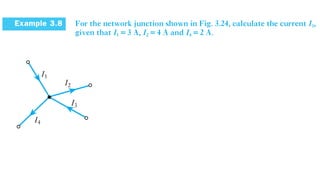
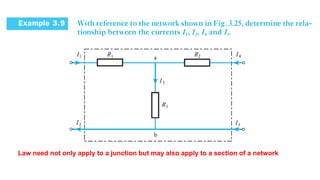
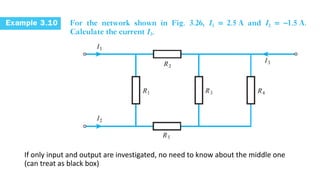
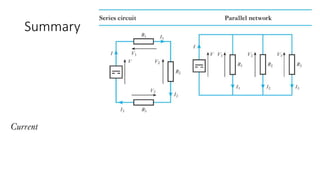
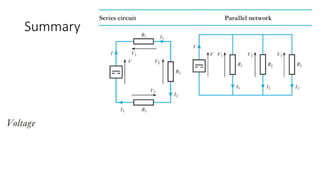
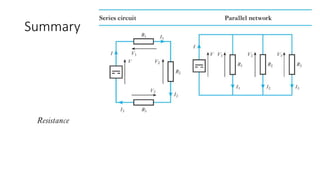
The document discusses current divider rule and Kirchhoff's laws. It provides an overview of the syllabus which includes topics like resistors, capacitors, inductors, semiconductor devices, transformers, motors and more. Kirchhoff's current law states that the algebraic sum of currents at any junction in an electrical network equals zero. The total resistance in a series circuit is greater than its largest resistance, while the total resistance in a parallel circuit is less than its smallest resistance.





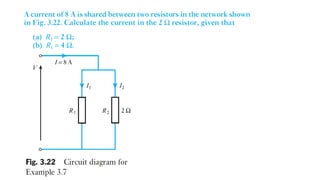




![Kirchhoff’s law
• First (current) law. At any instant the algebraic sum of
the currents at a junction in a network is zero.
Gustav Kirchhoff
[Source: Wikipedia]
Electric circuits,
Optics,
Spectroscopy,
Thermochemistry
etc..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l6currentdividerkcl-230129090159-8558836d/85/L6_Current-Divider_KCL-pptx-16-320.jpg)