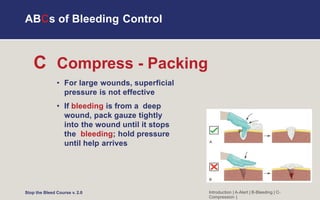
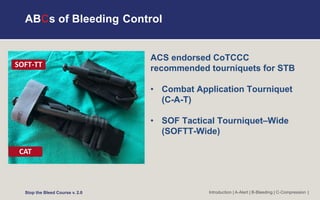
The document is a training course on how to stop bleeding from injuries. It teaches the ABCs of bleeding control: A is for Alert by calling 911, B is for finding Bleeding by locating wounds, and C is for Compressing bleeding through direct pressure, wound packing, or using a tourniquet. Personal safety is emphasized, and appropriate ways to apply pressure, pack wounds, and use tourniquets are demonstrated for arms, legs, neck, and other body parts in adults and children. Questions about special situations are addressed. The overall goal is to recognize life-threatening bleeding and take steps to stop it until emergency help arrives.