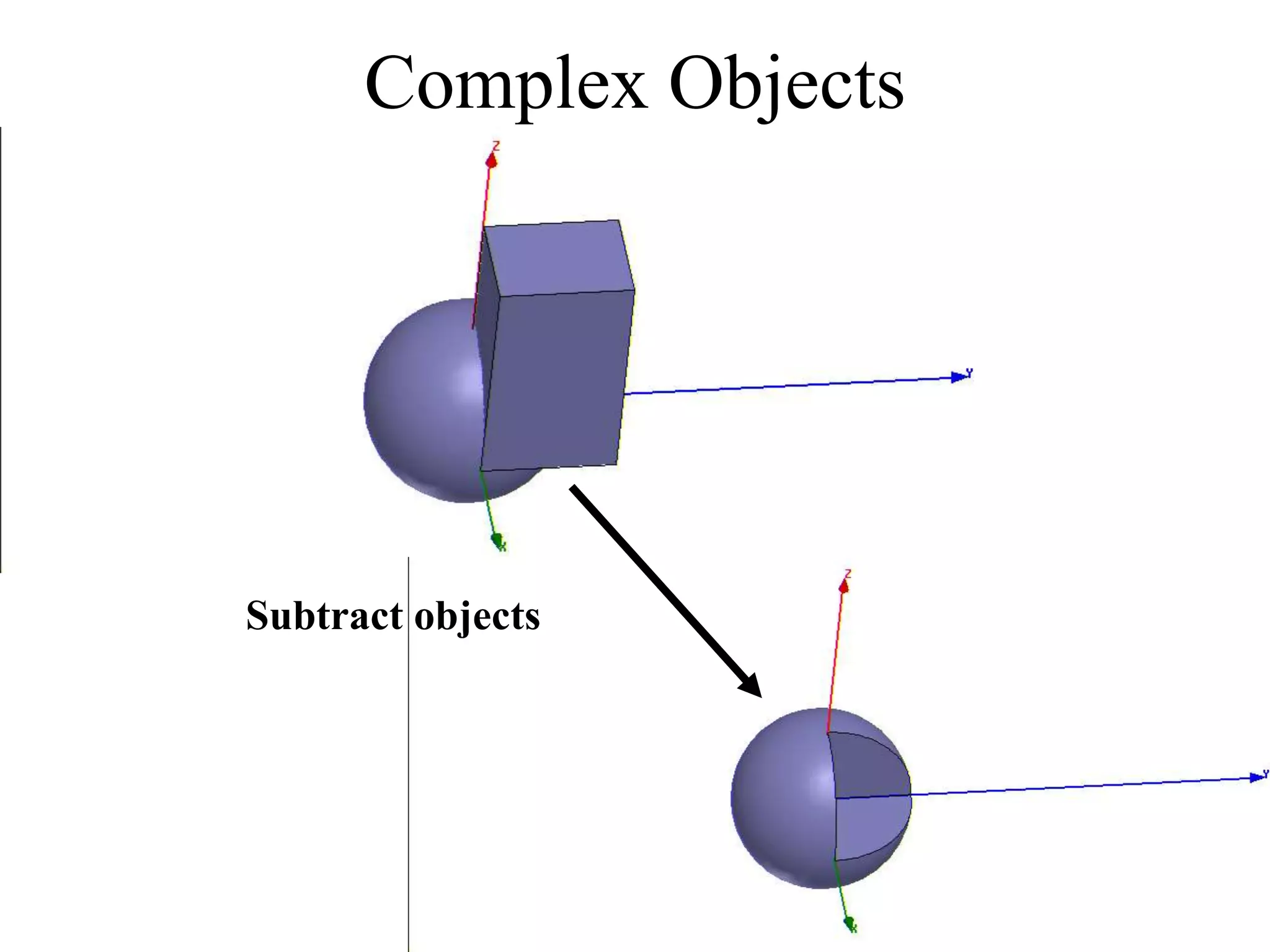
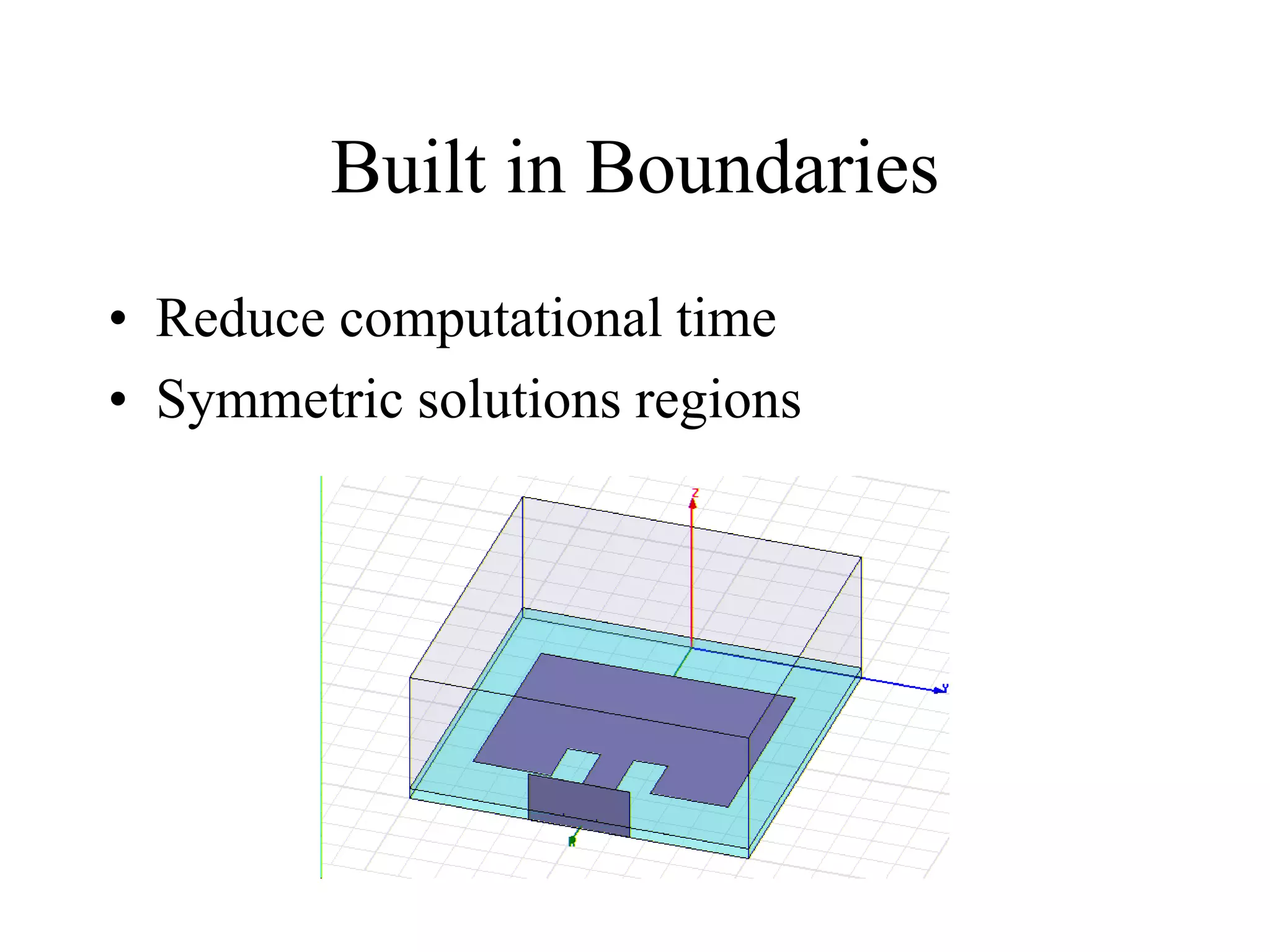
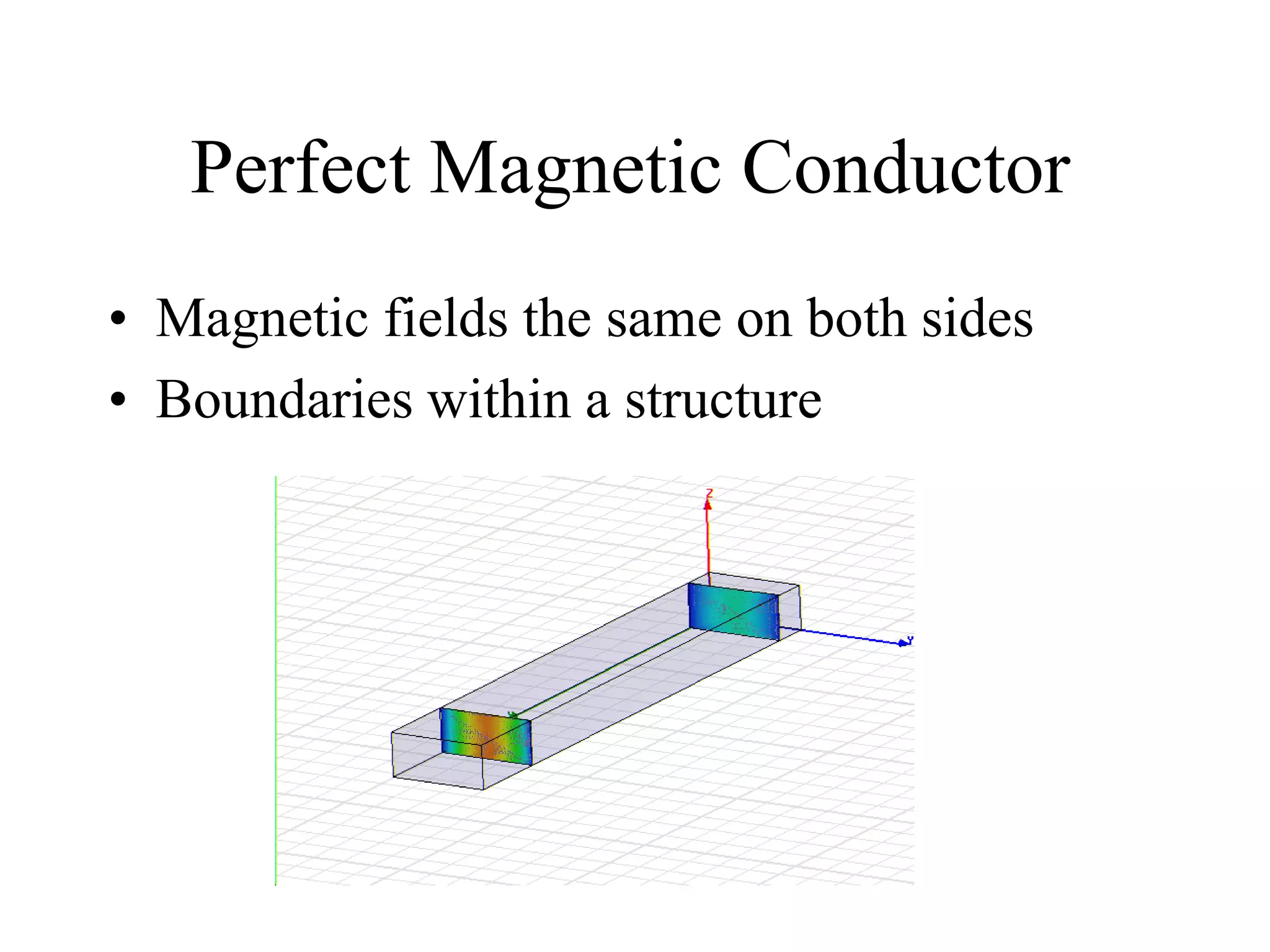
