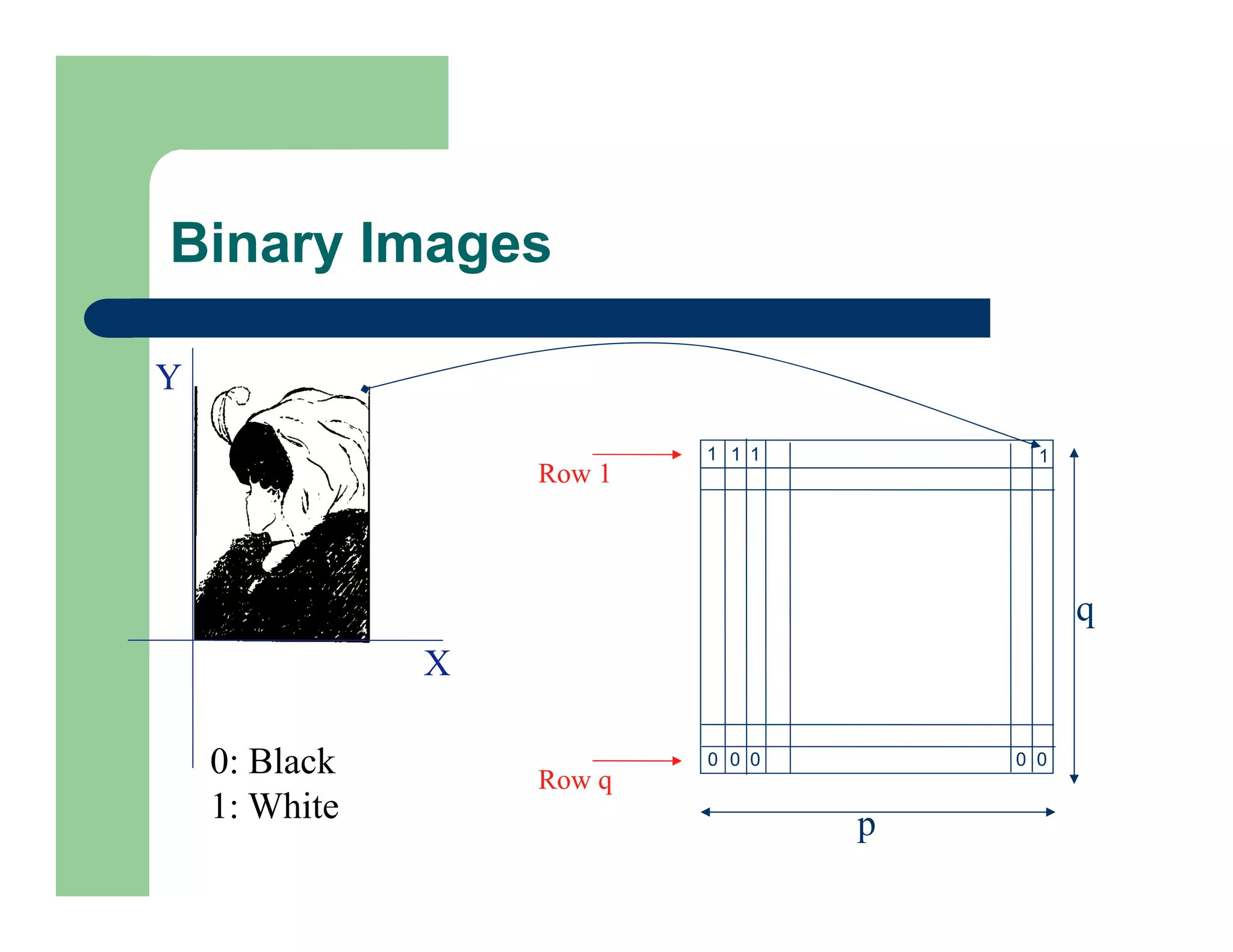
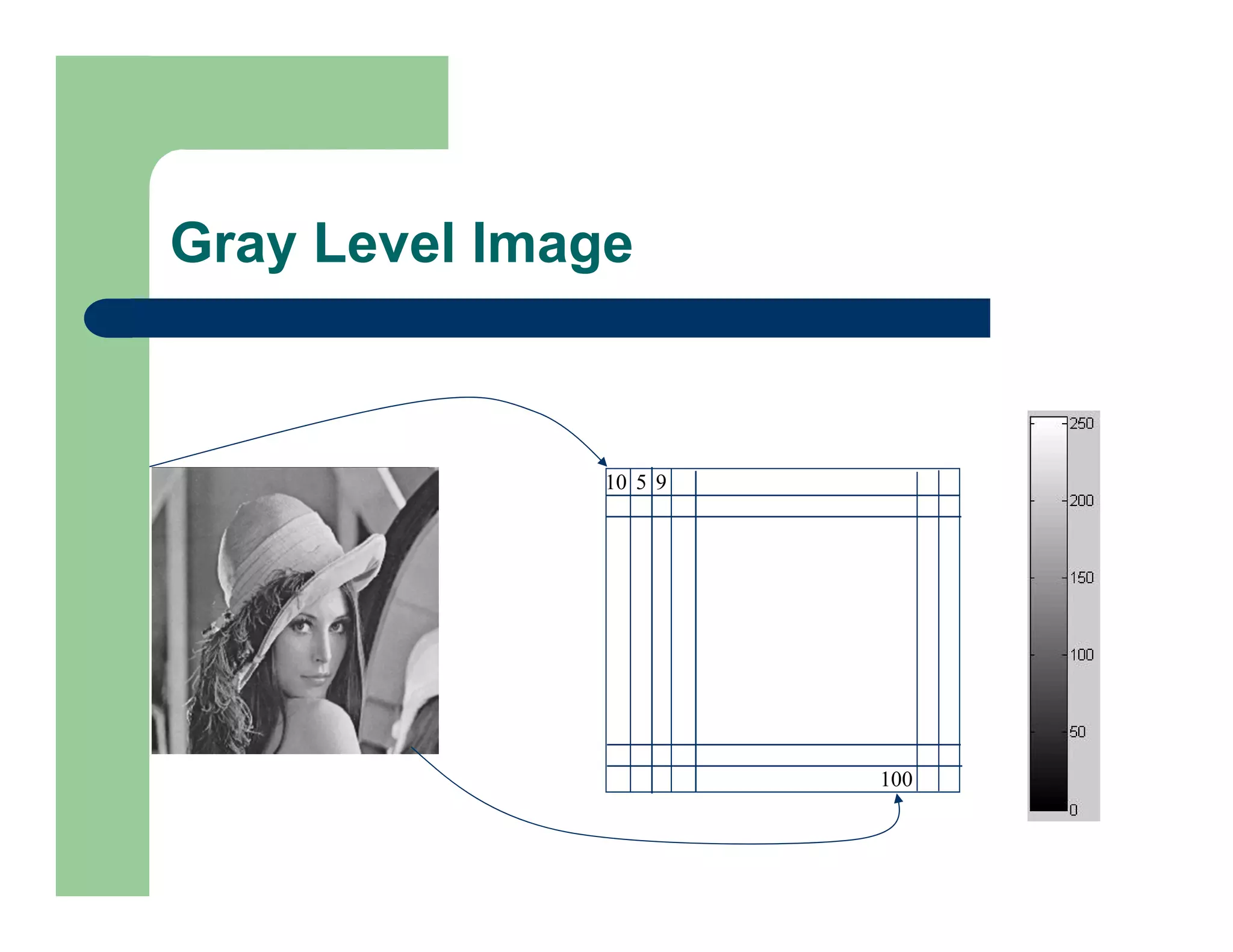
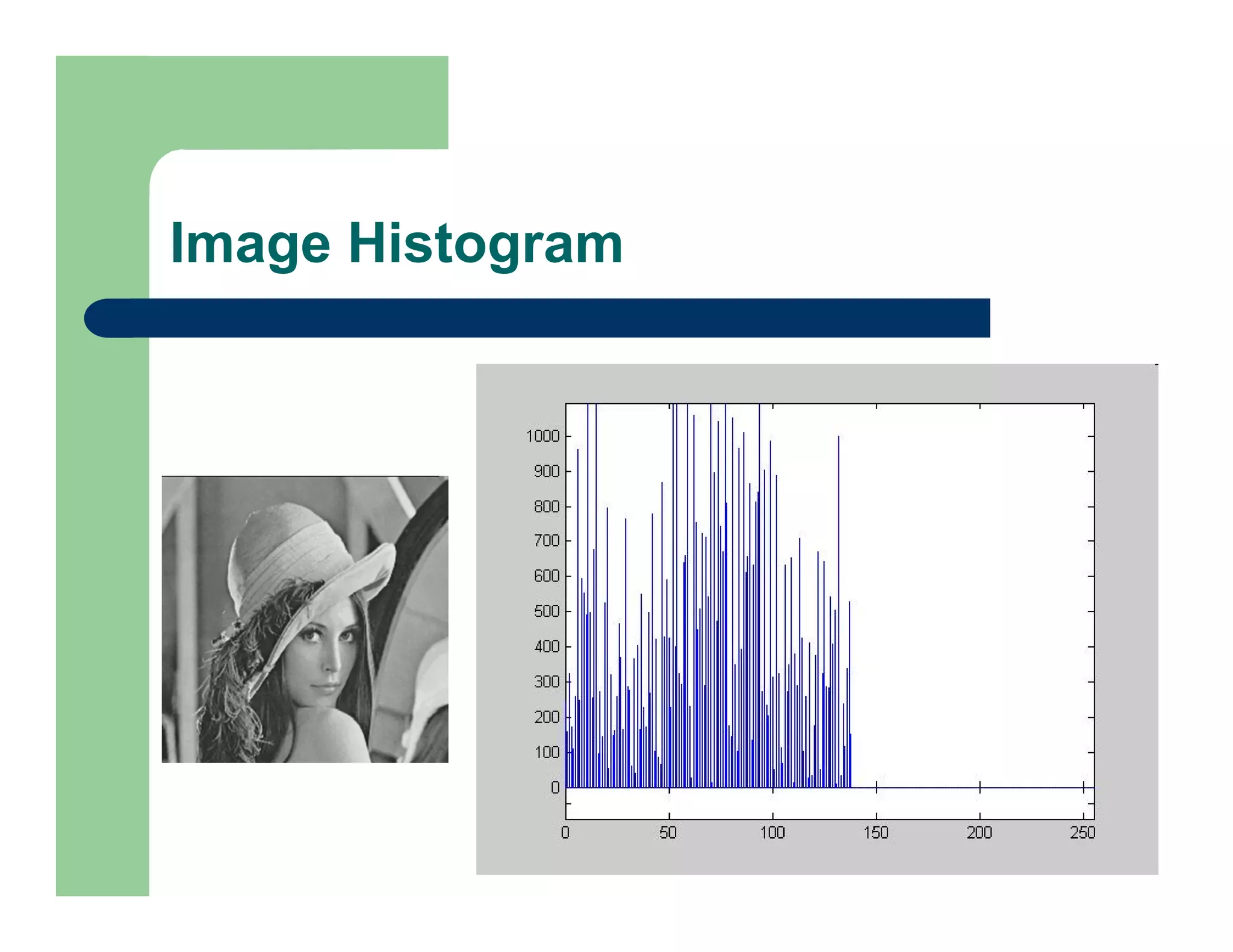
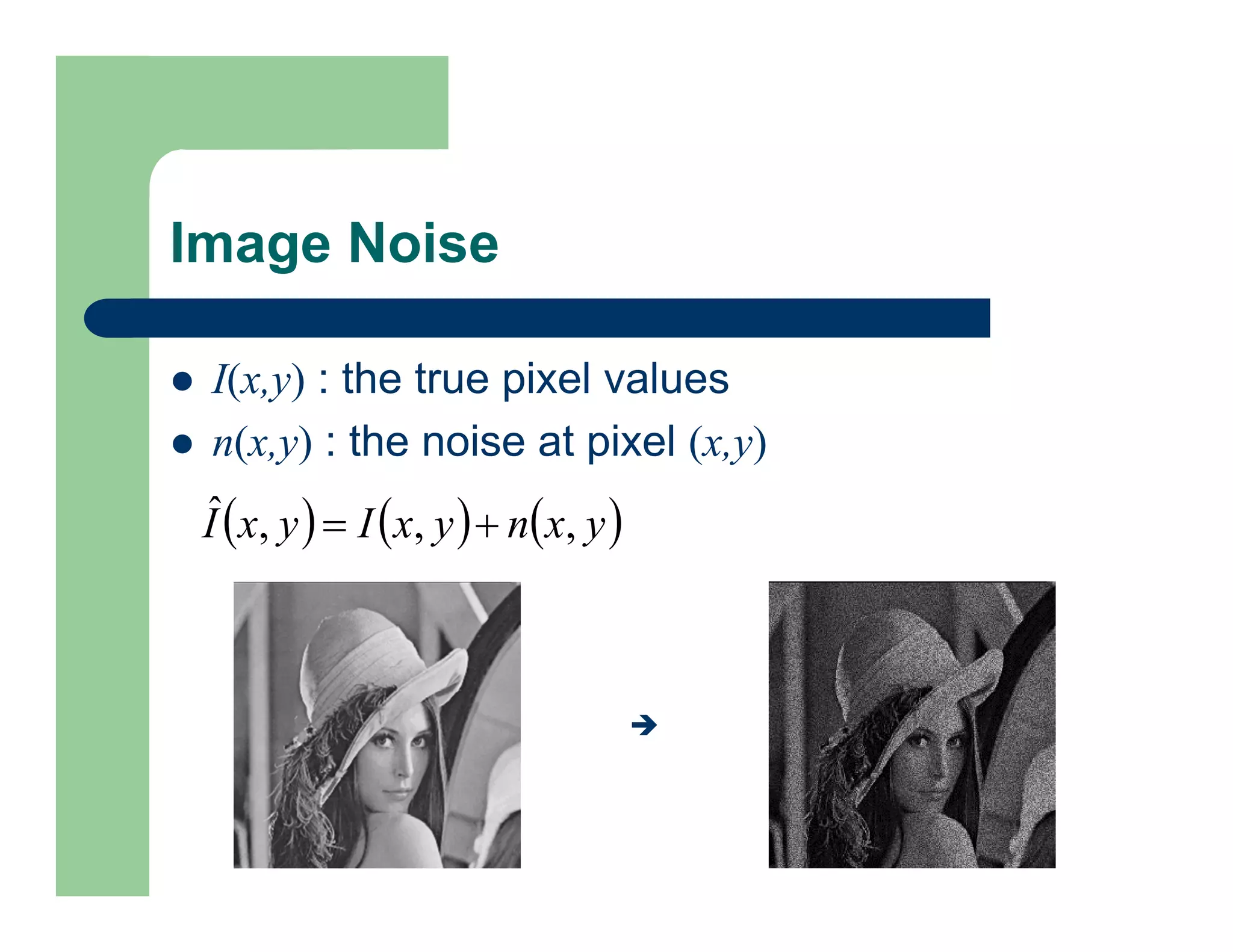
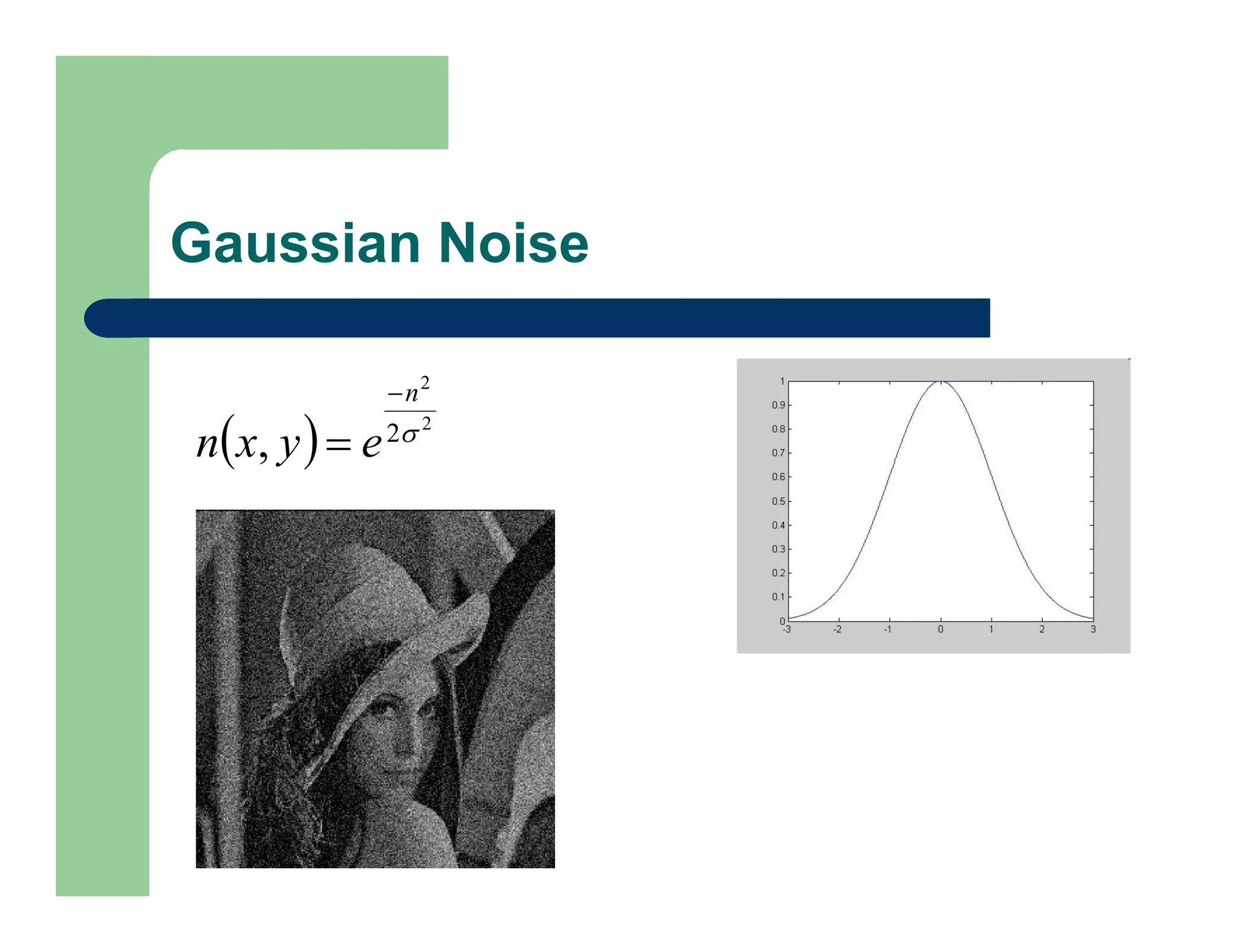
