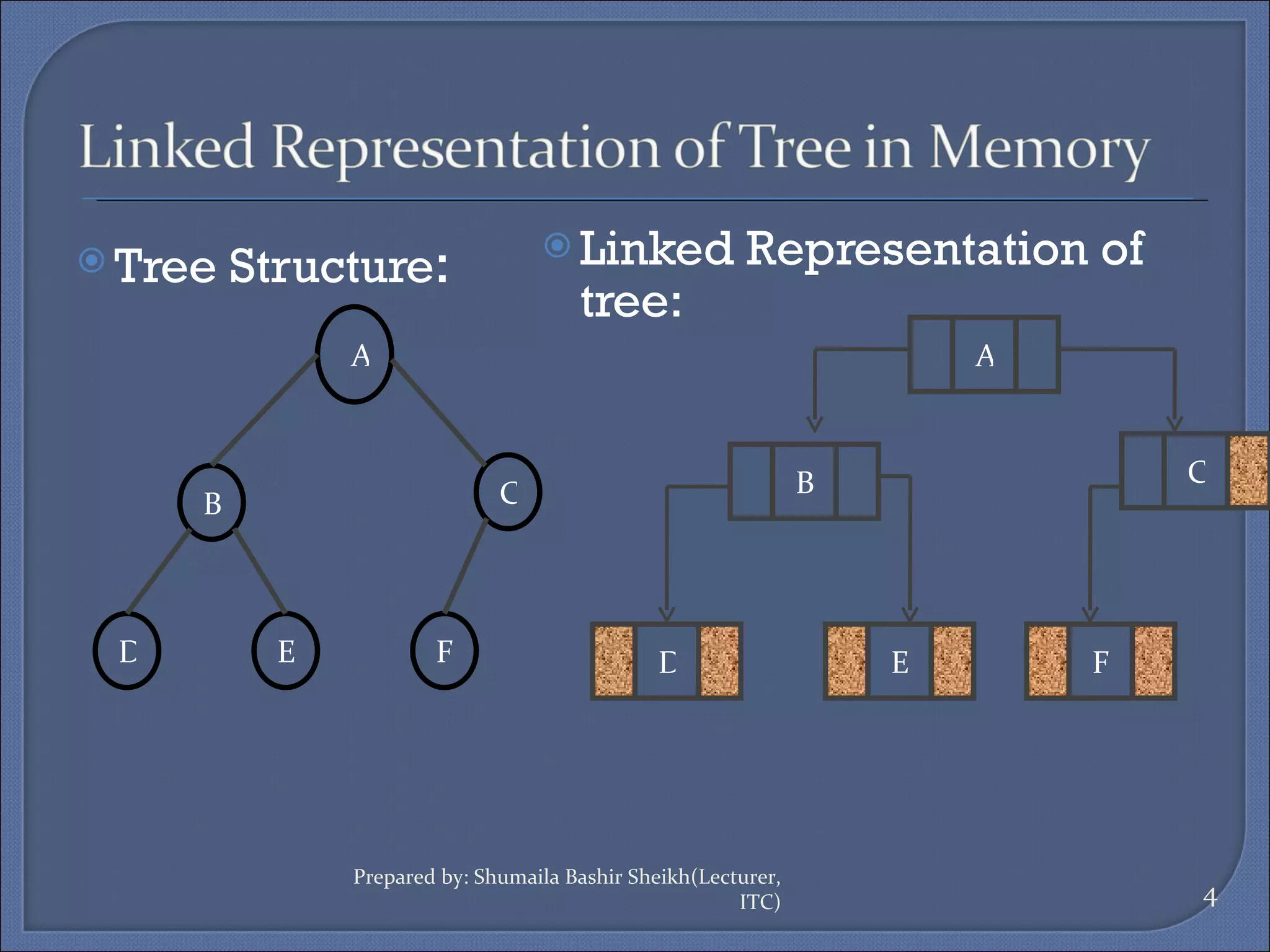
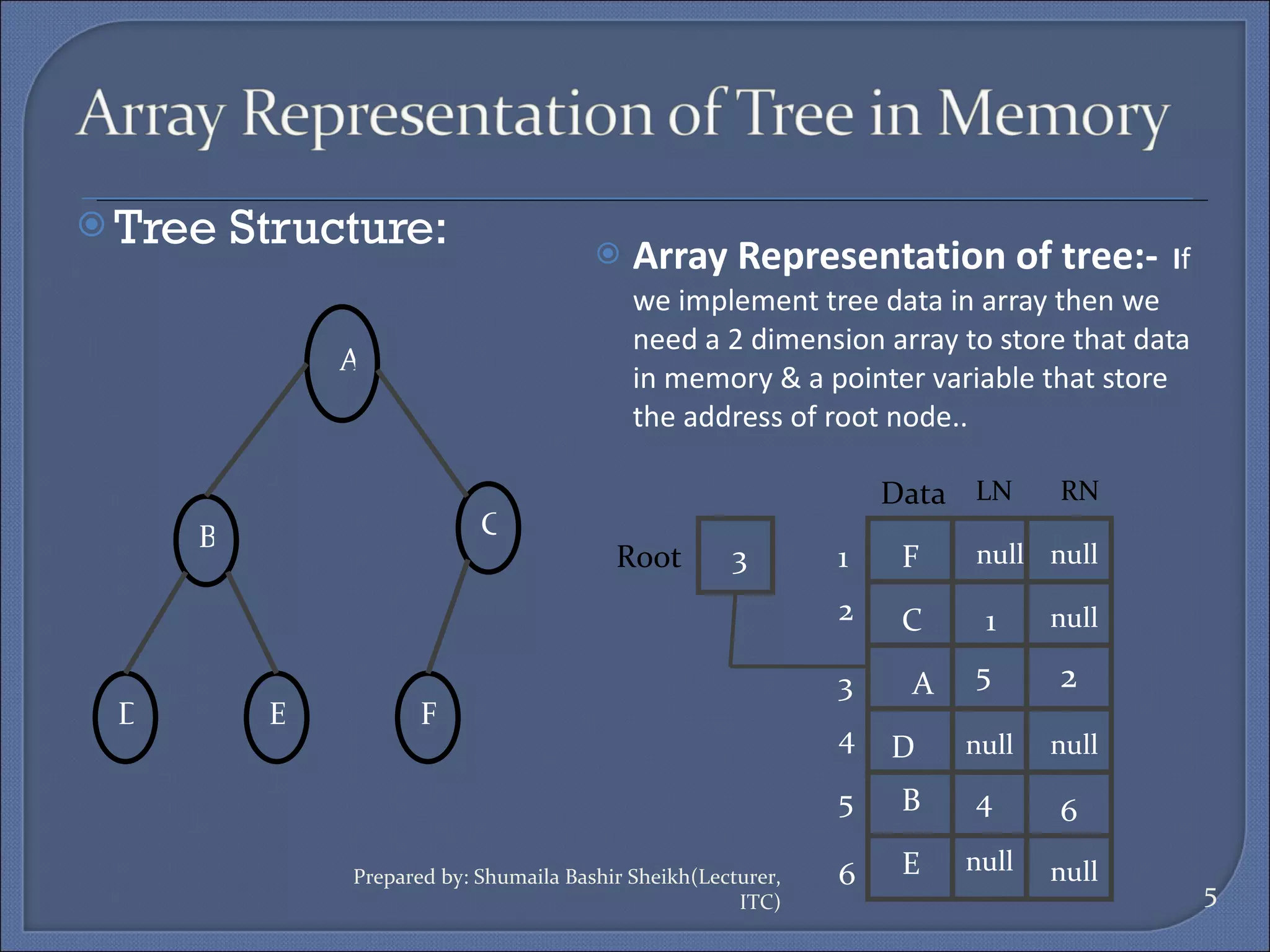
