This Patient Engagement Lunchtime Learning seminar was presented as a collaboration between the George & Fay Yee Centre for Healthcare Innovation and the Newfoundland & Labrador SUPPORT Unit.
It was originally streamed on March 11, 2025.
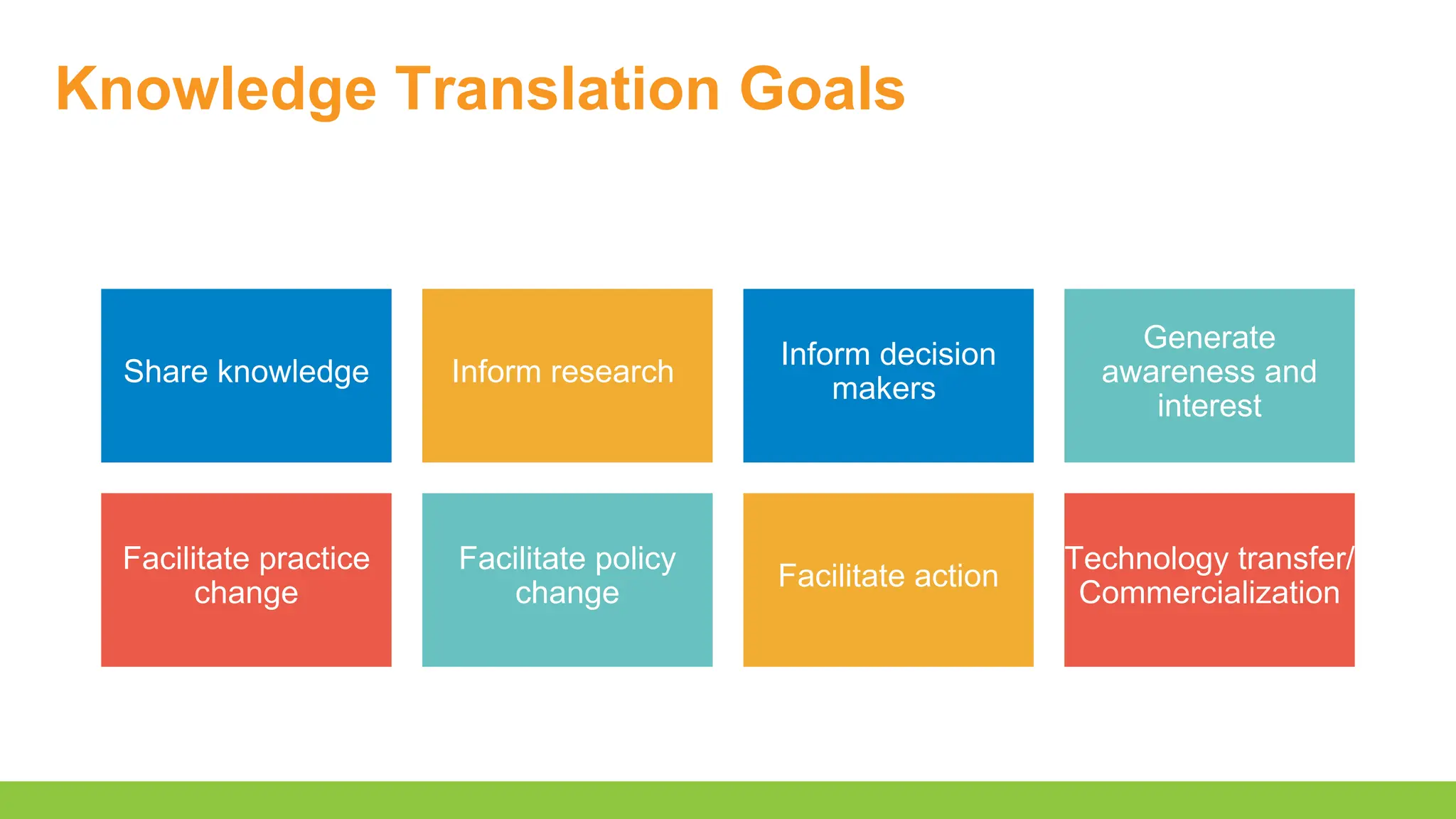