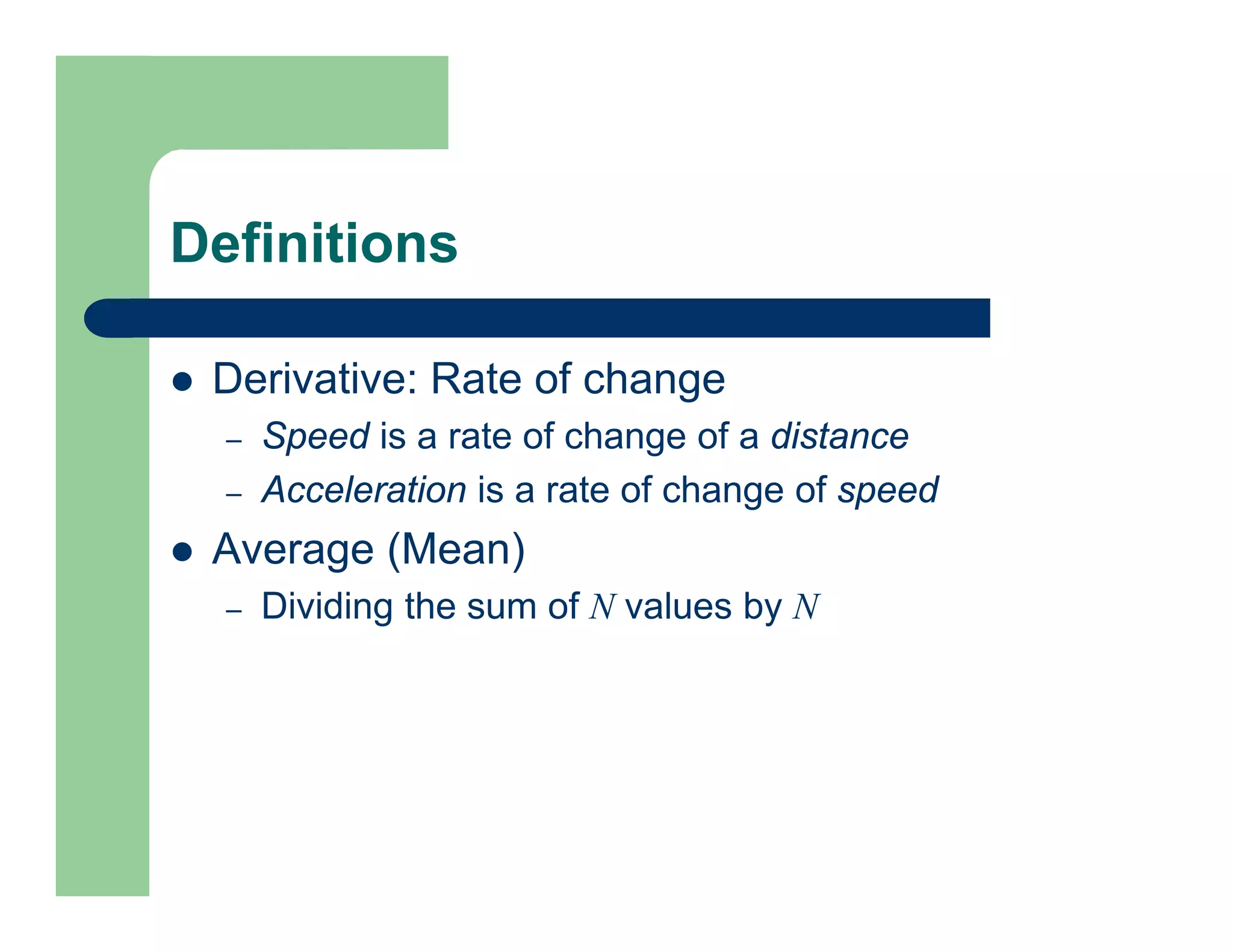
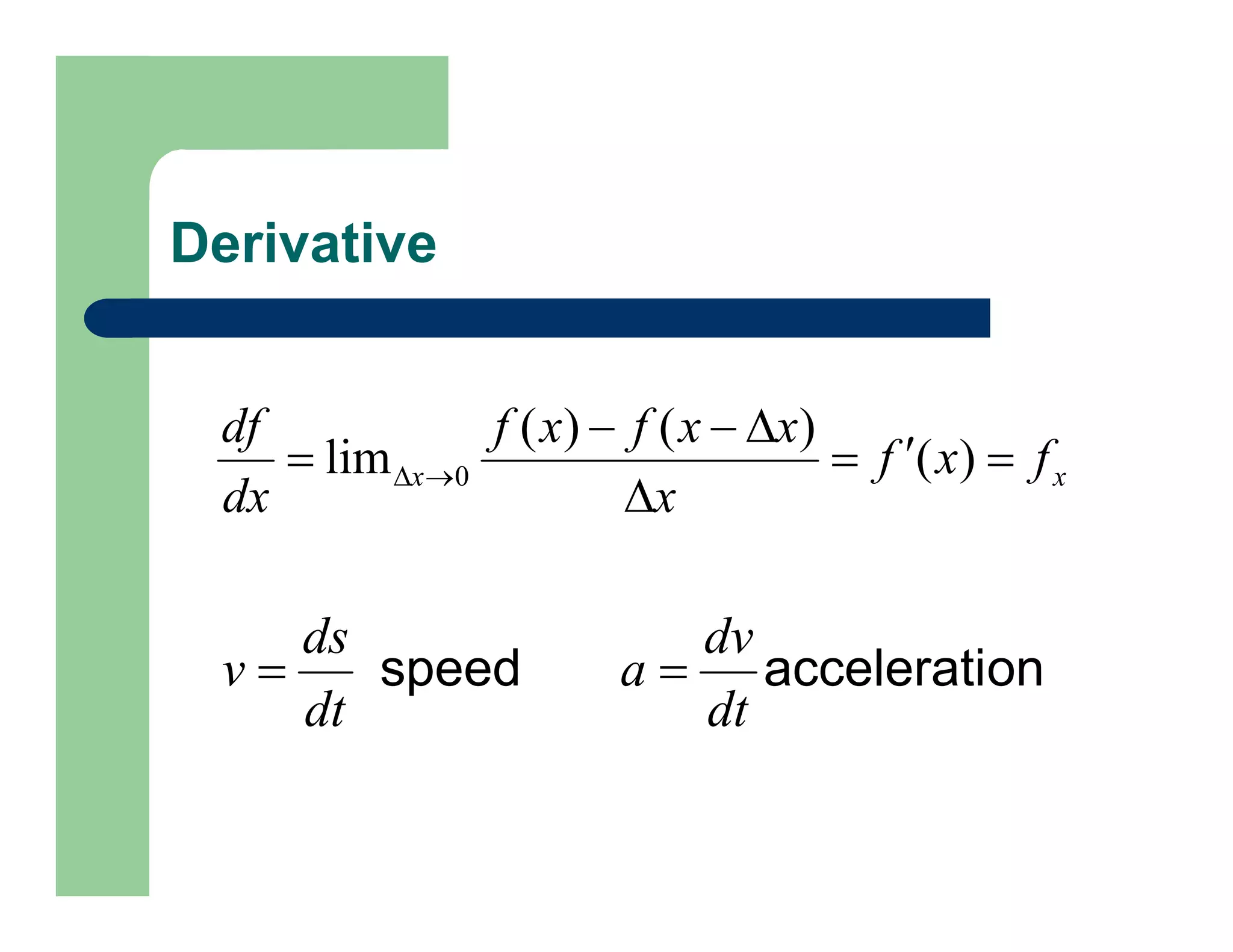
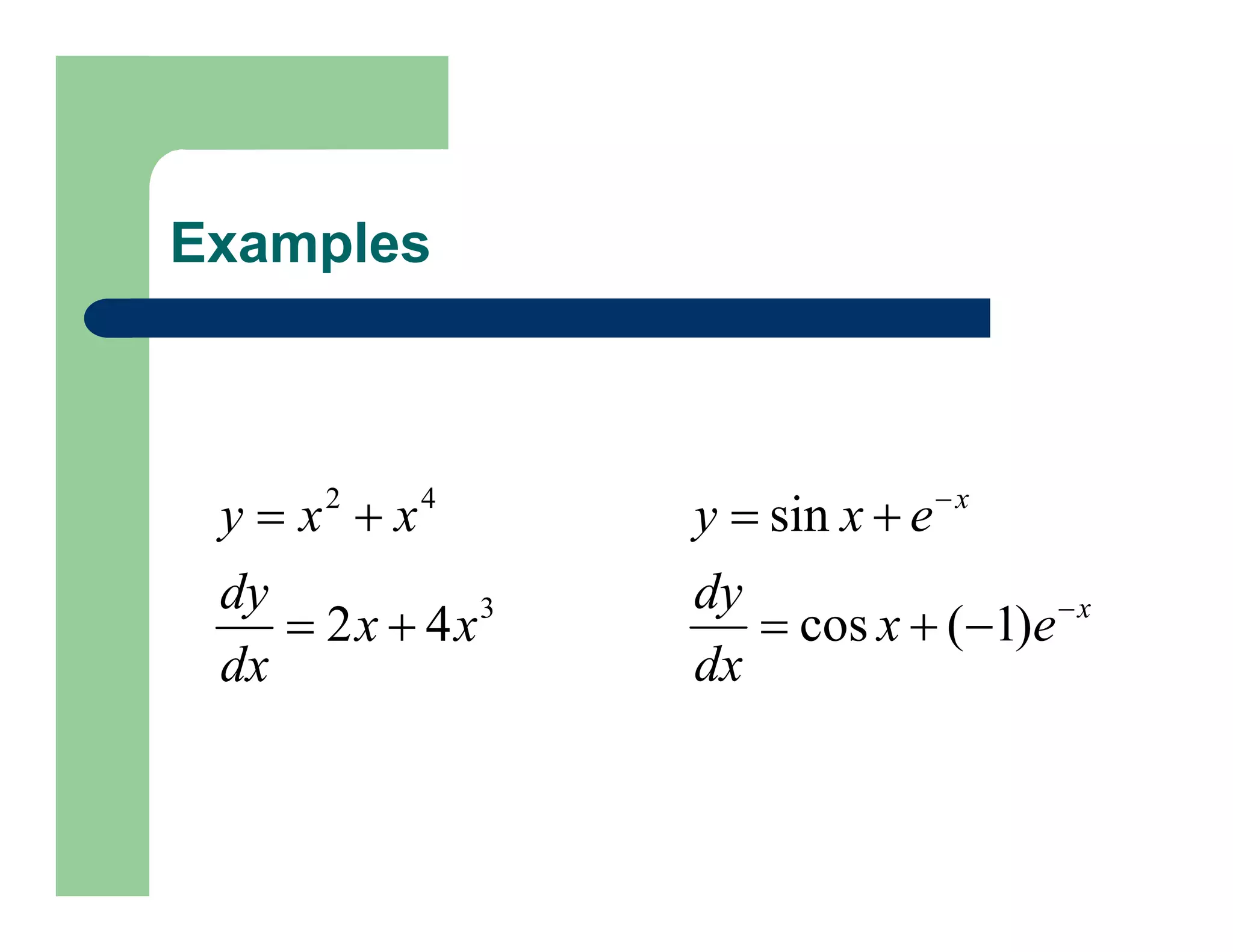
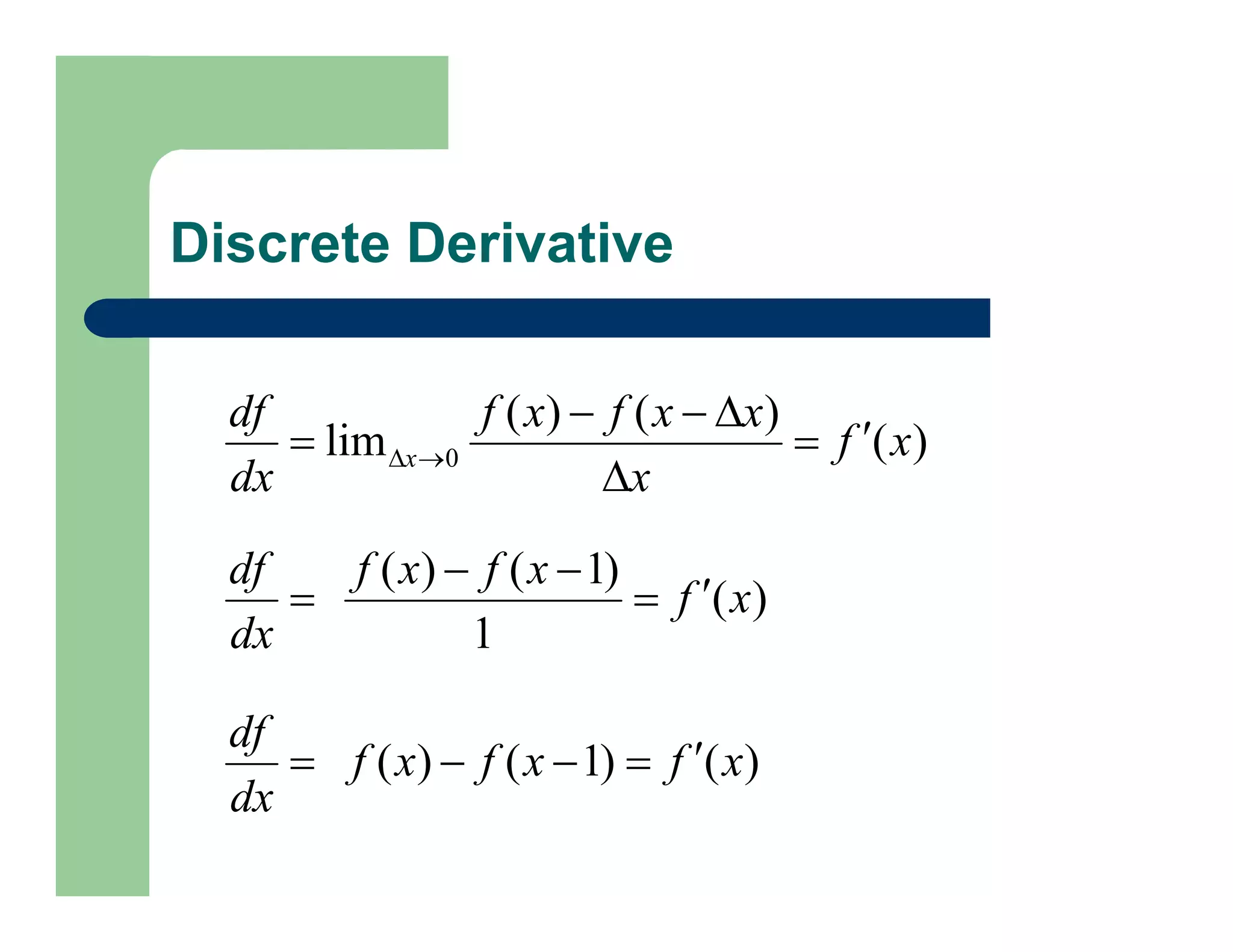
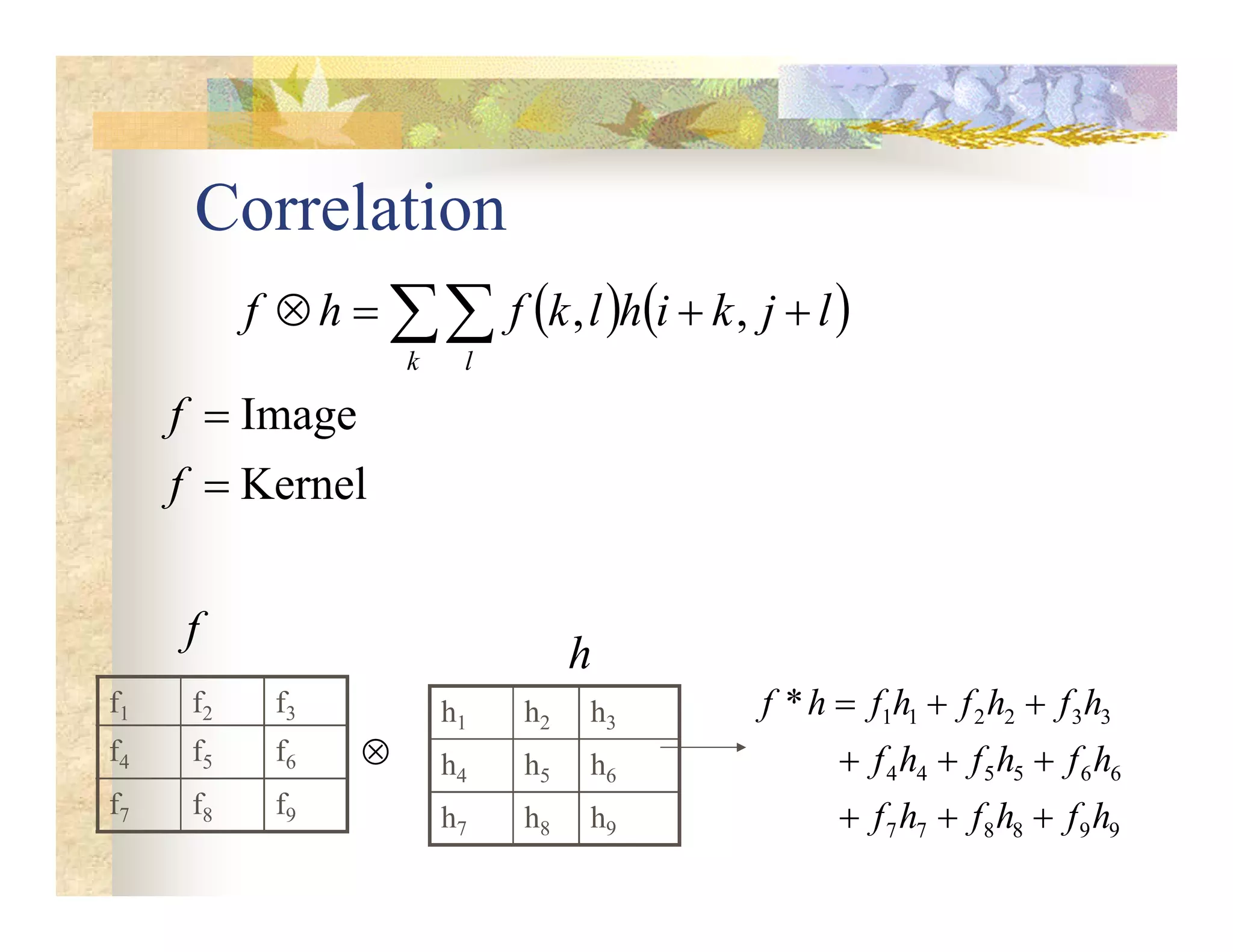
