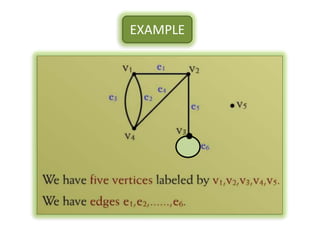
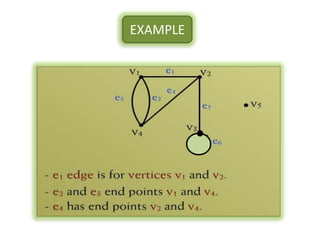
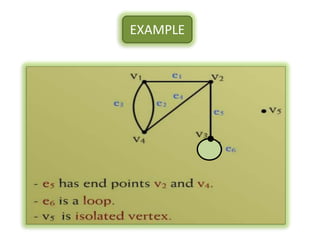
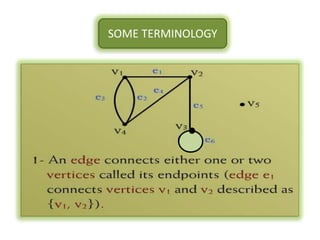
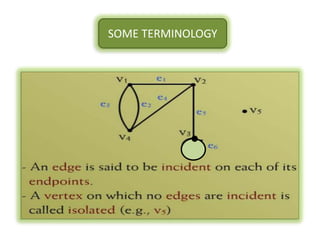
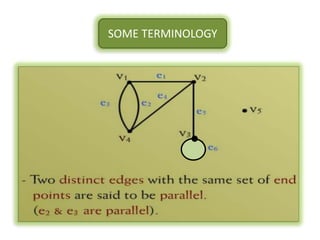
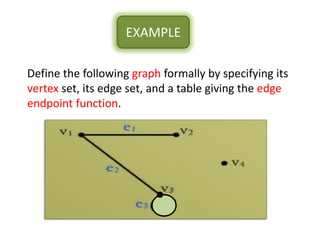
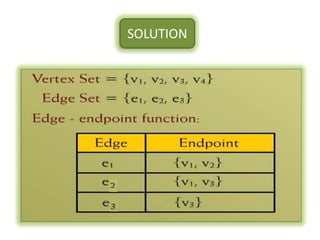
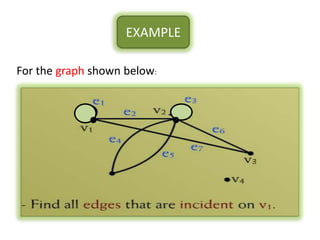
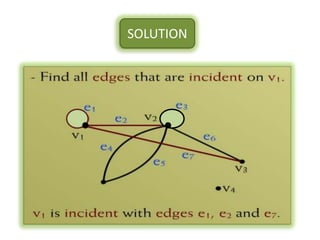
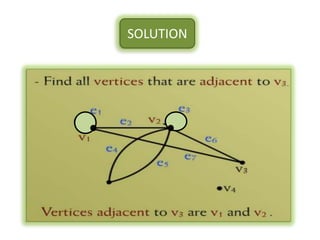
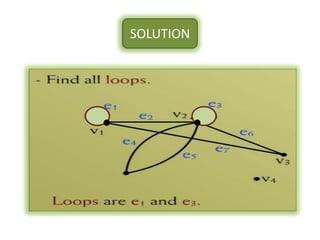
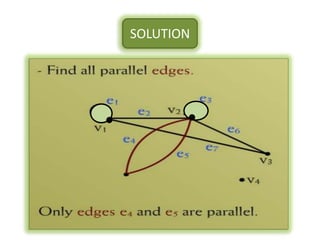
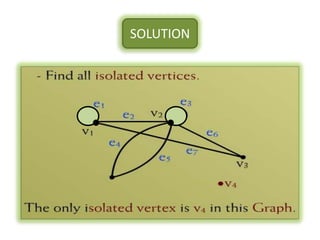
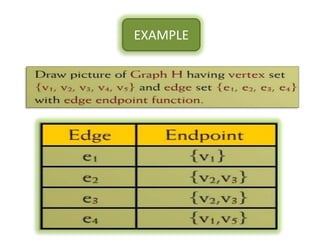
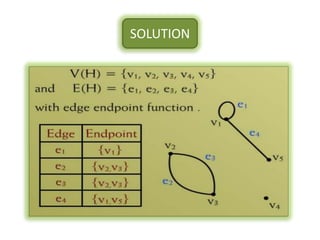
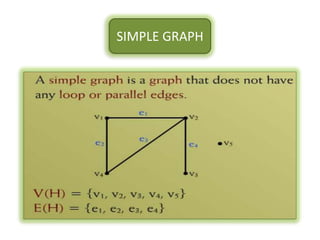
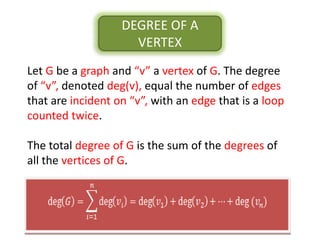
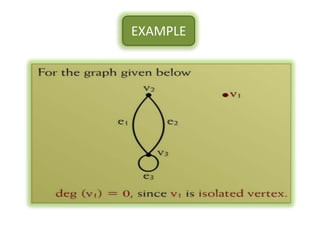
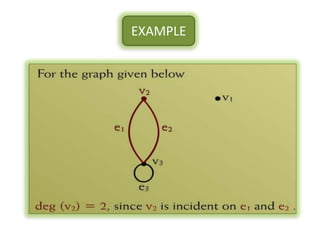
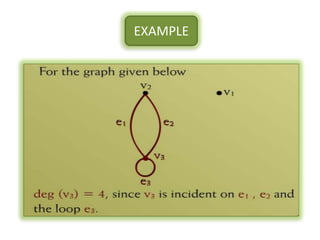
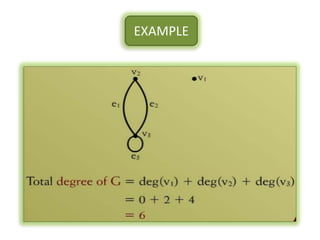
