Embed presentation

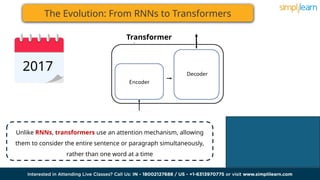
![The Evolution: From RNNs to Transformers
As she said this, she looked down at her hands...
['As', 'she', 'said', 'this', ',', 'she', 'looked', 'down', 'at', 'her', 'hands',
'...']
Encoding
Tokenization
Embeddings
Context Vector
Autoregressive
Generation
Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/largelanguagemodel-240809082244-29b76dac/85/Large-Language-Models-How-Large-Language-Models-Work-Introduction-to-LLM-Simplilearn-3-320.jpg)
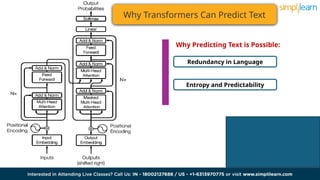
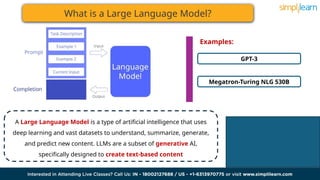


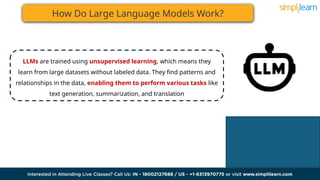


The document discusses the evolution of artificial intelligence from recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to transformers, highlighting the advantages of transformers like their attention mechanism. It explains large language models (LLMs), which leverage deep learning to generate and understand text, and outlines their training methods and various applications. Additionally, it addresses the benefits and challenges associated with LLMs, such as operational costs and ethical concerns.


![The Evolution: From RNNs to Transformers
As she said this, she looked down at her hands...
['As', 'she', 'said', 'this', ',', 'she', 'looked', 'down', 'at', 'her', 'hands',
'...']
Encoding
Tokenization
Embeddings
Context Vector
Autoregressive
Generation
Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/largelanguagemodel-240809082244-29b76dac/85/Large-Language-Models-How-Large-Language-Models-Work-Introduction-to-LLM-Simplilearn-3-320.jpg)








