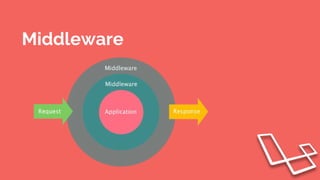
This document provides an overview of the Laravel framework, including:
- A brief history of Laravel and its origins from Ruby on Rails
- Instructions for installing Laravel and understanding its directory structure
- Explanations of core Laravel features like routing, Blade templating, Eloquent ORM, validation, and the service container
- Additional resources are provided for further exploring topics like middleware, collections, and customizing Laravel's functionality.










![Routing
- Named Routes
Route::get(‘/posts’ , [
‘uses’ => ‘PostsController@index’,
‘as’ => ‘posts.index’
]);
more at https://laravel.com/docs/5.4/routing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravelintake37alldays-170519123242/85/Laravel-intake-37-all-days-12-320.jpg)


![Blade
- printing sections :- @yield(‘content’)
- including :- @include(‘scripts’)
- Including with parameters :-
@include(‘post.form’,[‘method’ => ‘POST’])
more at https://laravel.com/docs/master/blade#introduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravelintake37alldays-170519123242/85/Laravel-intake-37-all-days-15-320.jpg)


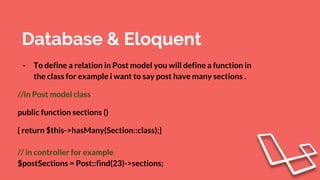
![Database & Eloquent
- DB::table(‘posts’)->insert(
[‘title’ => ‘first post title’ , ‘desc’ => ‘first post desc ‘]
); //inserting a row
- DB::table('posts')->where(‘id’ , 1)->delete(); //deletes a row
- DB::table(‘posts’)->where(‘id’ , 1)
->update( [ ‘title’ => ‘changed title post ] );
//update the post title only](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravelintake37alldays-170519123242/85/Laravel-intake-37-all-days-18-320.jpg)




![Request Validation
- In Controller :-
$this->validate( $request , [
‘title ‘ => ‘required ‘,
‘desc’ => ‘required|max:255’
] ,
[
‘title.required’ => ‘title is required to be filled ‘ ,
‘desc.max’ => ‘description max num of chars is 255 ‘
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravelintake37alldays-170519123242/85/Laravel-intake-37-all-days-24-320.jpg)