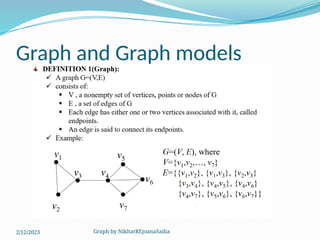
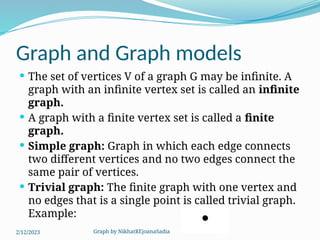
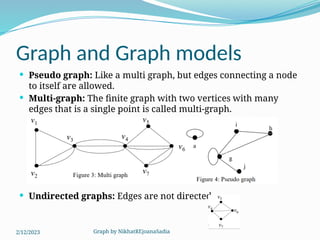
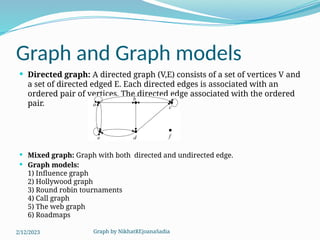
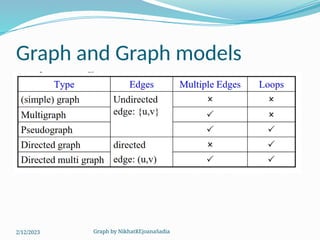
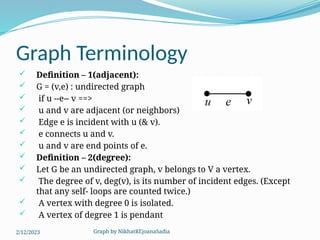
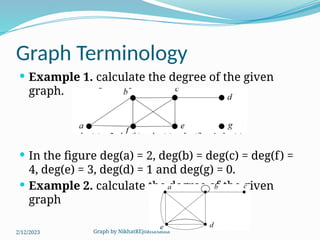
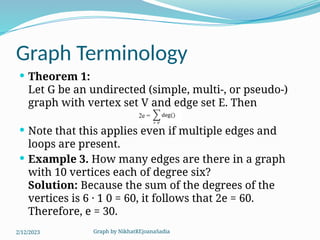
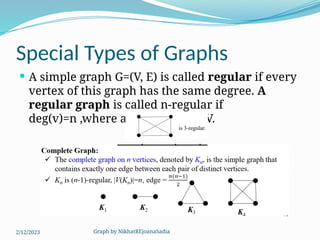
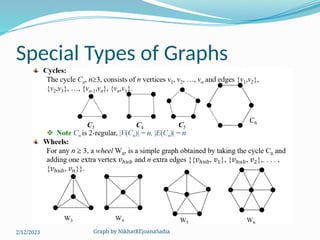
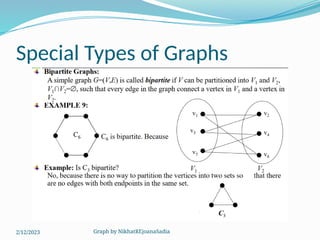
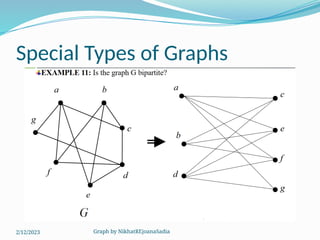
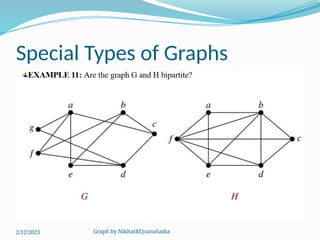
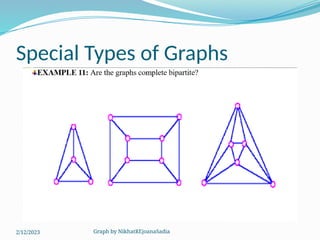
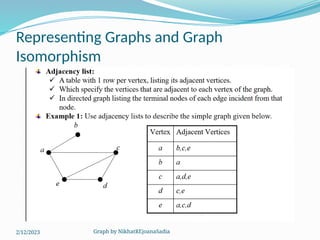
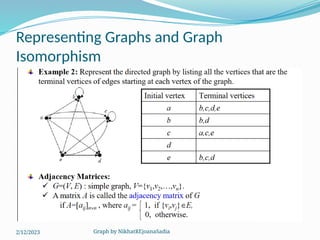
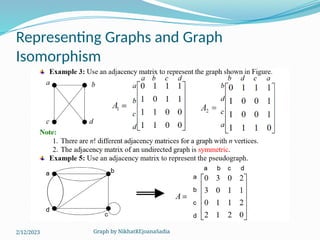
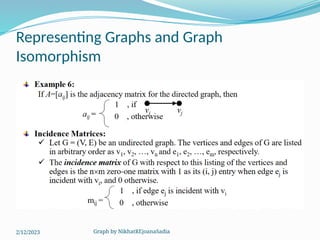
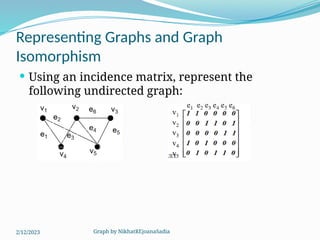
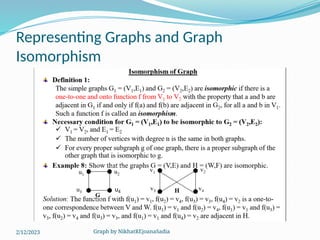
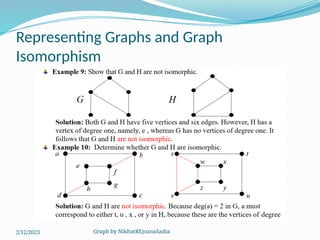
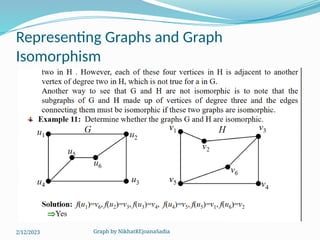
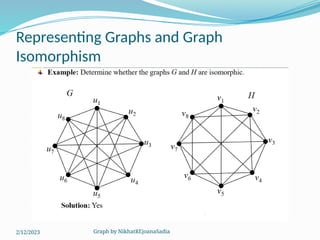
