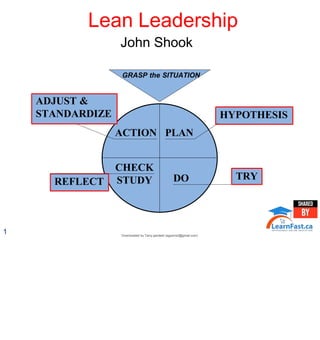
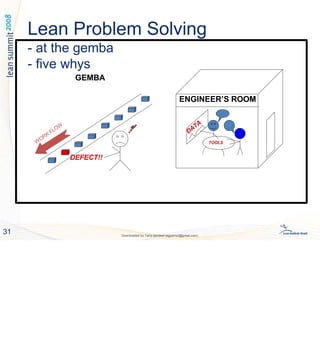
The document discusses lean leadership principles. A lean leader leads differently than traditional leaders by setting visions, building empowering systems, and influencing through coaching and questioning rather than dictating. A lean leader develops people by facilitating learning through tools like standardized work and the PDCA cycle. The lean leader's role is to get others to think and take initiative by asking questions, avoiding giving direct answers, and addressing barriers that discourage independent problem solving.