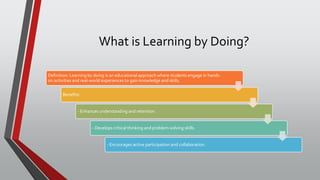
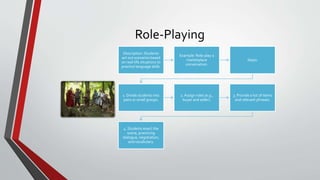
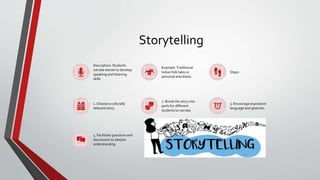
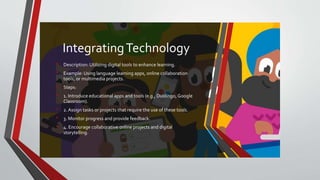
The document outlines the 'learning by doing' educational approach, emphasizing hands-on activities and real-world experiences to enhance student engagement, understanding, and critical skills. It provides various methods such as role-playing, storytelling, group discussions, project-based learning, experiential learning, and technology integration, along with examples and implementation steps. The document also offers tips for effective implementation and a case study highlighting successful outcomes.