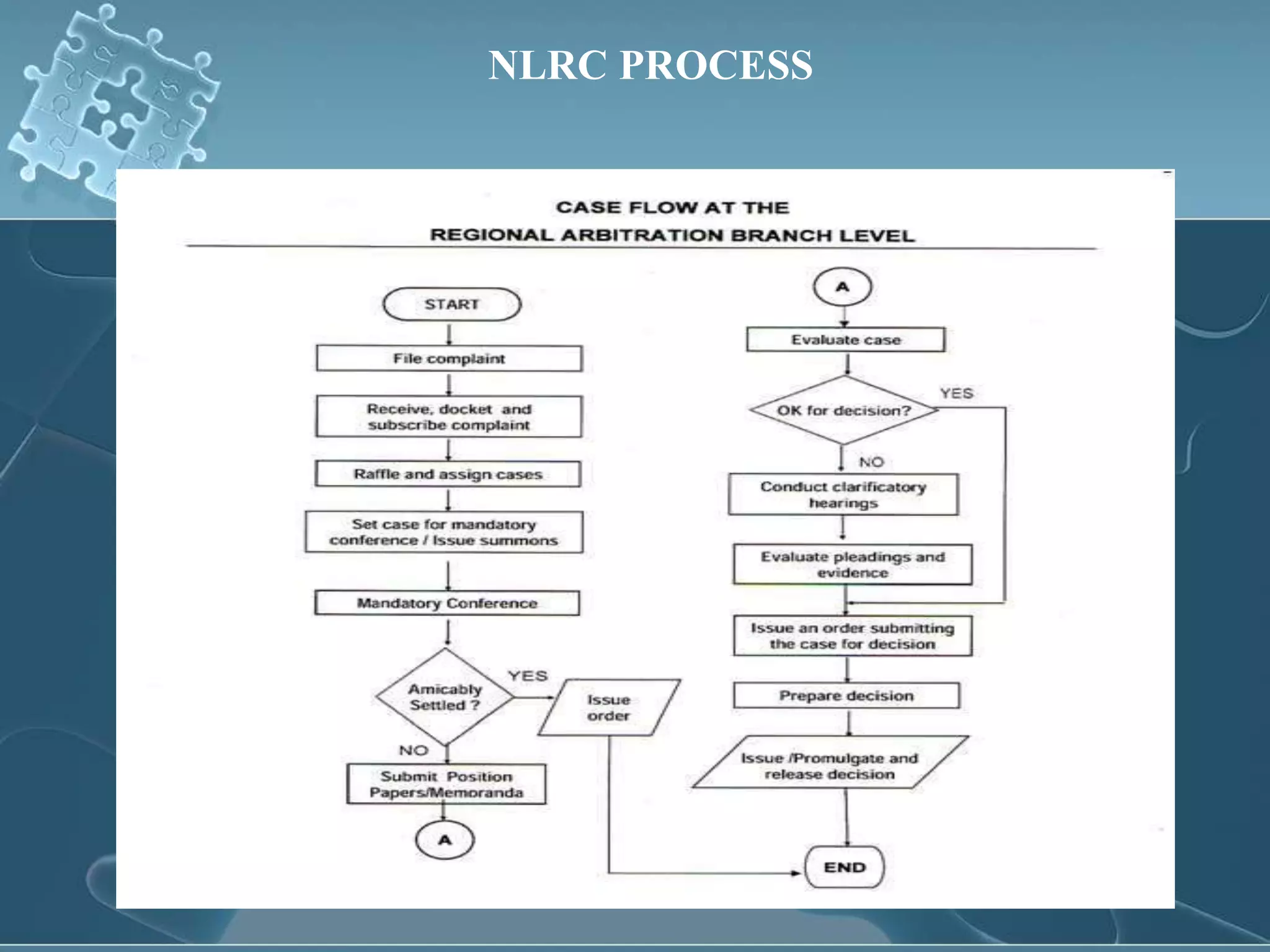
This document provides an overview of labor-management relations in the Philippines. It defines labor relations and discusses the governing rules and principles, including labor standards law and the Labor Code. It then describes labor relations as a personnel management function, involving administering collective bargaining contracts and solving day-to-day labor issues. The document also examines sources of labor problems like dissatisfaction, the human needs related to work, and annoyances in labor relations from the perspectives of both workers and employers. Finally, it discusses labor unions and their role in representing workers, as well as types of unions, union security, and the International Labor Organization.