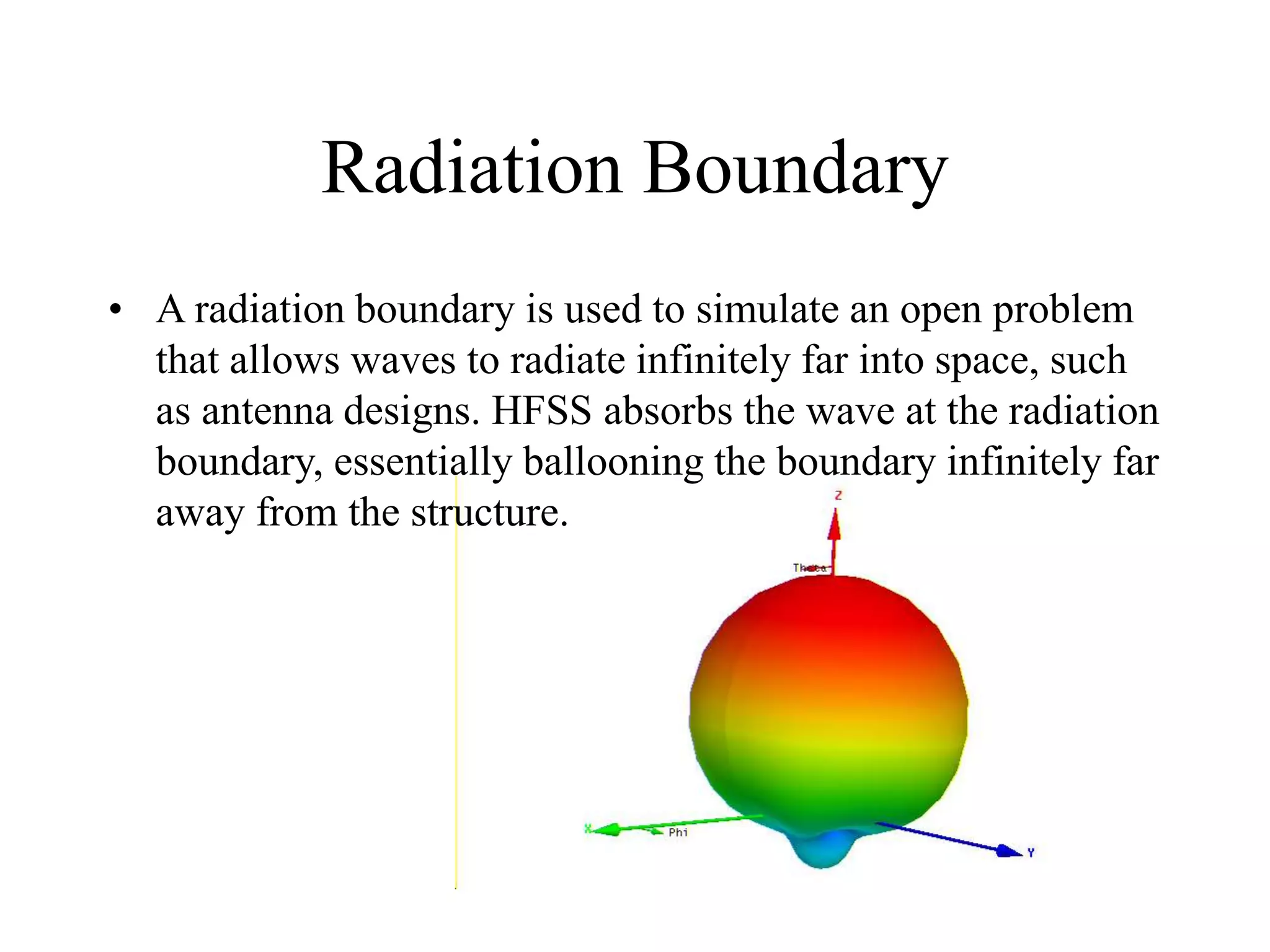
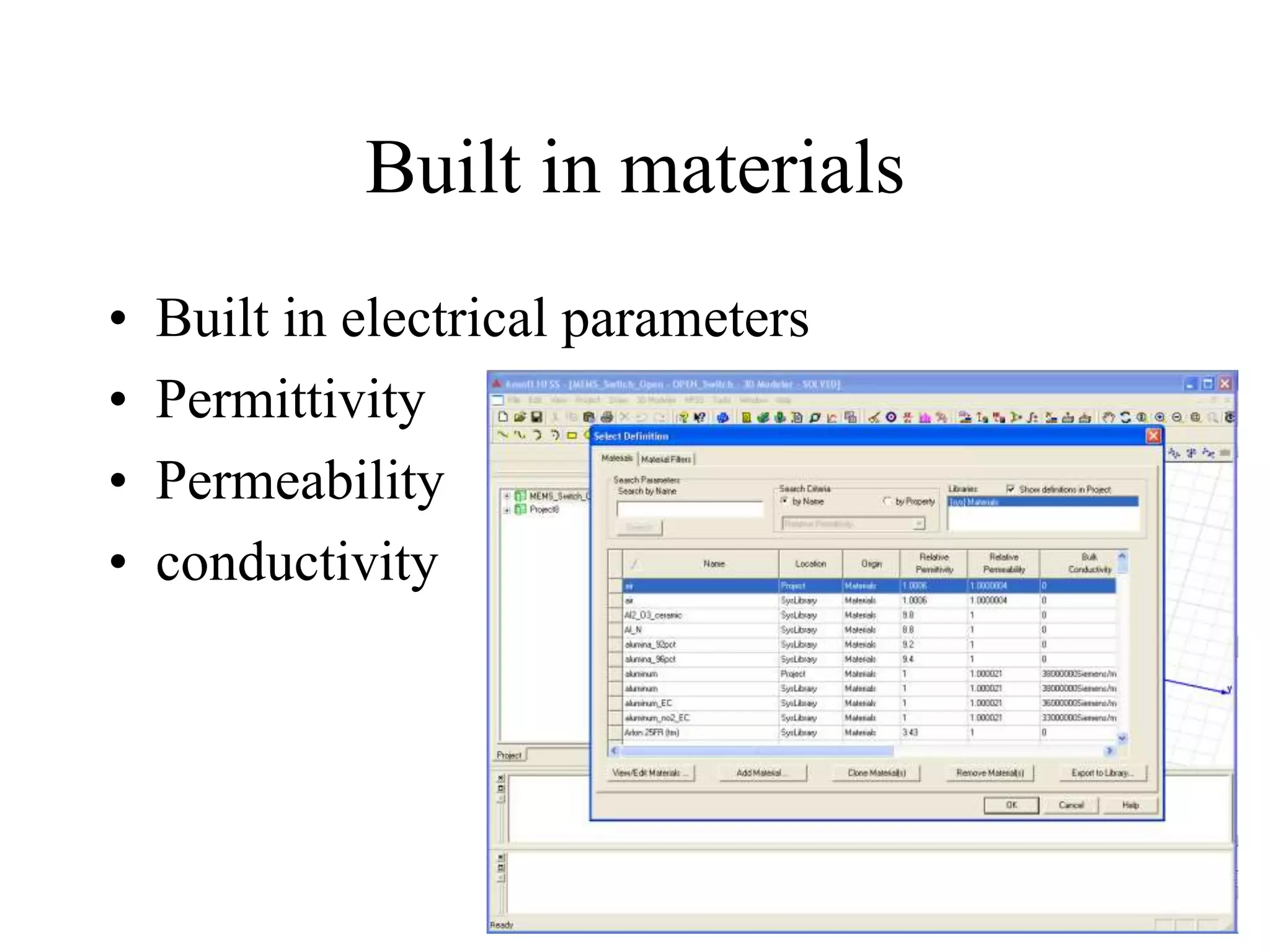
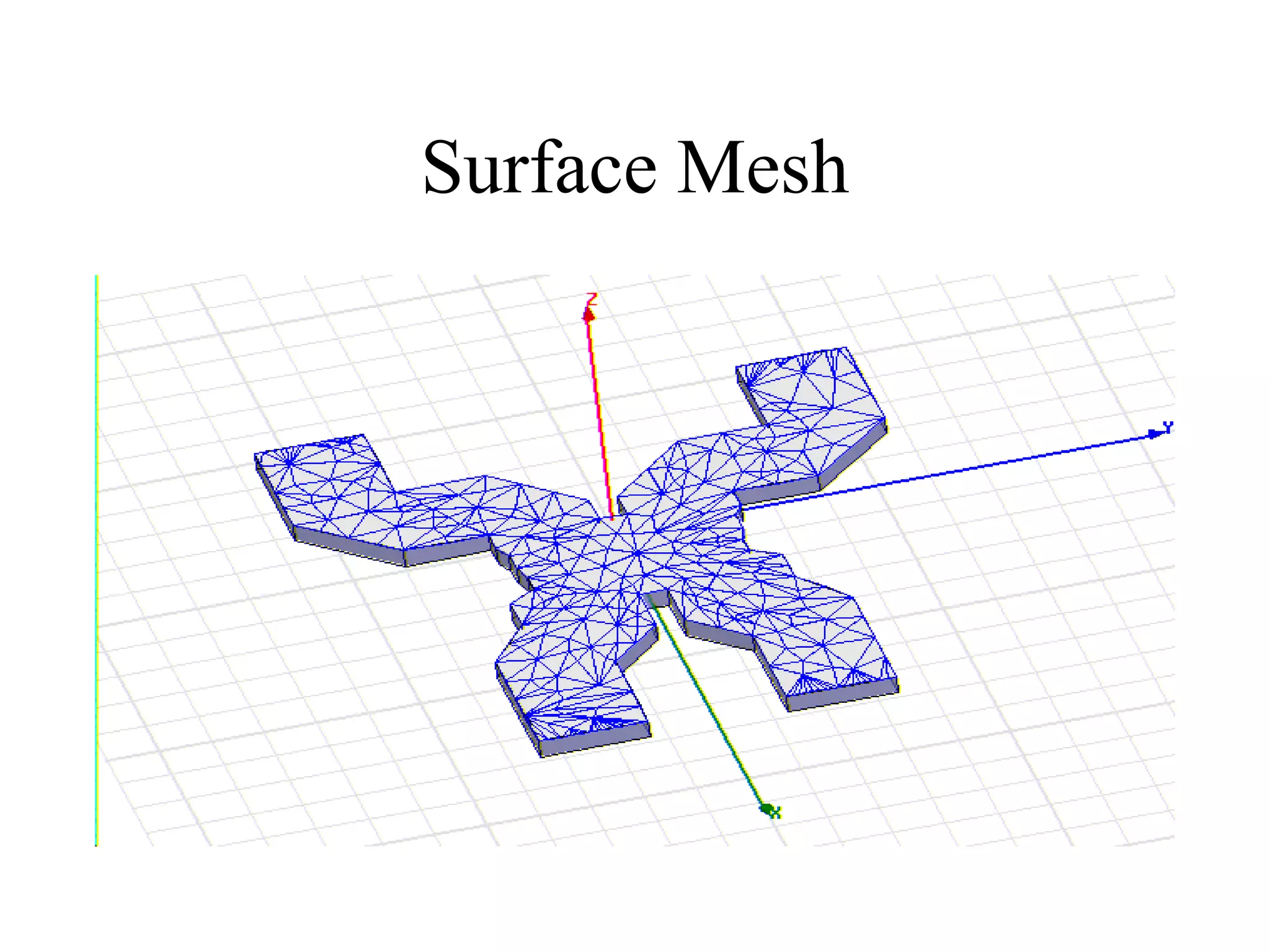
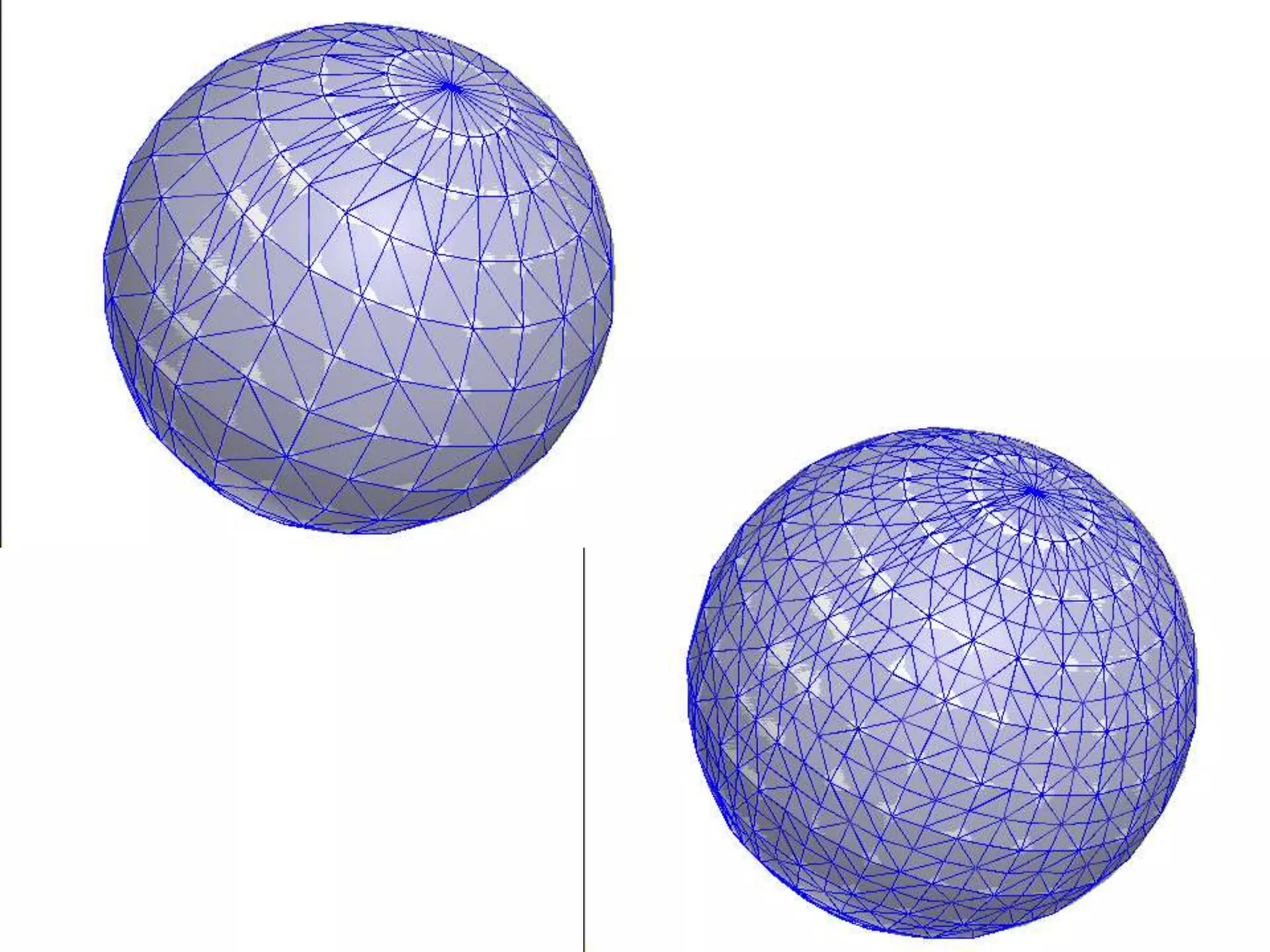
