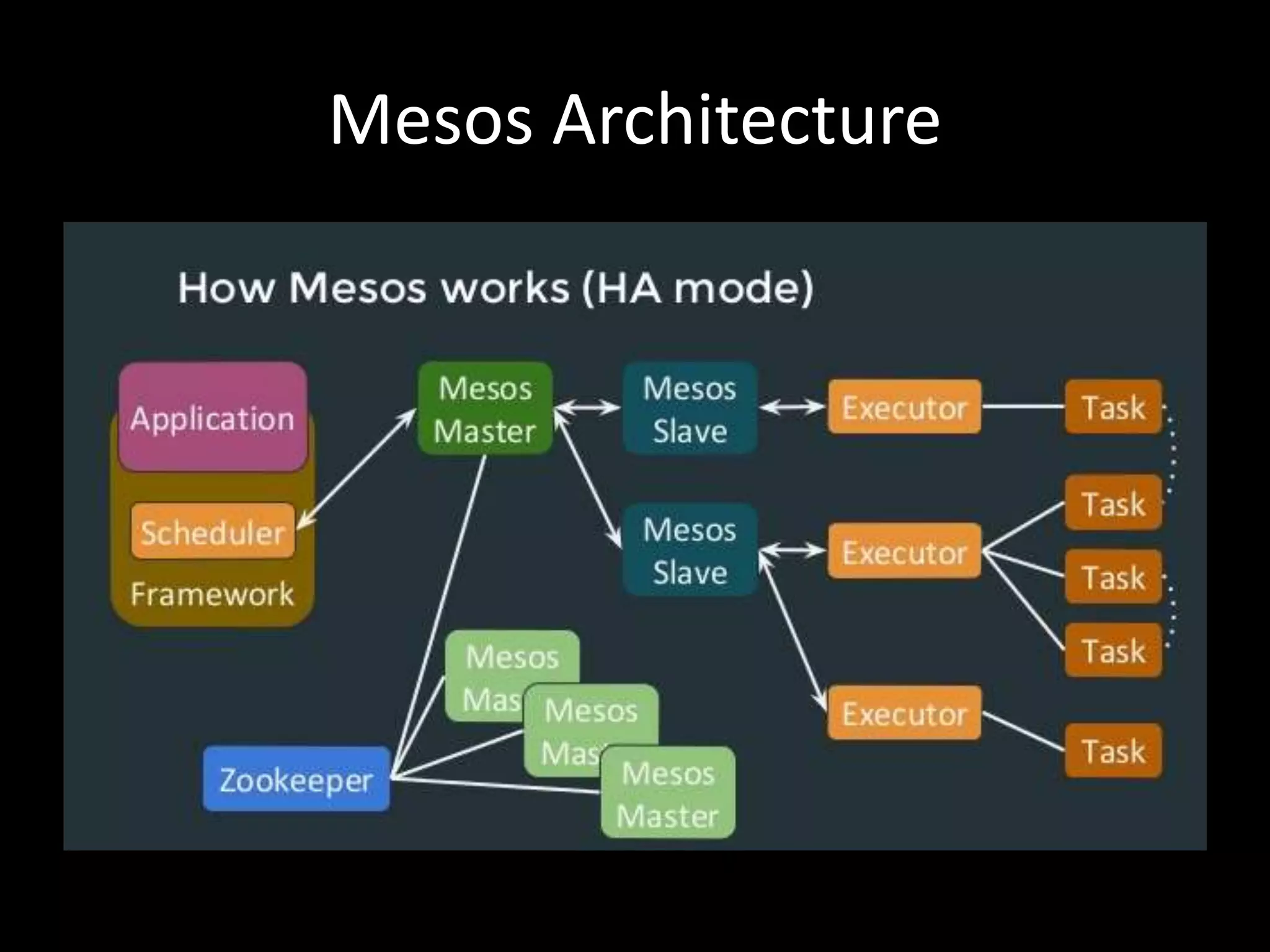
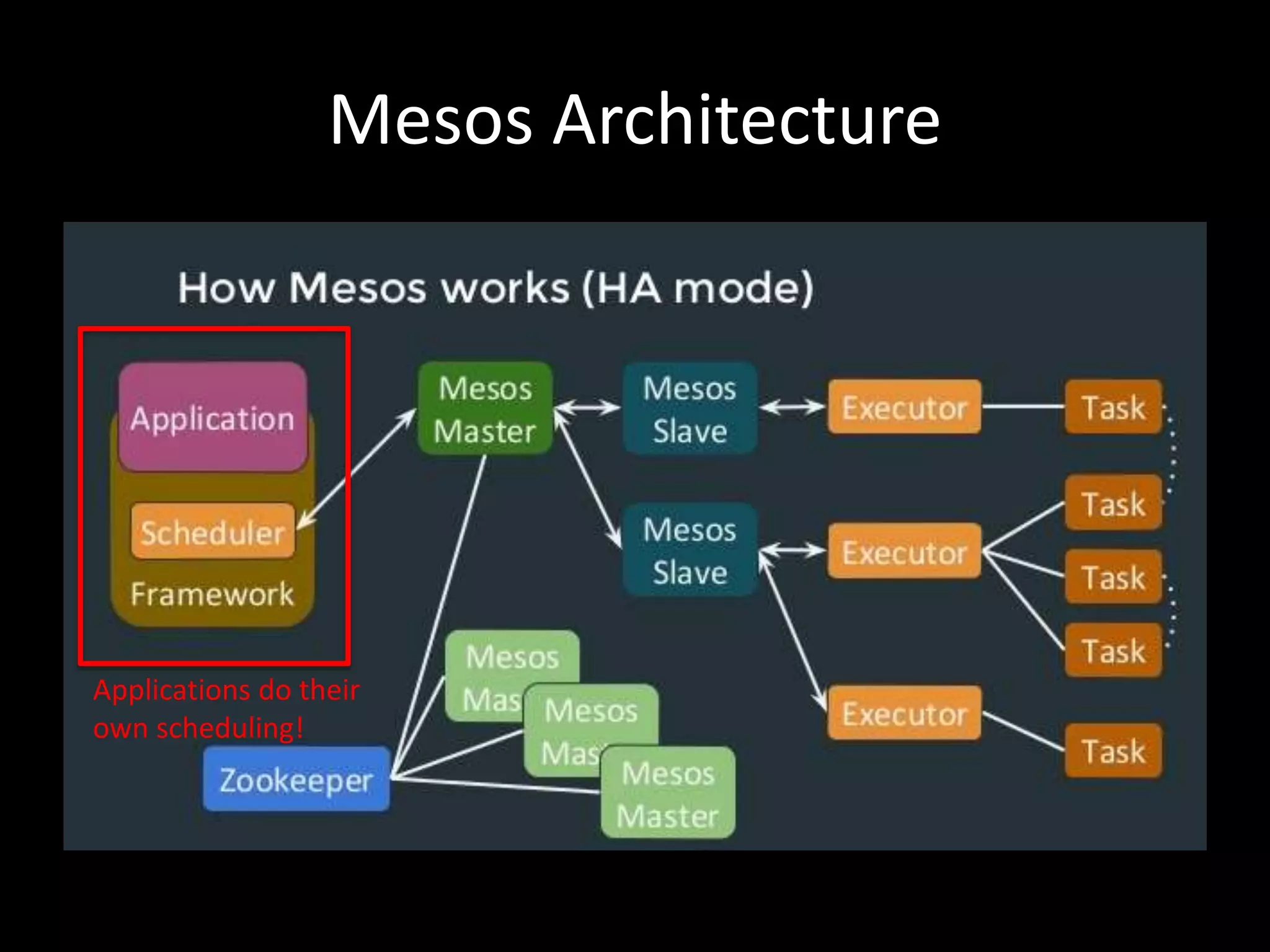
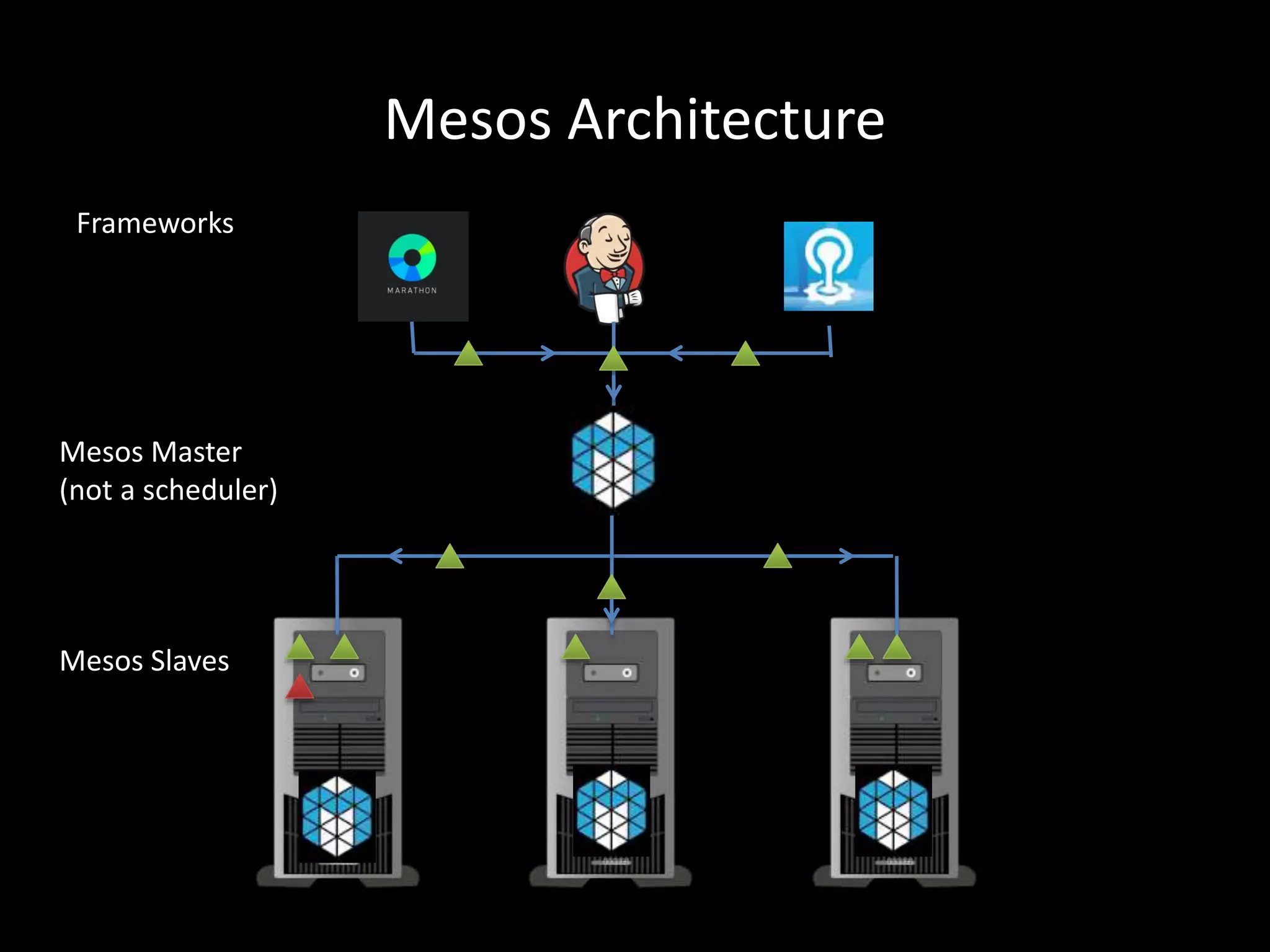
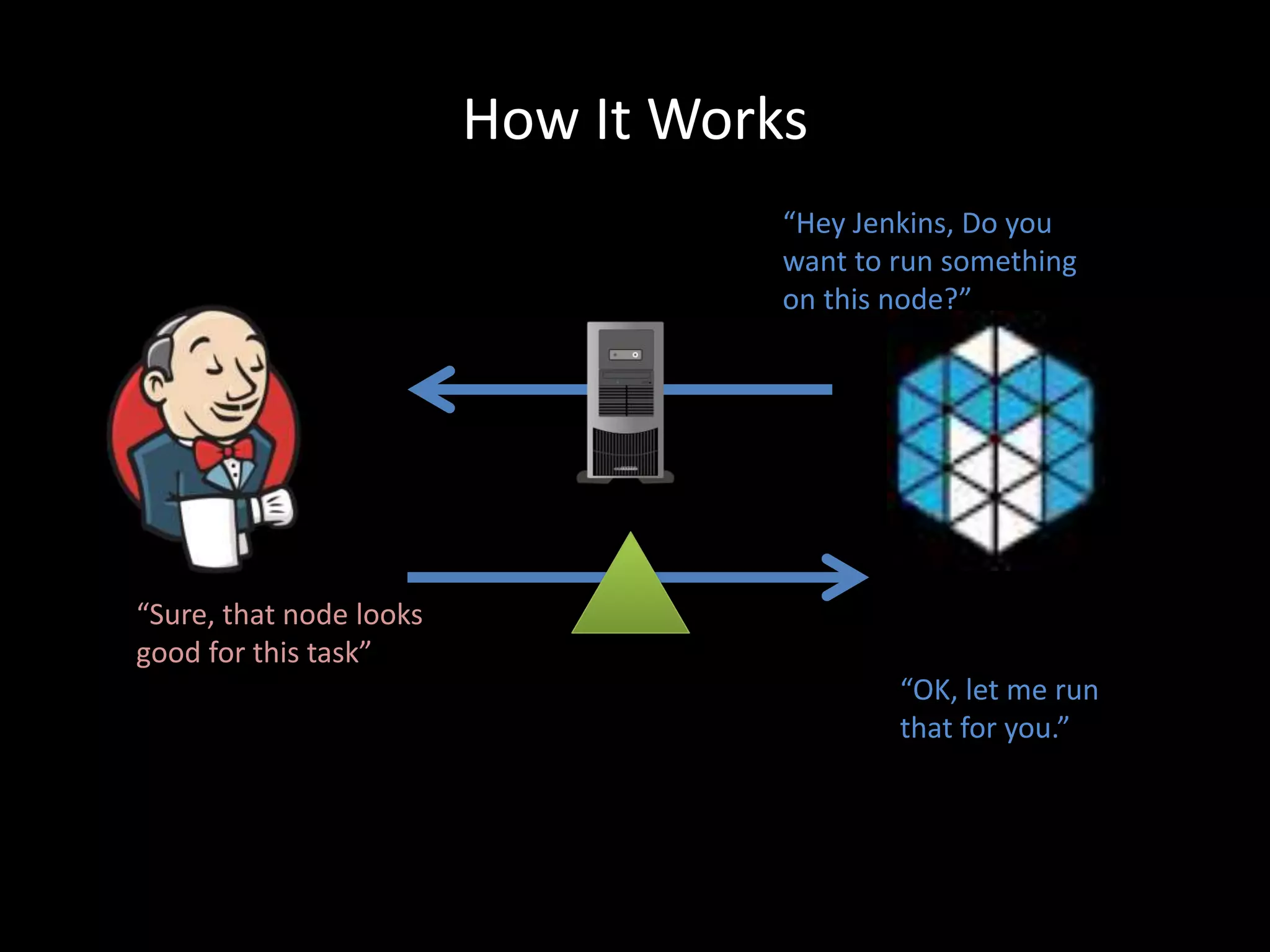
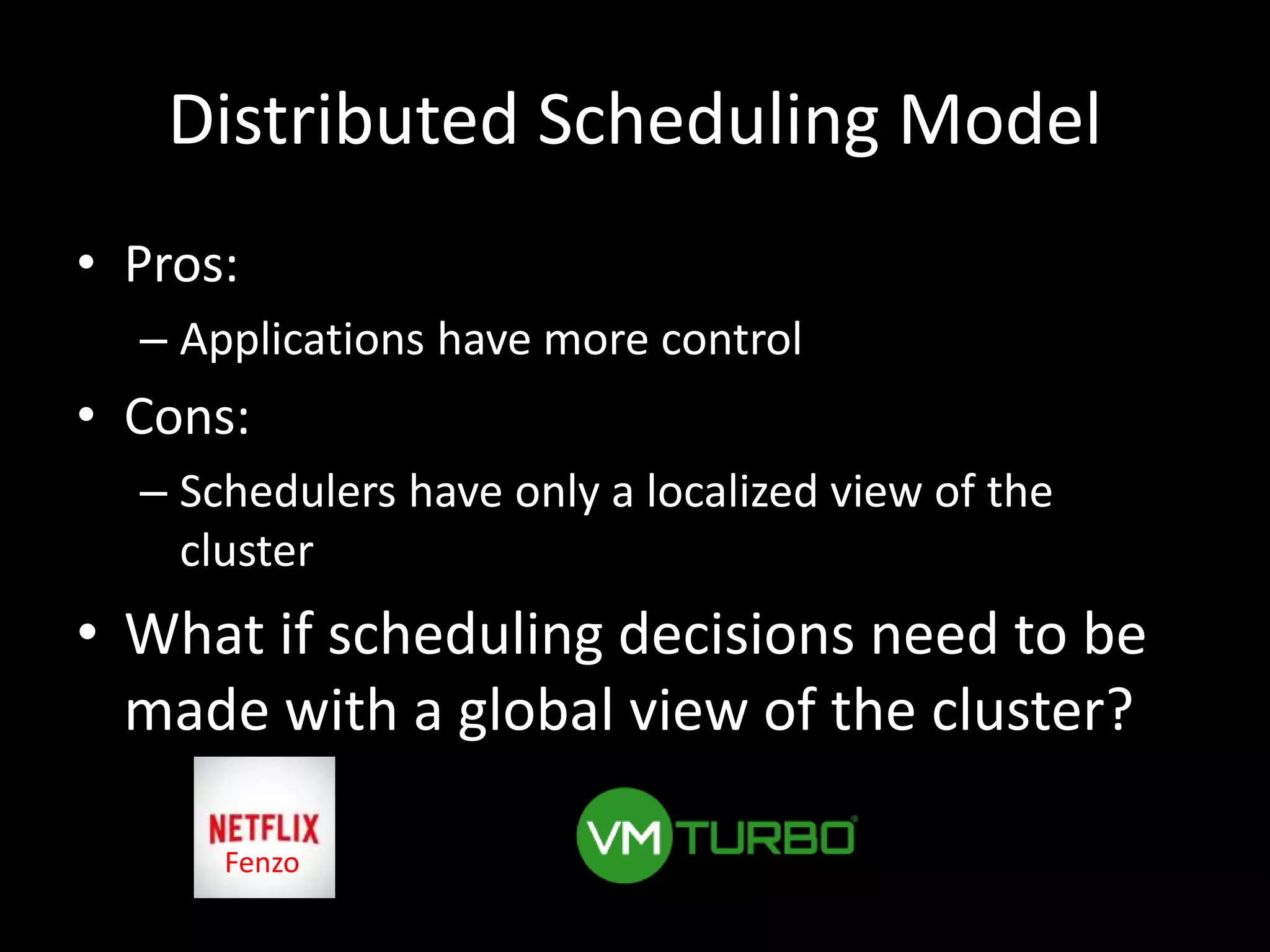
