Embed presentation
Download to read offline


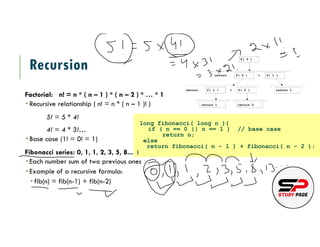


This document discusses recursion, which is a technique for solving problems by breaking them down into smaller subproblems and solving those subproblems recursively until reaching a base case. It provides examples of recursive functions like calculating factorials and the Fibonacci sequence. Recursion involves functions that call themselves, breaking a problem into smaller calls until a base case is reached. While recursion and iteration both involve repetition, they differ in how termination is handled - recursion relies on reaching a base case while iteration uses an explicit loop condition. Both techniques can result in infinite loops if not implemented properly.




