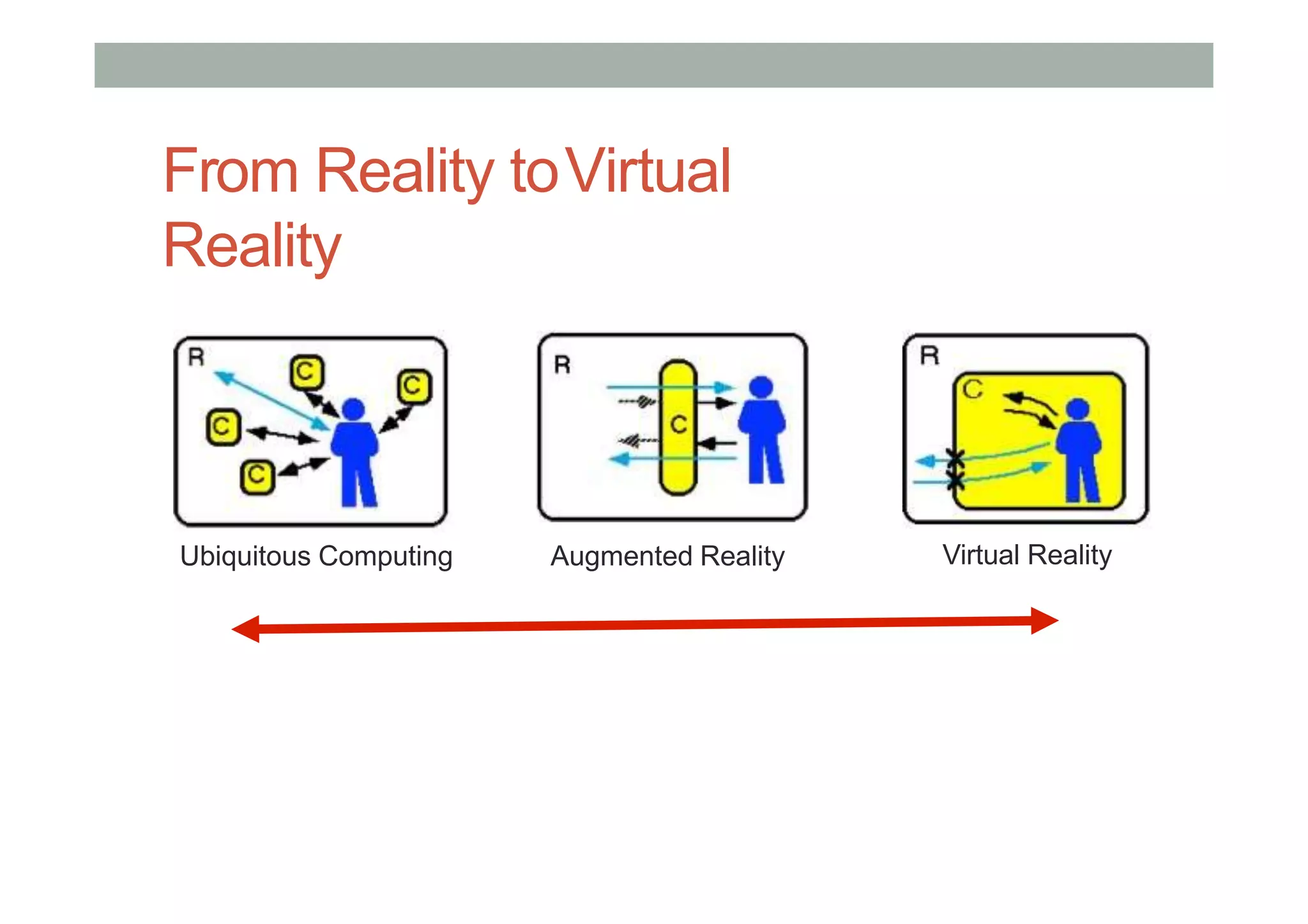
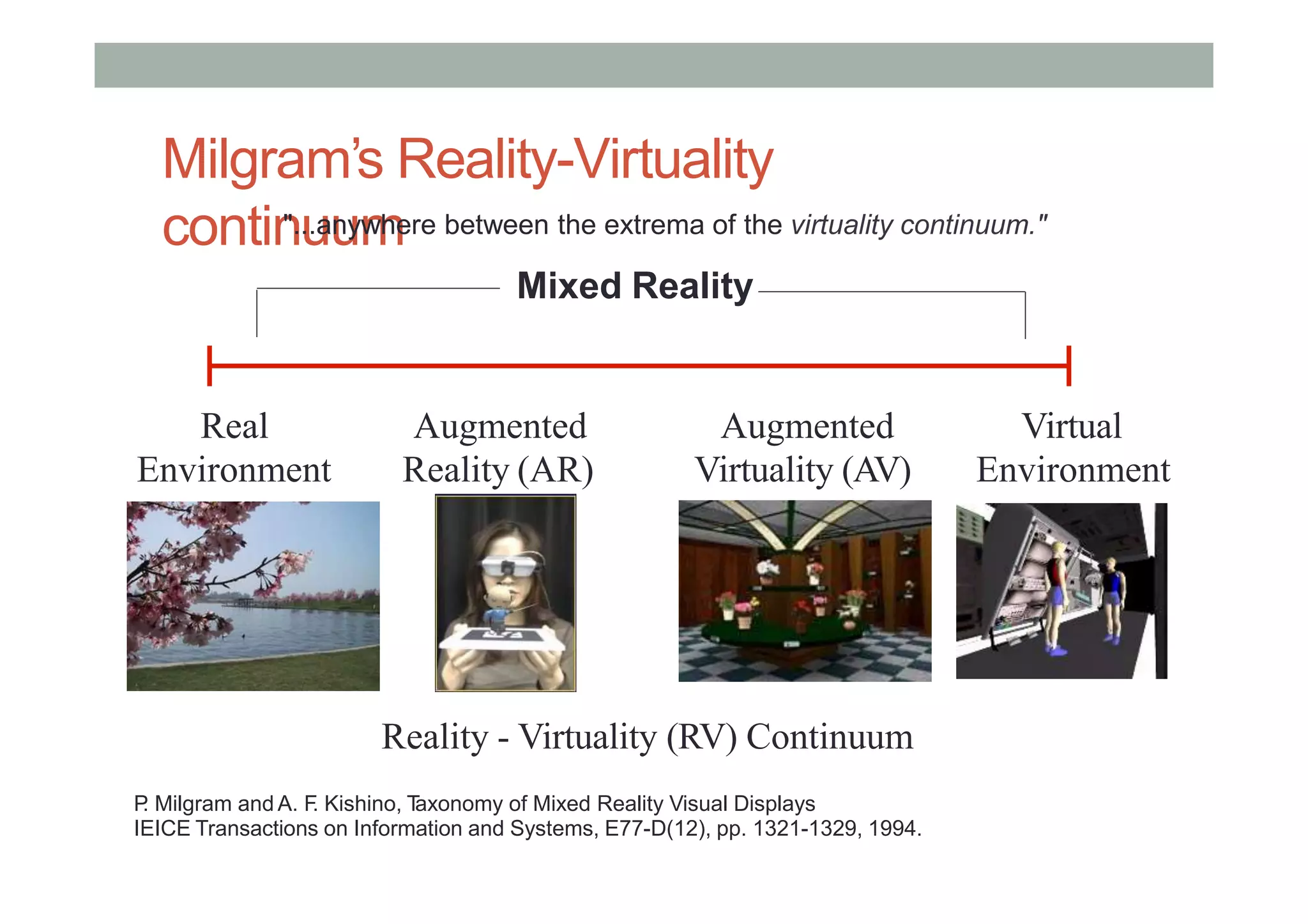
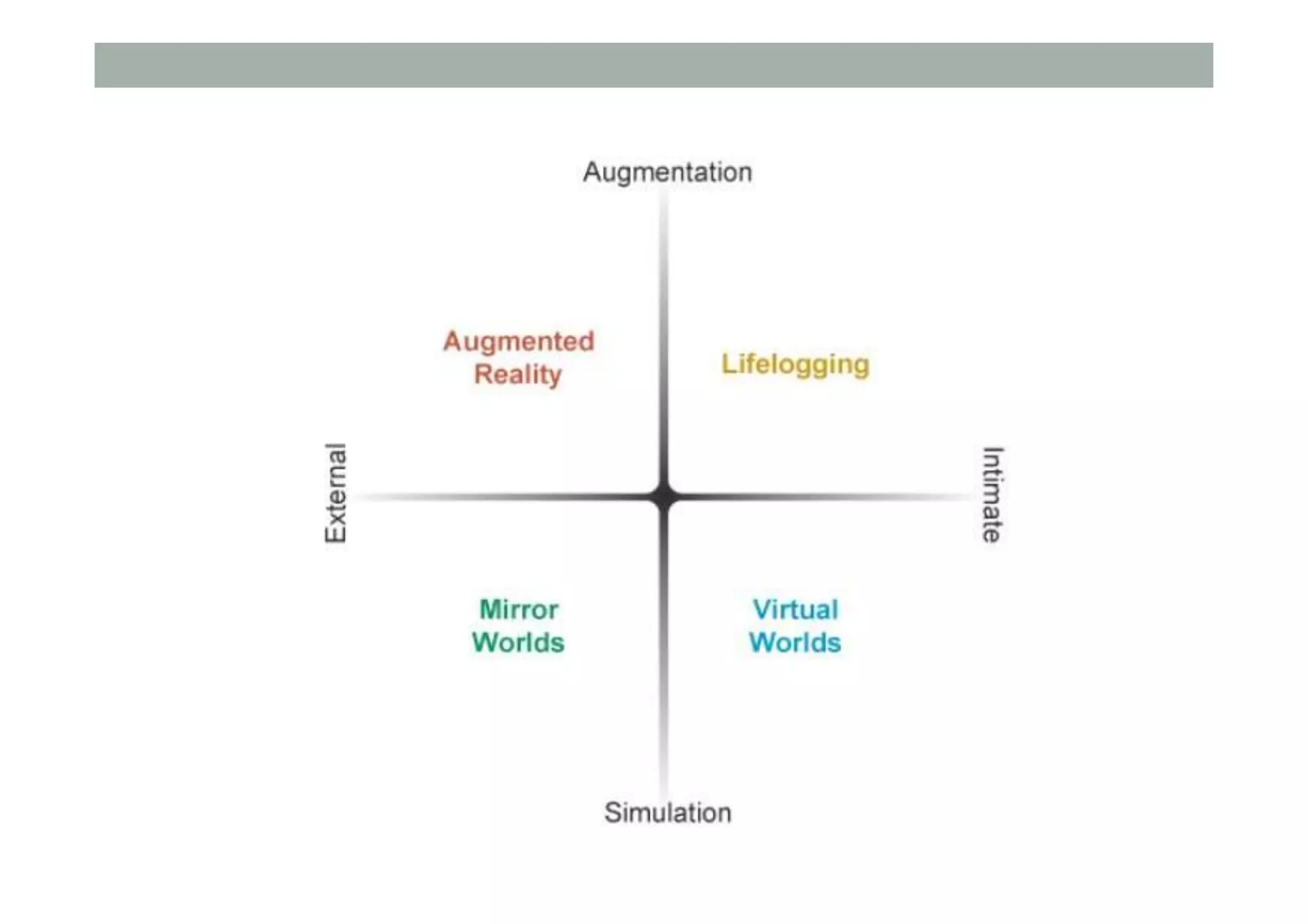
This lecture provided an introduction to virtual systems and discussed various definitions and classifications of virtual reality (VR). It defined VR in terms of the required technology including stereoscopic displays, wide field of view, and low latency head tracking. VR was also defined based on the sense of presence and telepresence. The lecture discussed VR along a mixed reality continuum and how it relates to augmented reality, augmented virtuality, and ubiquitous computing. Finally, it introduced the concept of a metaverse as the convergence of virtually enhanced physical and physically persistent virtual spaces.


















![Augmented Reality
Definition
•Defining Characteristics [Azuma
97]
• Combines Real andVirtual Images
• Both can be seen at the same time
• Interactive in real-time
• The virtual content can be interacted
with
• Registered in 3D
• Virtual objects appear fixed in space
Azuma, R. T. (1997). A survey of augmented reality. Presence, 6(4), 355-385.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture01-230507064836-1d9f79c7/75/Lecture-01-pptx-28-2048.jpg)