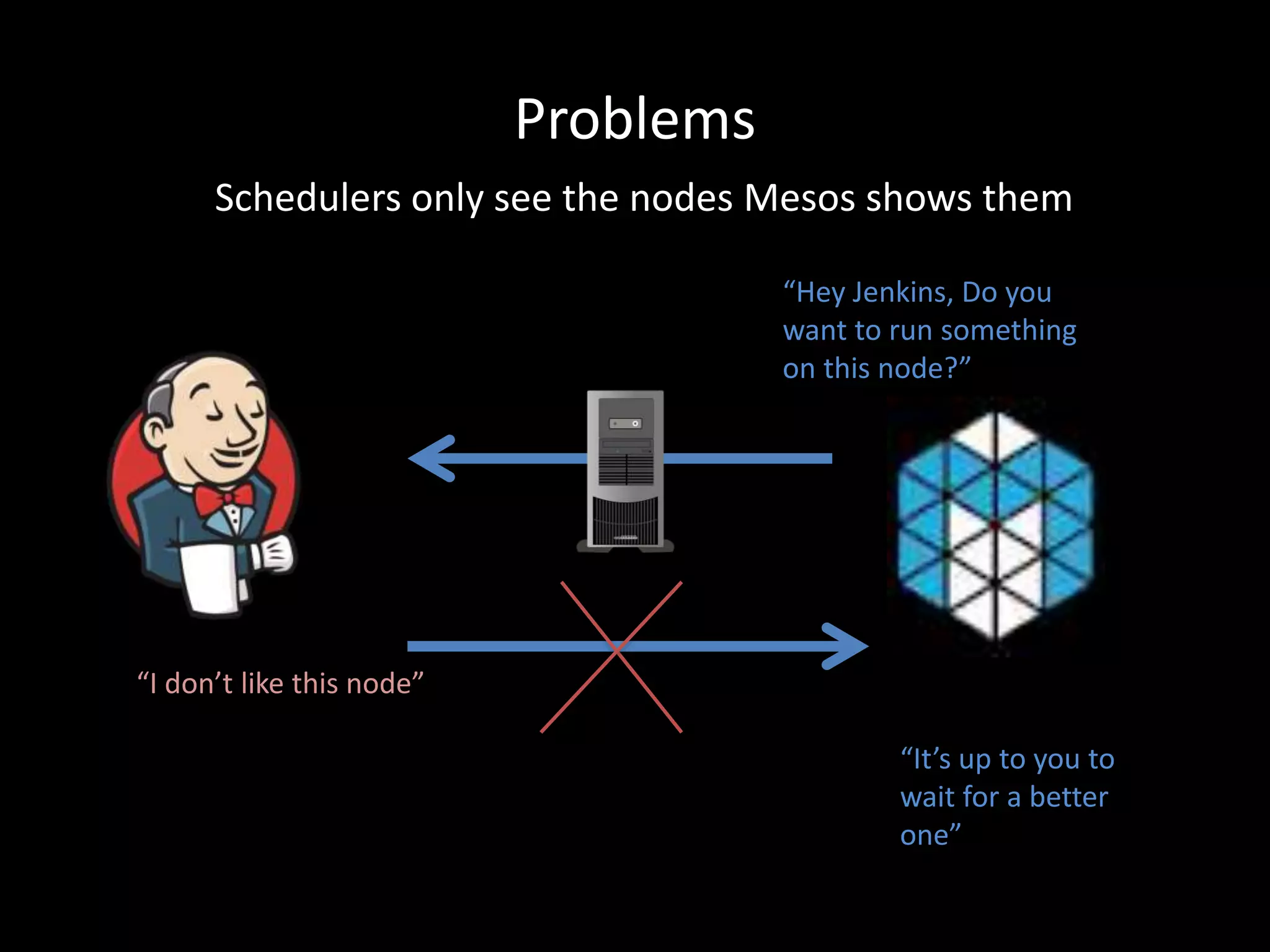
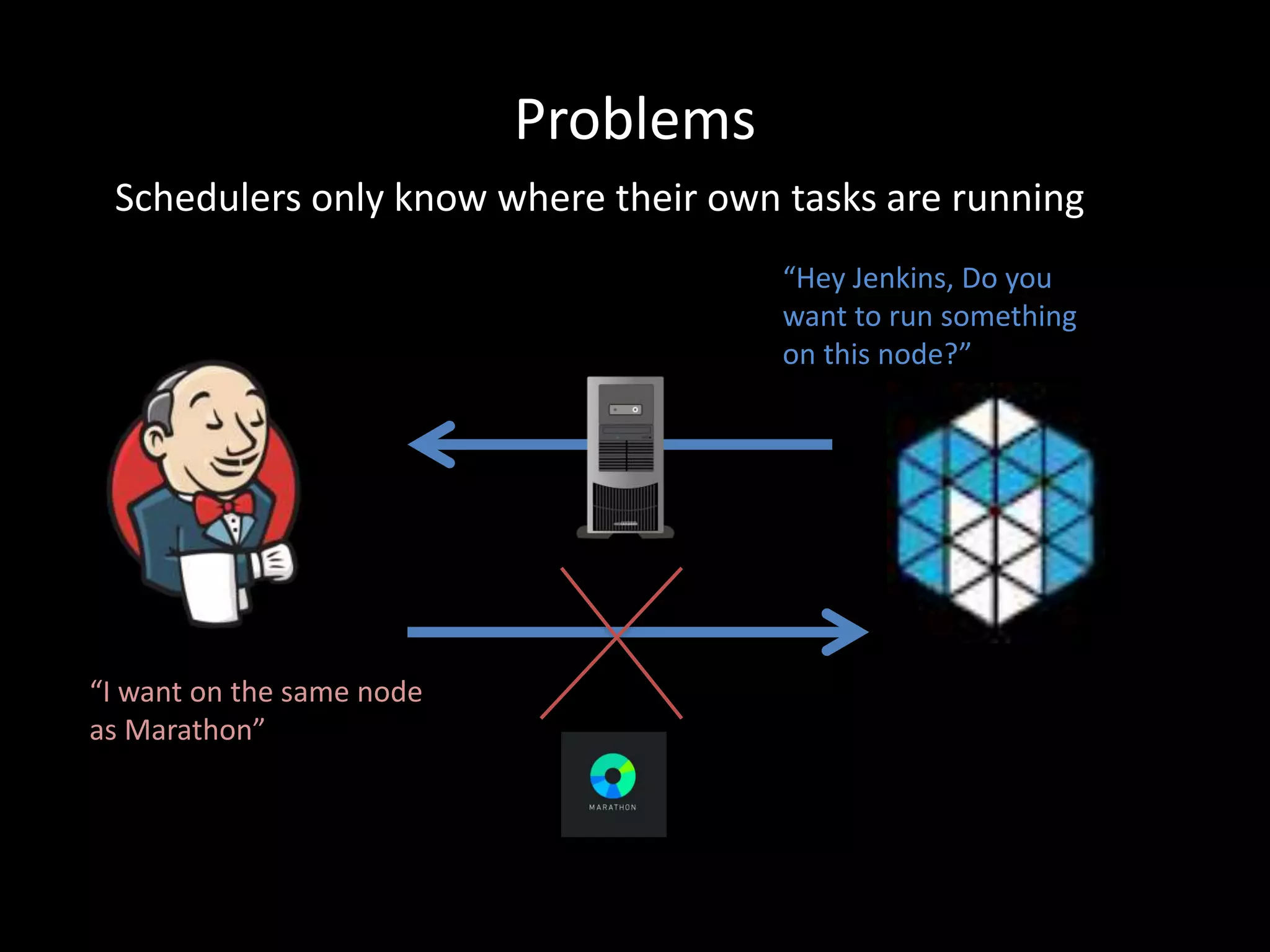
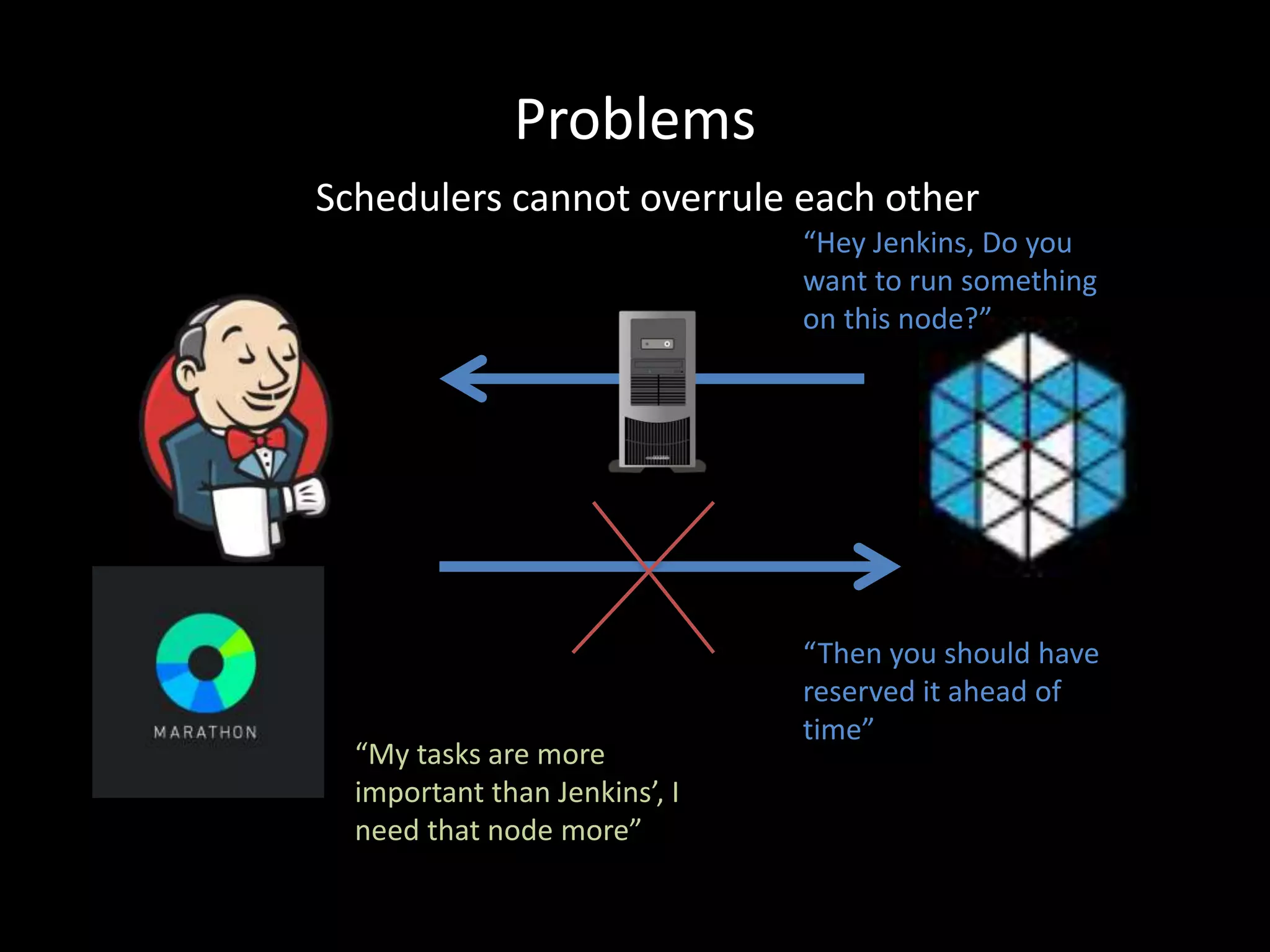
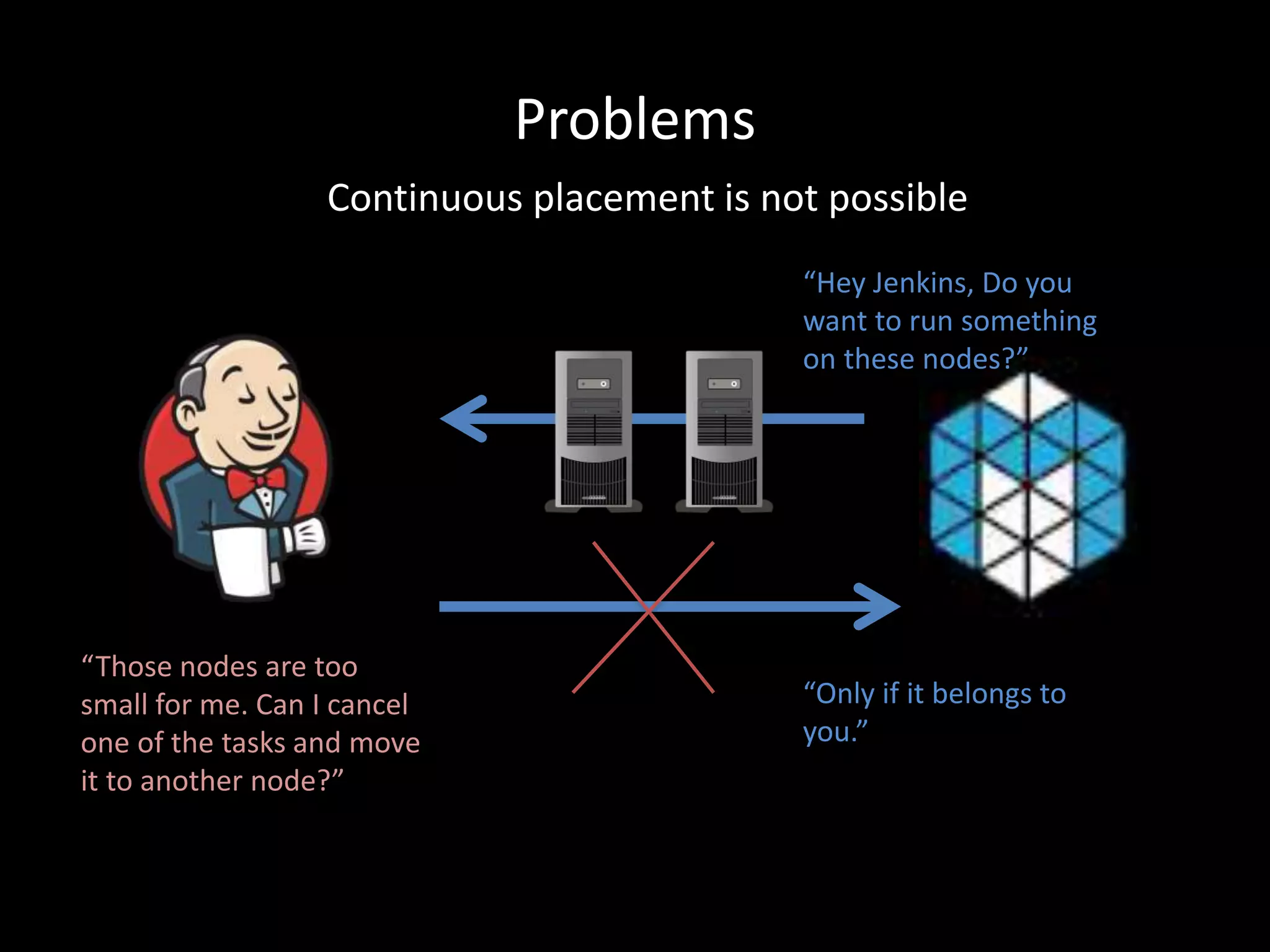
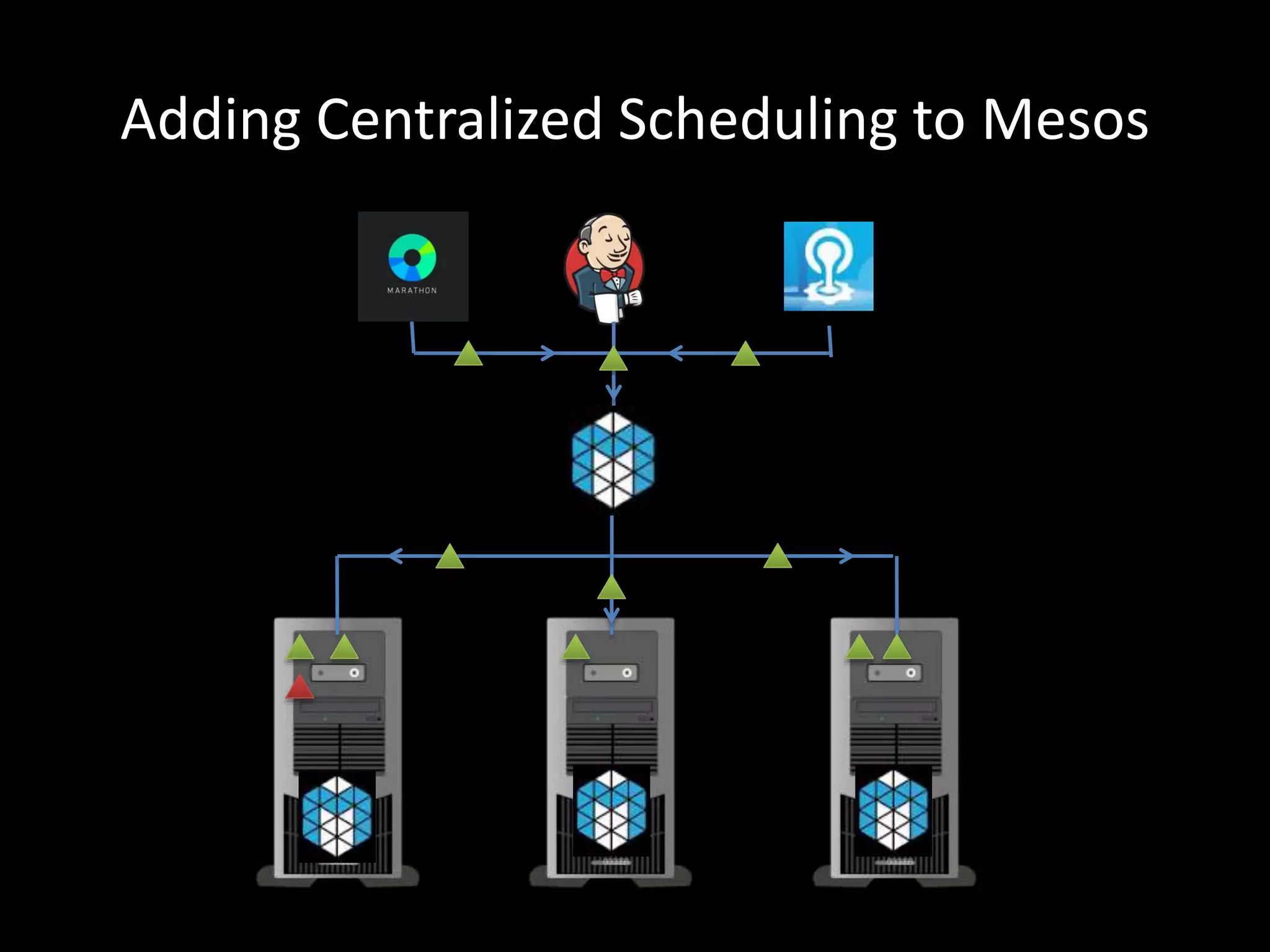
