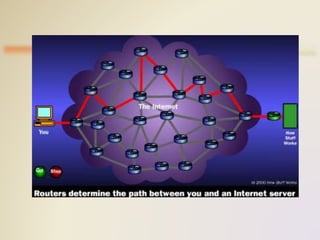
The Internet is a global network that connects computers around the world using wires like phone lines. It allows for communication through email and accessing information for research, shopping, news, and entertainment. Key terms include the World Wide Web (WWW), browsers like Chrome and Firefox that view web pages, search engines that help locate information, URLs that uniquely identify web pages, and HTML that defines the structure and layout of web pages.