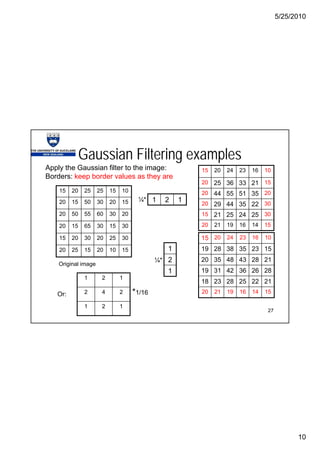
Gaussian filtering is used to blur images and remove noise and detail using a Gaussian function. The Gaussian function is a bell-shaped curve that is defined by a mean and standard deviation. When used for filtering, the Gaussian function is represented as a kernel that is convolved with an image. Larger standard deviation values produce more blurring. Gaussian filtering is commonly used as a pre-processing step for tasks like edge detection.