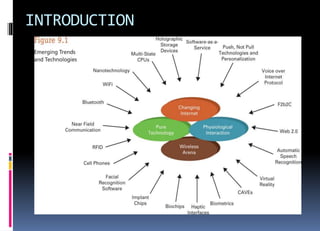
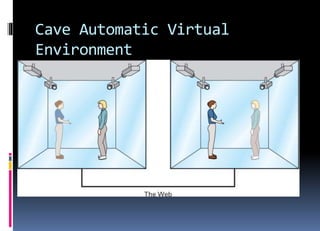
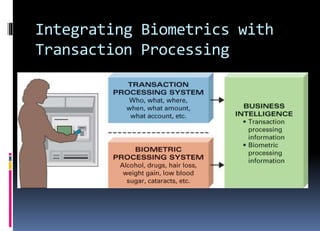
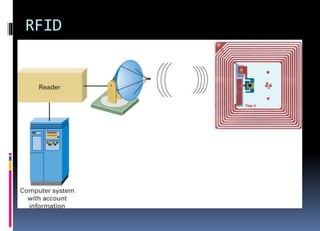
The document discusses emerging technologies and their impact on society. It describes how businesses will be able to push customized offerings to individuals using technologies like location-aware devices and robust personal profiles. New models like factory-to-business-to-consumer allow for highly personalized products. Physiological interfaces and biometrics will allow for more natural human-computer interaction through speech recognition, virtual reality environments, and sensors that integrate biological data with transactions. Radio frequency identification and other wireless technologies enable new applications but also raise privacy concerns. Overall, the text emphasizes the importance of using technology ethically for the benefit of society and closing the digital divide.