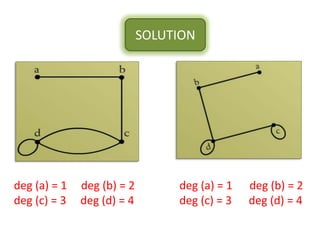
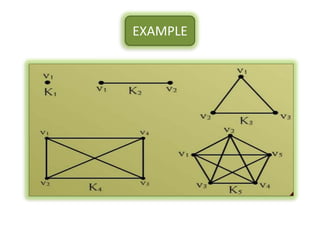
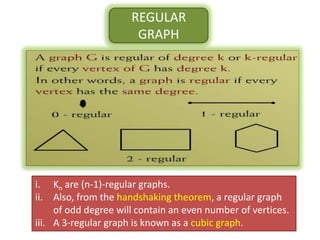
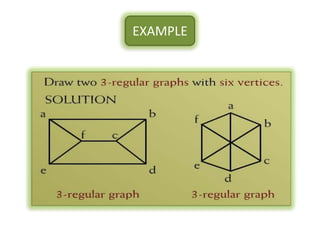
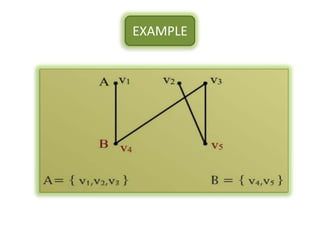
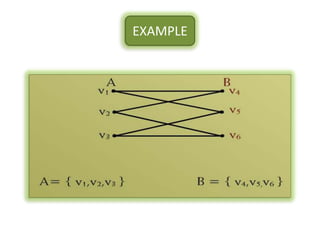
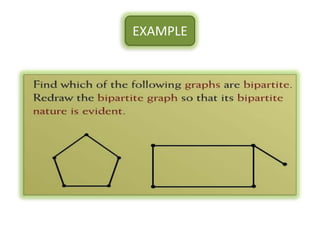
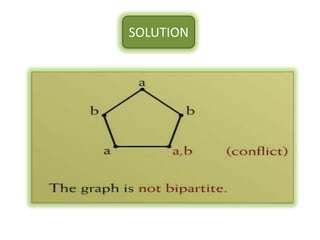
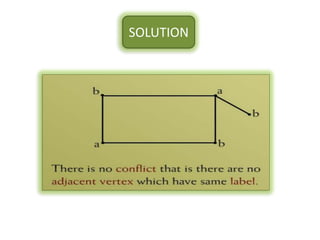
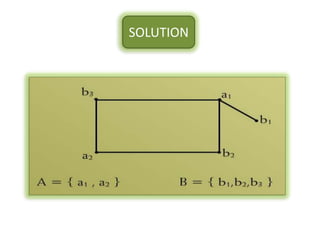
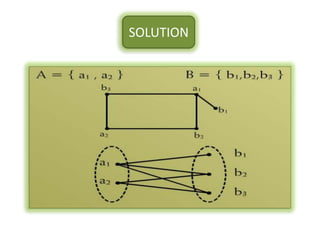
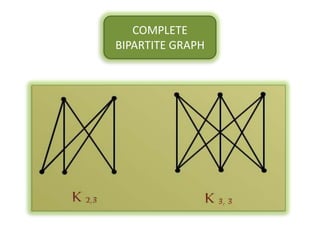
The document is a lecture on discrete structures focusing on graph theory, outlining definitions and terminology such as vertices and edges. It discusses concepts including the degree of a vertex, the handshaking theorem, and provides examples and exercises related to simple, complete, and bipartite graphs. Additionally, it highlights properties of regular graphs and cubic graphs.