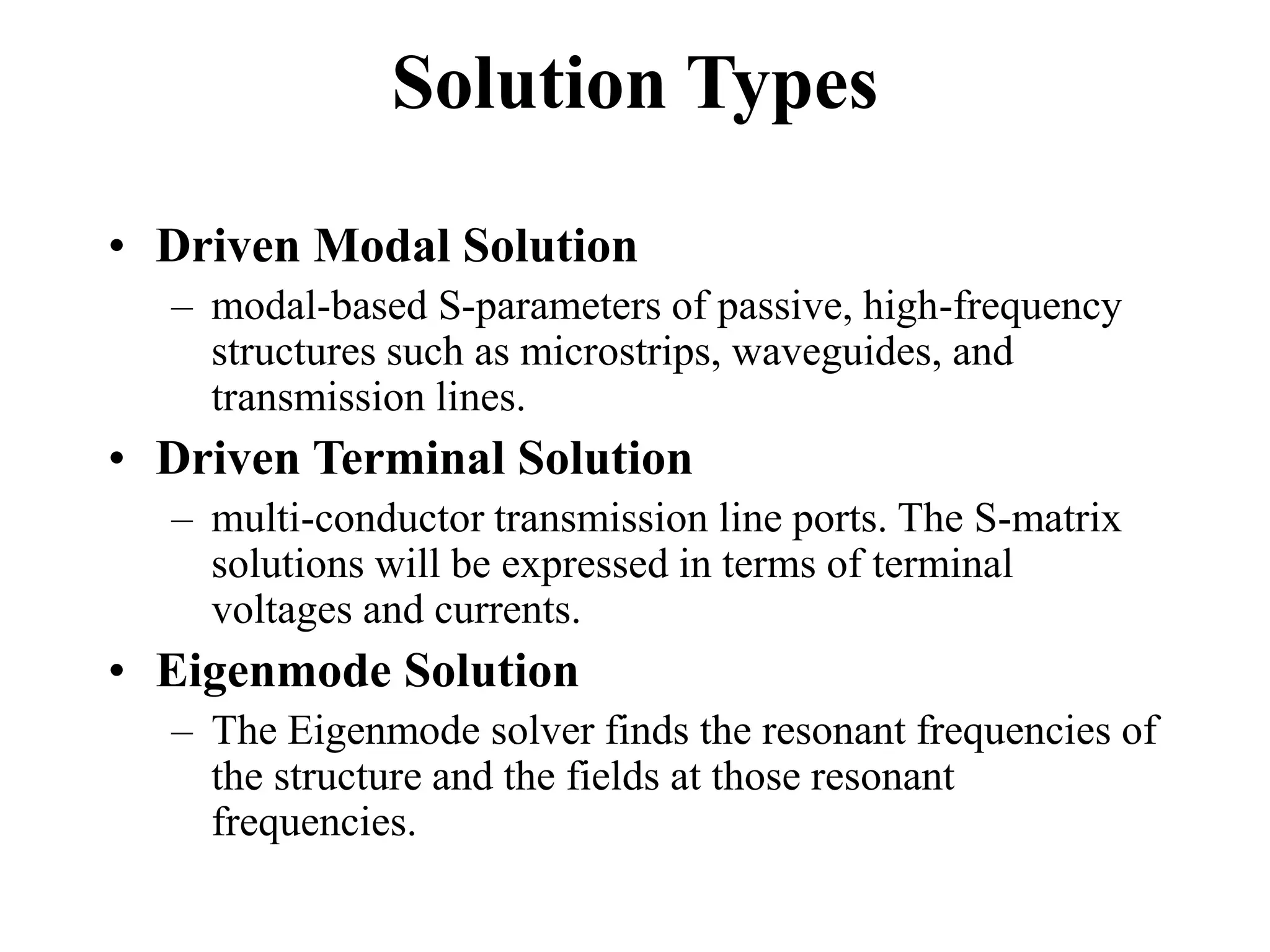
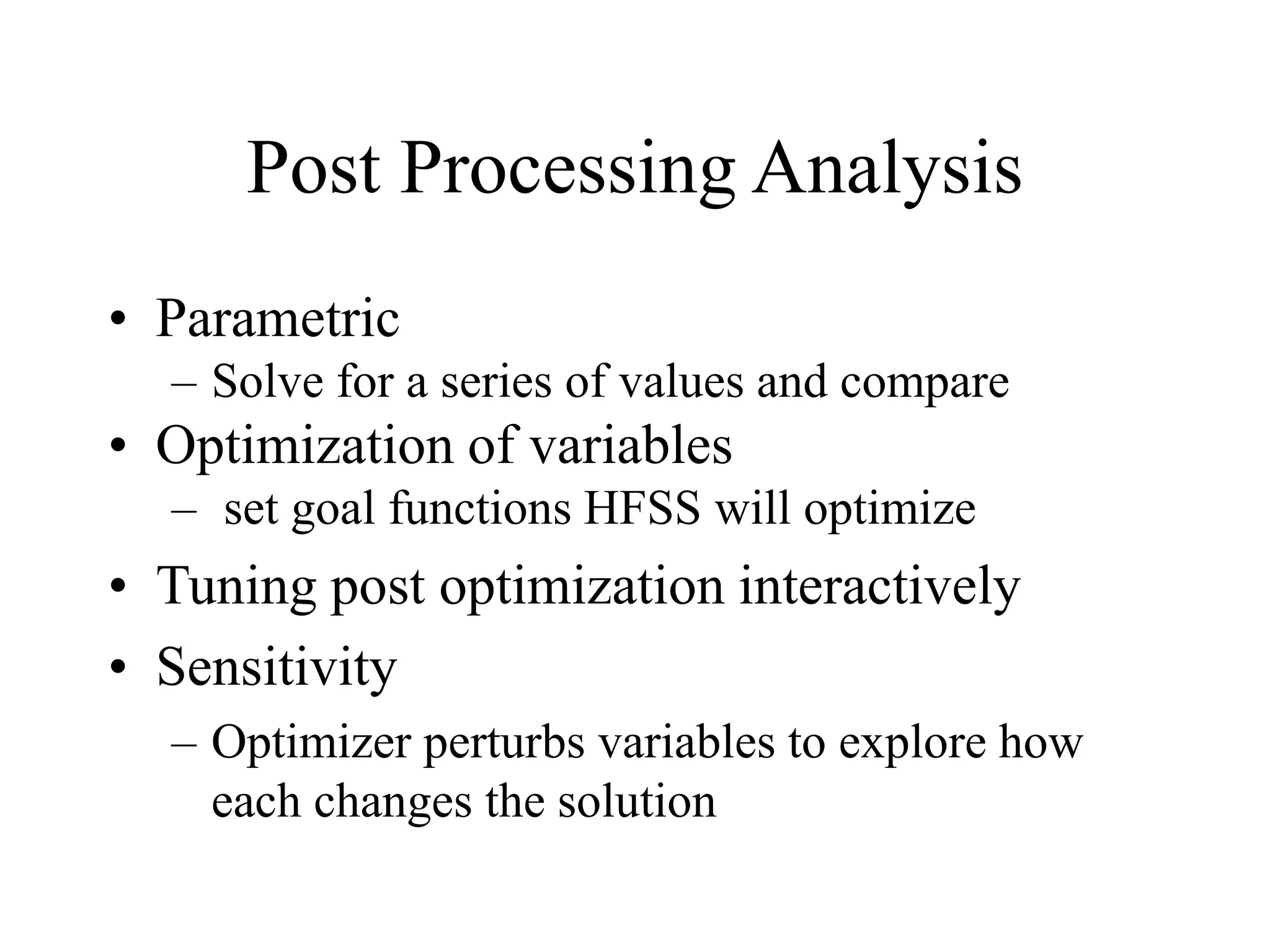
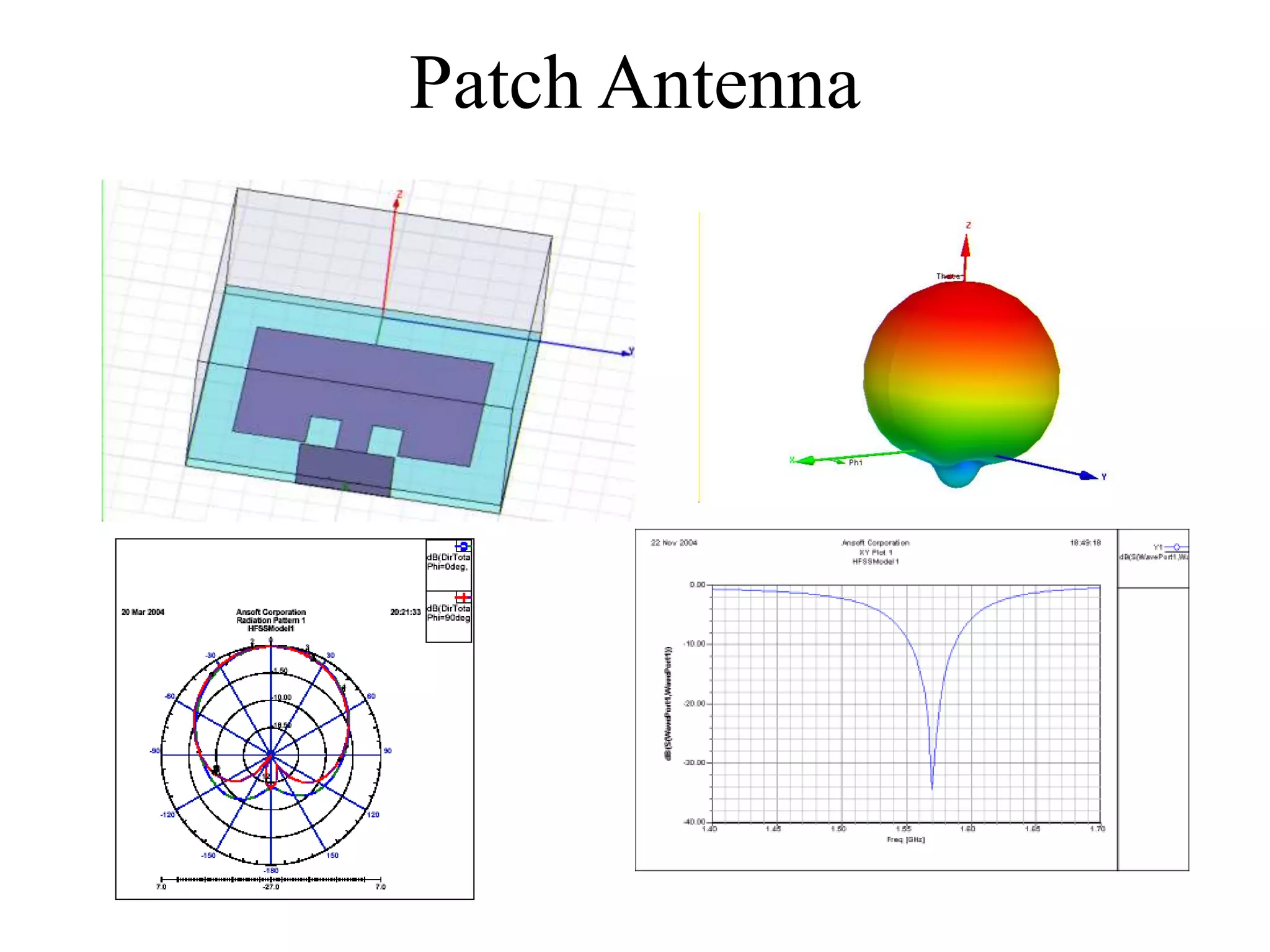
