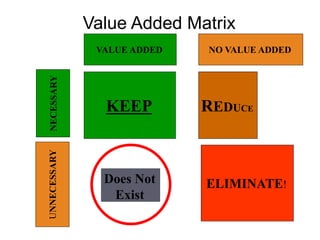
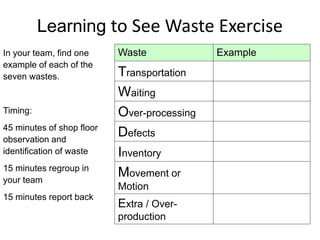
The document discusses lean philosophy and various aspects of waste. It defines lean as identifying and removing waste from any process. It outlines the seven forms of waste as transportation, waiting, over-processing, defects, inventory, unnecessary movement or motion, and overproduction. The document also discusses topics like value-added activities, the Toyota production system's pursuit of eliminating muda, muri, and mura, and using tools like a value-added matrix to classify activities.