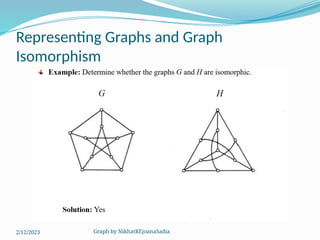
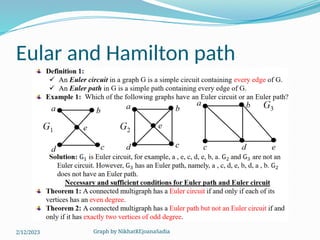
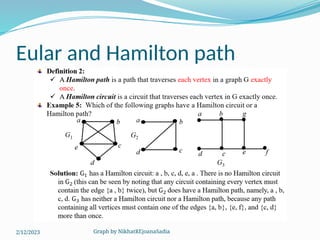
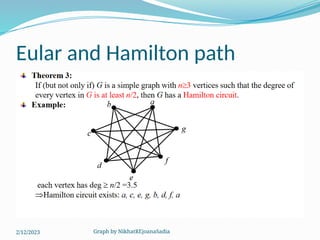
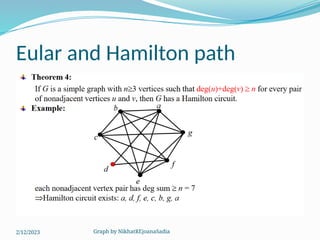
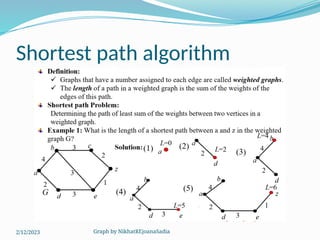
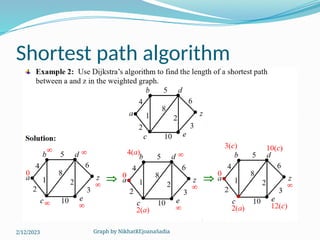
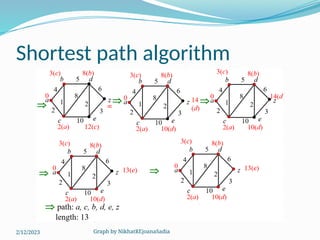
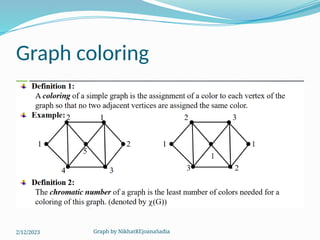
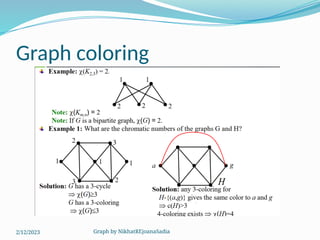
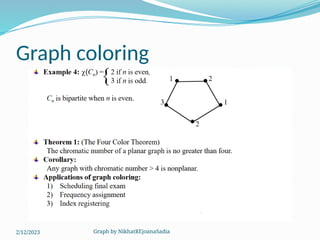
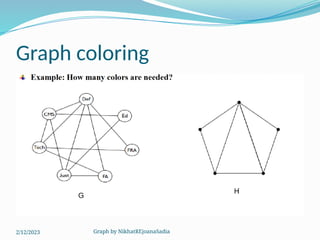
The document covers various concepts in graph theory, including definitions of different types of graphs such as infinite, finite, simple, trivial, pseudo, multi-, directed, and mixed graphs. It explains key terminologies like adjacency, degree, in-degree, out-degree, and special types of graphs such as regular graphs. Additionally, it discusses graph representation techniques and algorithms like Dijkstra's for finding shortest paths in graphs.