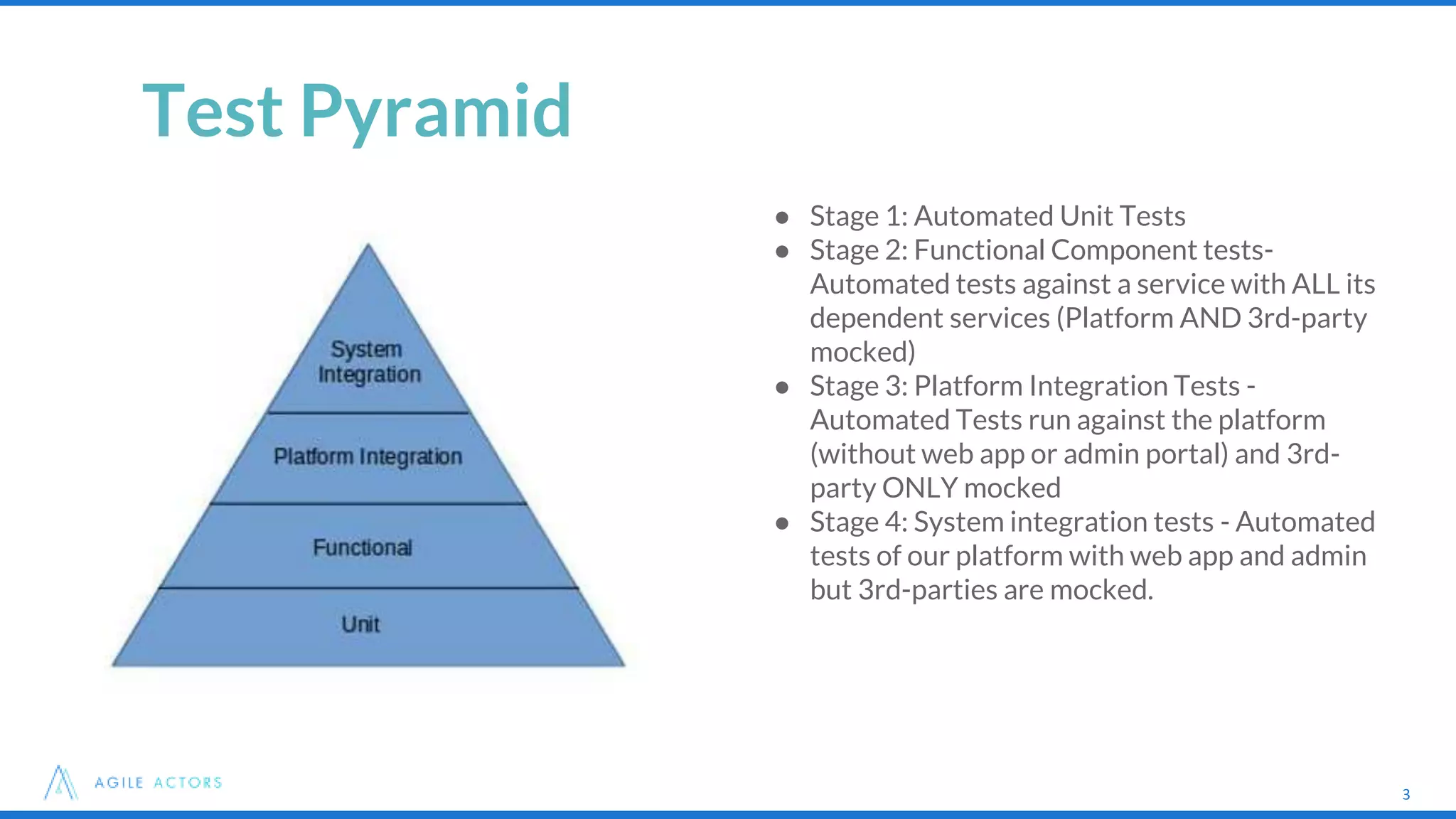
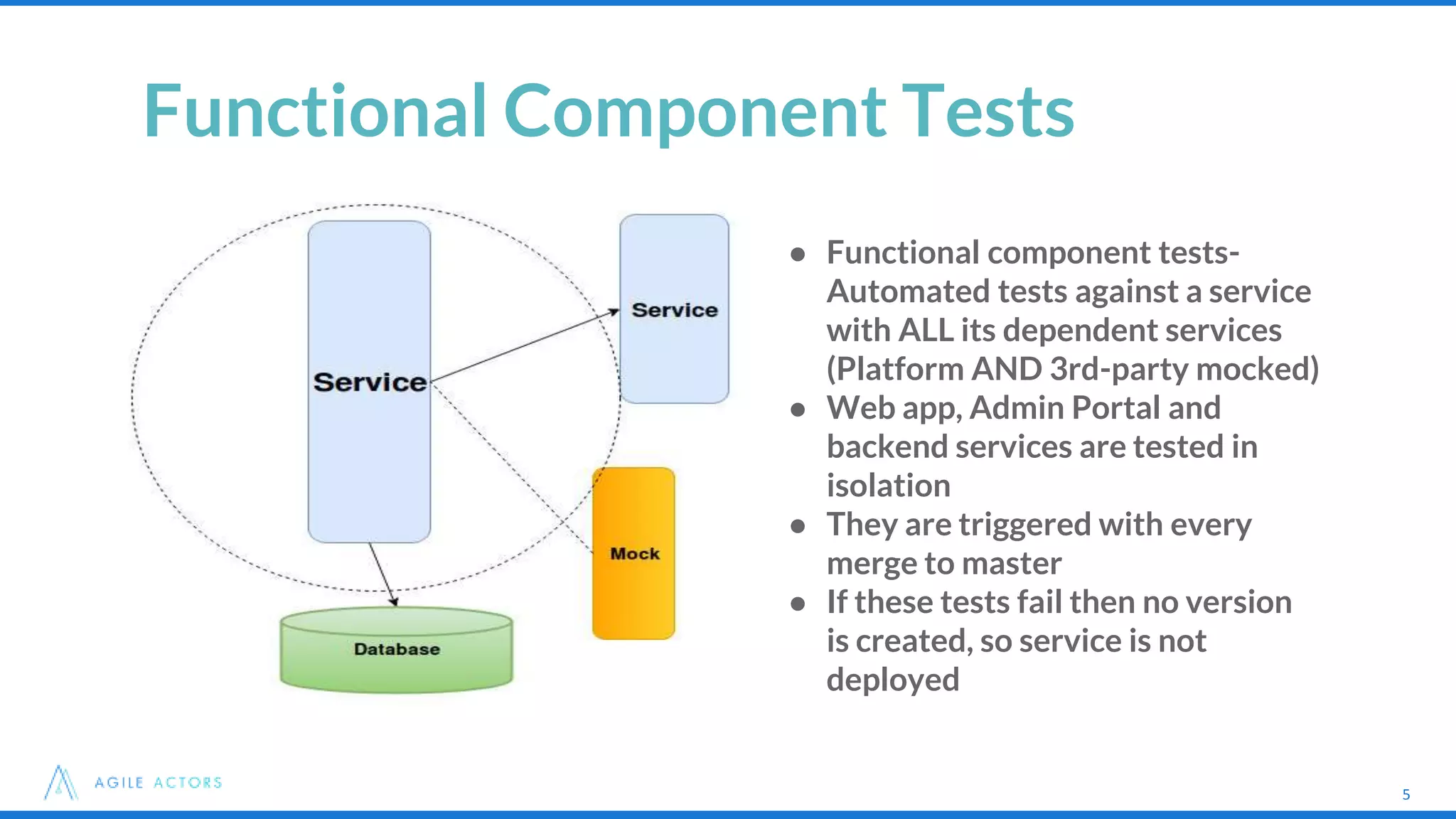
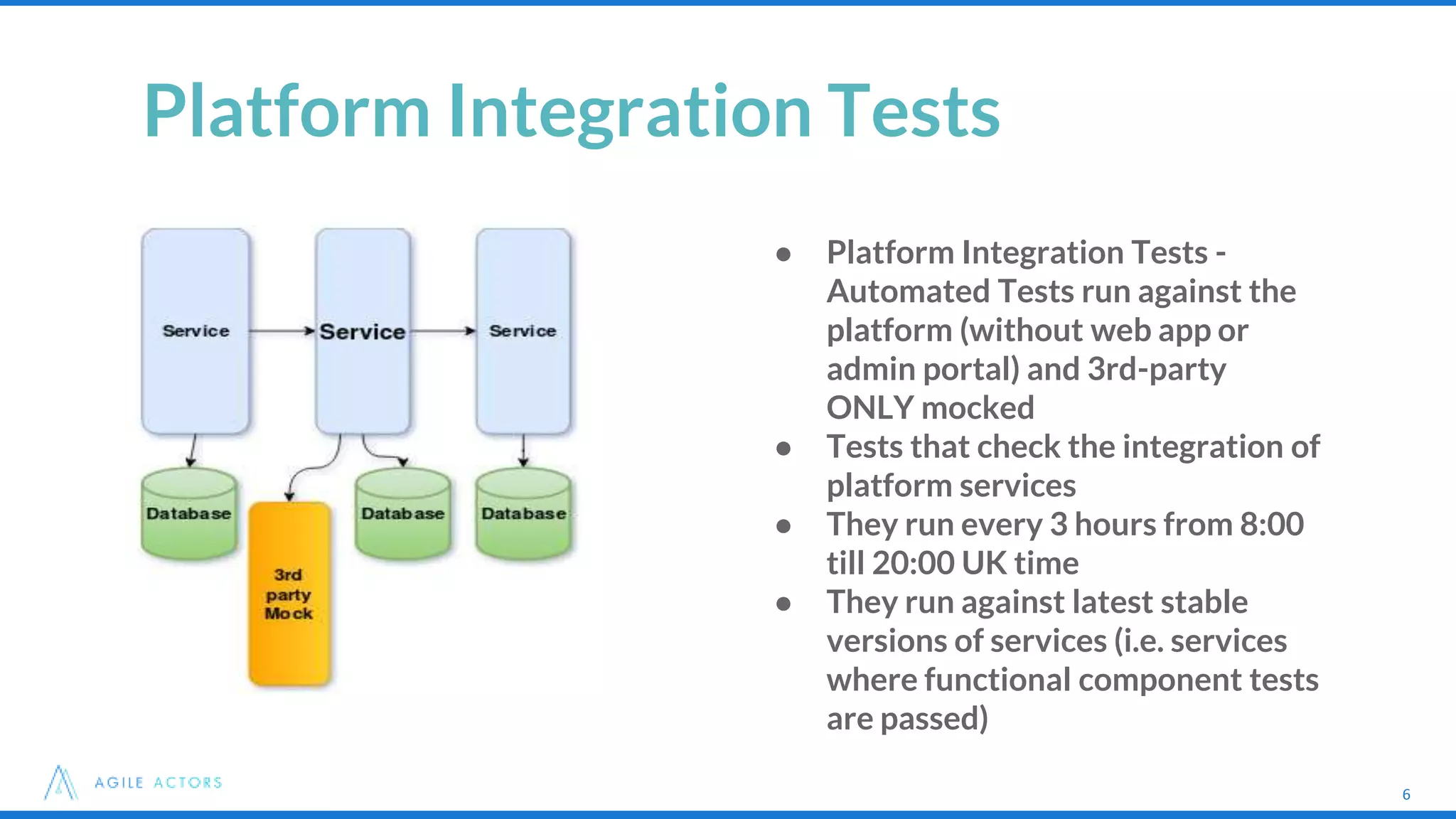
