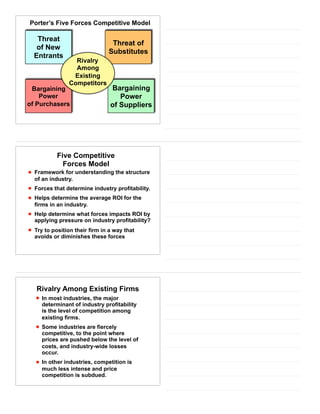
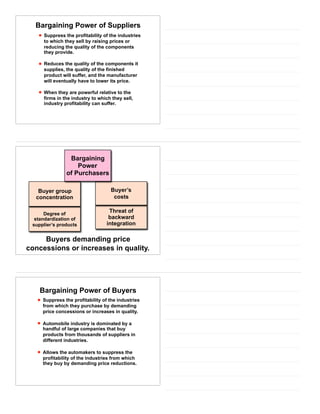
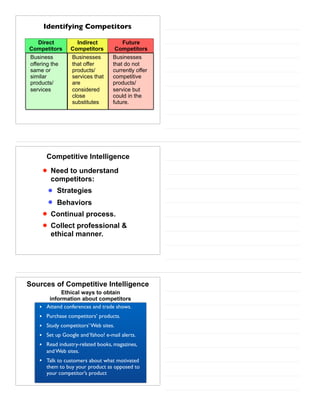
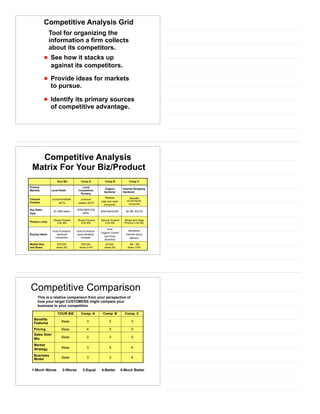
The document provides an overview of industry and competitor analysis. It discusses analyzing industries to understand environmental trends, business trends, and key questions to assess industry attractiveness. It also covers analyzing competitors to identify direct, indirect, and future competitors. Tools discussed include Porter's Five Forces model to evaluate competitive forces in an industry, and a competitive analysis grid to organize information about competitors. The goal of industry and competitor analysis is to help firms understand opportunities and position themselves strategically within their industry.