Key objectives include:
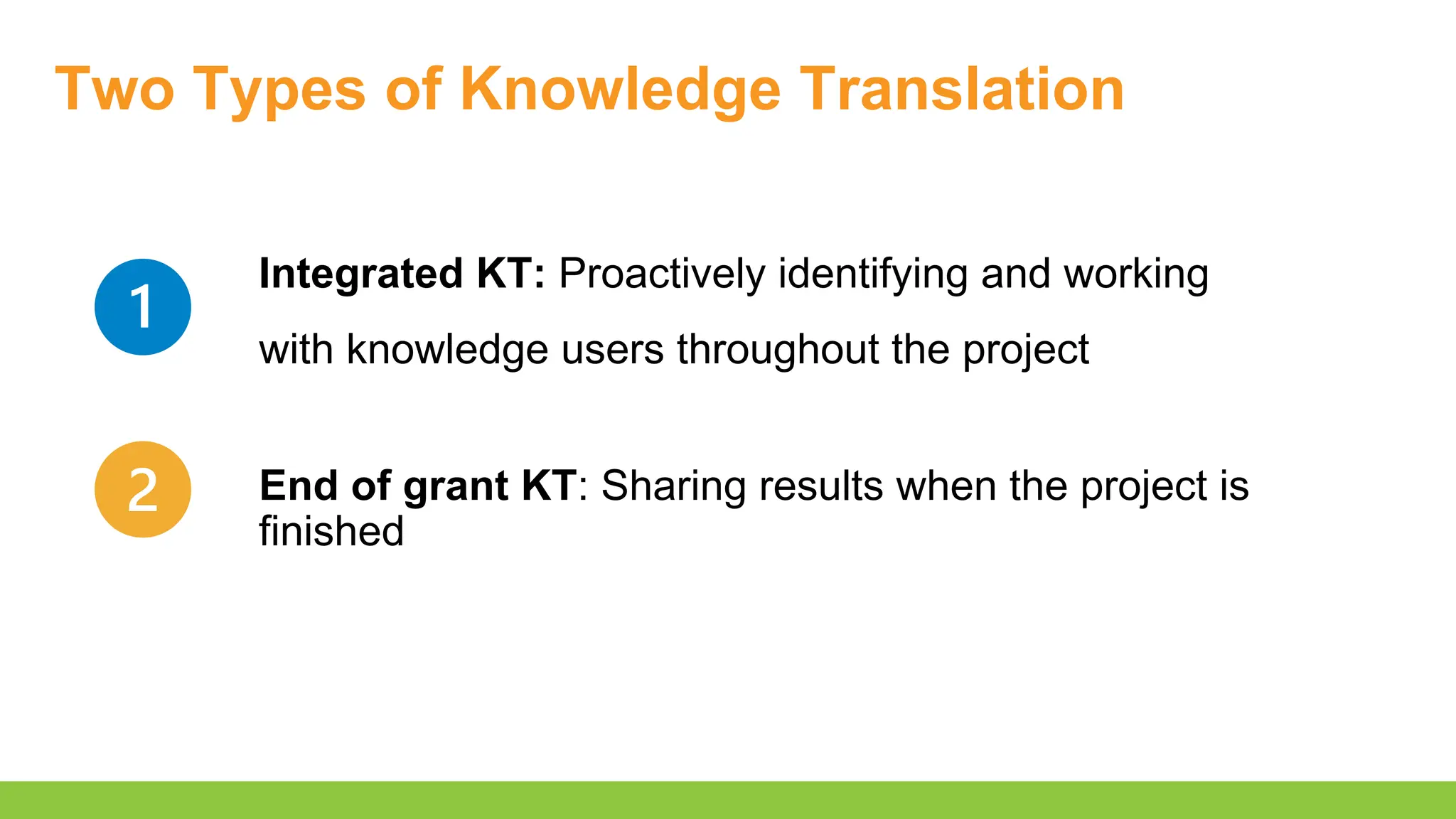
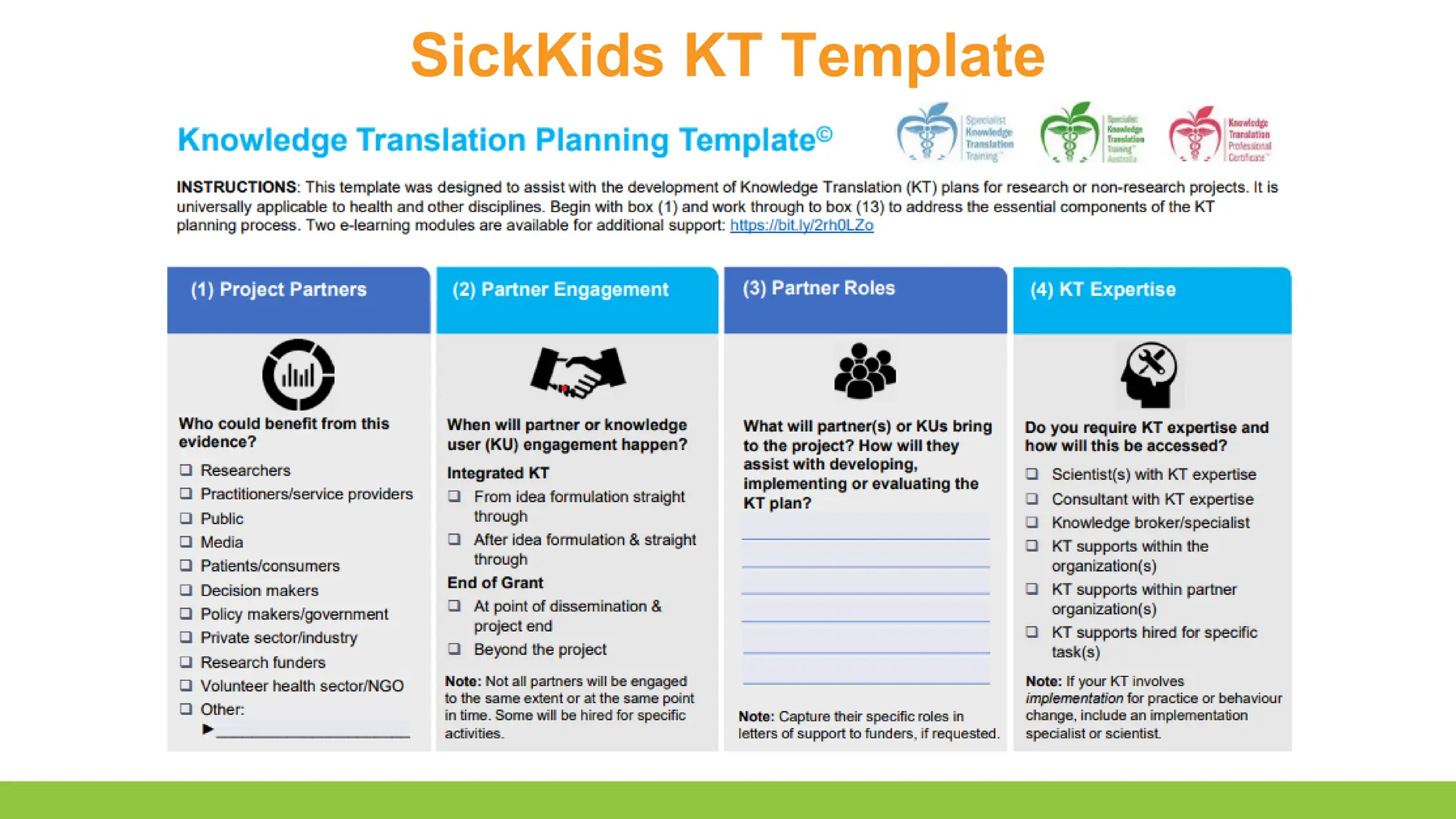