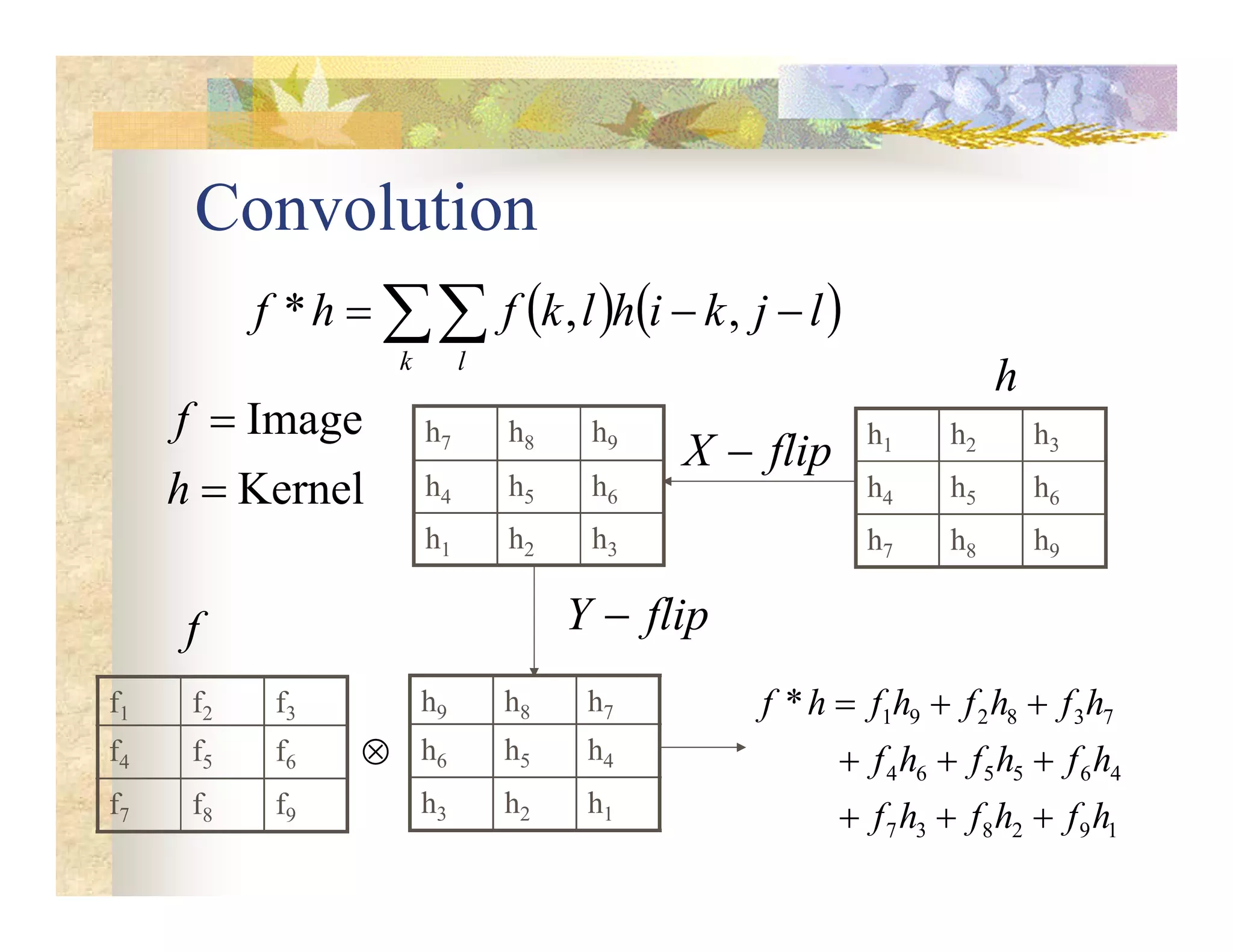
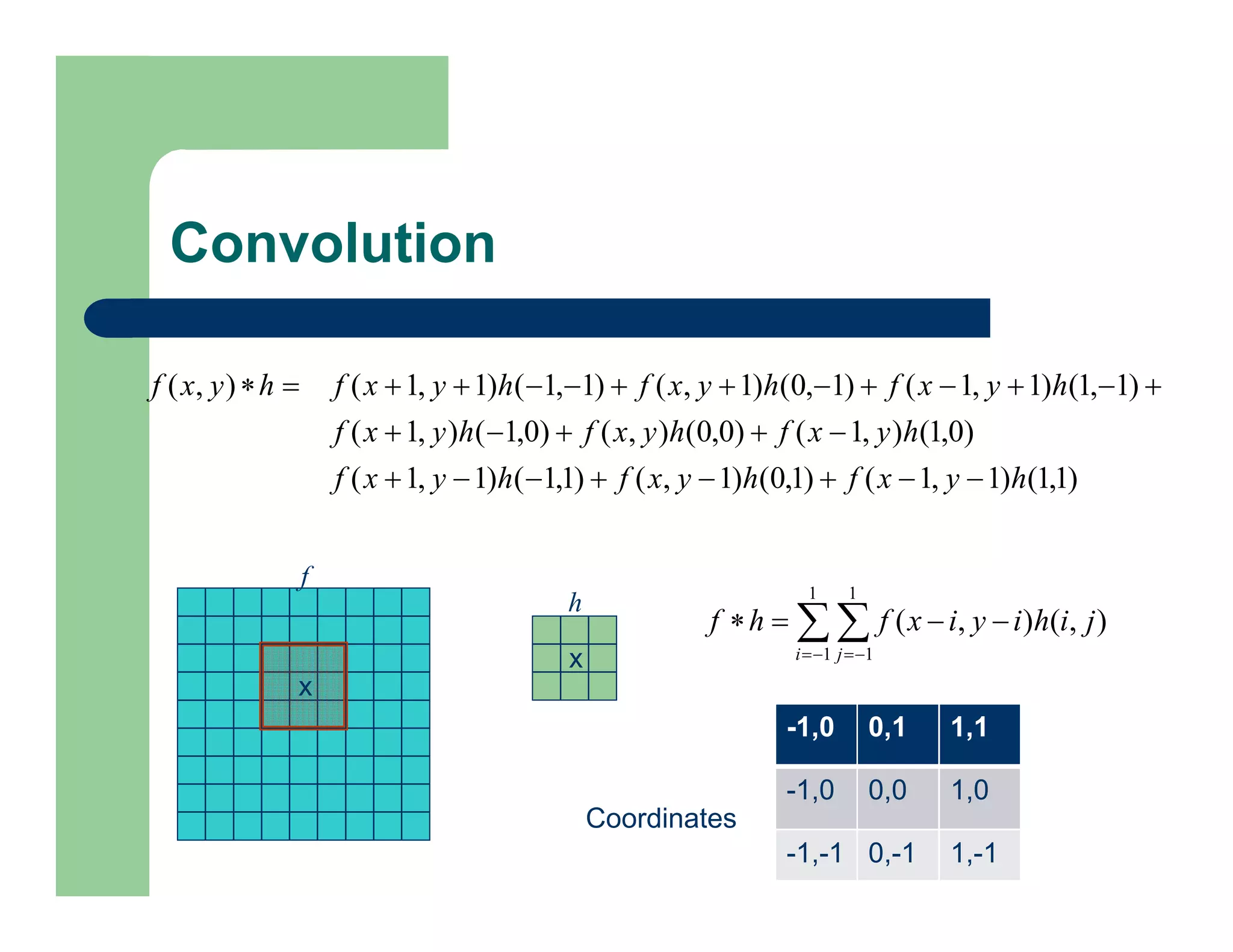
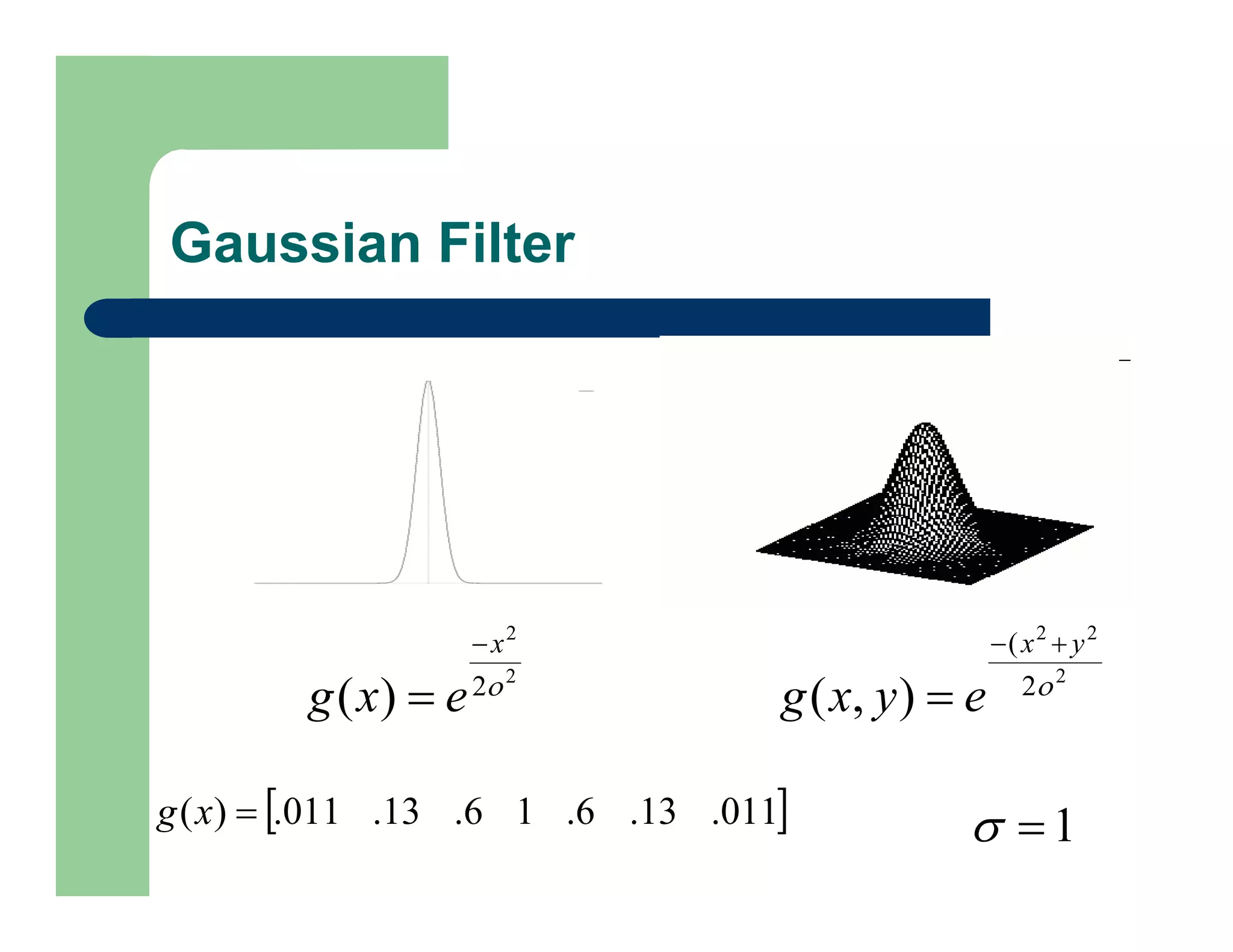
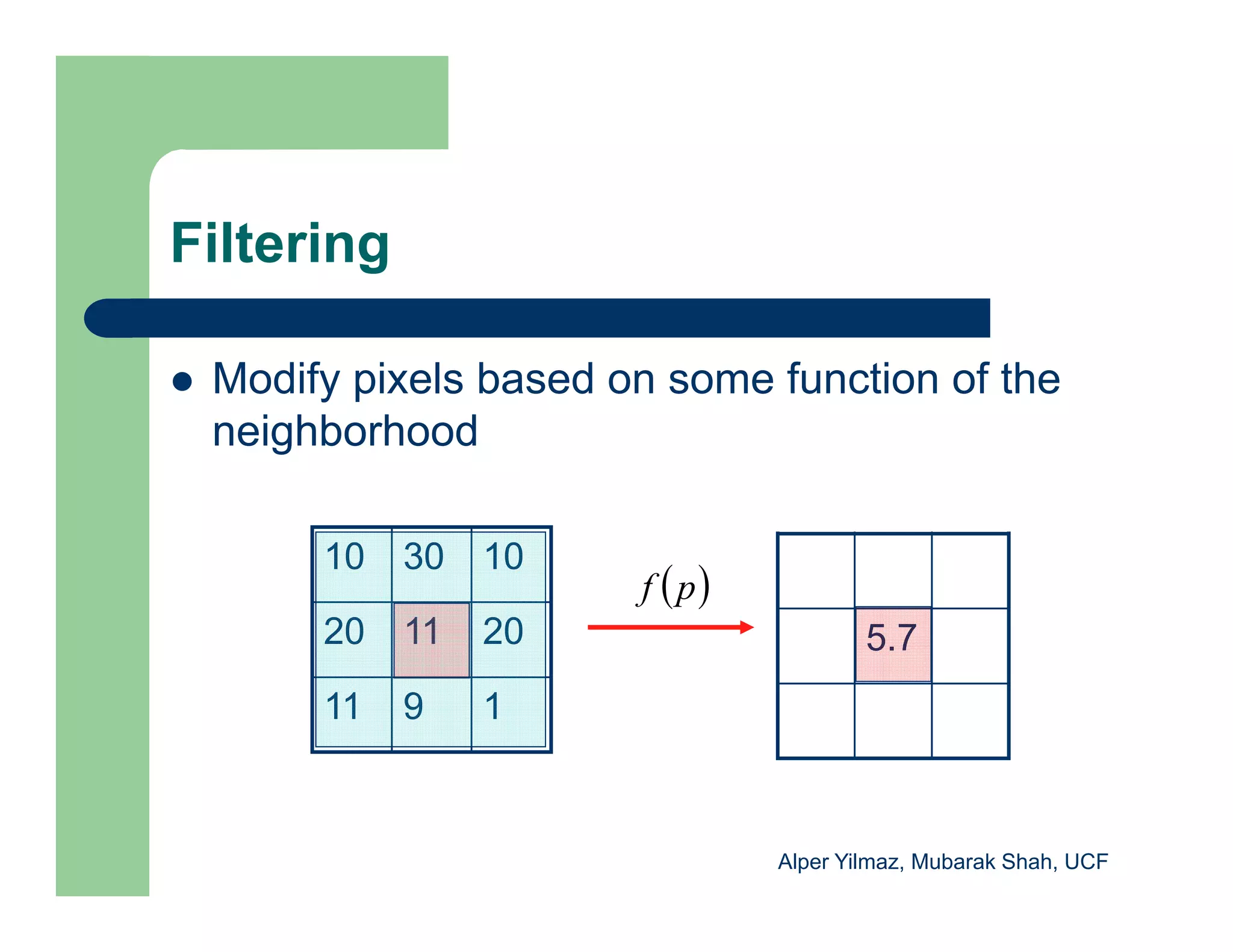
