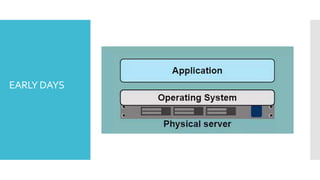
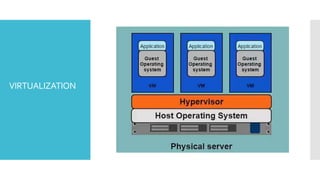
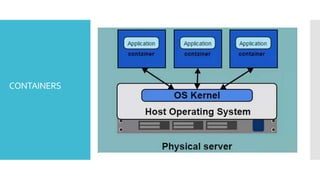
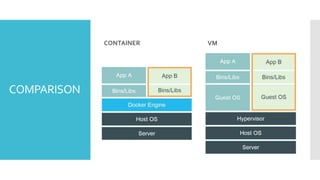
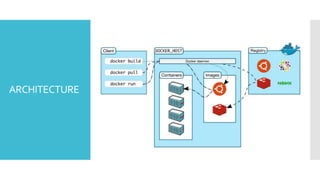
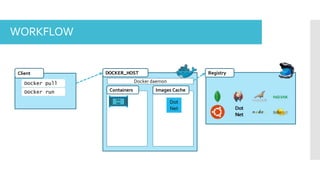
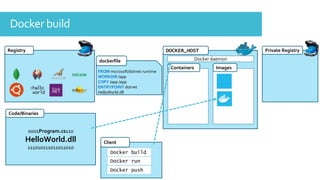
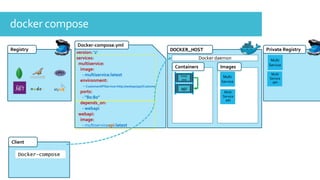
The document discusses Docker, an open-source platform for automating application deployment through lightweight containers. It covers key topics including the benefits and drawbacks of virtualization versus containers, Docker commands, best practices, and various use cases such as microservices and CI/CD. The presentation also briefly touches on Docker's functionalities in cloud environments.