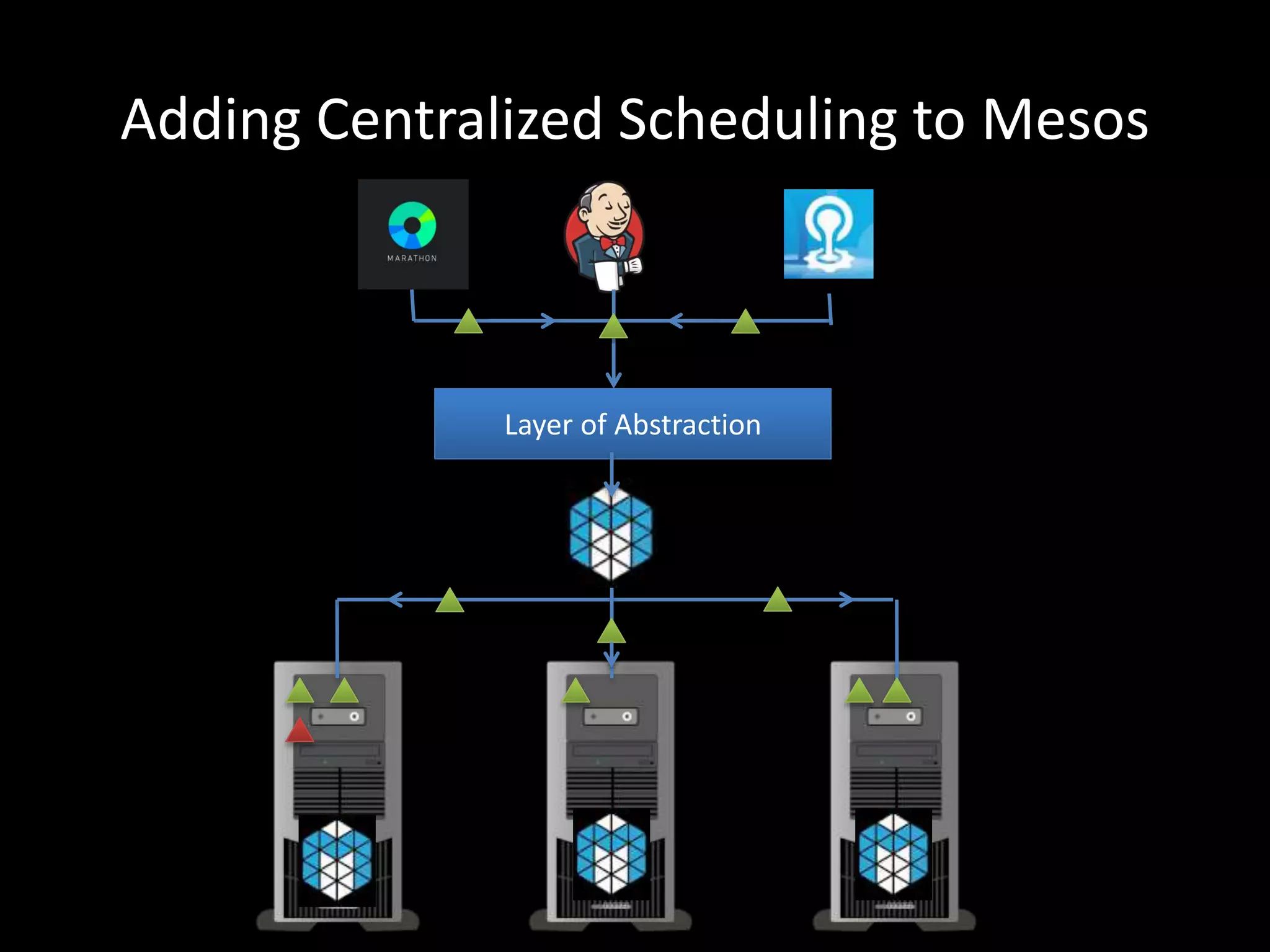
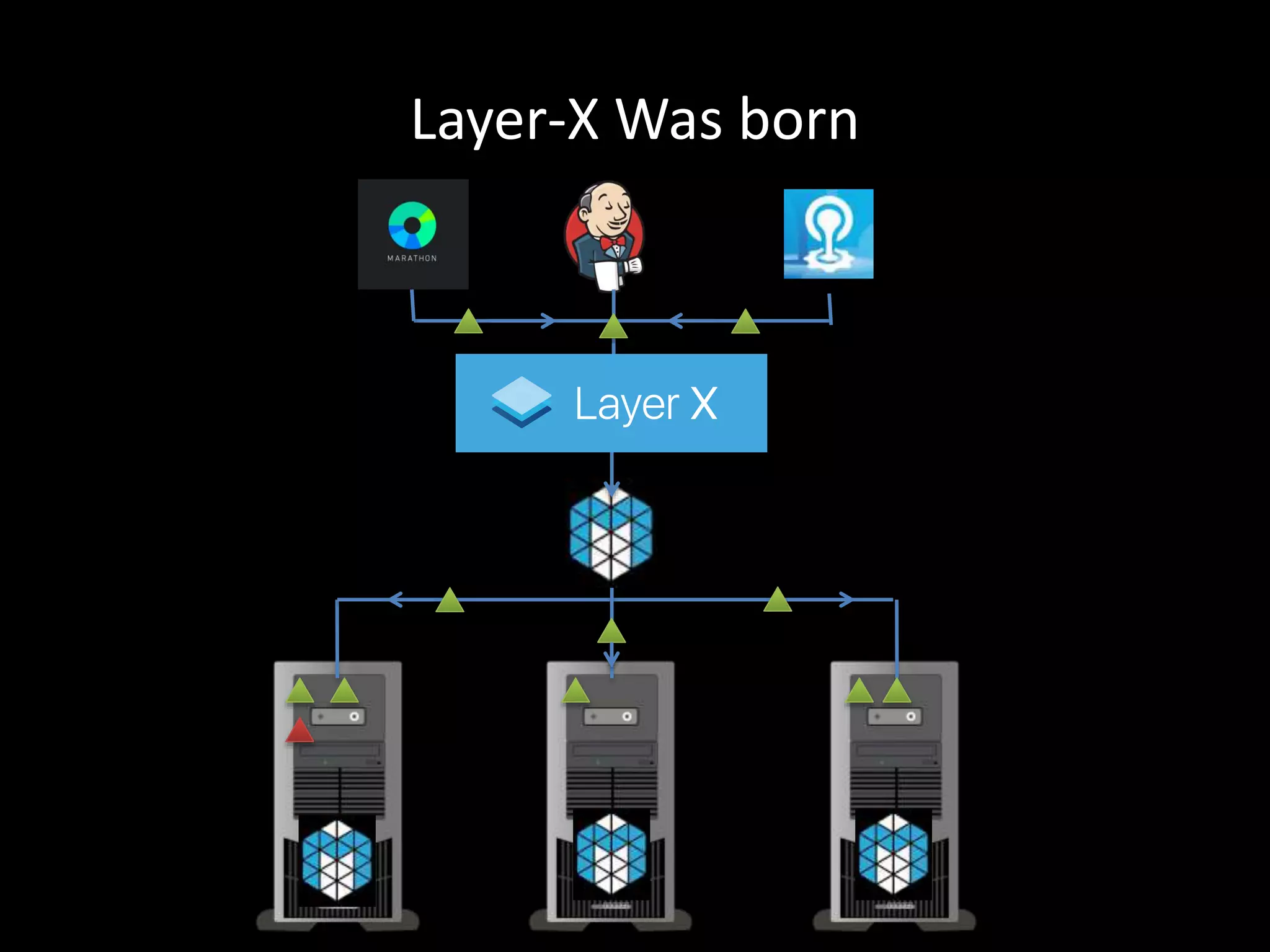
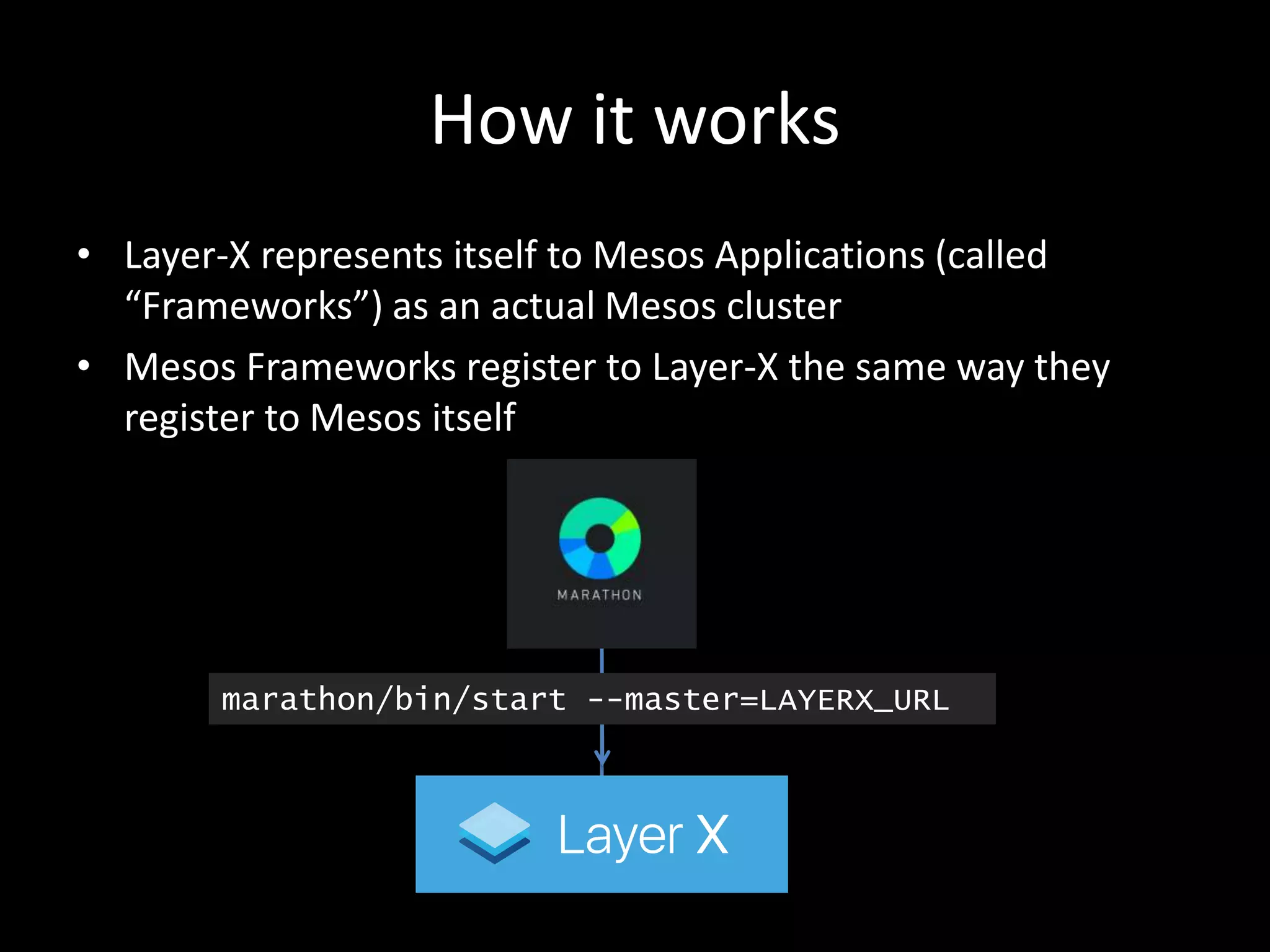
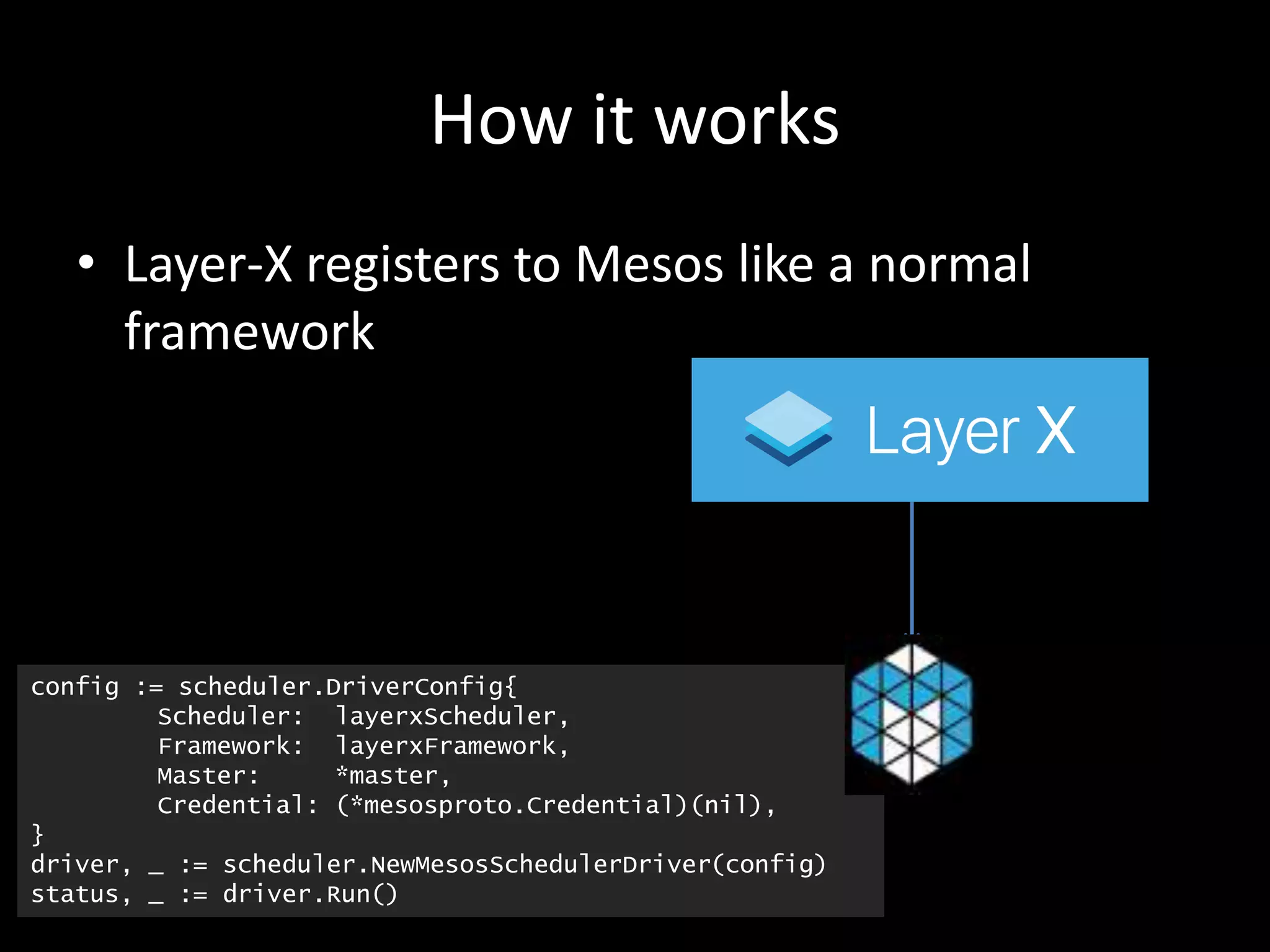
