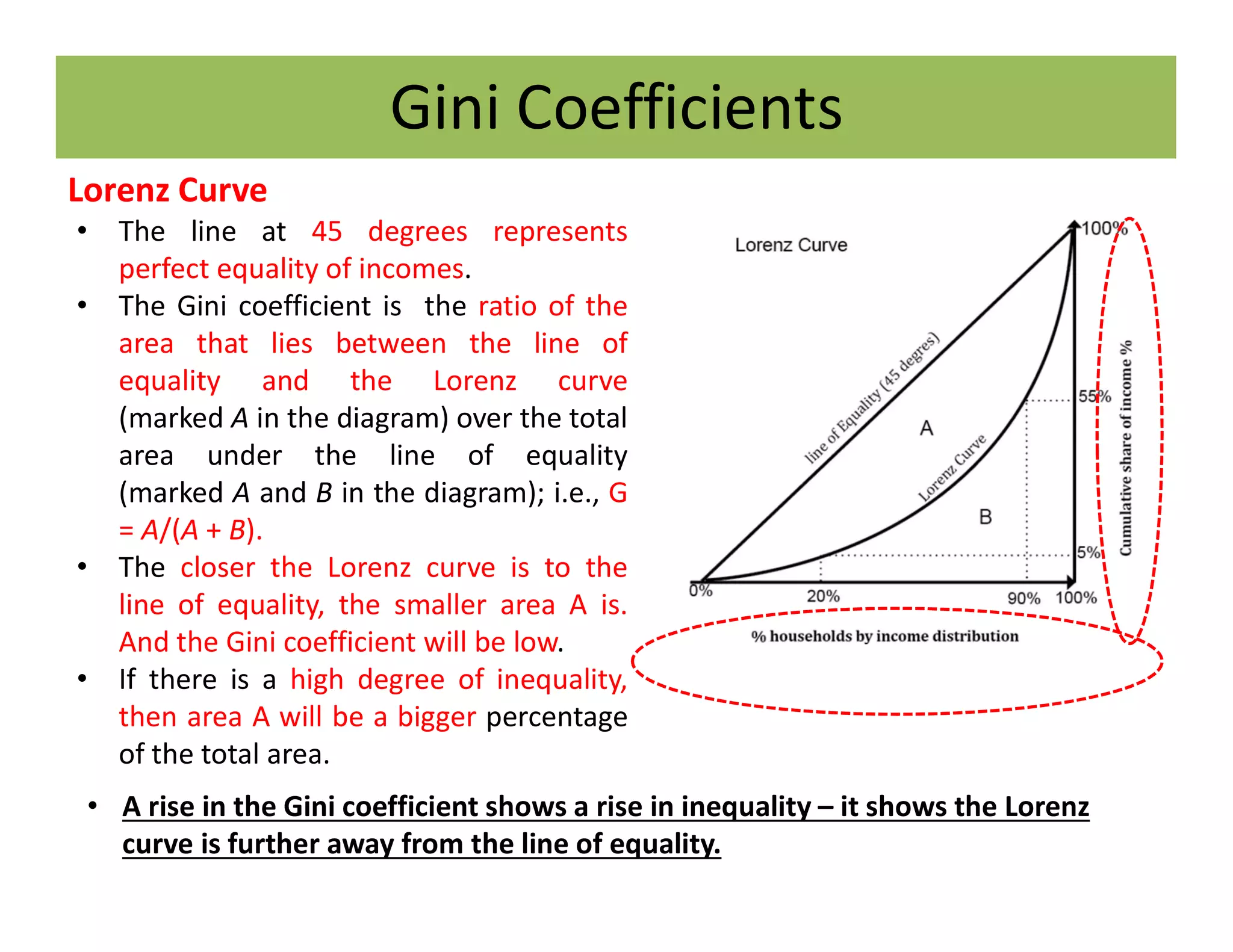
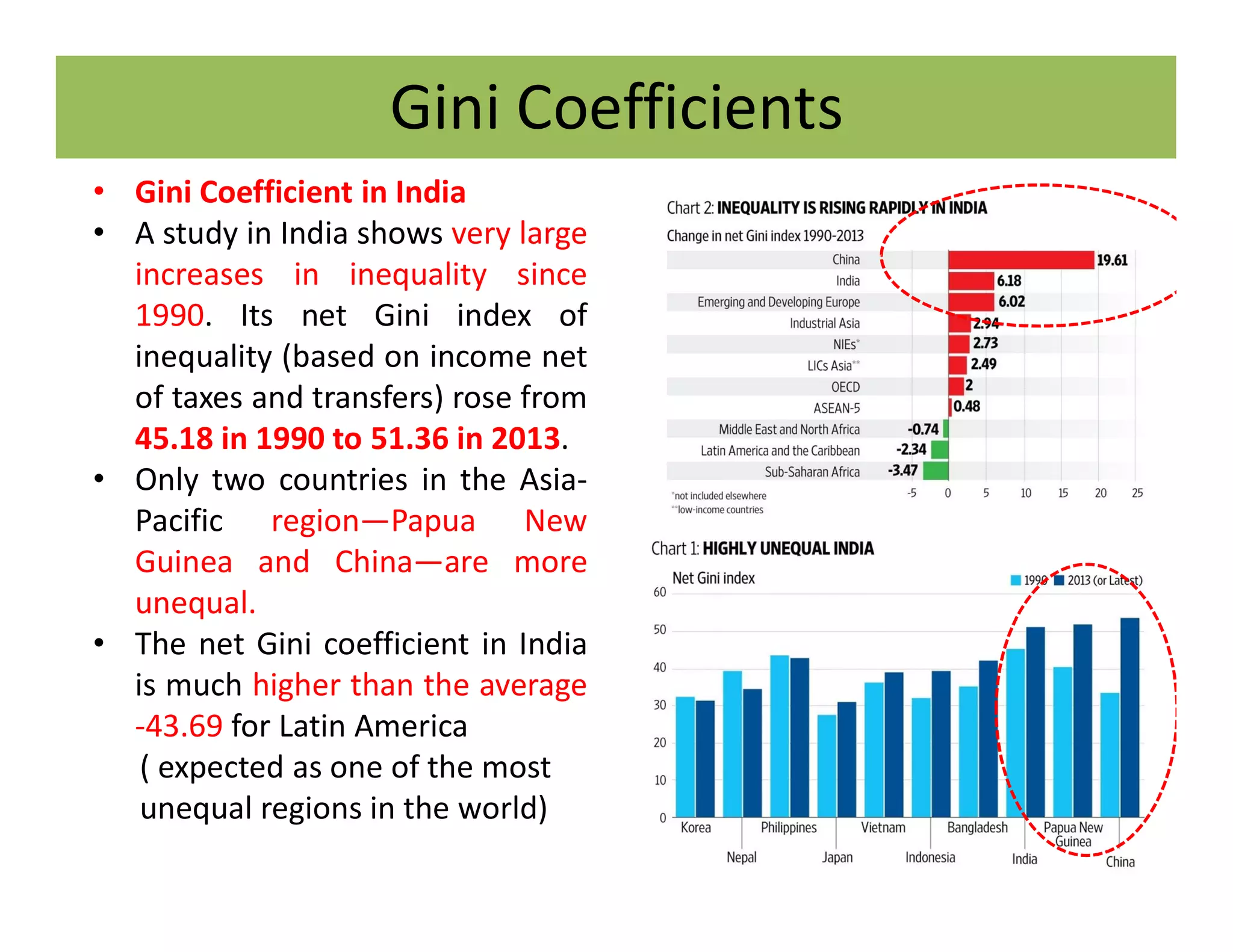
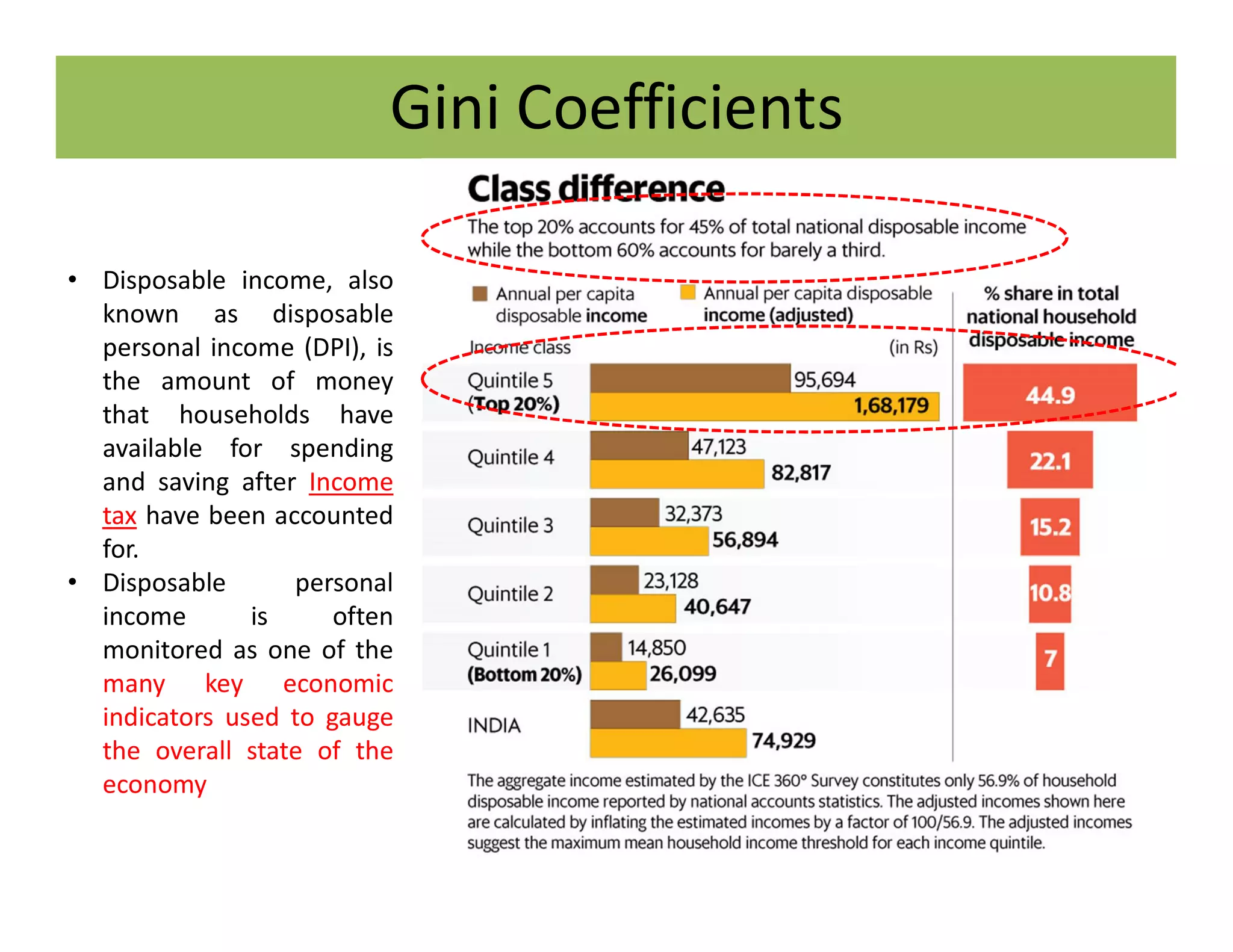
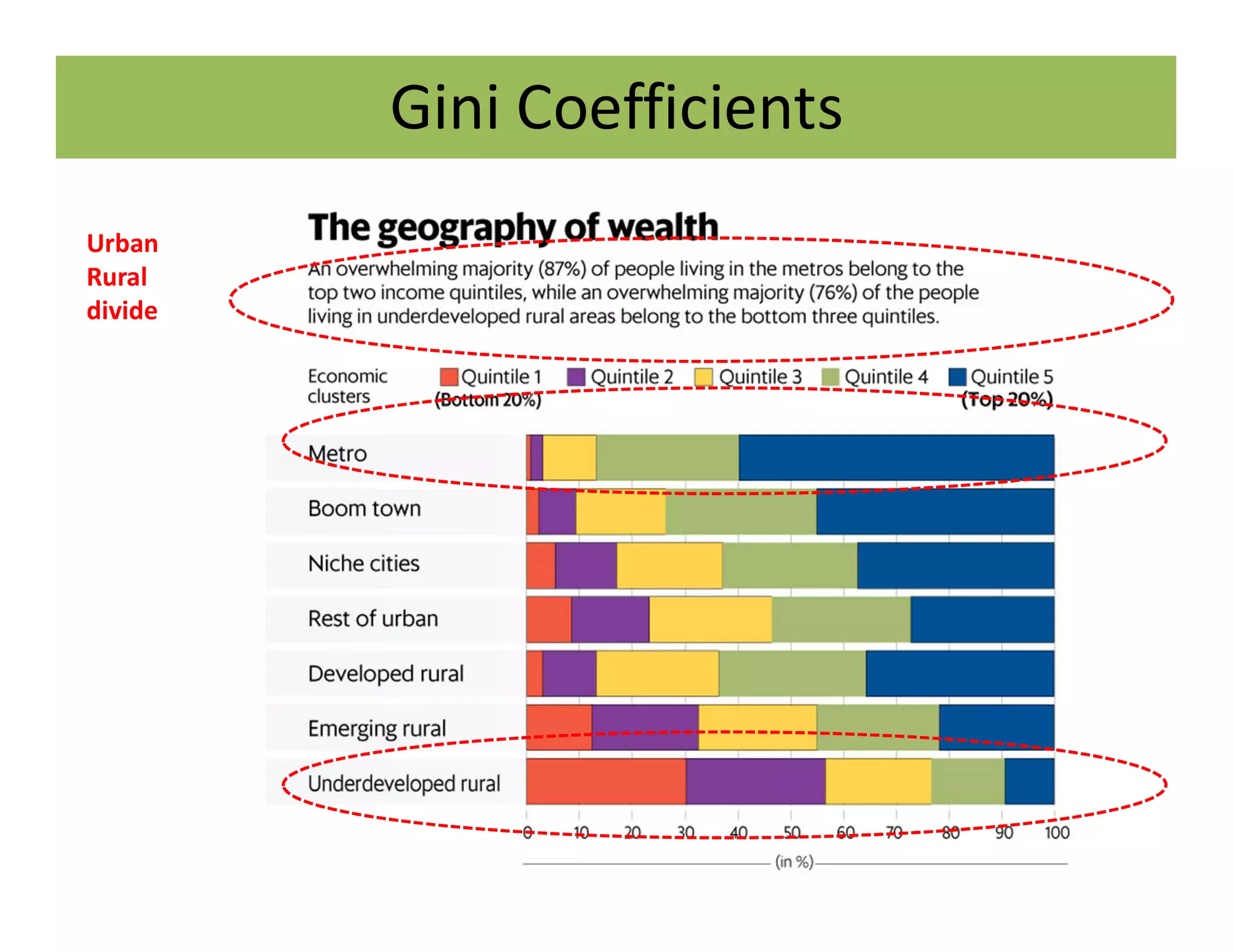
