The document discusses various types of security interests in South African law including mortgages, cession in security, hypothecs, and liens. It provides details on:
1) How a mortgage is created through a mortgage agreement and registration in the Deeds Registry, and the rights of the mortgagee including to accruals on the property.
2) Cession in security which involves a debtor ceding personal rights to a creditor as security for a debt.
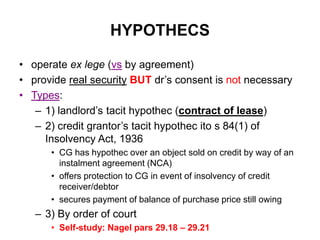
3) Hypothecs which provide real security over property without the owner's consent in certain situations like with a landlord or credit grantor.
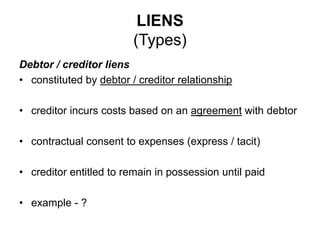
4) Liens which give a right of retention to someone in possession of property who has