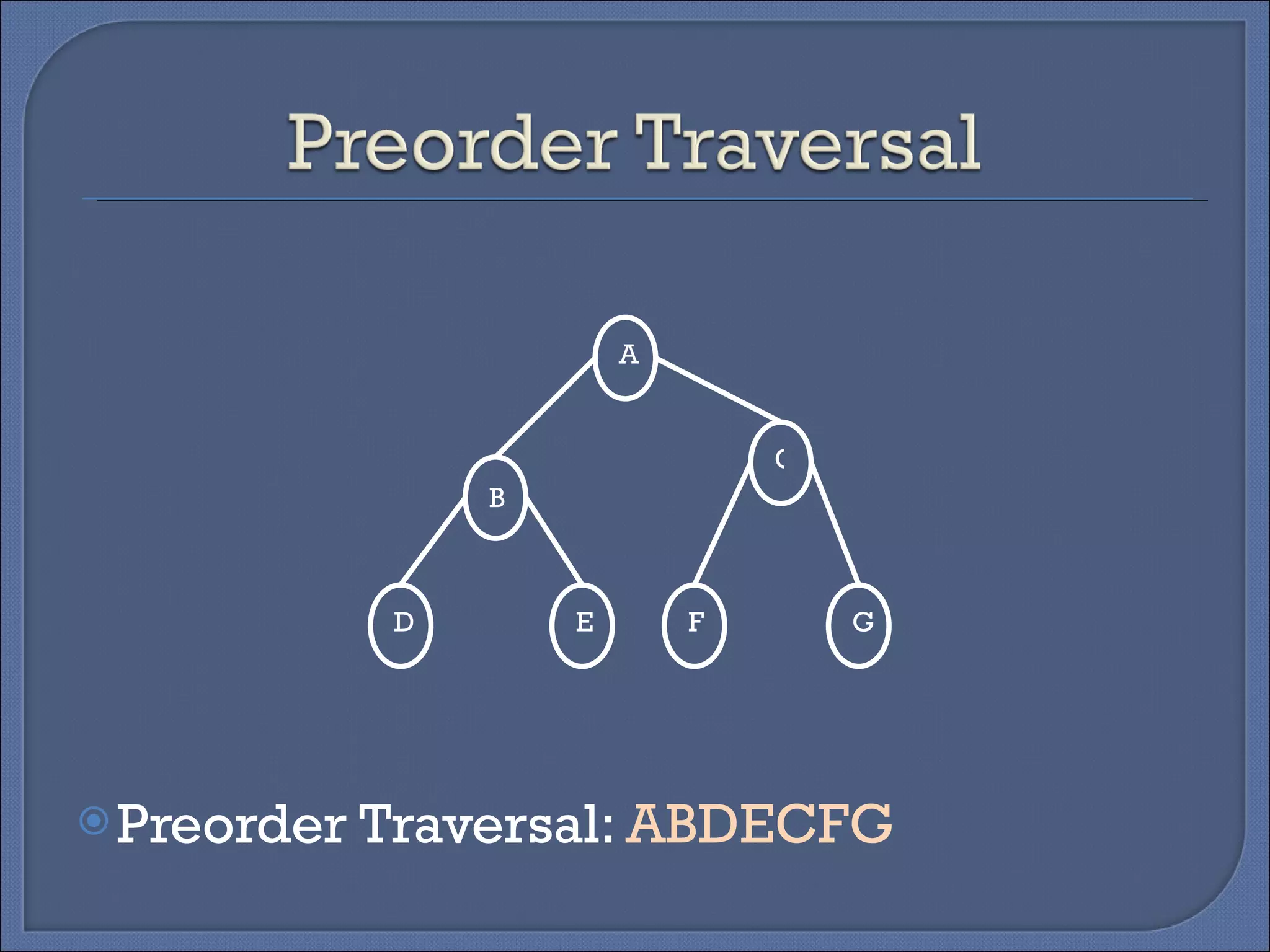
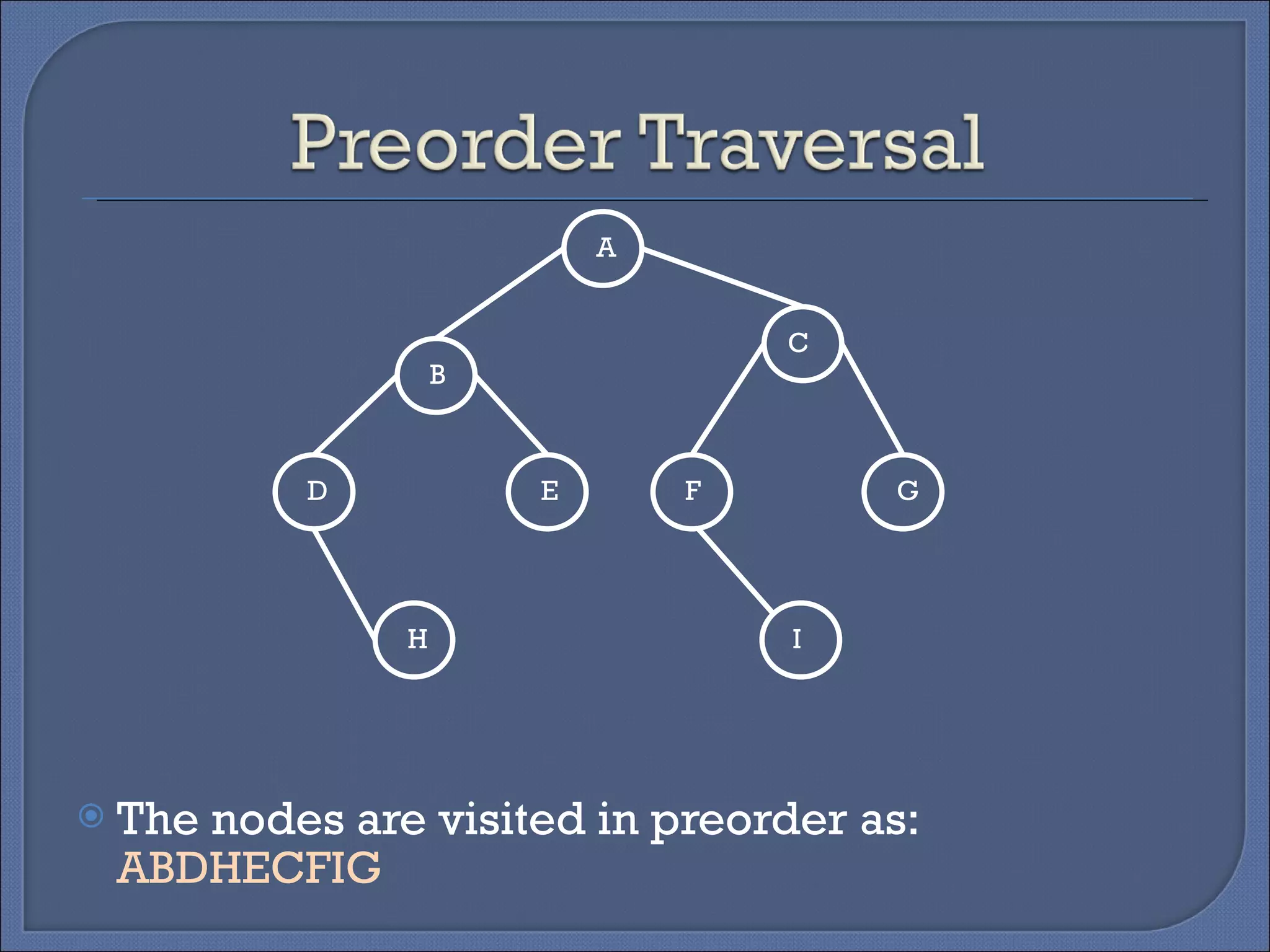
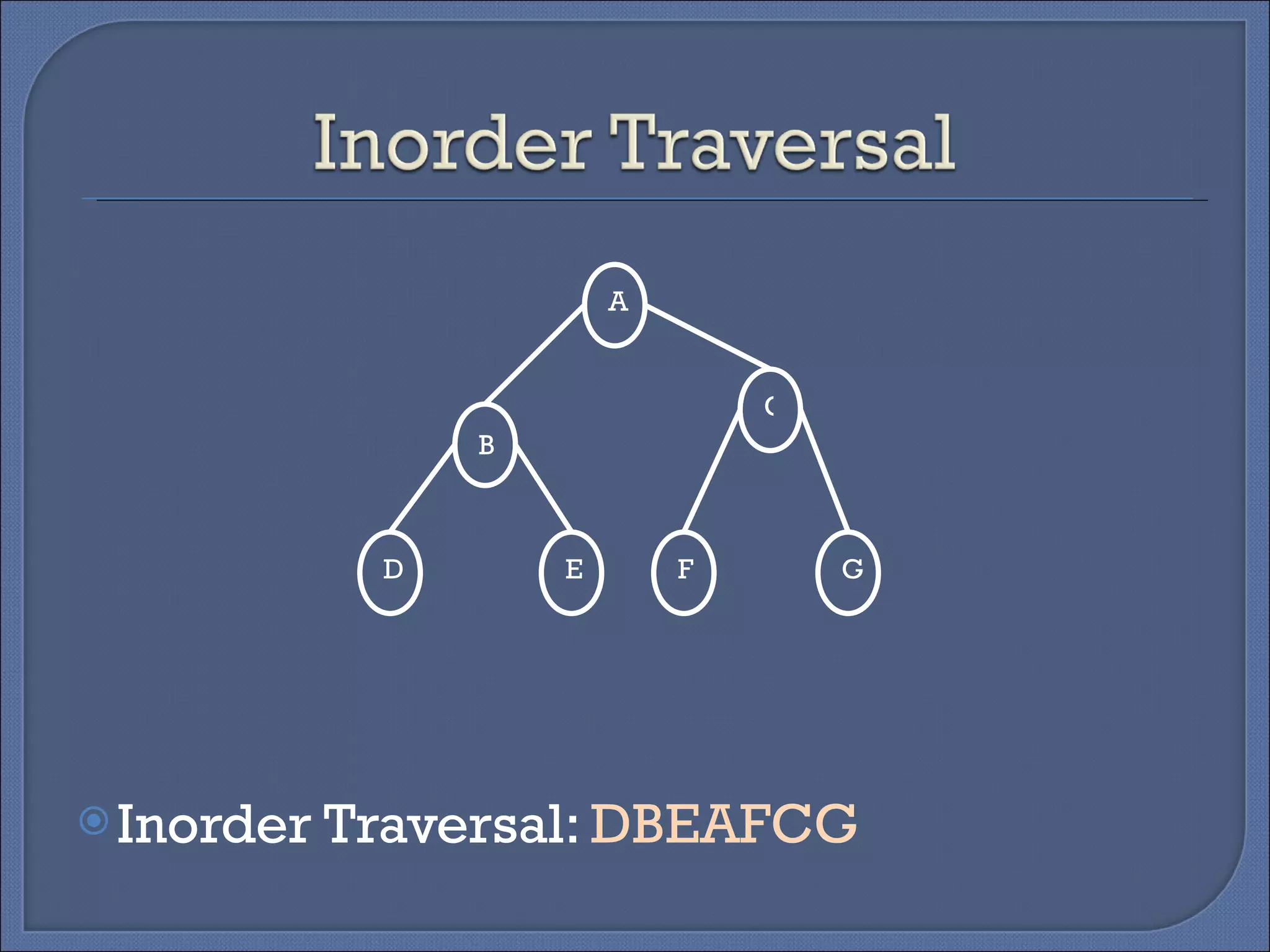