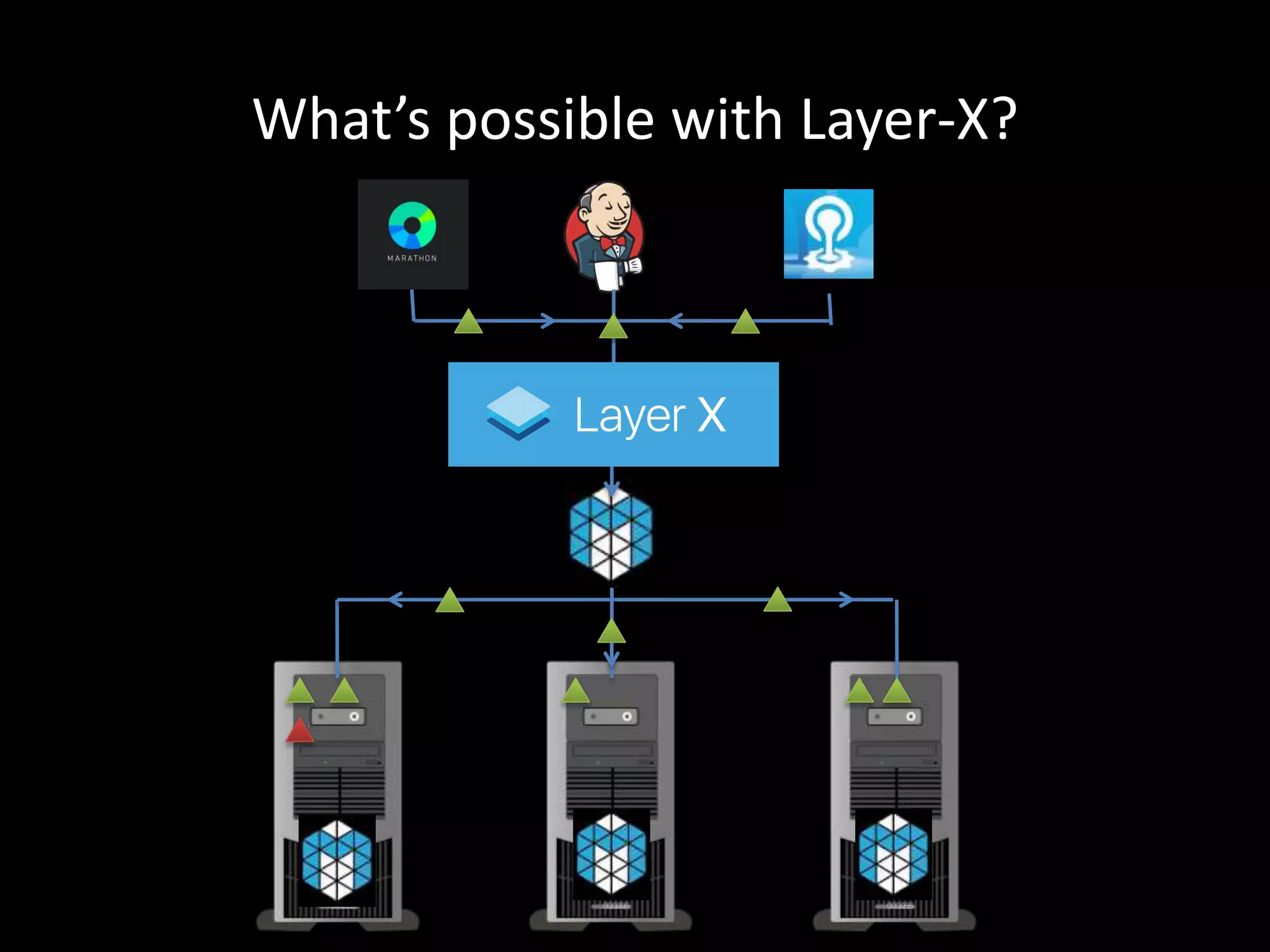
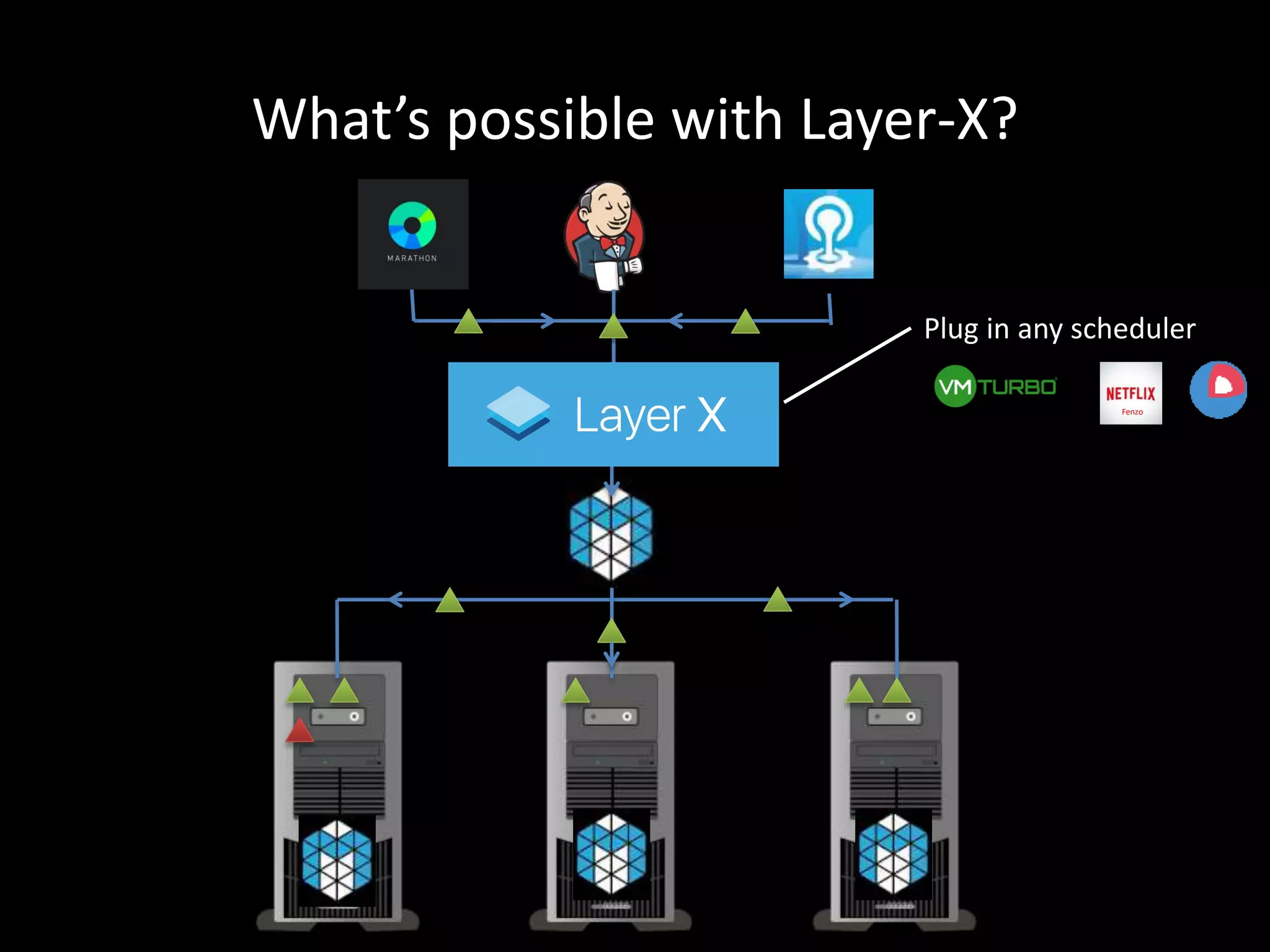
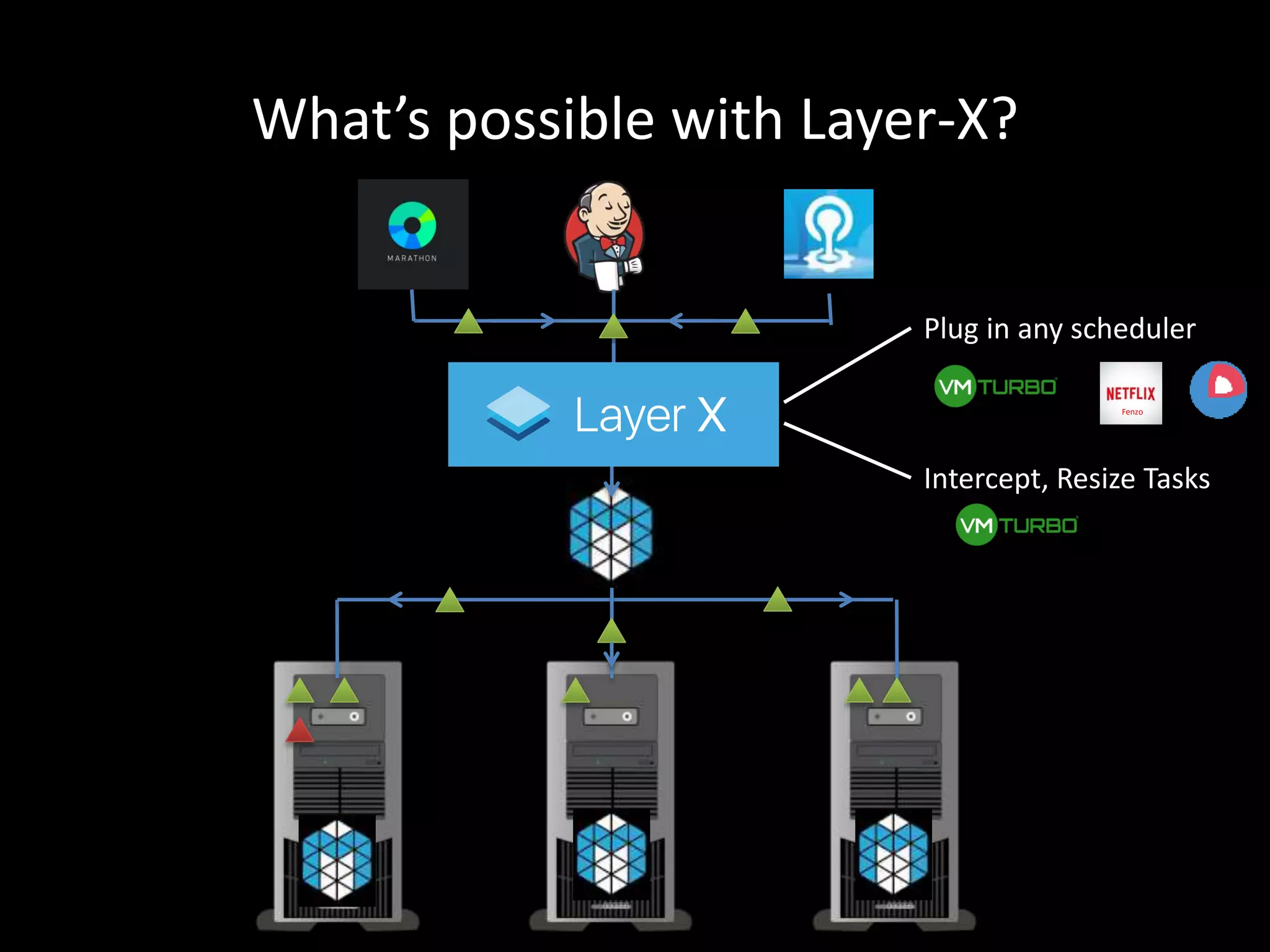
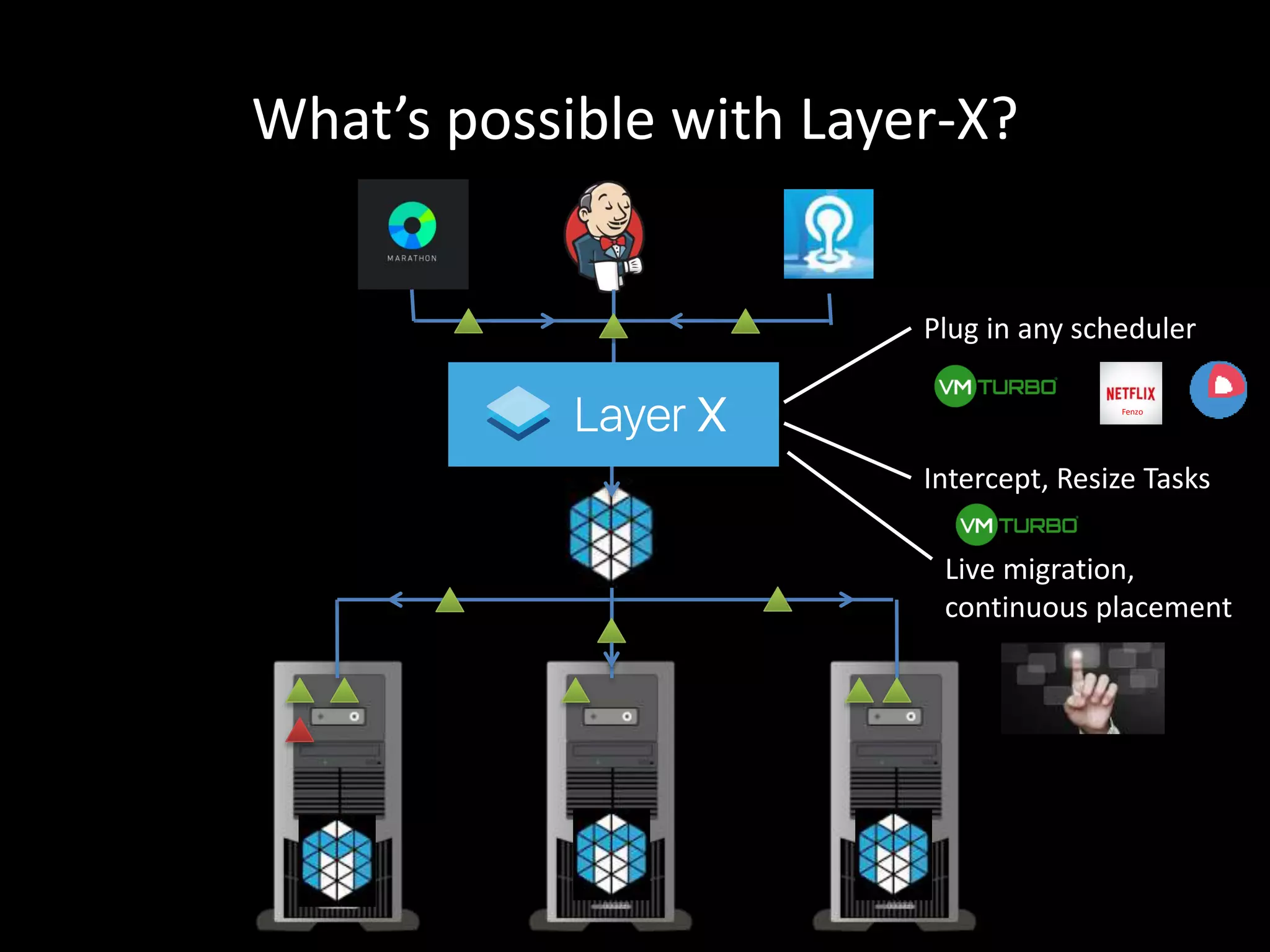
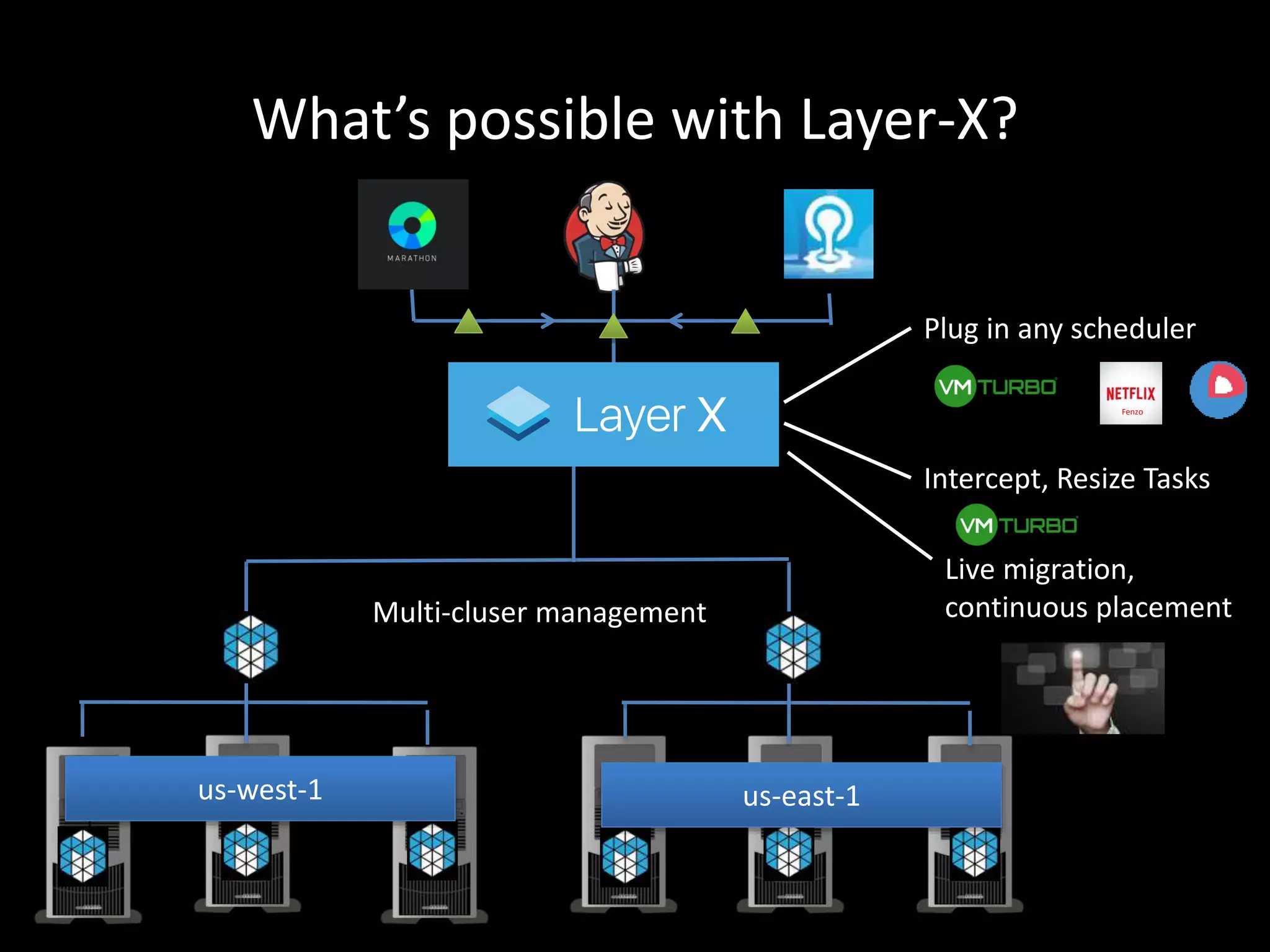