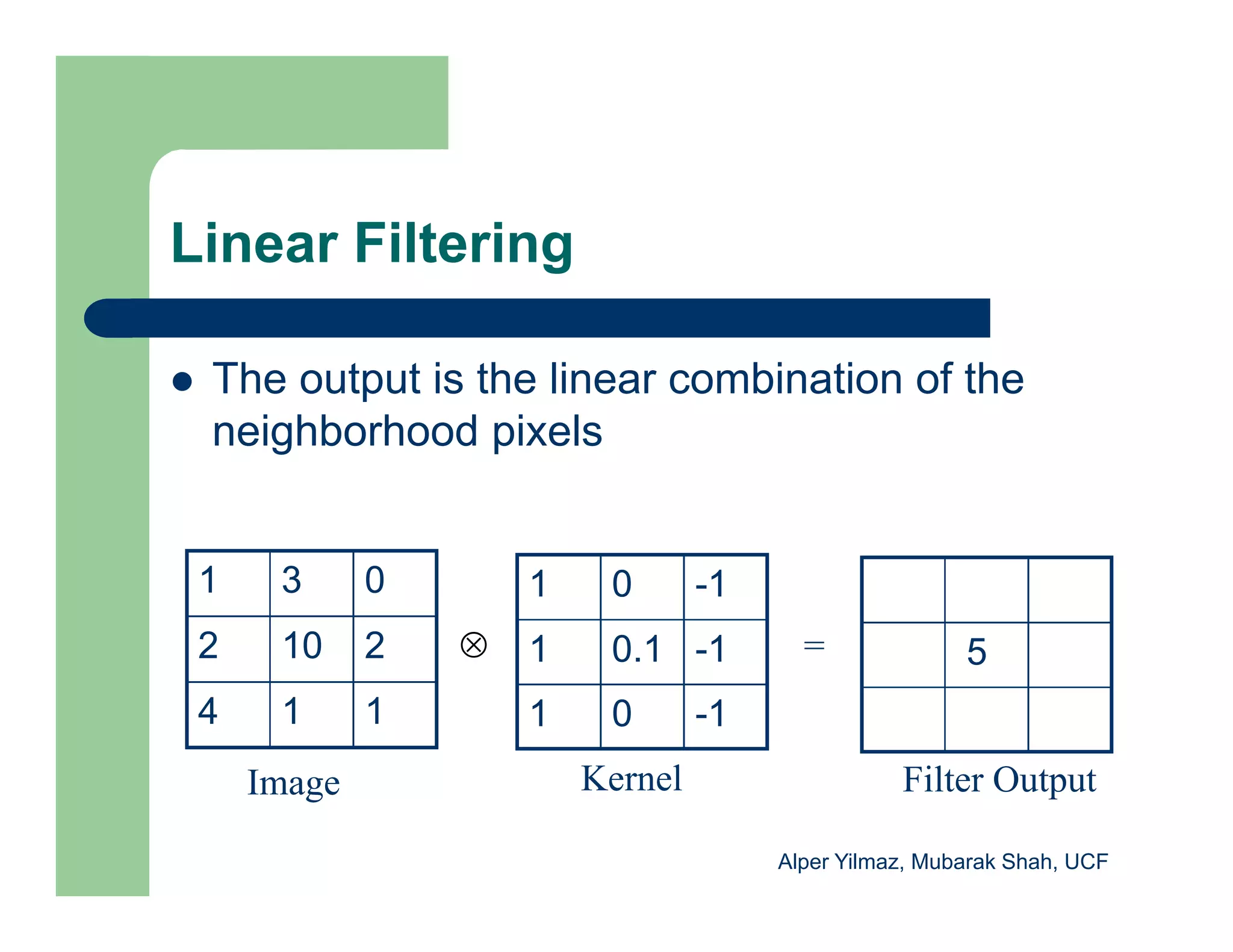
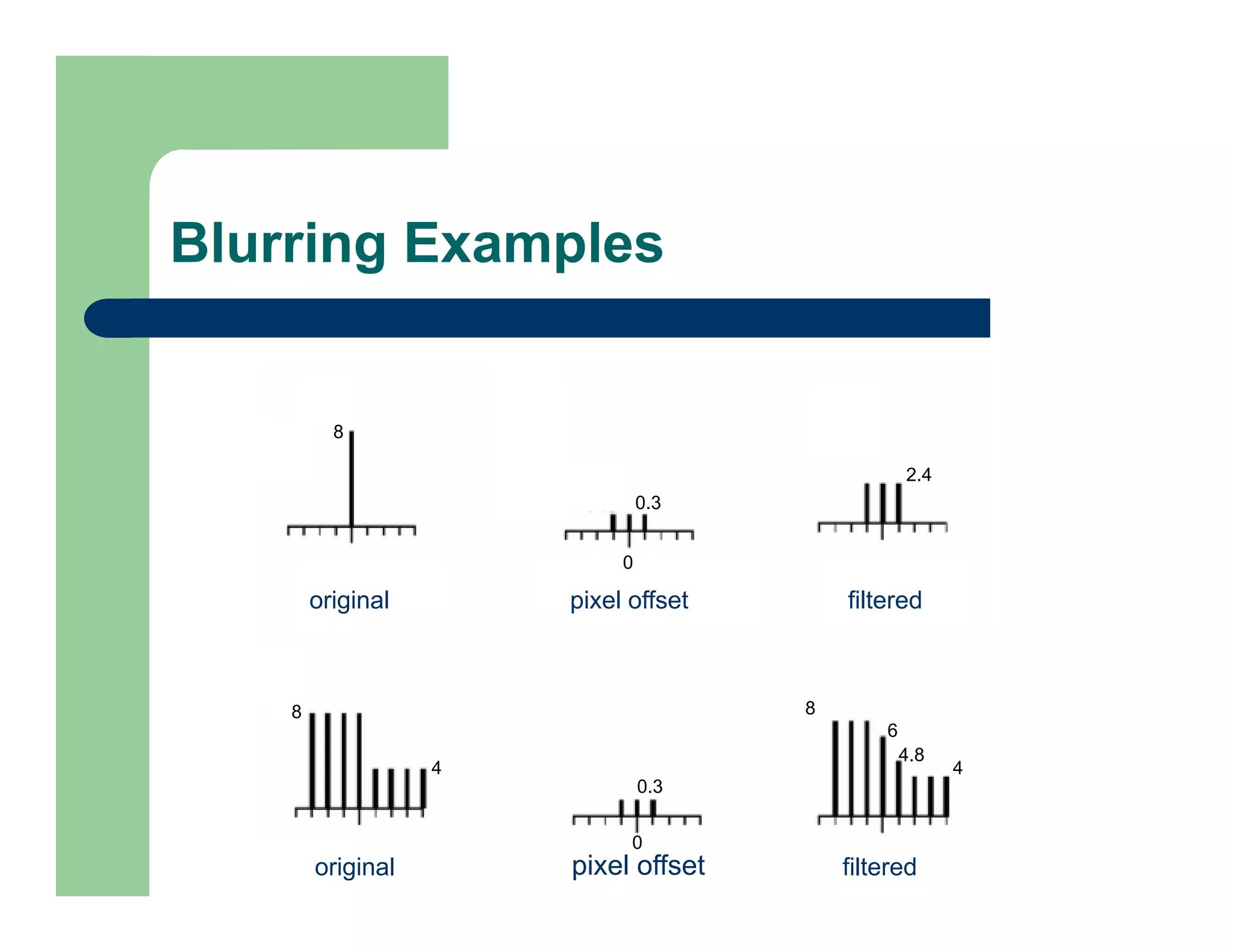
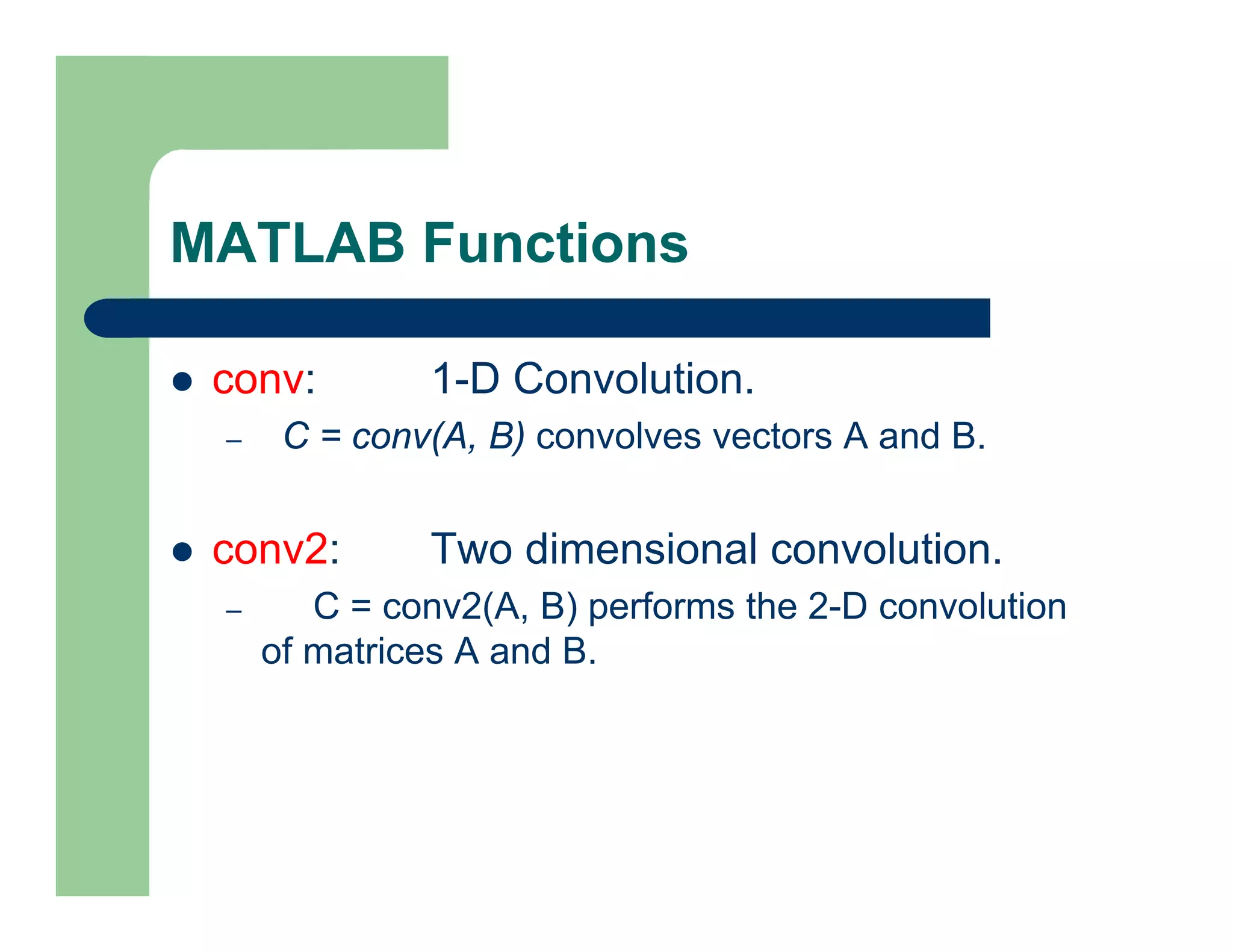
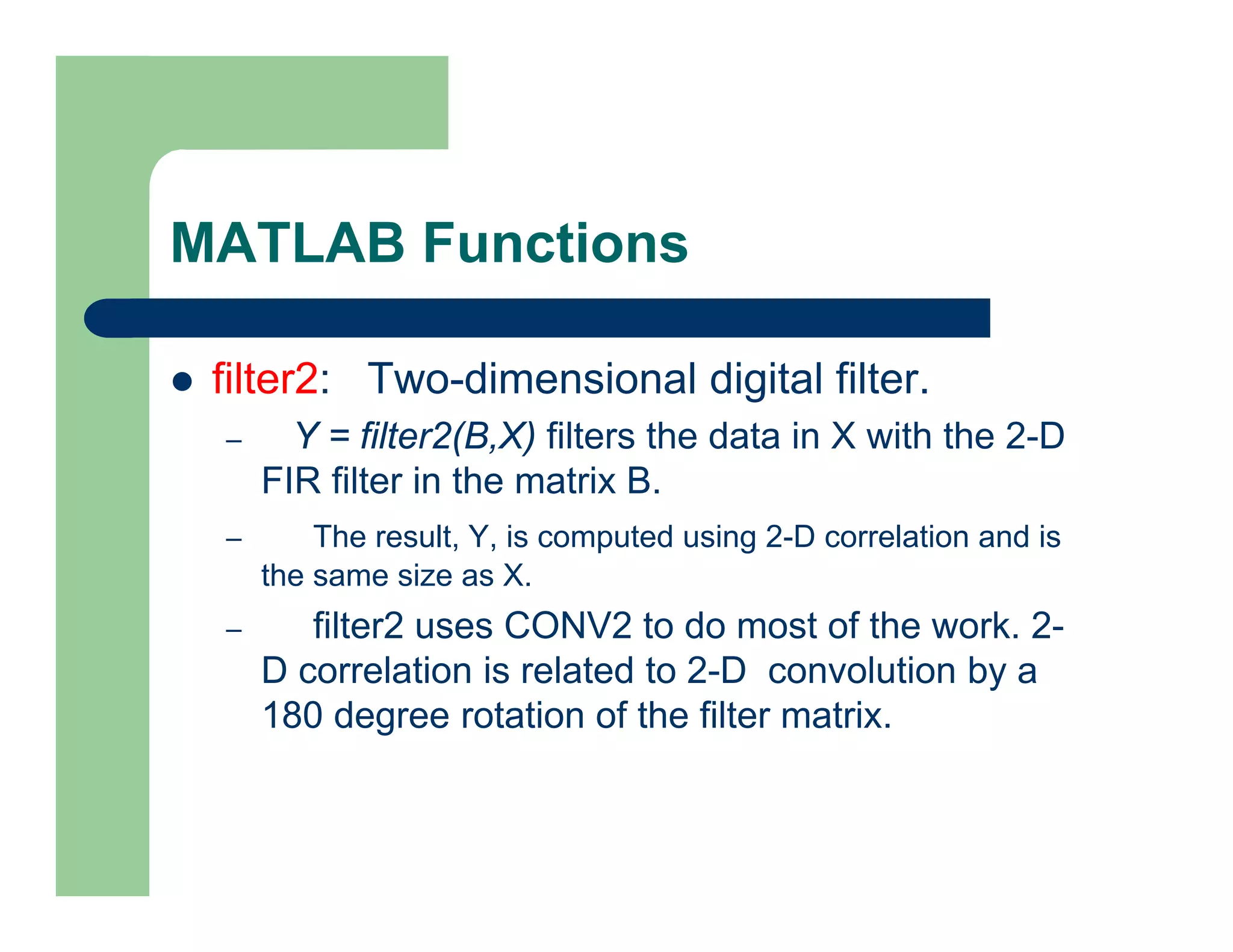
The document outlines concepts in computer vision, specifically focusing on image filtering techniques, image noise, and derivatives. It covers various types of images (binary, grayscale, color), the effect of noise on pixel values, and mathematical definitions of derivatives. Additionally, it provides examples of discrete derivatives, convolution operations, and MATLAB functions for implementing these concepts in image processing.