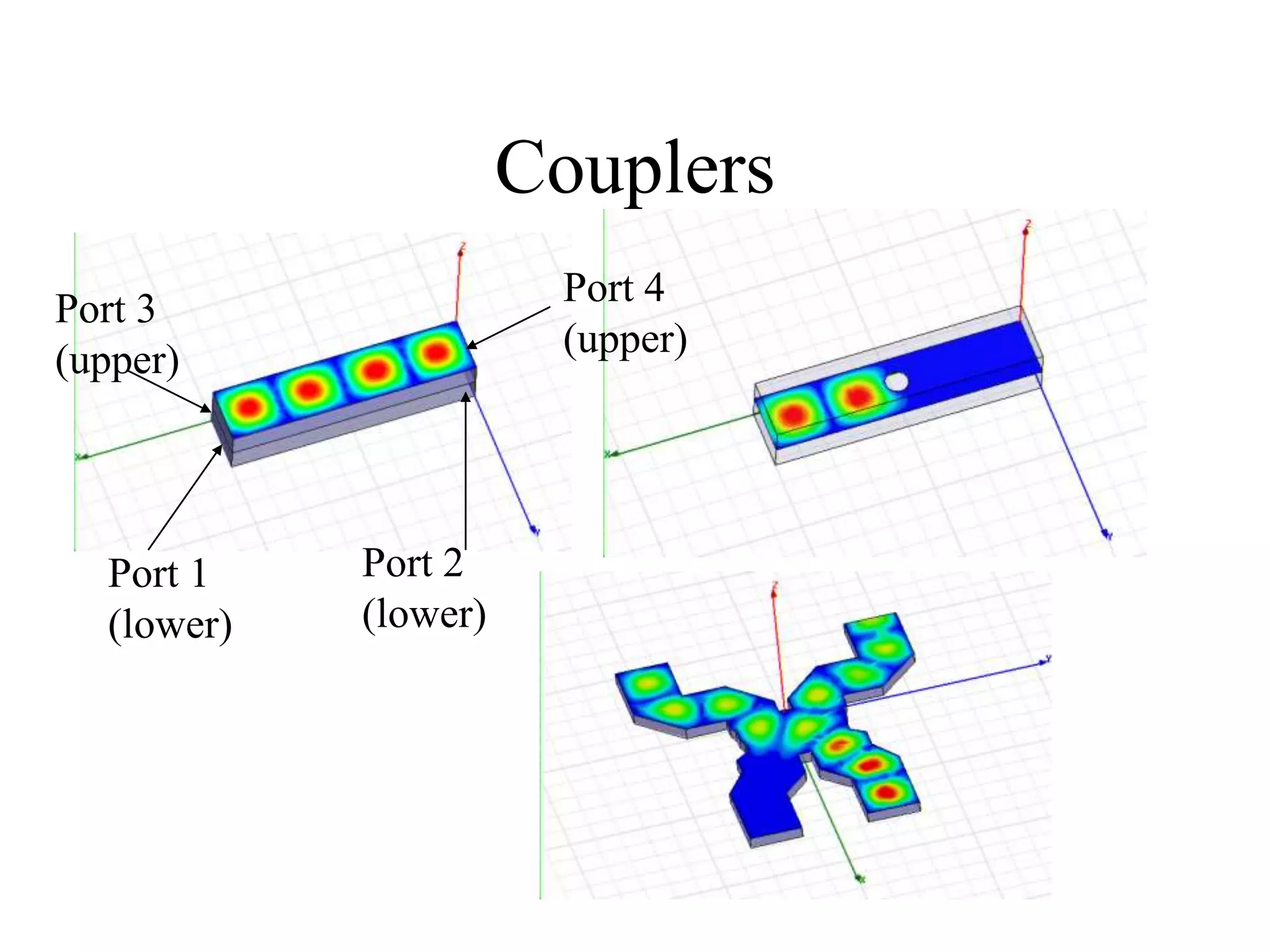
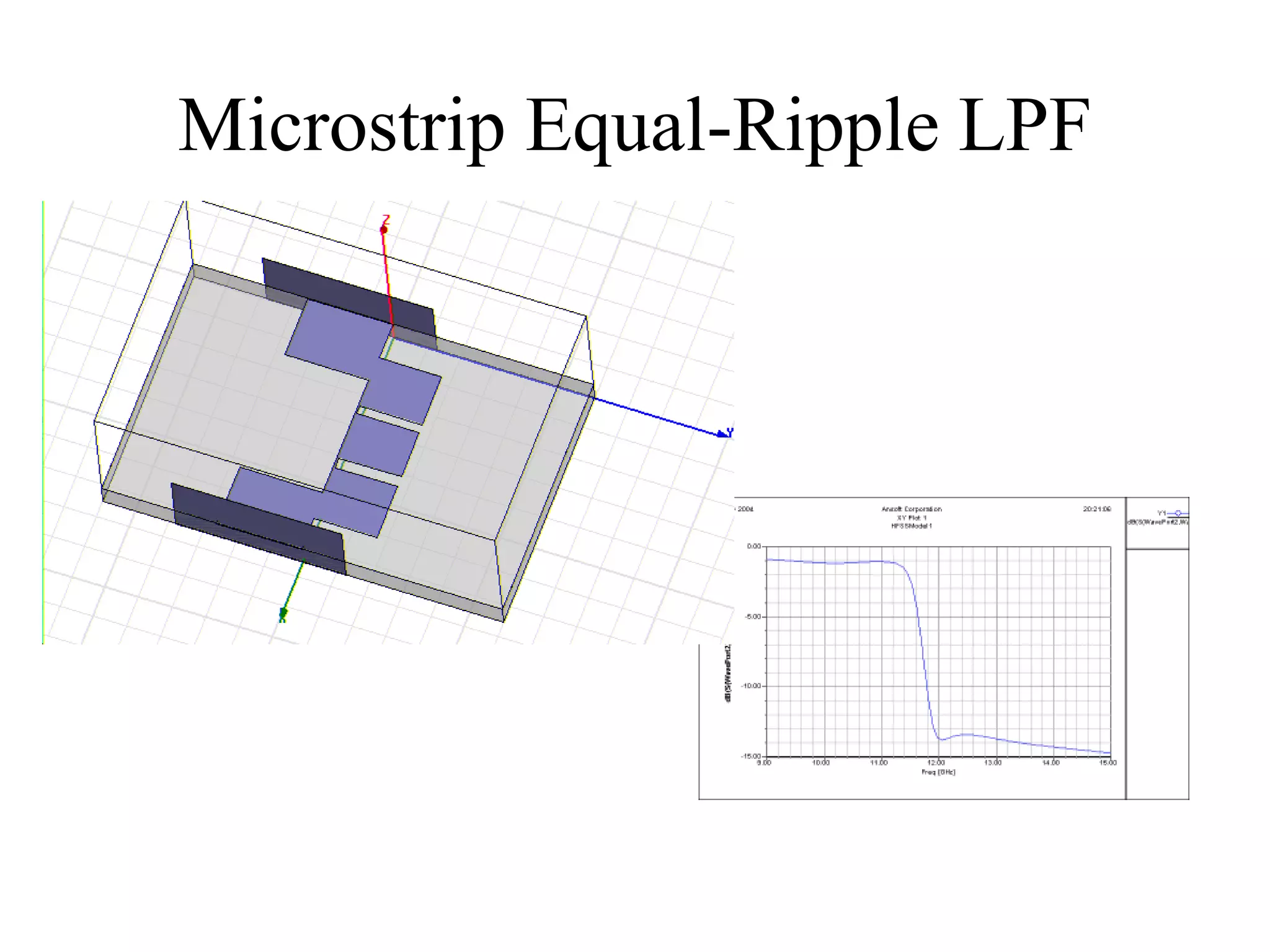
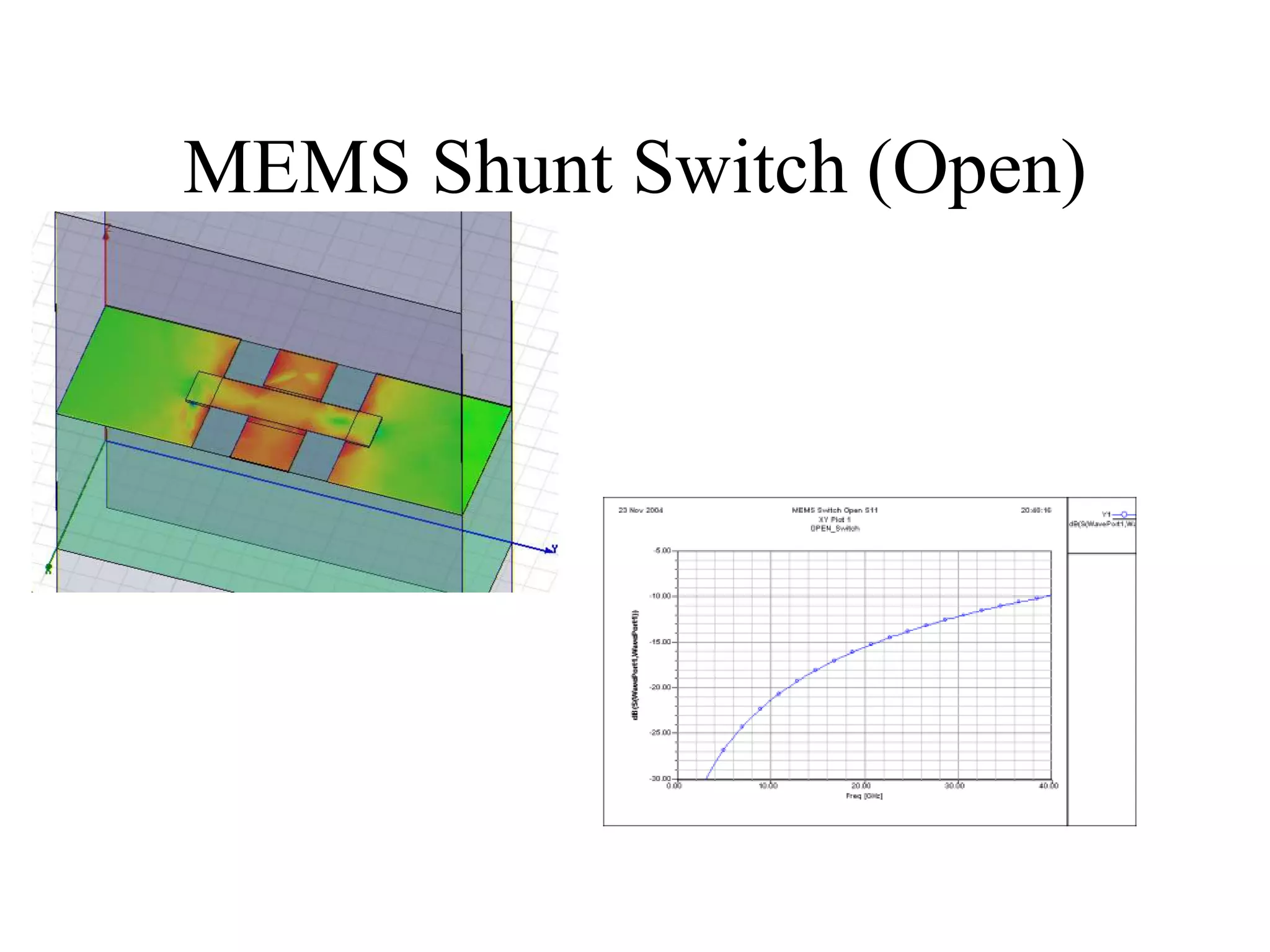
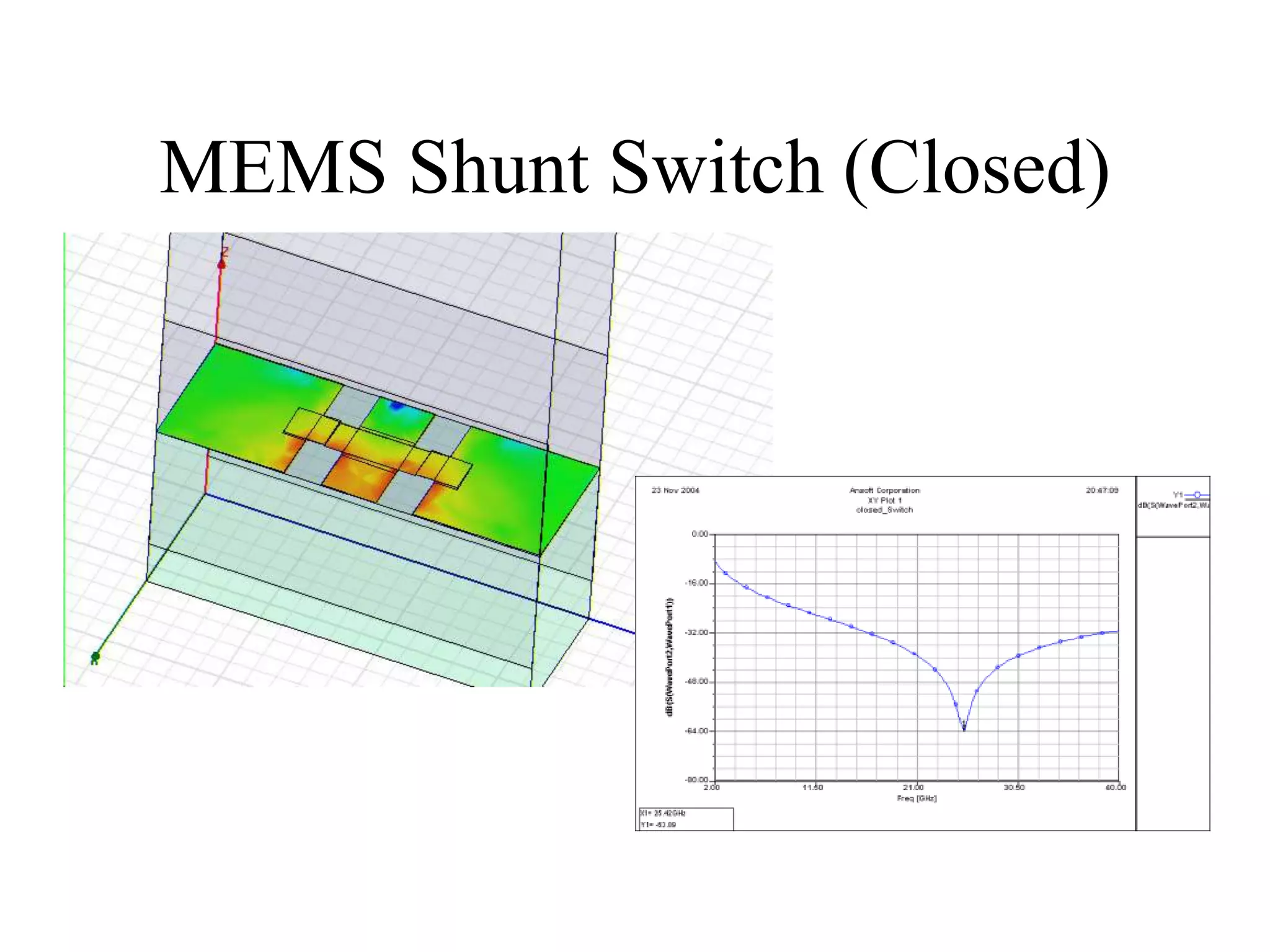