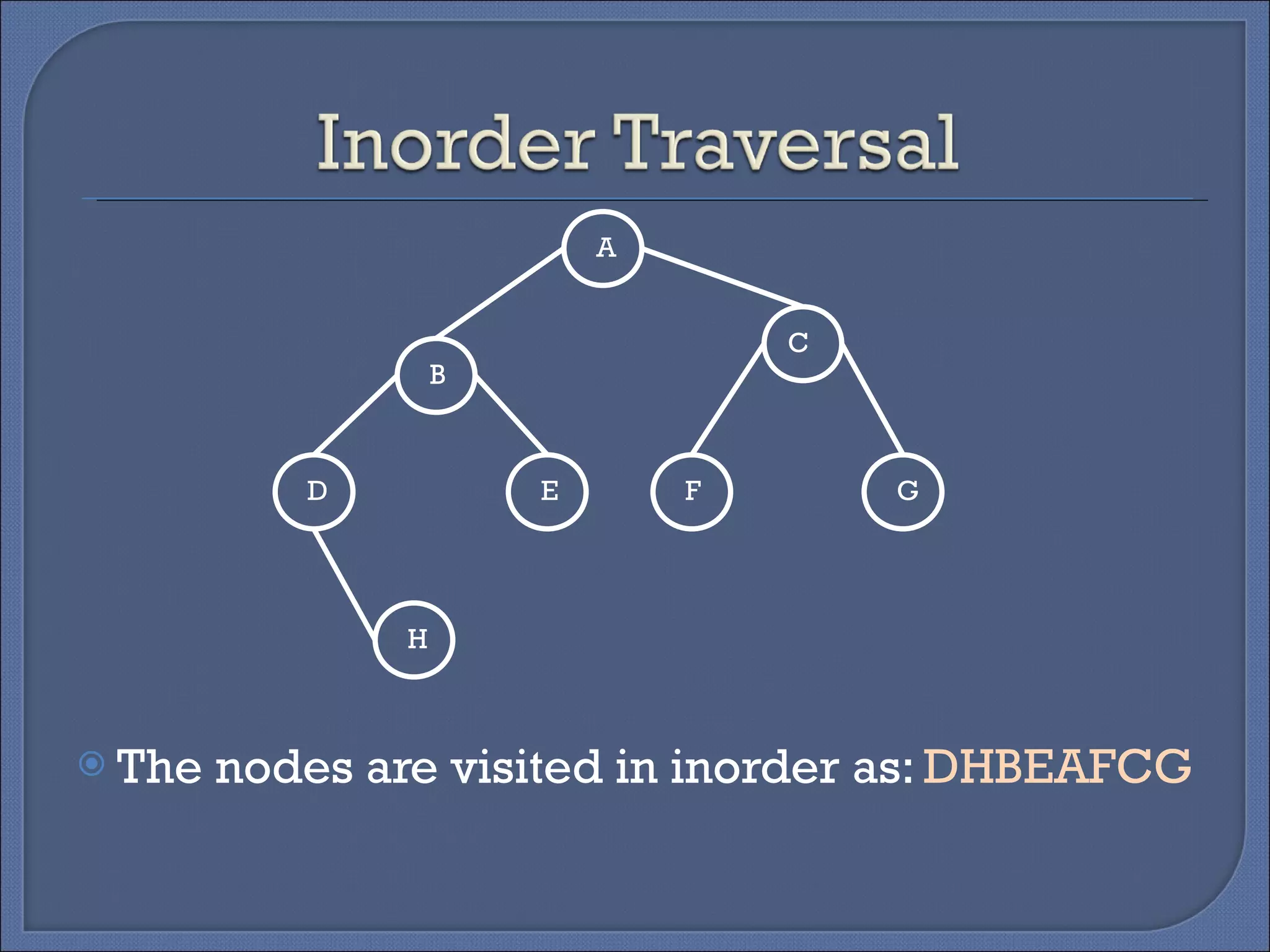
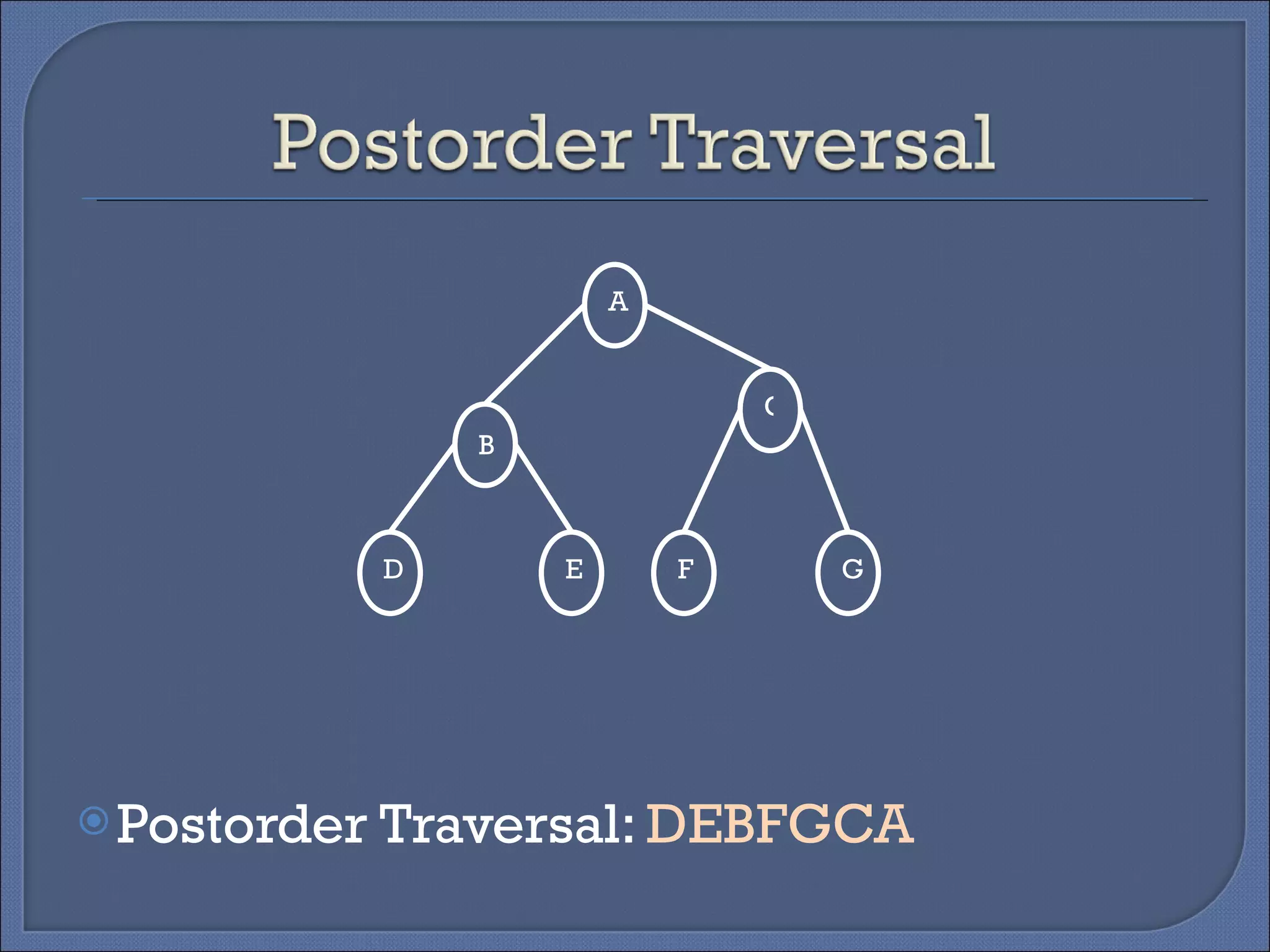
