This document provides information on identifying and distinguishing between different Staphylococcus species through various tests and growth characteristics. Key points include:
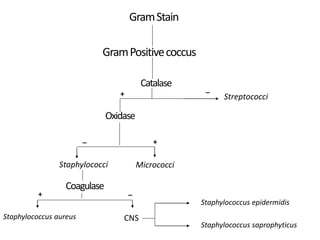
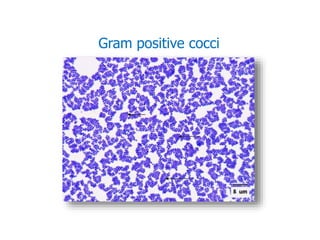
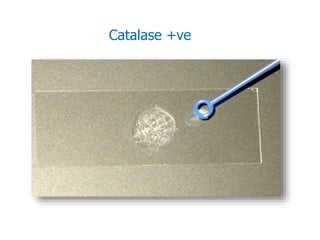
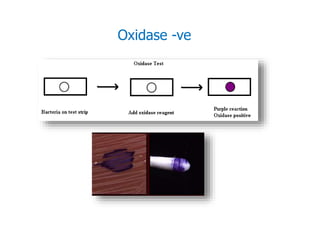
- Staphylococci are gram-positive cocci that are catalase positive and oxidase negative.
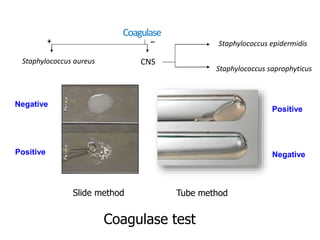
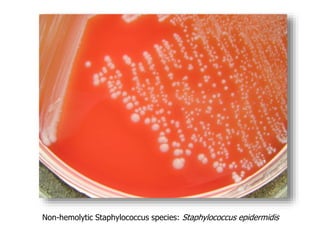
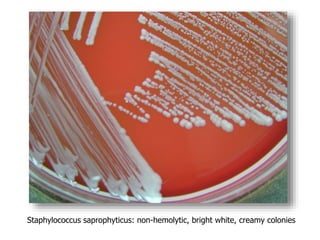
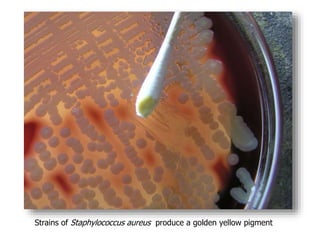
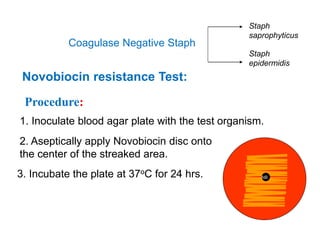
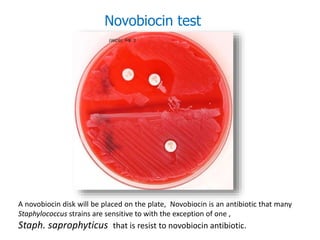
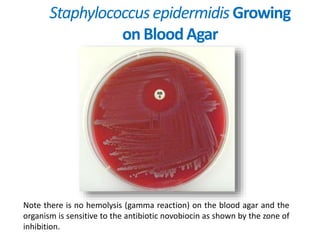
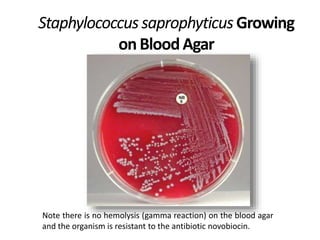
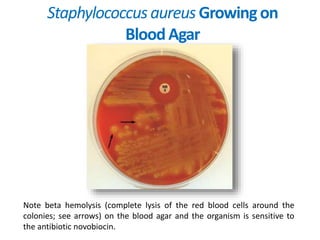
- Coagulase testing and novobiocin resistance testing can differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci like S. epidermidis.
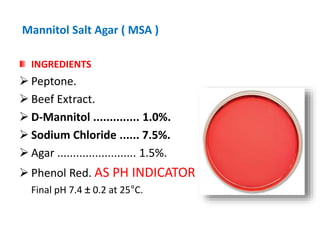
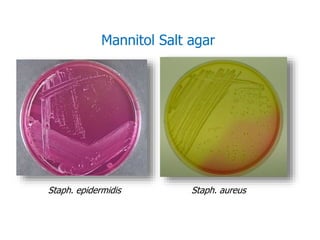
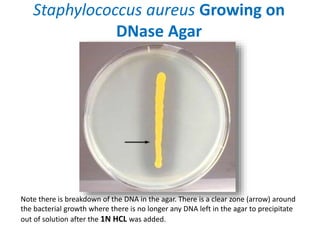
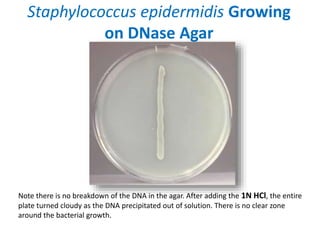
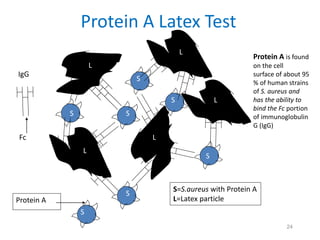
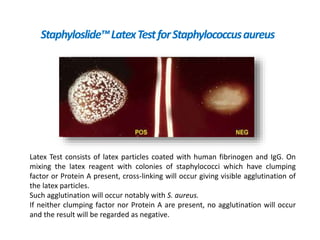
- Mannitol fermentation on Mannitol Salt Agar and DNase testing can further distinguish between staphylococcal species. Protein A testing specifically identifies S. aureus.