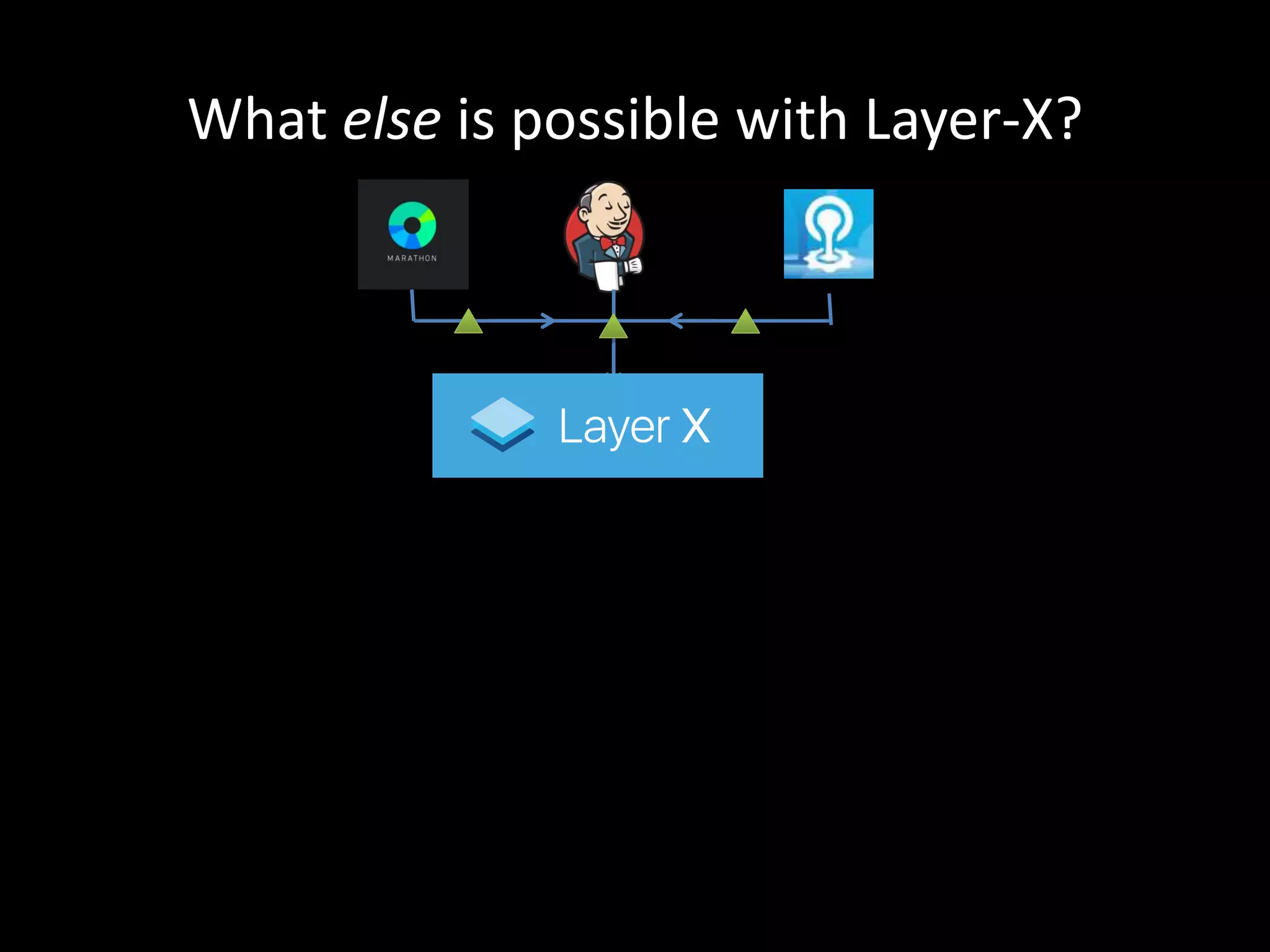
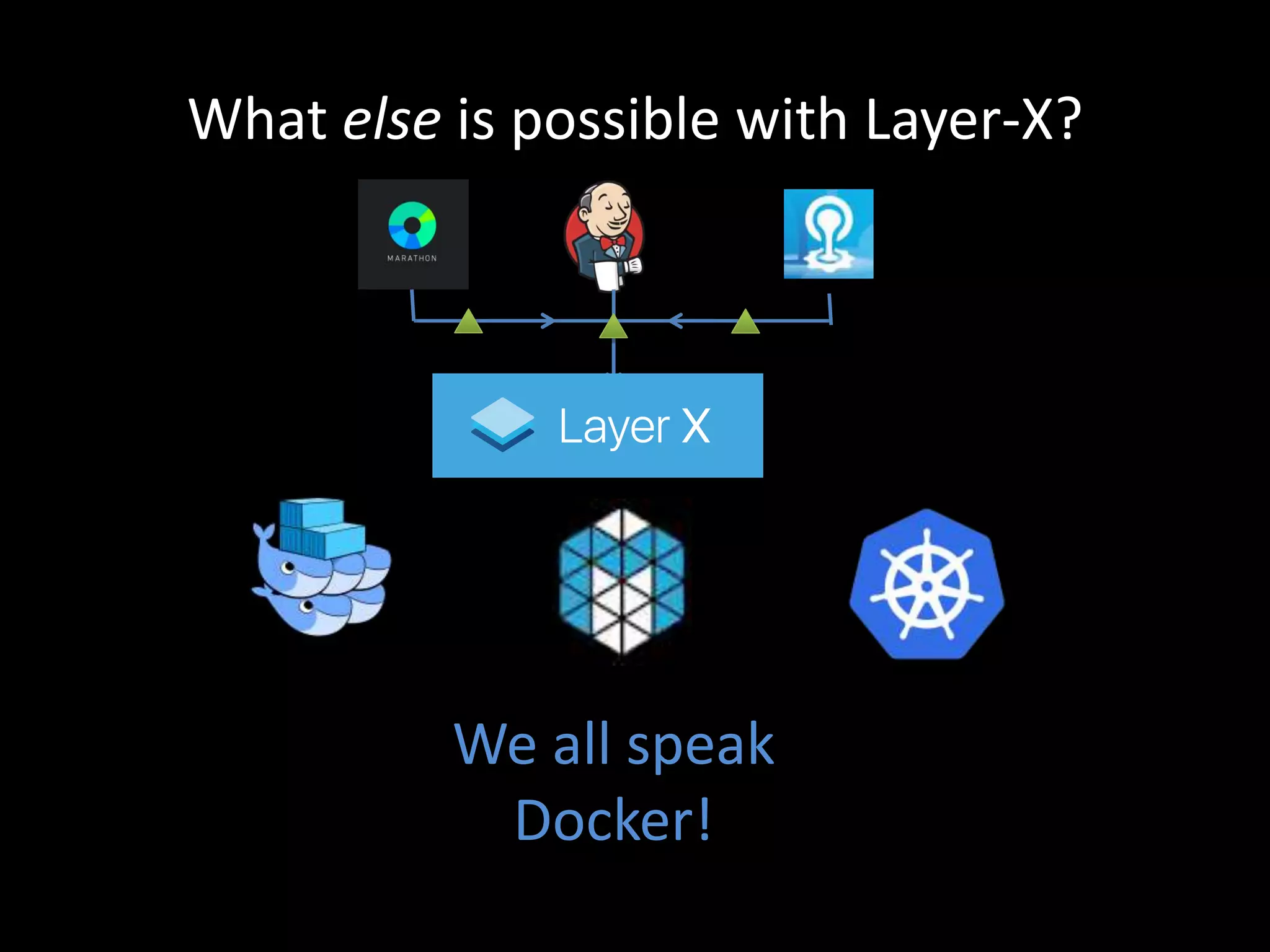
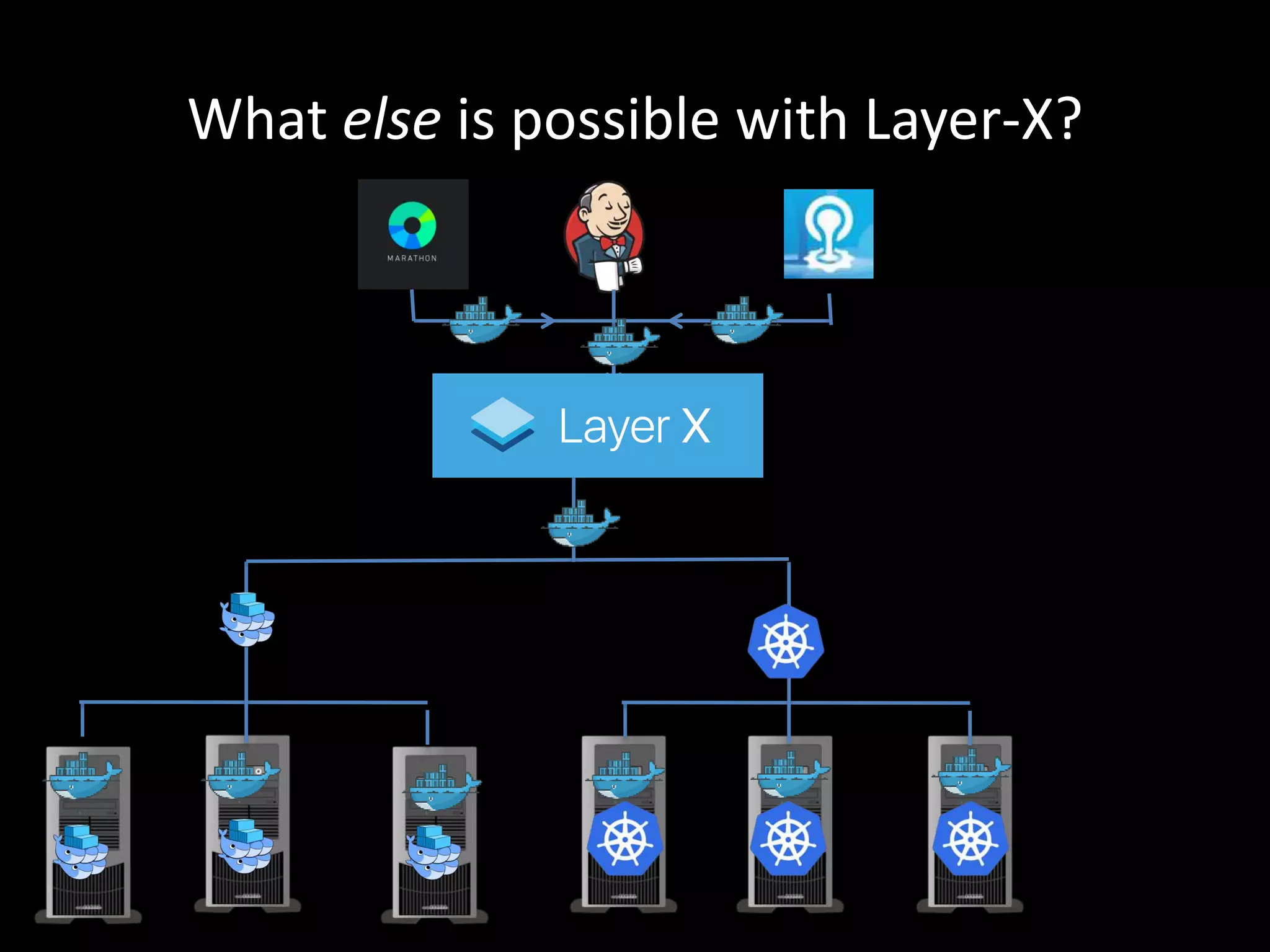
Centralized Scheduling made Simple describes Layer-X, a new open source project that adds centralized scheduling capabilities to Mesos. Layer-X acts as a proxy between Mesos and applications, collecting all task and resource information to give its scheduling component a global view of the cluster. This allows Layer-X to support advanced scheduling features like live task migration, multi-cluster management, and plugging in external schedulers like Fenzo that make decisions based on cluster-wide state. The document outlines how Layer-X works and interacts with Mesos and applications, and future plans to support more cluster managers and open source the project.