![Example
0
5
20
15
5
10
5
0
)
(
0
0
5
15
0
5
5
0
)
(
20
20
20
25
10
10
15
10
)
(
x
f
x
f
x
f
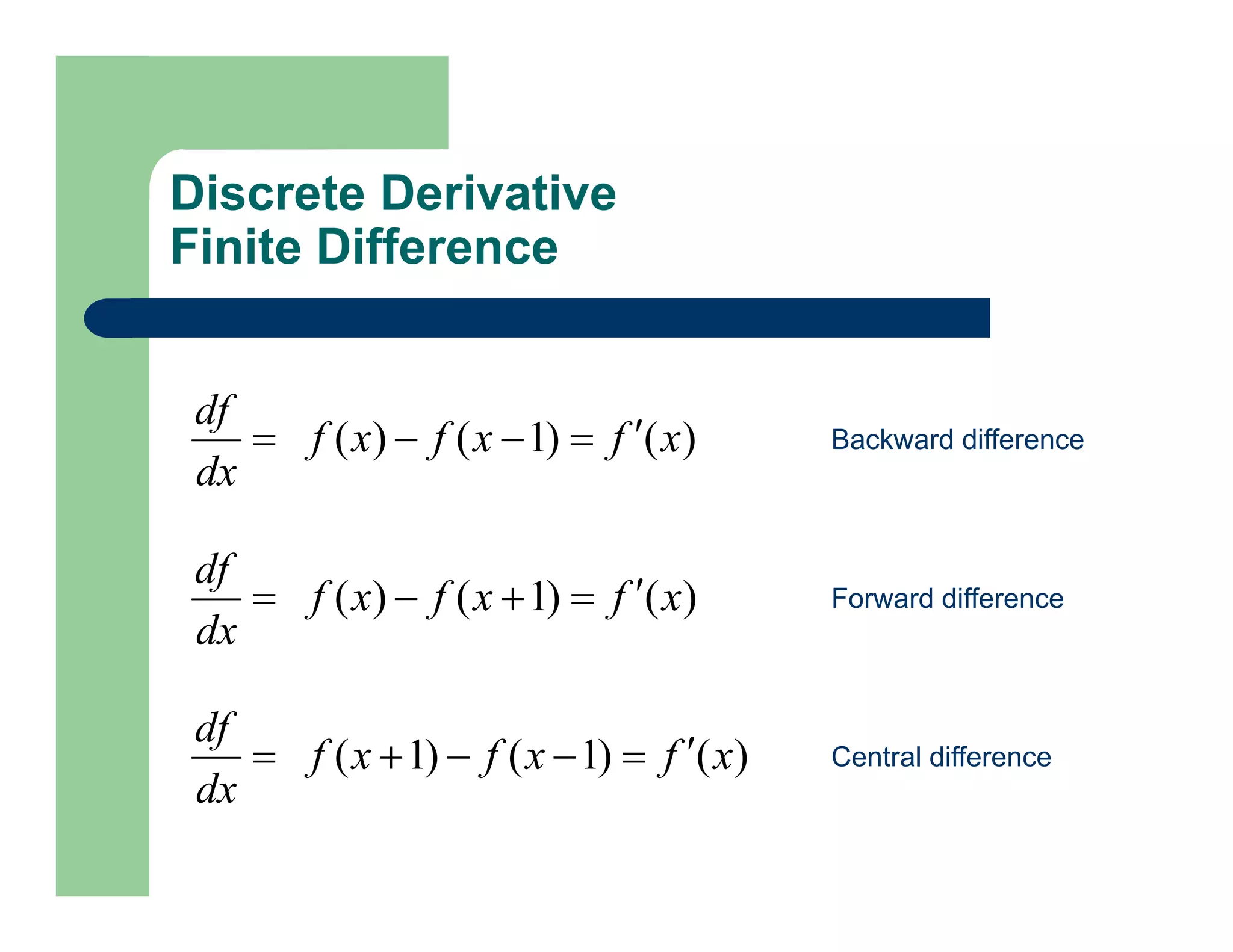
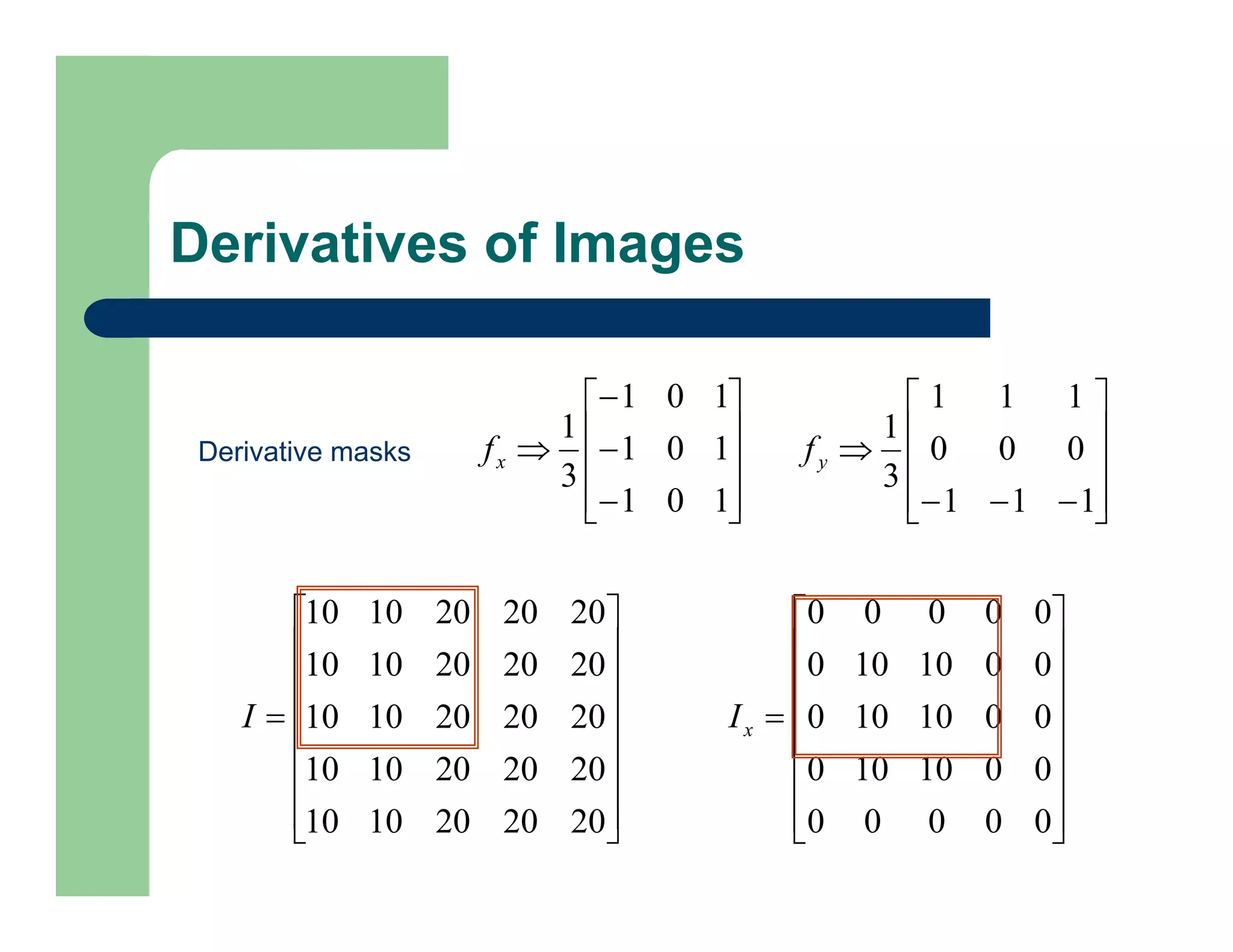
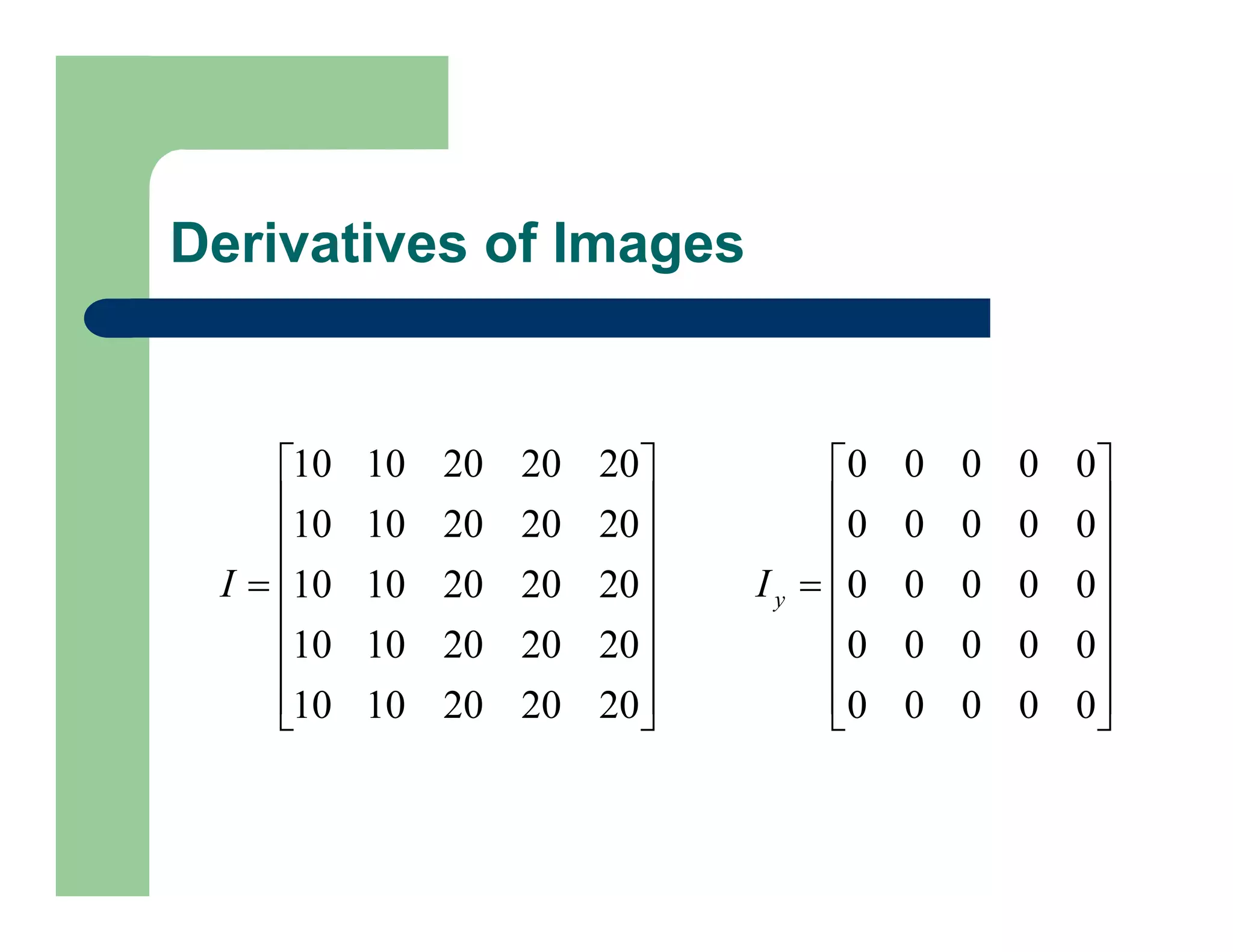
Derivative Masks
Backward difference
Forward difference
Central difference
[-1 1]
[1 -1]
[-1 0 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-filtering-230423220822-2df907c9/75/Lecture-2-Filtering-pdf-18-2048.jpg)








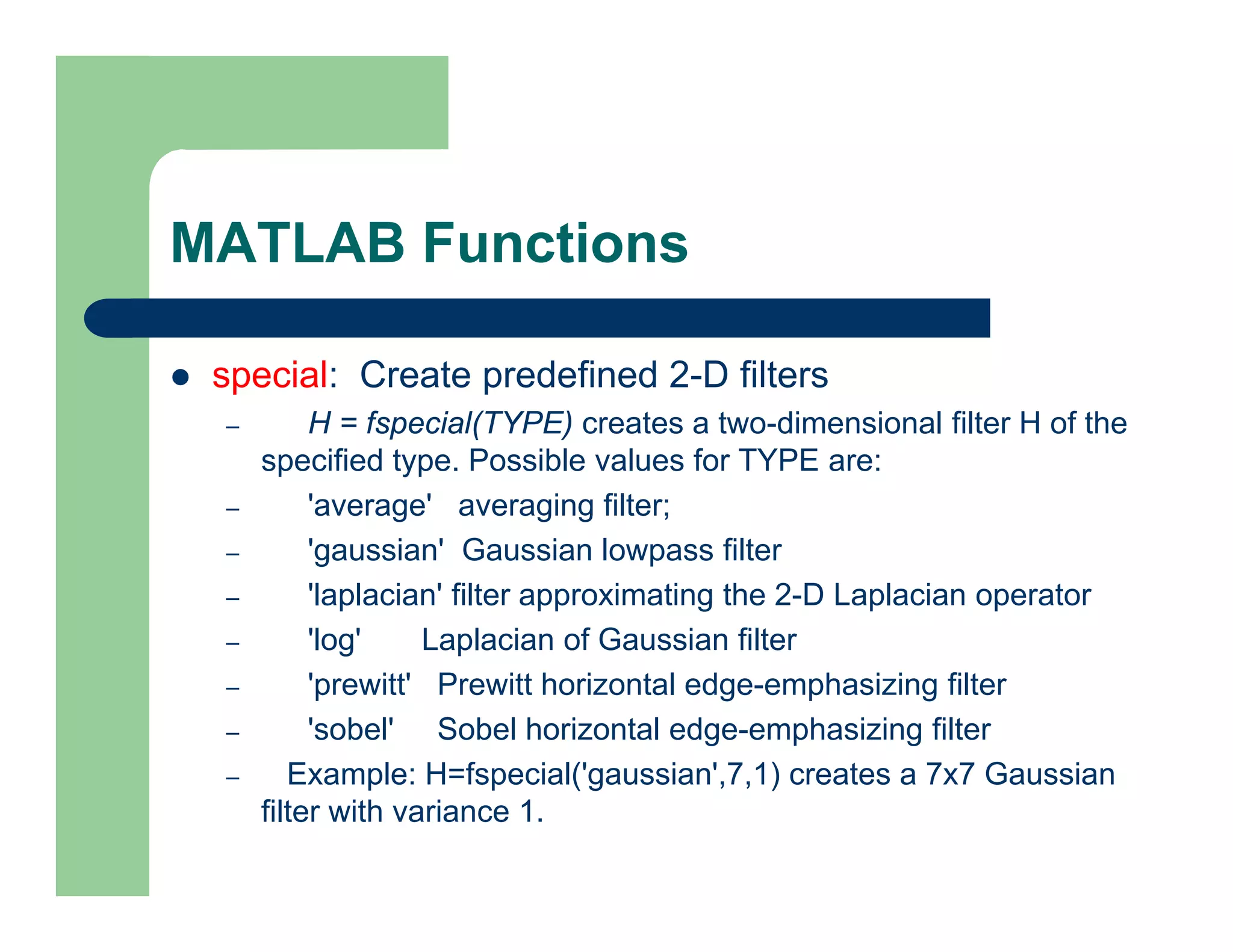
