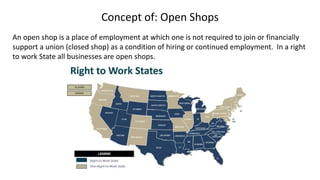
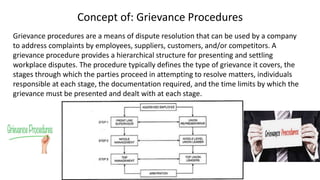
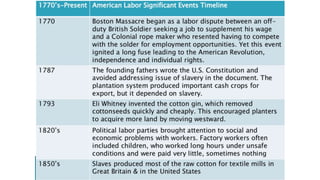
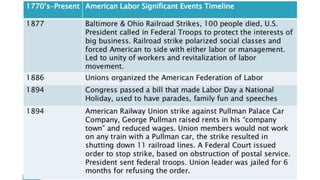
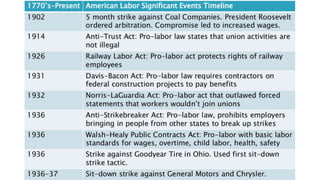
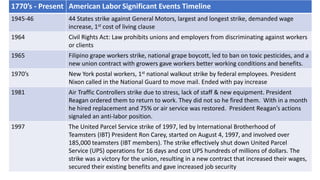
This document discusses the U.S. Department of Labor and provides background information on concerns of American workers. It lists eight common concerns of American workers, including maintaining a standard of living with rising costs, workplace safety, job security, advancement opportunities, discrimination, communication issues, human resources policies, and benefits beyond pay like healthcare and retirement. The document requires the reader to contact a local labor union to learn about the issues most important to them and how the organization is structured. It also defines key concepts related to labor unions like collective bargaining, negotiation, union and open shops, grievance procedures, and strikes.