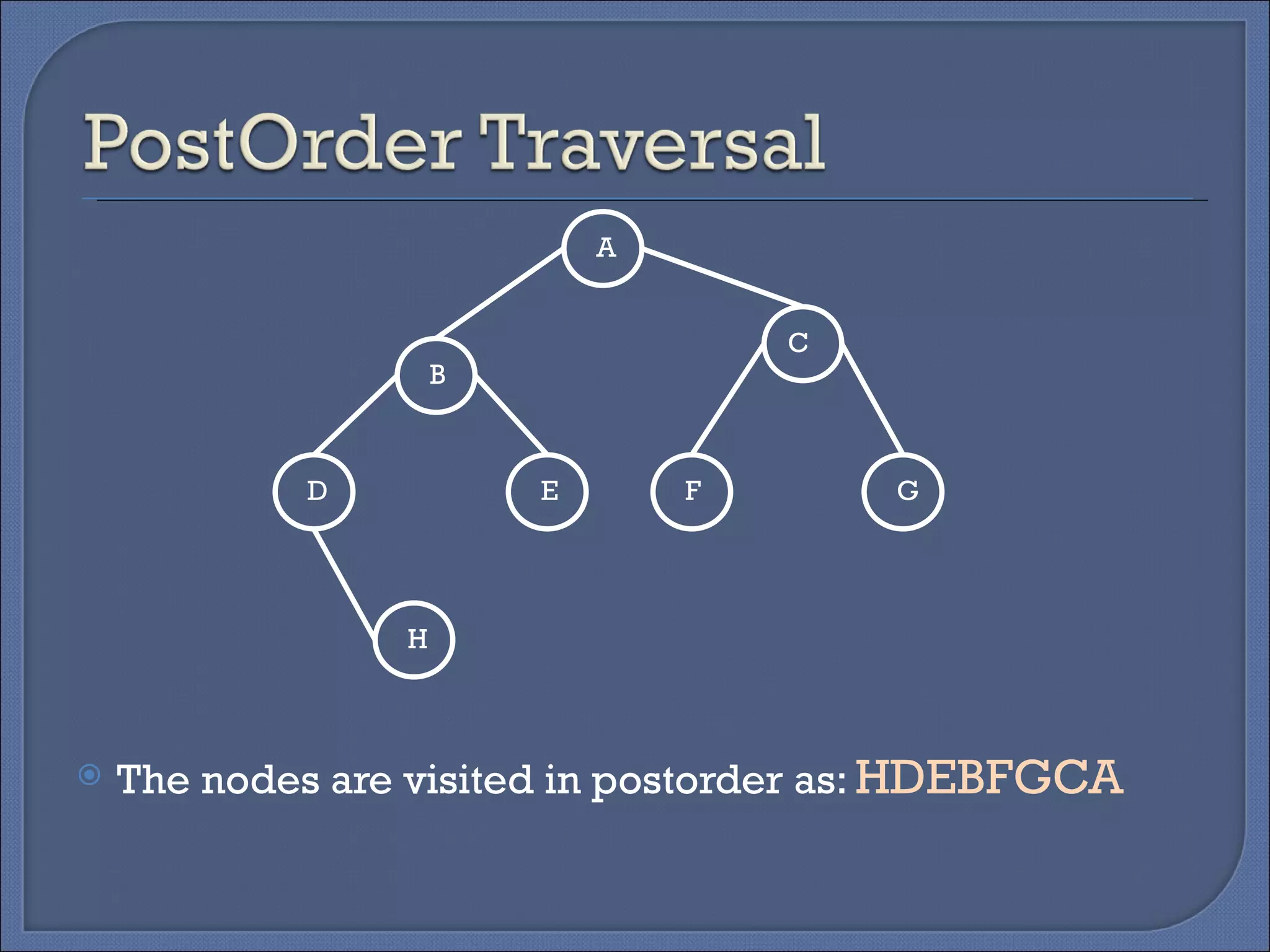
Binary trees can be implemented using two representations: linked and array. The linked representation stores each node as a structure with data, left child, and right child pointers. The array representation stores tree data in a 2D array with a root pointer variable. There are four basic tree operations: traversing, searching, inserting, and deleting. Traversing involves visiting nodes in different orders like preorder, inorder, and postorder.