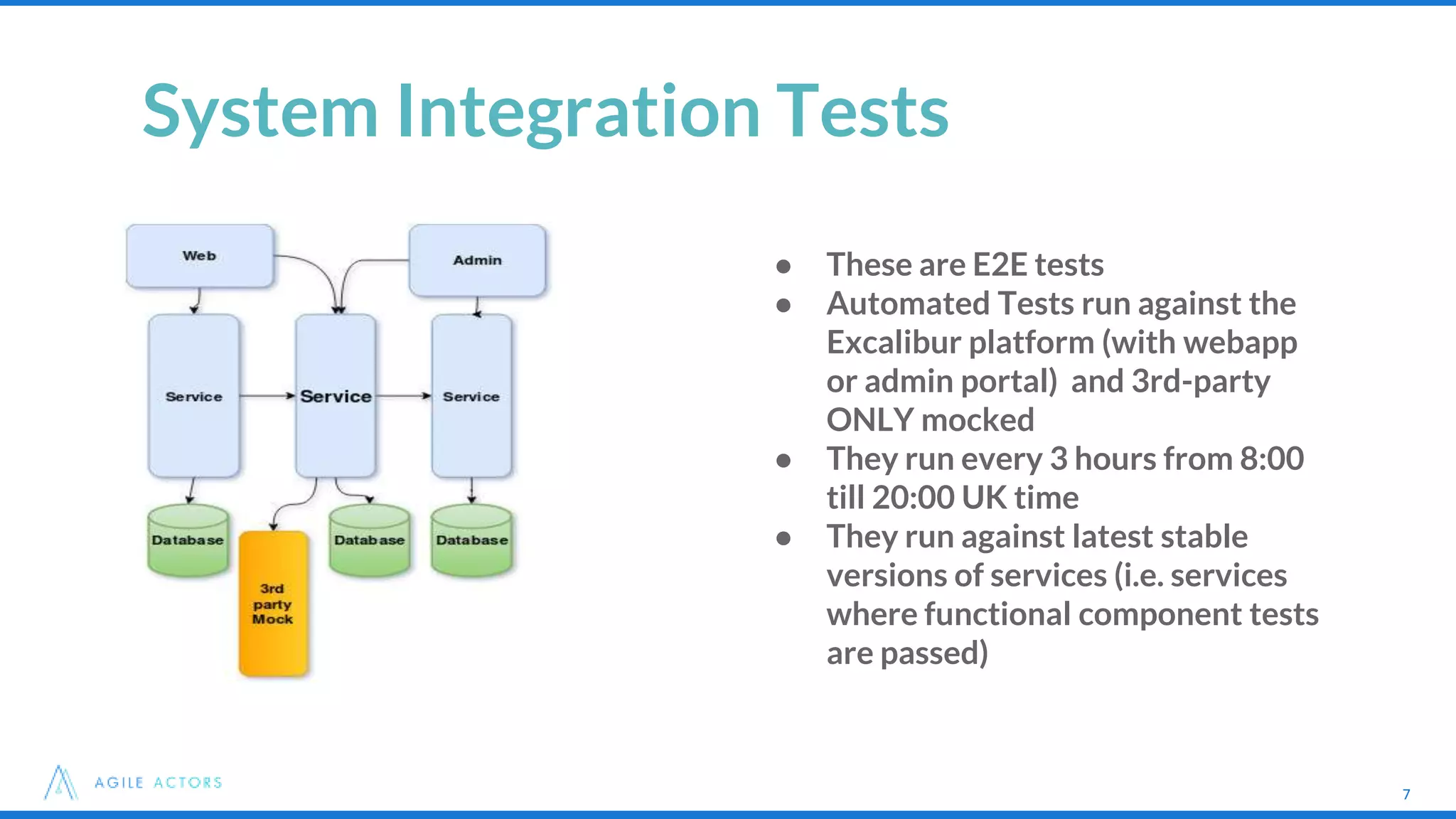
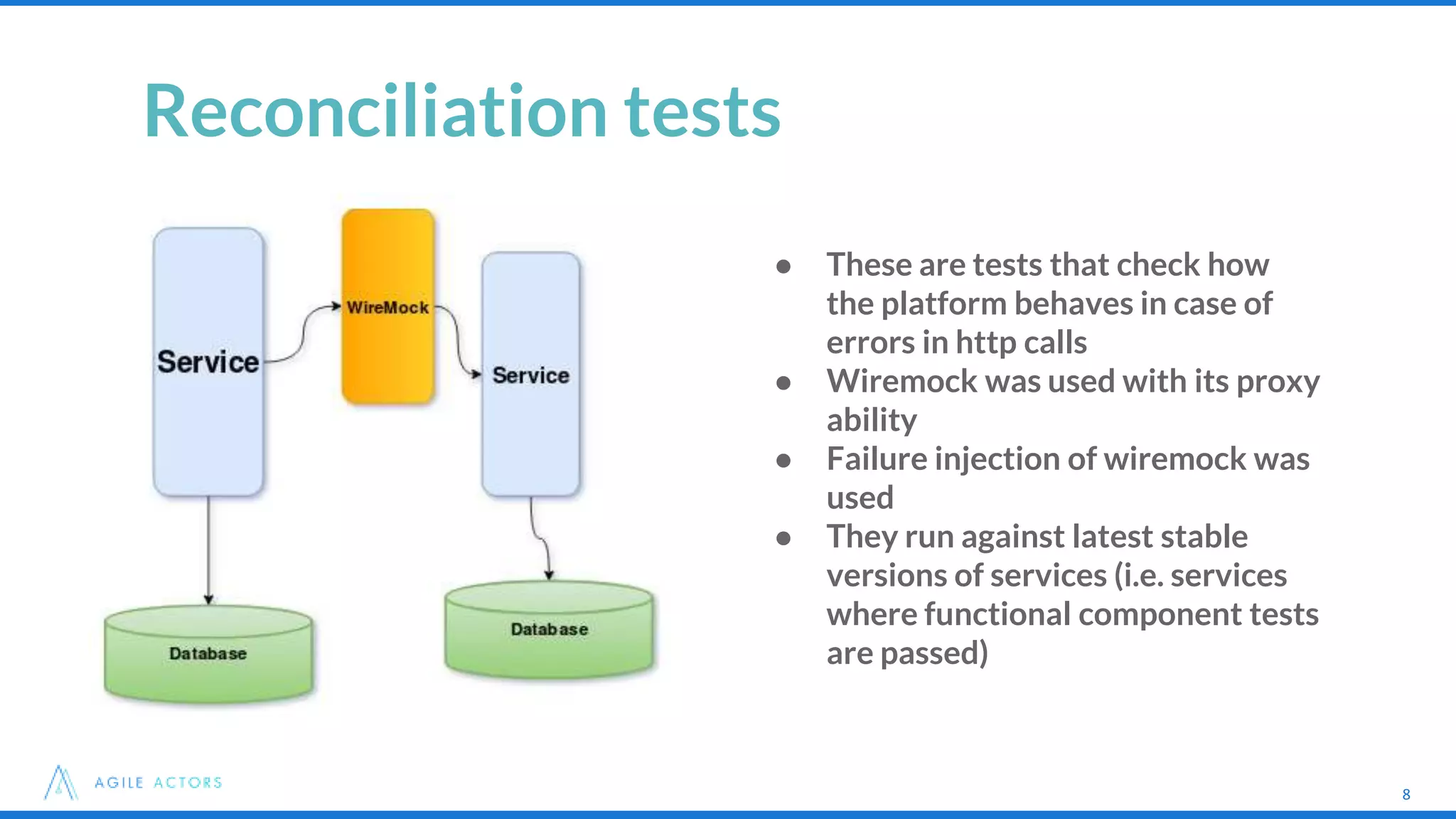
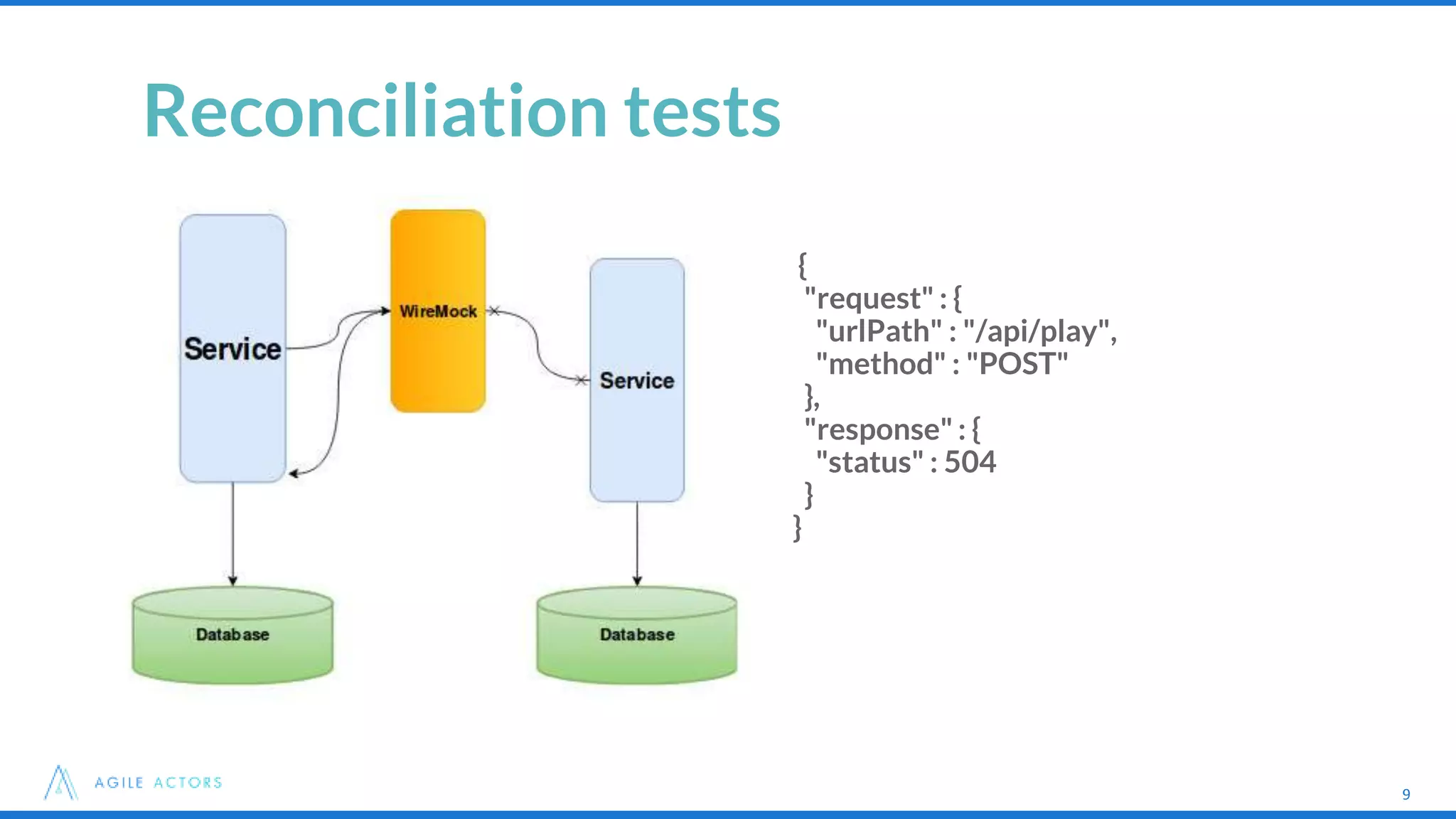
This document discusses testing strategies for microservices at an iLottery platform built with a microservices architecture. It outlines a test pyramid with four levels of automated tests - unit tests, functional component tests, platform integration tests, and system integration tests. It also describes the tools used for different types of tests, including Spock, Groovy, Wiremock, and Geb/Spock for UI tests. Lessons learned include introducing contract-driven testing and increasing collaboration between QA and the software engineer in test role.