![MATLAB Functions
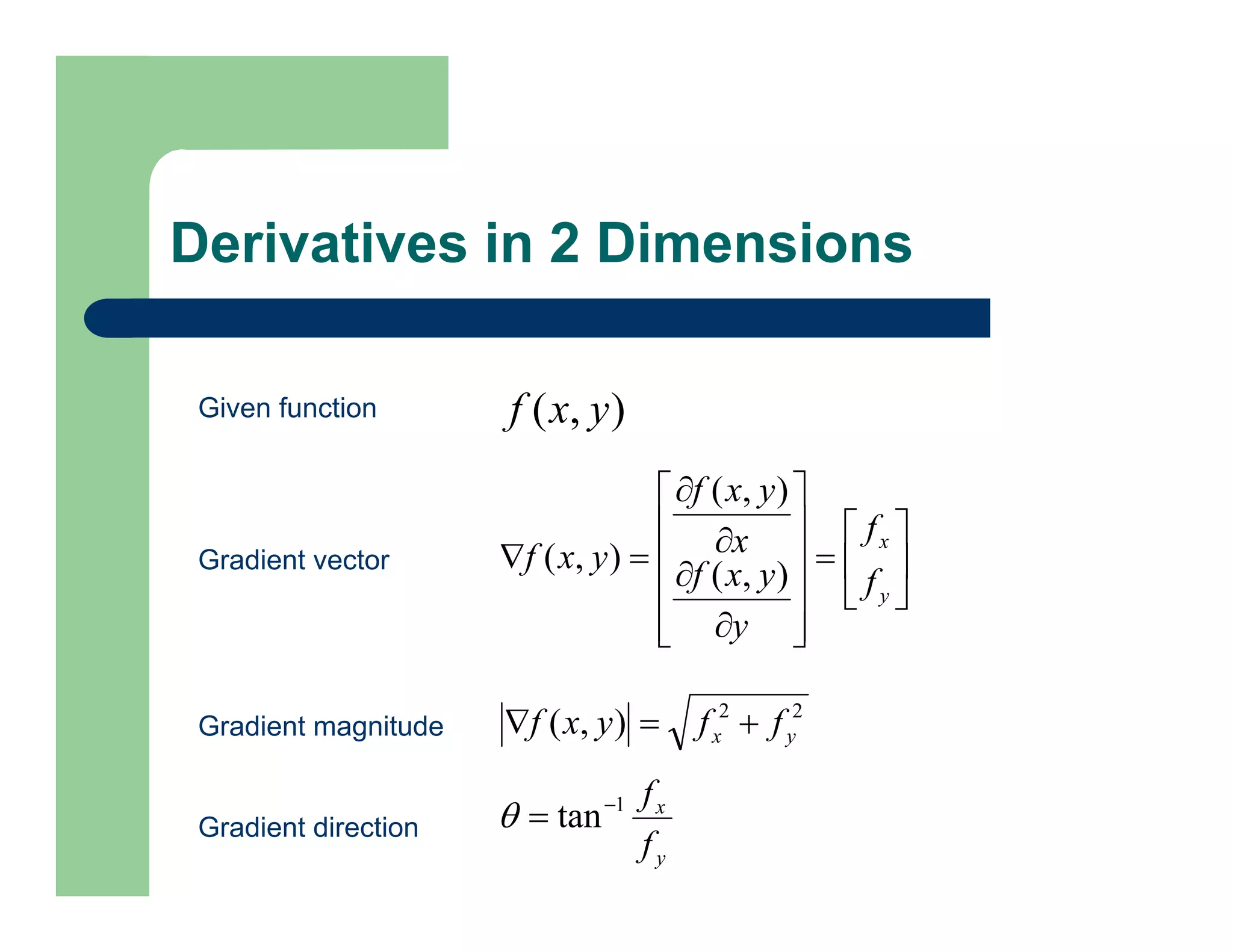
gradient: Approximate gradient.
– [FX,FY] = gradient(F) returns the numerical
gradient of the matrix F. FX corresponds to dF/dx,
FY corresponds to dF/dy.
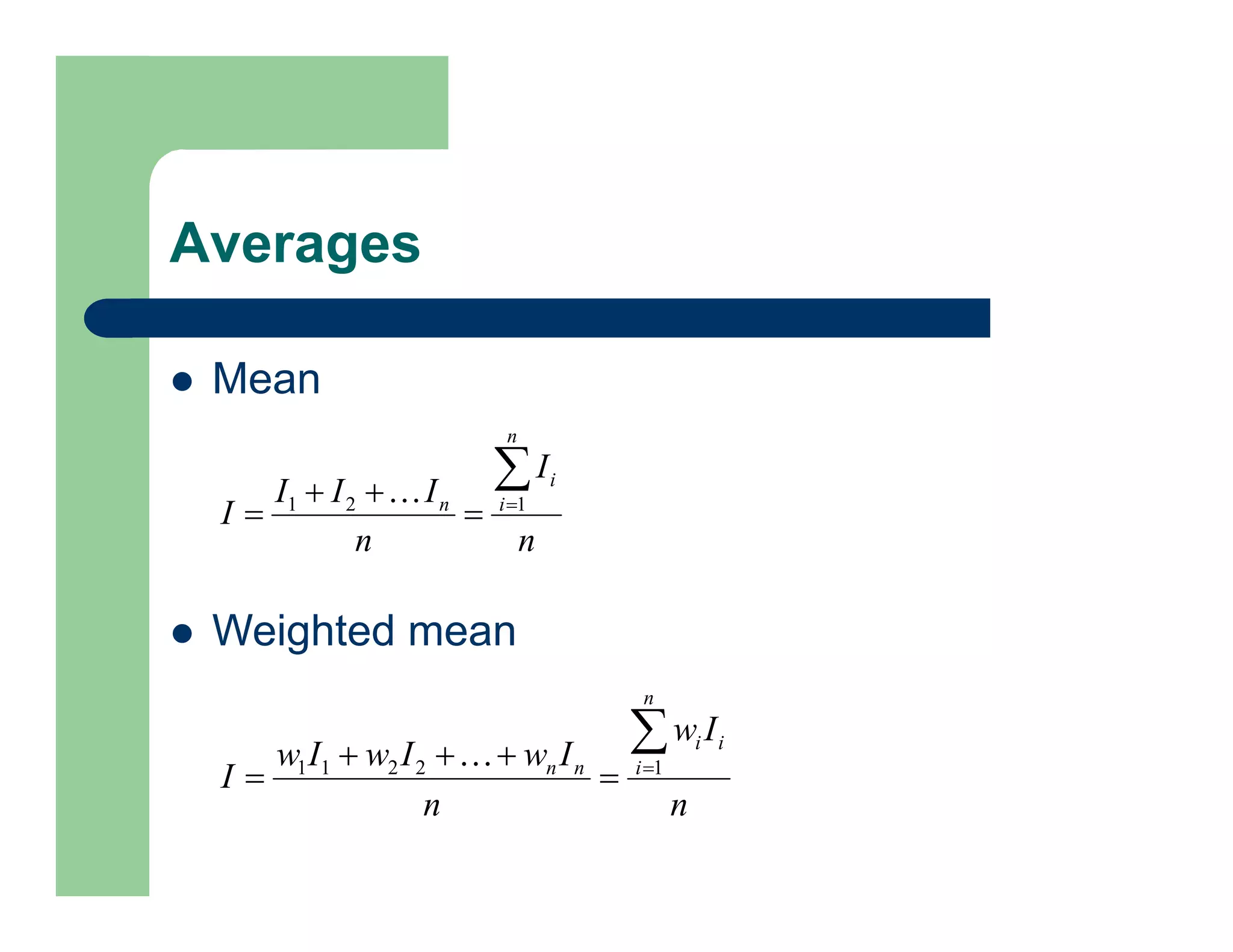
mean: Average or mean value.
– For vectors, mean(X) is the mean value
(average) of the elements in X.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-filtering-230423220822-2df907c9/75/Lecture-2-Filtering-pdf-40-2048.jpg)