This document discusses binary trees, including:
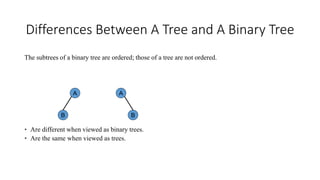
- The differences between binary trees and regular trees in how subtrees are ordered.
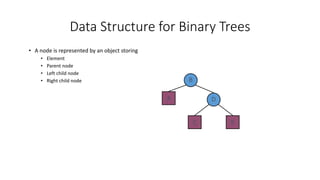
- Common data structures used to represent binary trees in code.
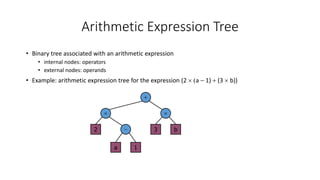
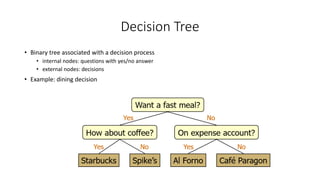
- Examples of binary trees used for arithmetic expressions and decision making.
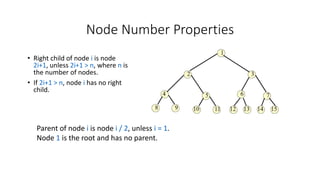
- Properties of binary trees like the maximum number of nodes at each depth and for trees of a given height.
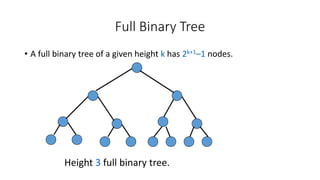
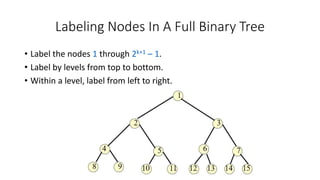
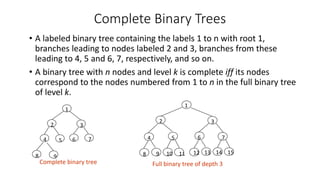
- The concepts of full and complete binary trees and how they are structured and labeled.