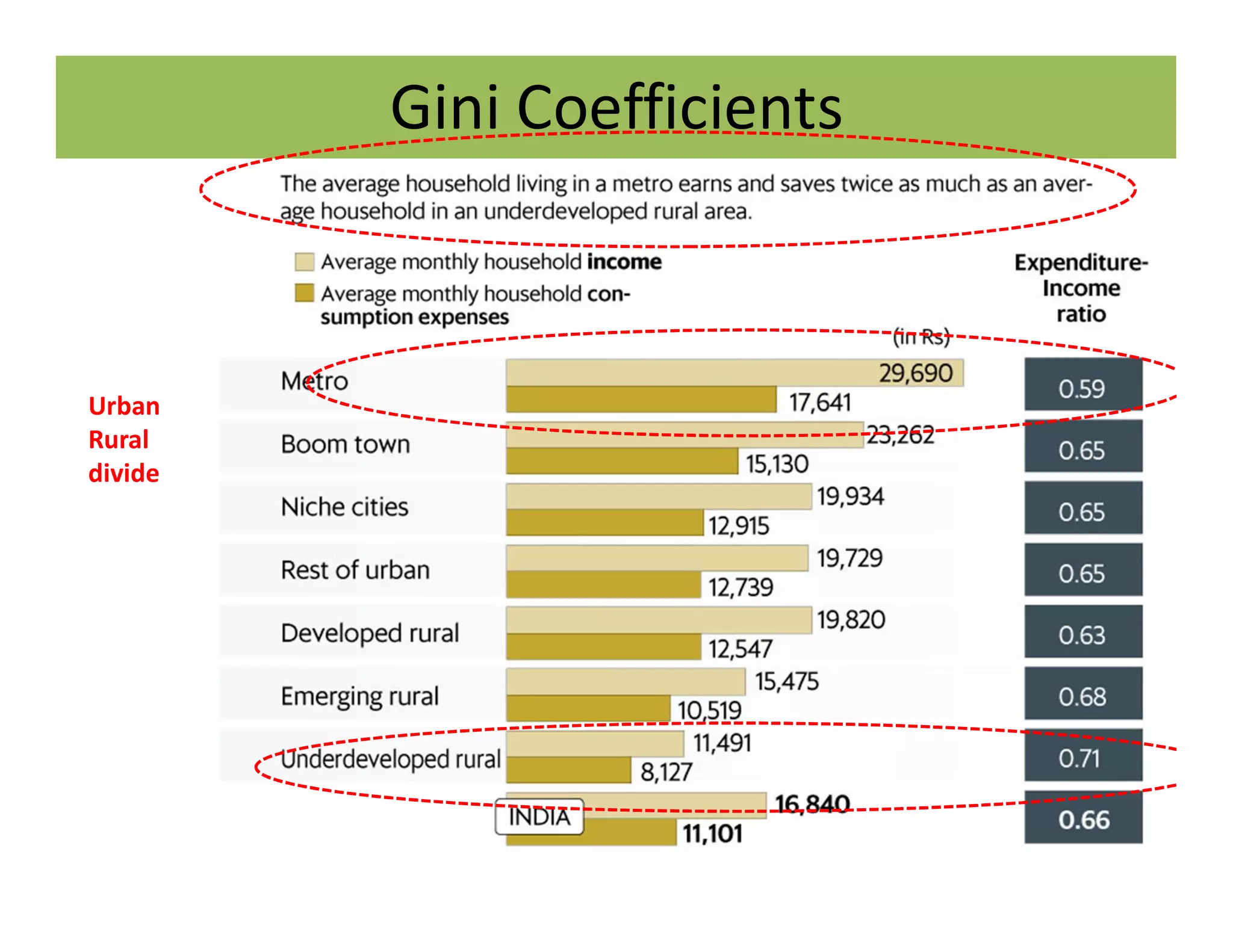
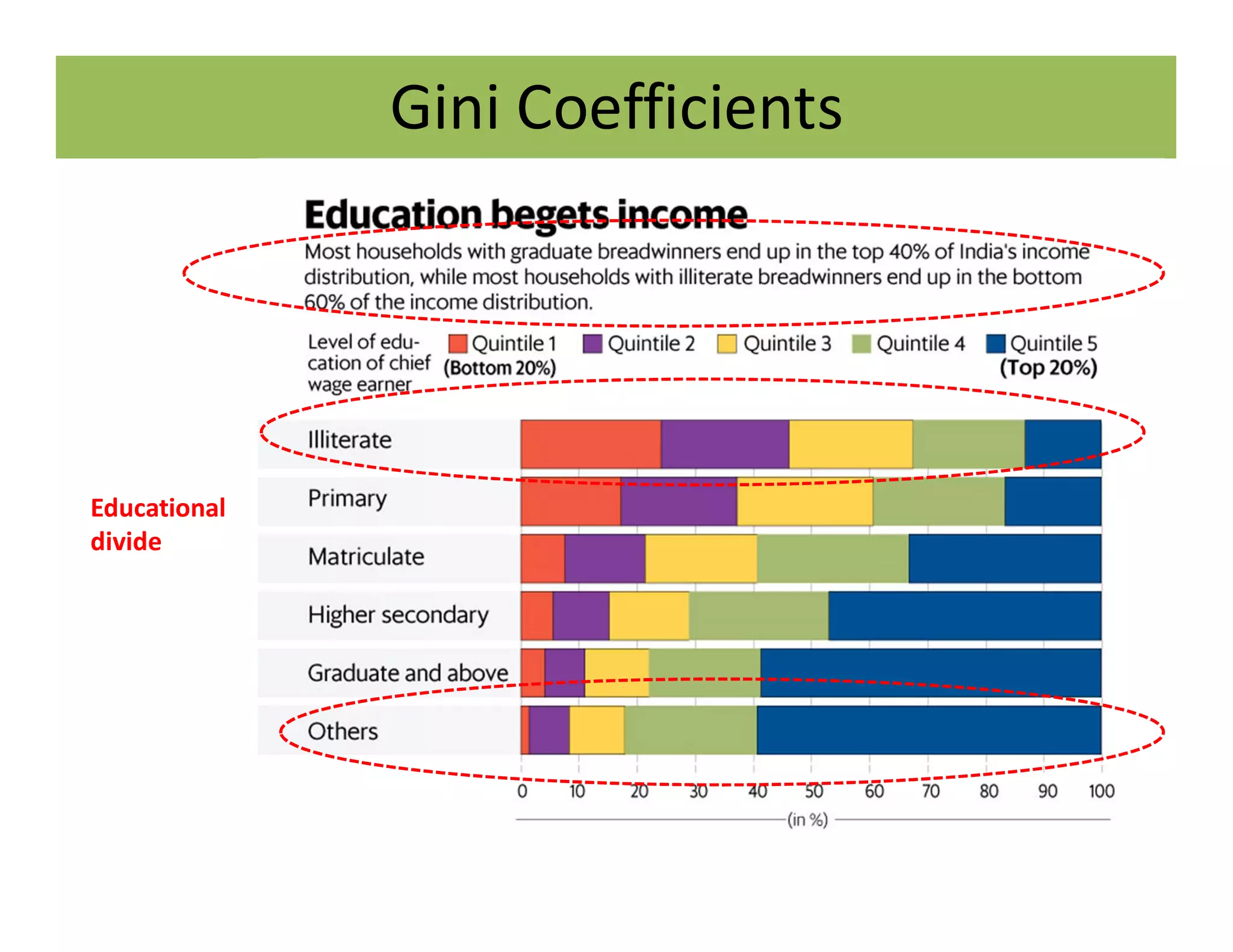
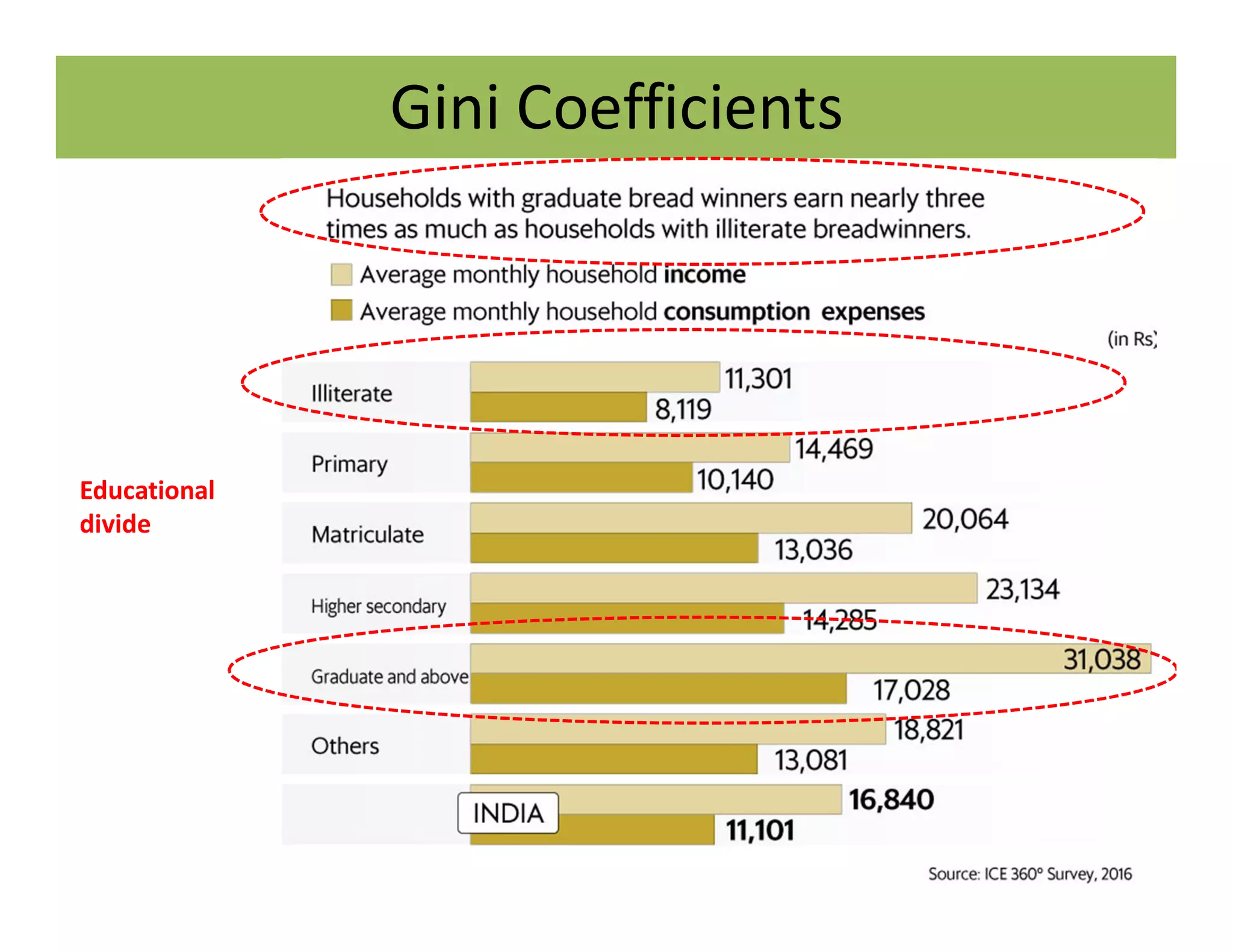
