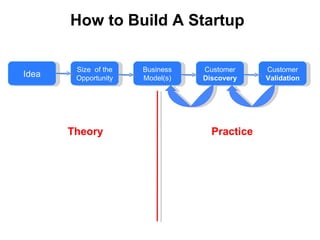
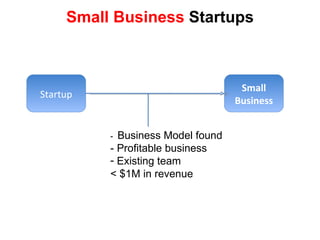
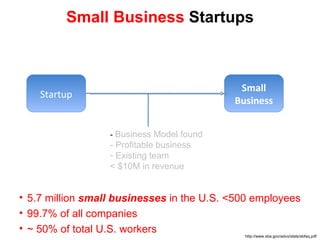
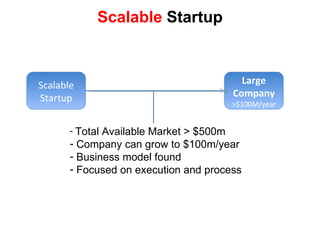
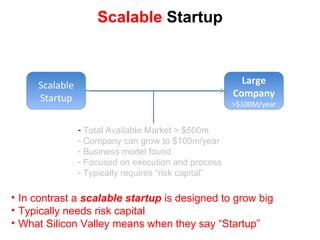
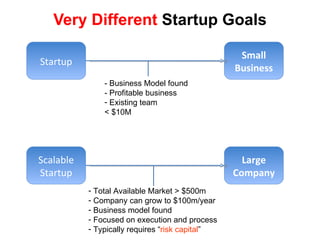
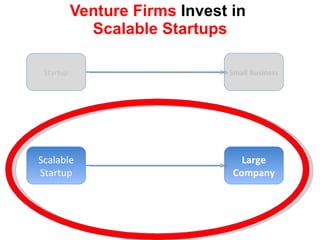
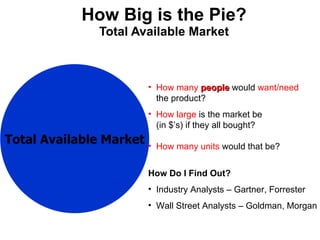
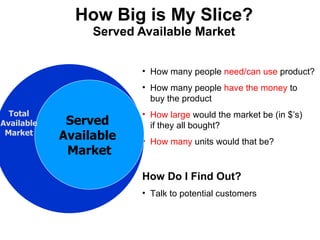
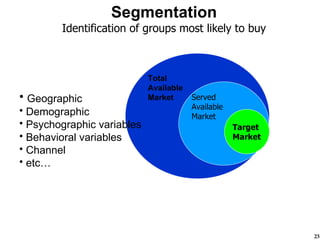
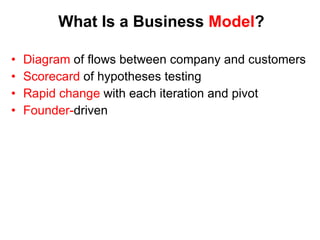
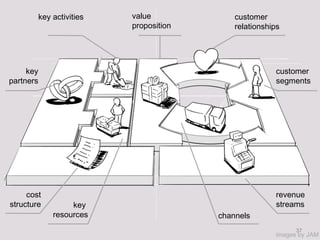
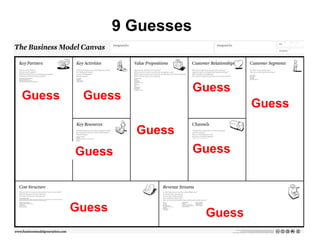
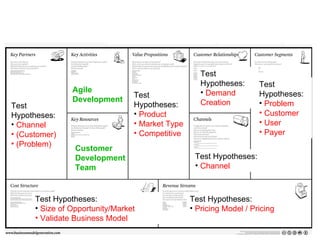
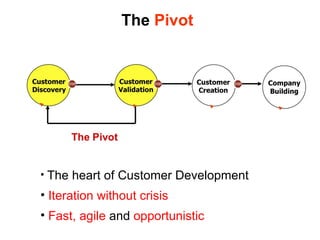
The document discusses the Lean Startup methodology as a practical approach to developing a startup through customer engagement and iteration rather than traditional business planning. It emphasizes the creation of a validated business model and the use of customer development and agile development techniques for rapid product iteration. Key topics include market analysis, business model components, and the importance of understanding customer needs and relationships.