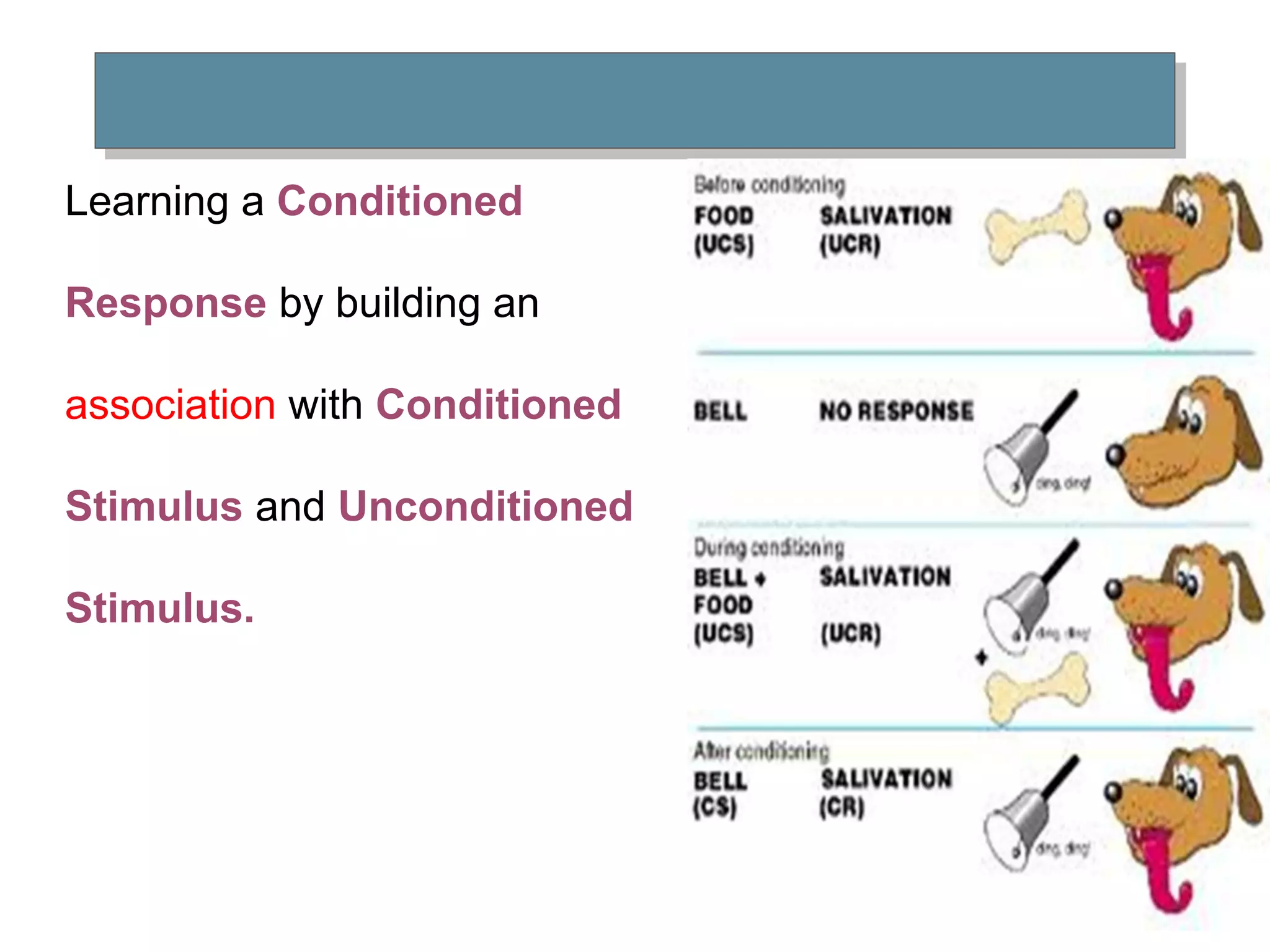
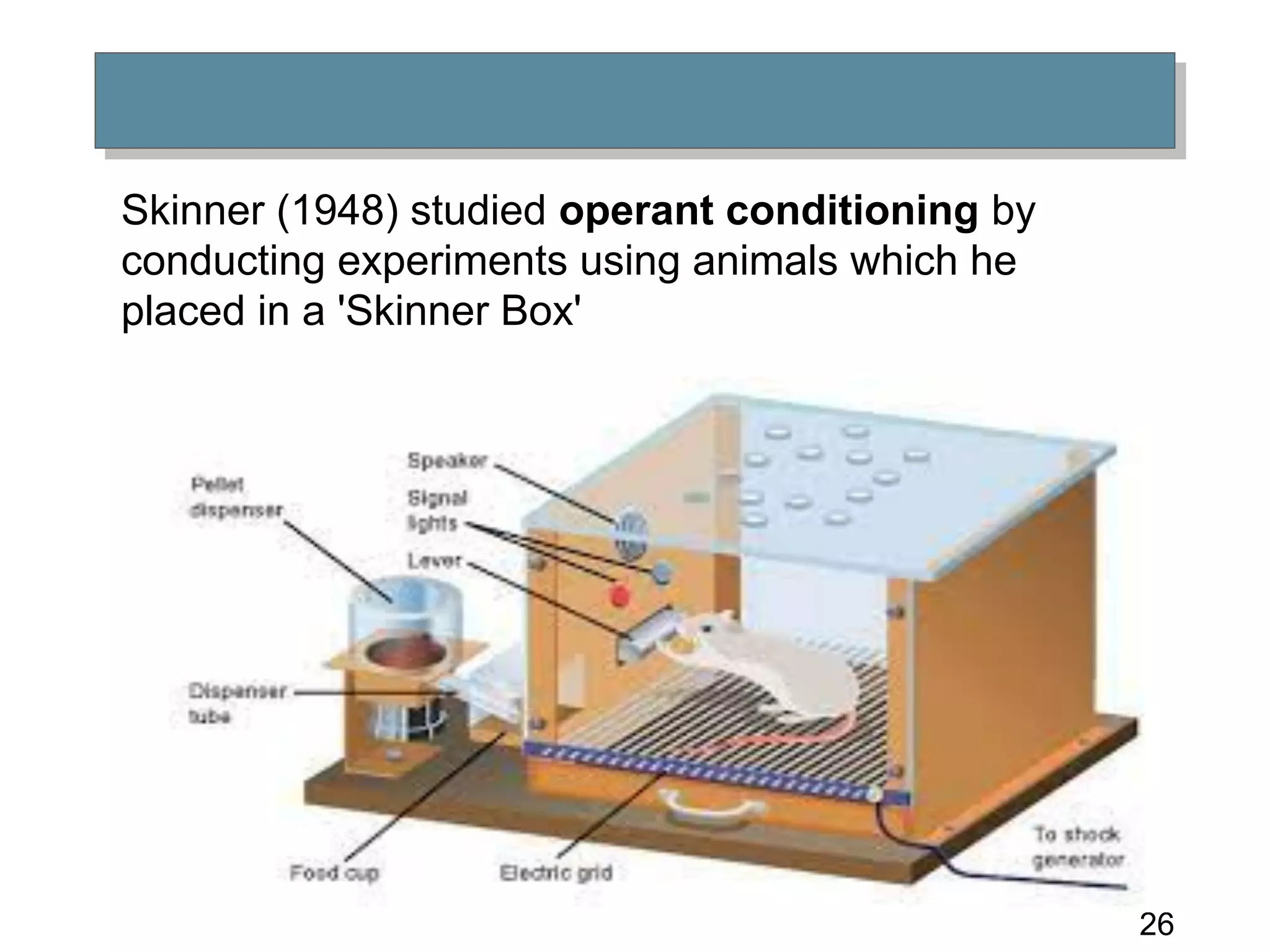
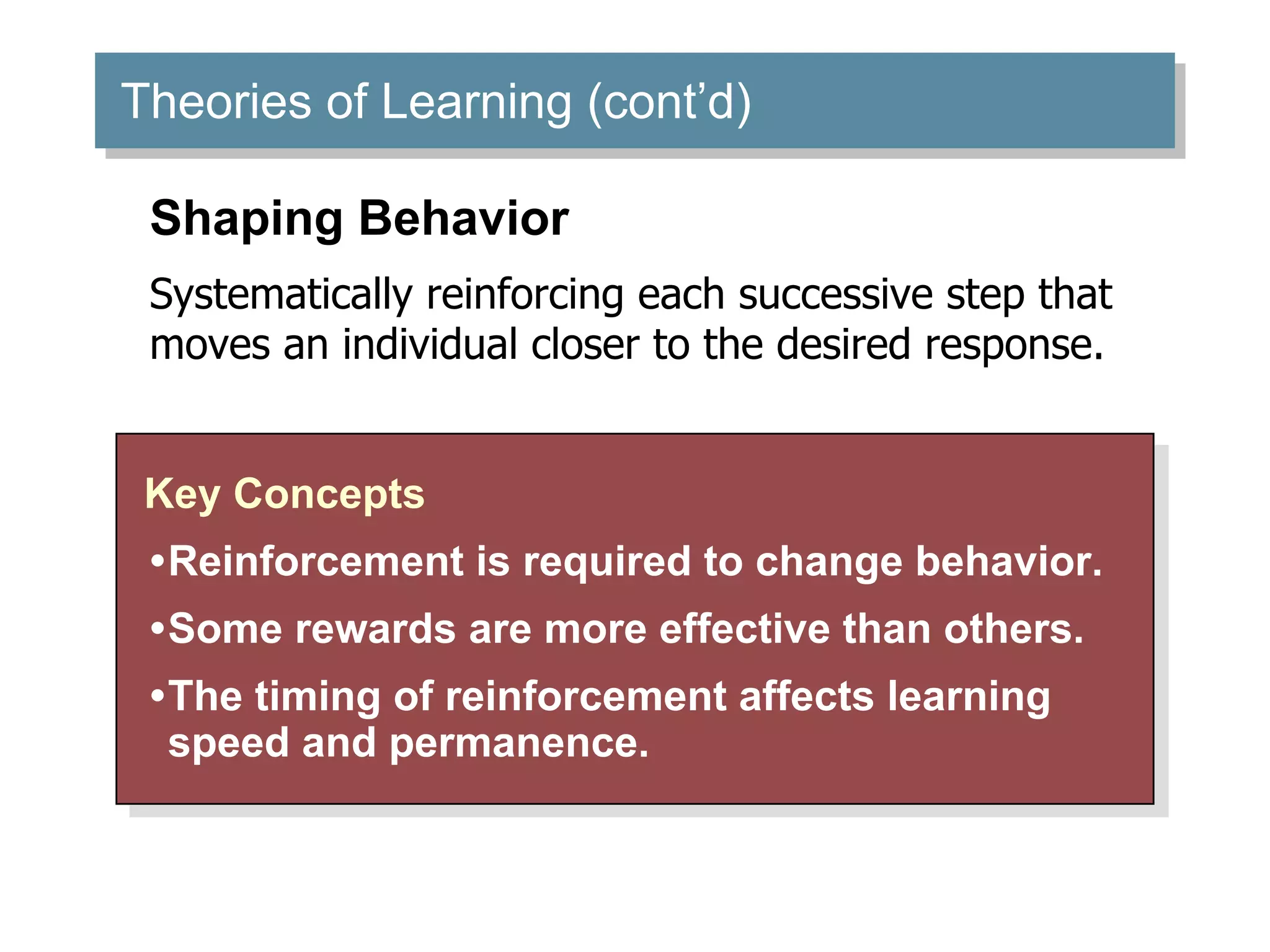
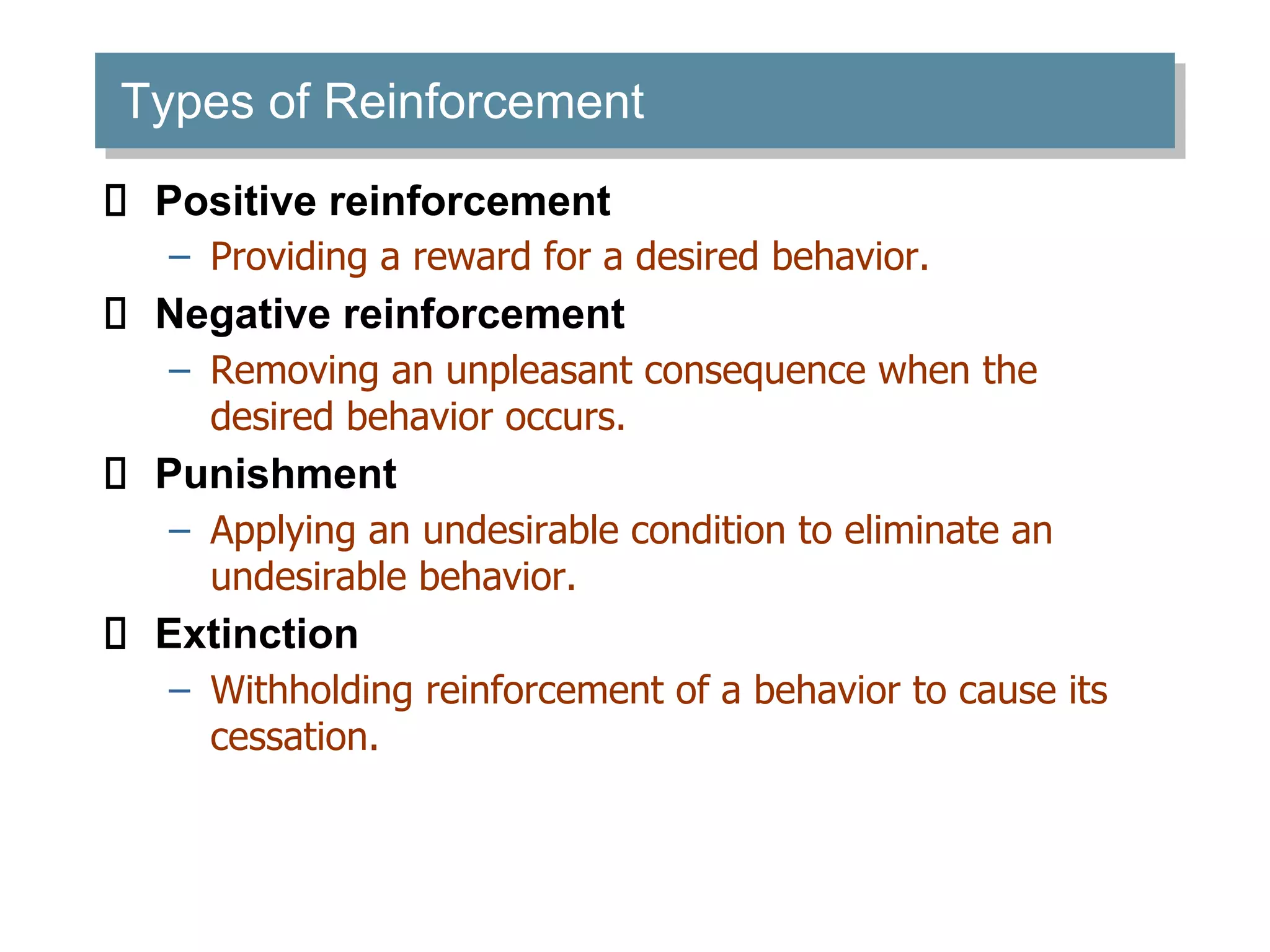
Learning involves relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience. There are several theories of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and social learning theory. Classical conditioning involves building associations between stimuli through experiences. Operant conditioning proposes that behaviors can be learned through reinforcement or punishment. Reinforcement strengthens behaviors while punishment weakens them. Social learning theory suggests people can learn through observing and imitating others.