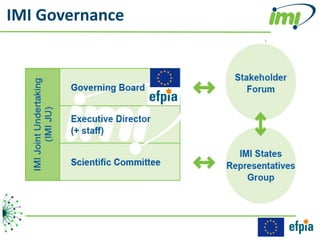
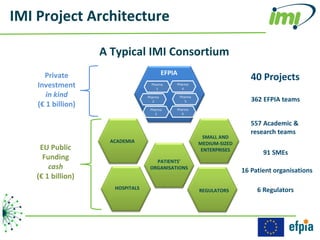
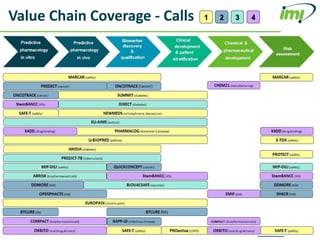
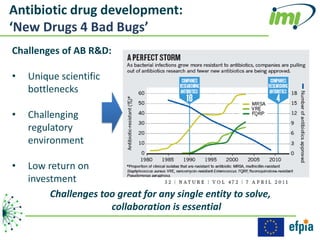
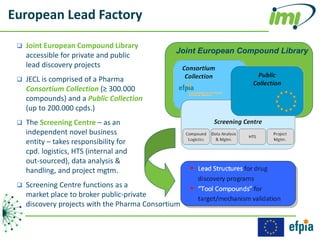
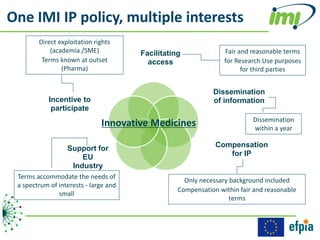
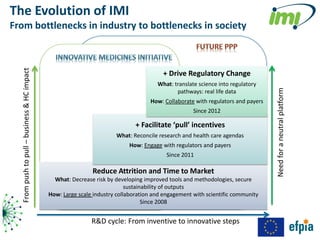
The document discusses the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI), which aims to enhance drug development through public-private partnerships (PPPs) in Europe. It highlights the challenges in reaching international agreements, funding obstacles, and the need for collaboration in addressing health care and societal issues. IMI fosters industry collaboration, engages various stakeholders, and promotes intellectual property agreements to improve innovation and reduce time to market.