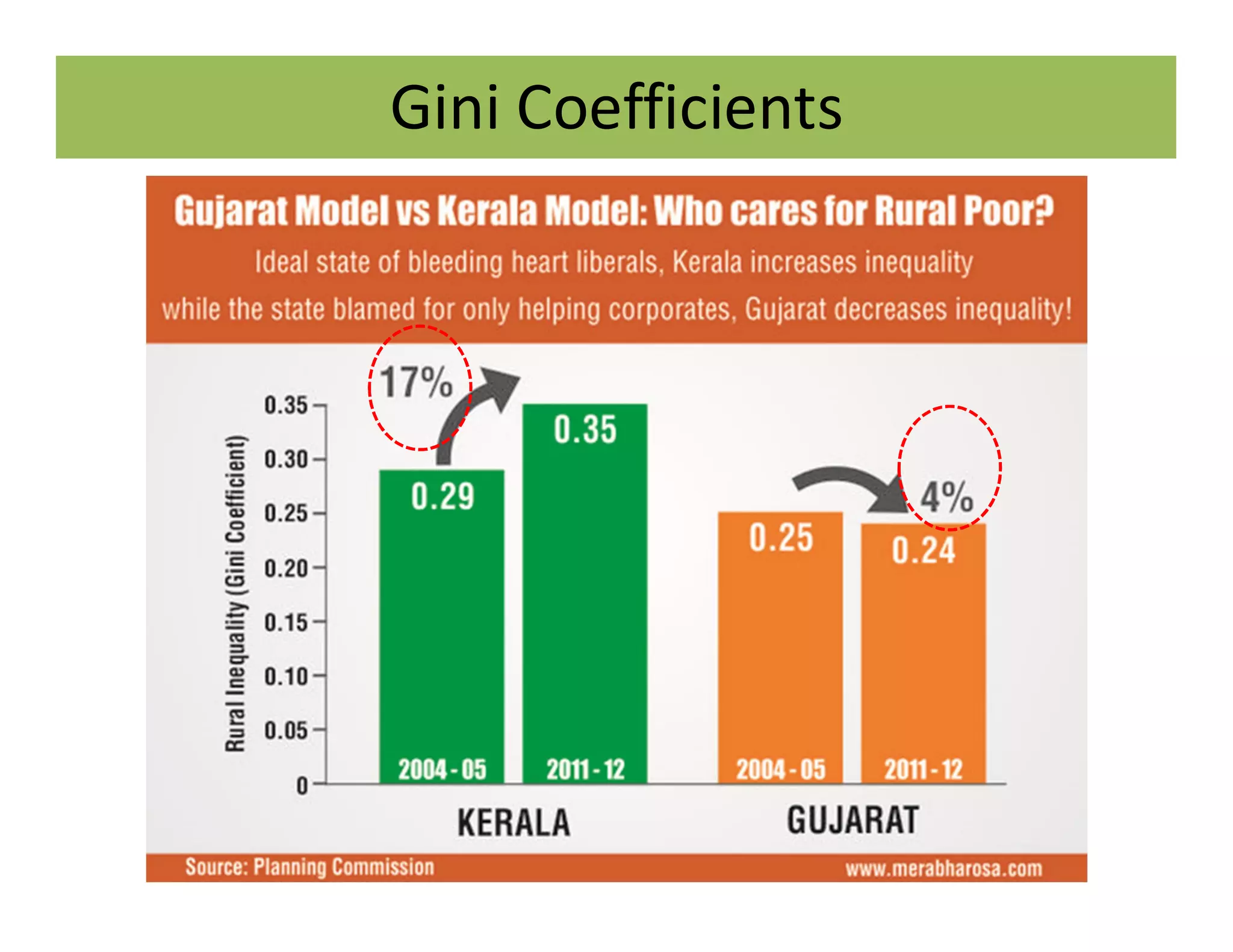
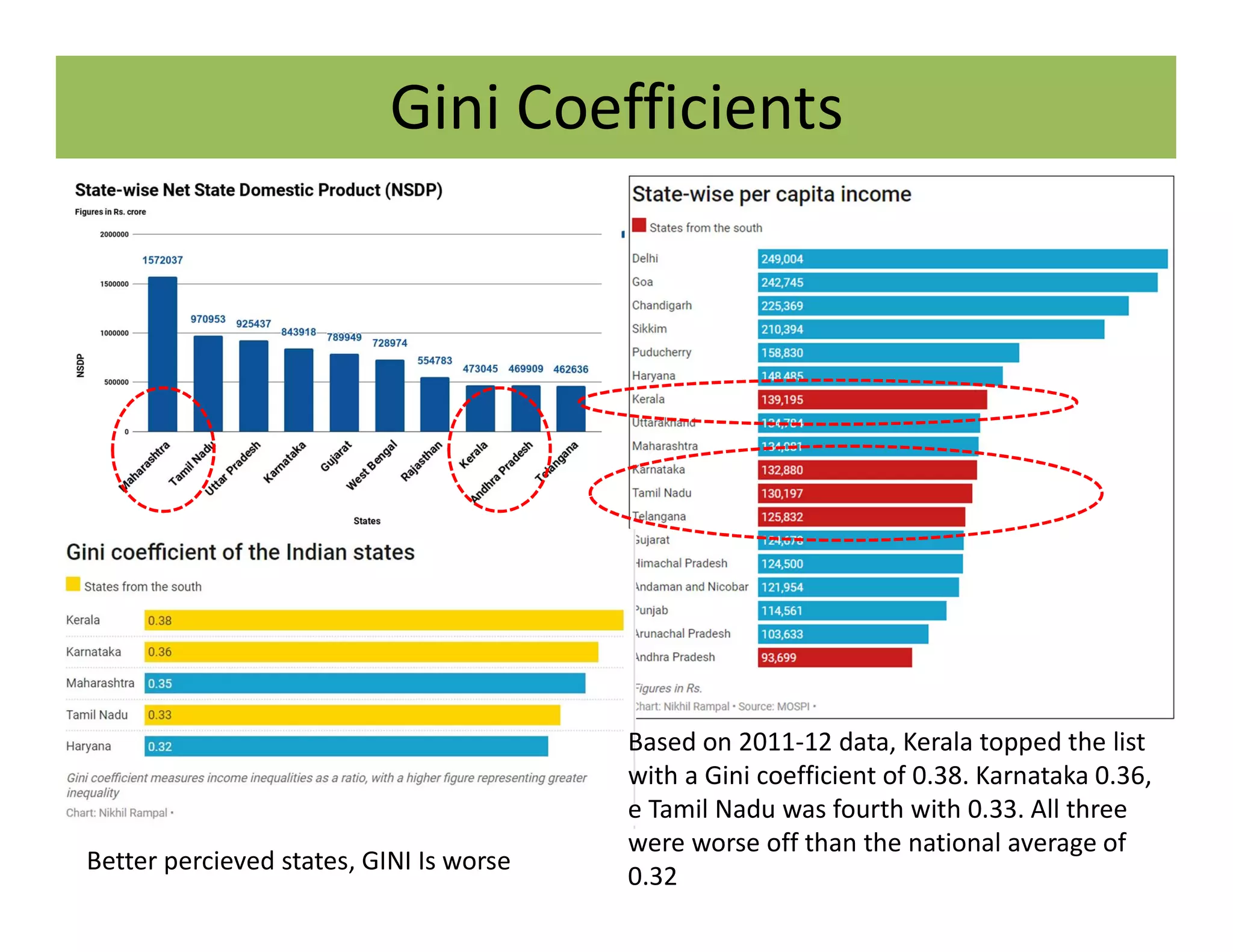
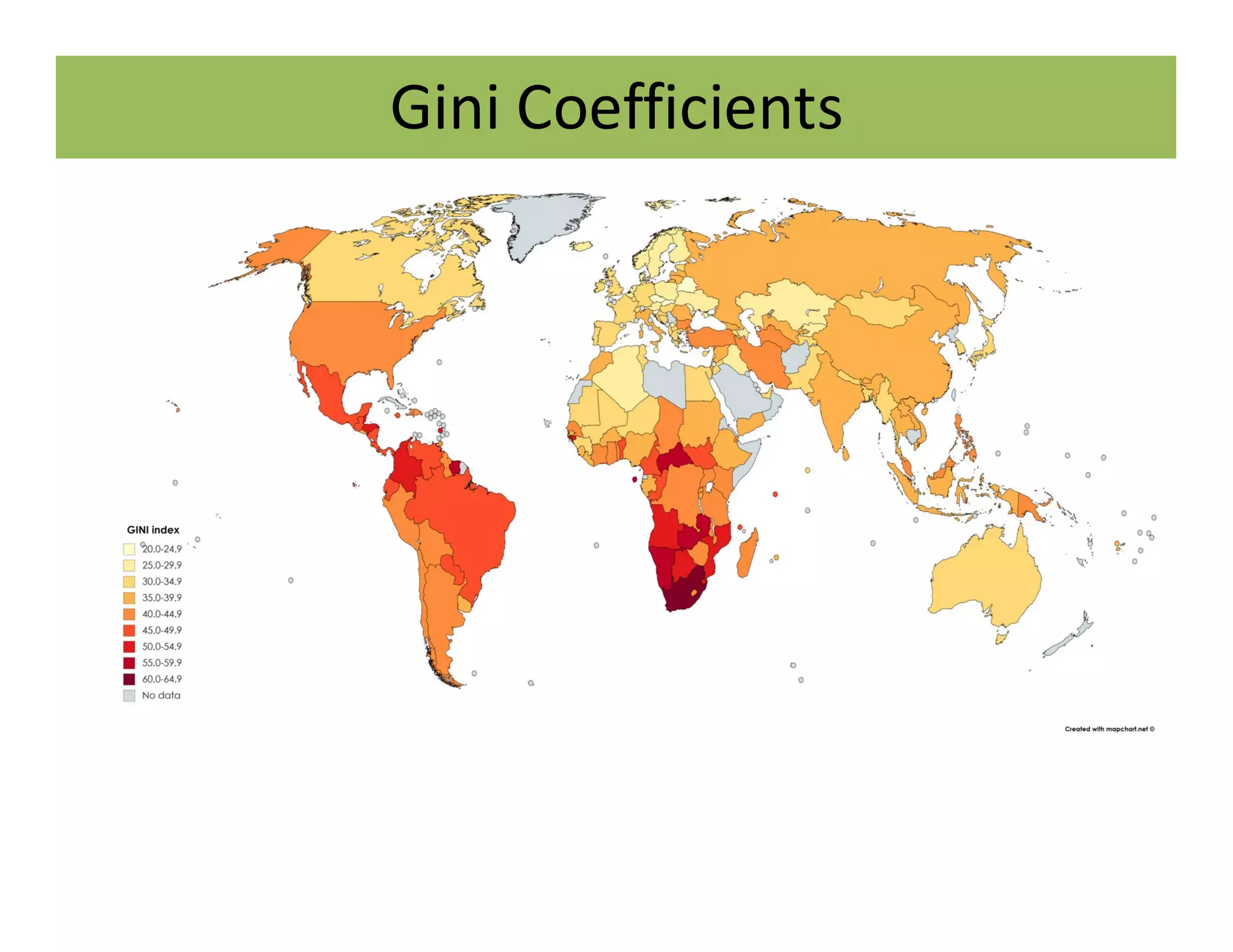
The document discusses the Gini coefficient, a measure of statistical dispersion used to represent income inequality. It defines the Gini coefficient and how it is calculated based on the Lorenz curve. A Gini coefficient of zero represents perfect equality while one represents maximum inequality. The document provides examples of Gini coefficient calculations for different countries and regions in India. It analyzes India's rising Gini coefficient and the high levels of inequality in the country with the top 10% owning over 75% of the wealth. Causes of inequality like urban-rural and education divides are examined. States with traditionally high development like Kerala are found to have Gini coefficients worse than the national average.