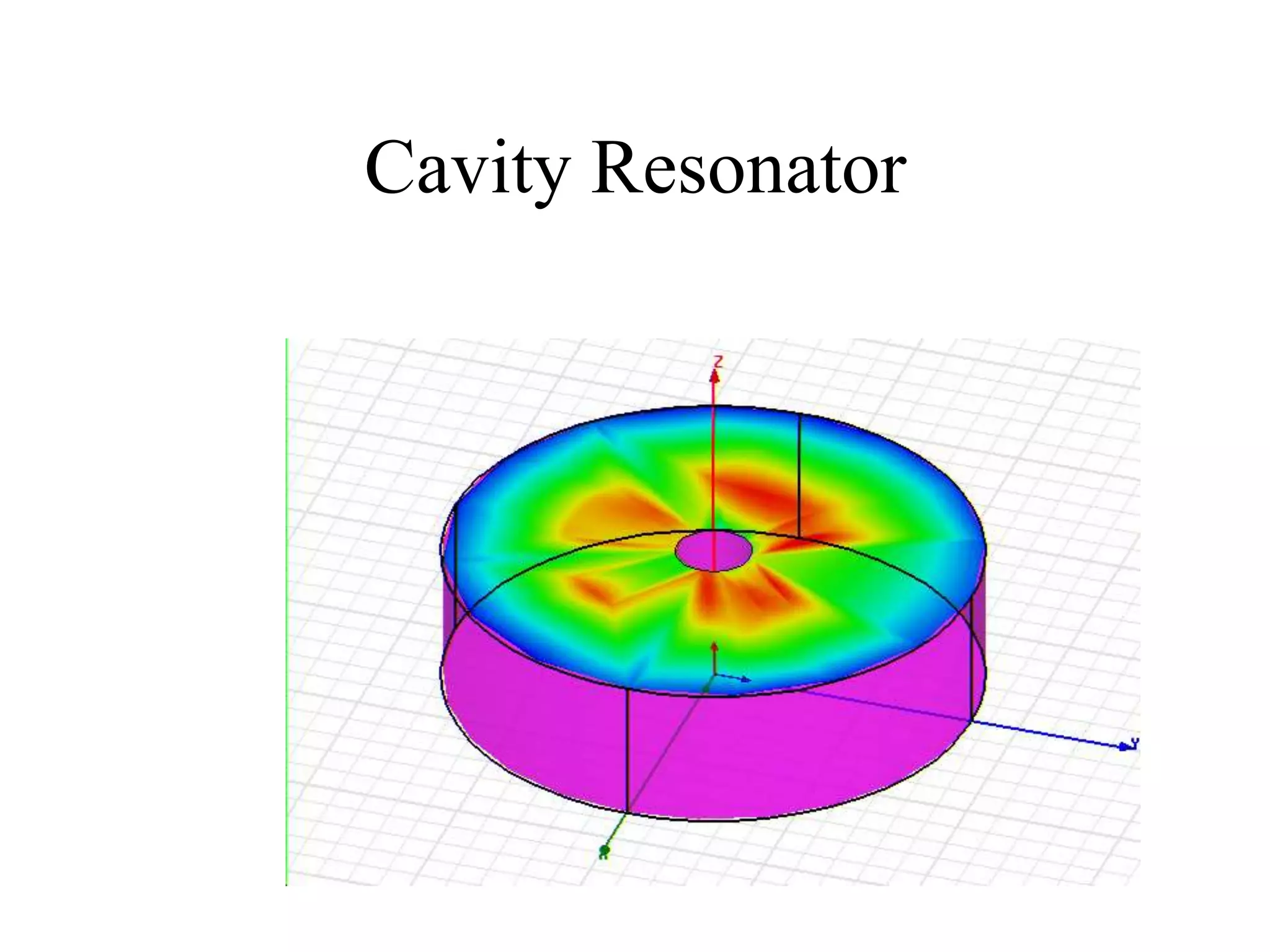
HFSS is a 3D electromagnetic simulation software that uses the finite element method. It can model passive structures and has features like adaptive meshing, user-defined mesh constraints, and built-in boundary conditions like perfect electric conductor and perfect magnetic conductor. HFSS also has built-in materials, mesh refinement options, and allows driven modal, driven terminal, and eigenmode solution types for analysis of structures like antennas, transmission lines, and resonators.