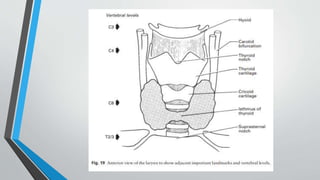
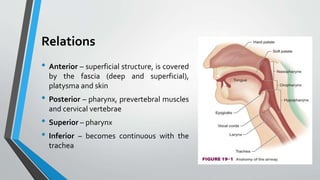
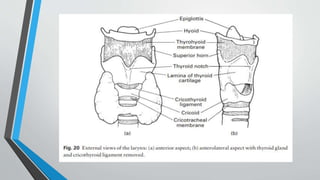
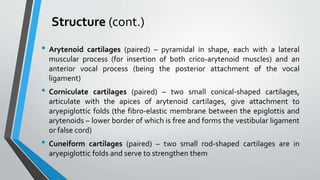
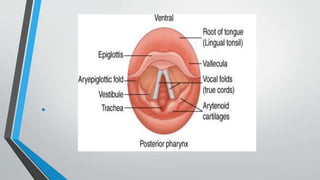
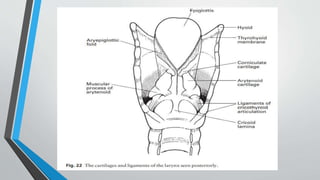
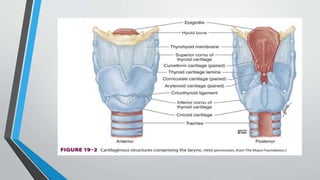
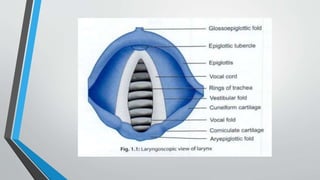
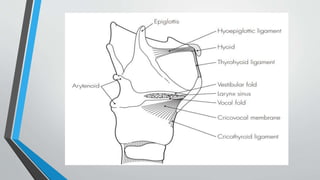
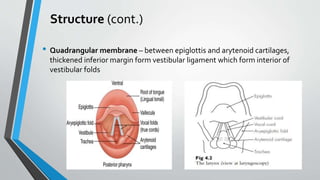
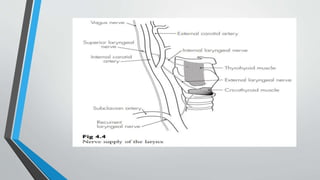
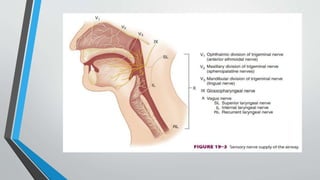
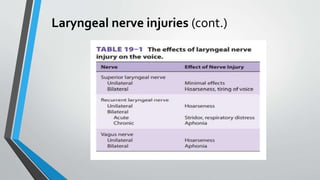
The larynx is a voice-producing organ located between the root of the tongue and the trachea, comprising various muscles, cartilages, and ligaments. It features nine cartilages, including the epiglottis, thyroid, and cricoid cartilages, alongside numerous intrinsic and extrinsic muscles that enable voice modulation and airway control. The larynx's blood supply comes from thyroid arteries, while nerve supply is primarily through branches of the vagus nerve, and injuries can lead to voice quality deterioration or airway problems.