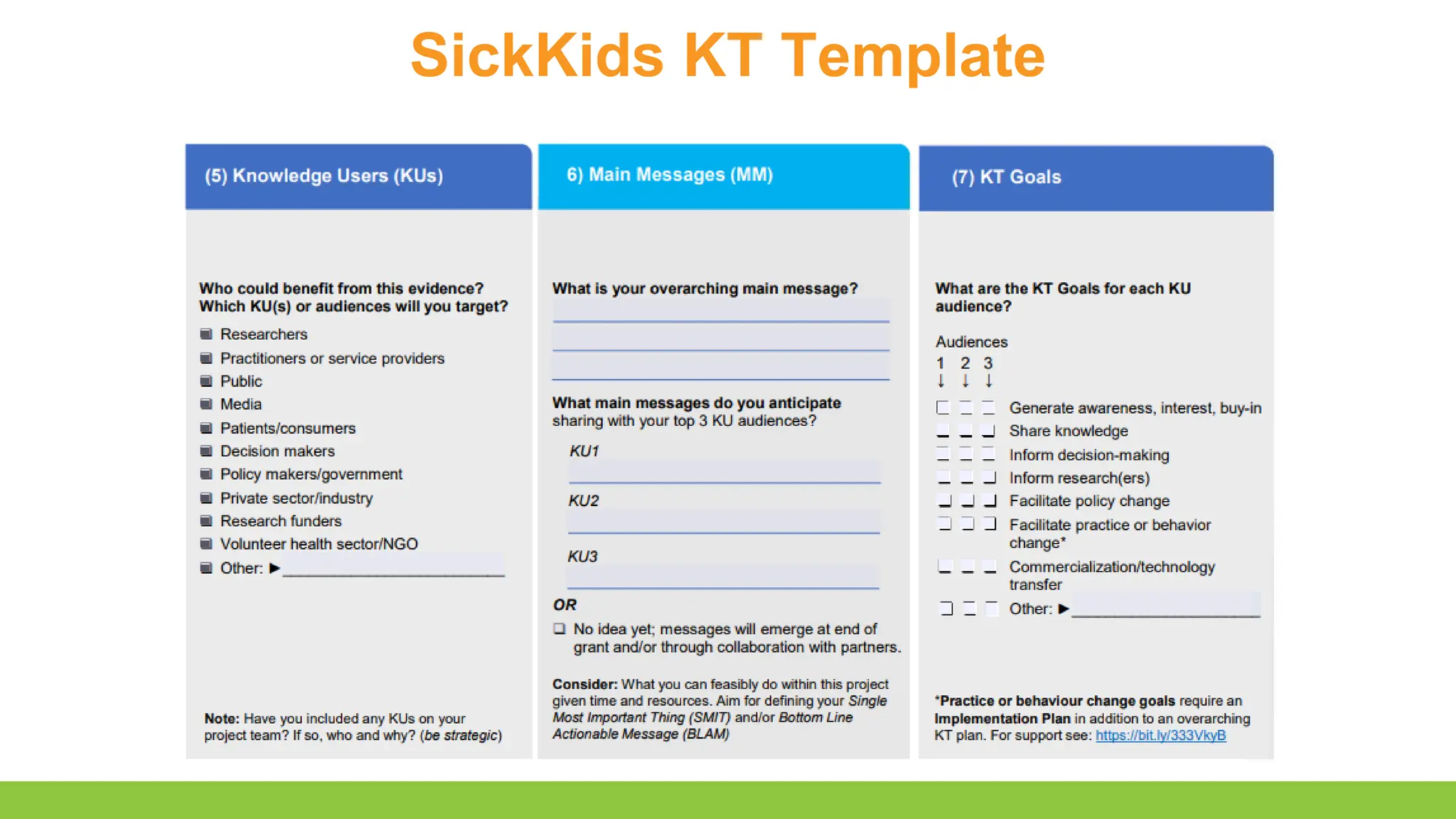
- Conceptualizing a knowledge translation plan
- Describe the key characteristics of a knowledge translation plan
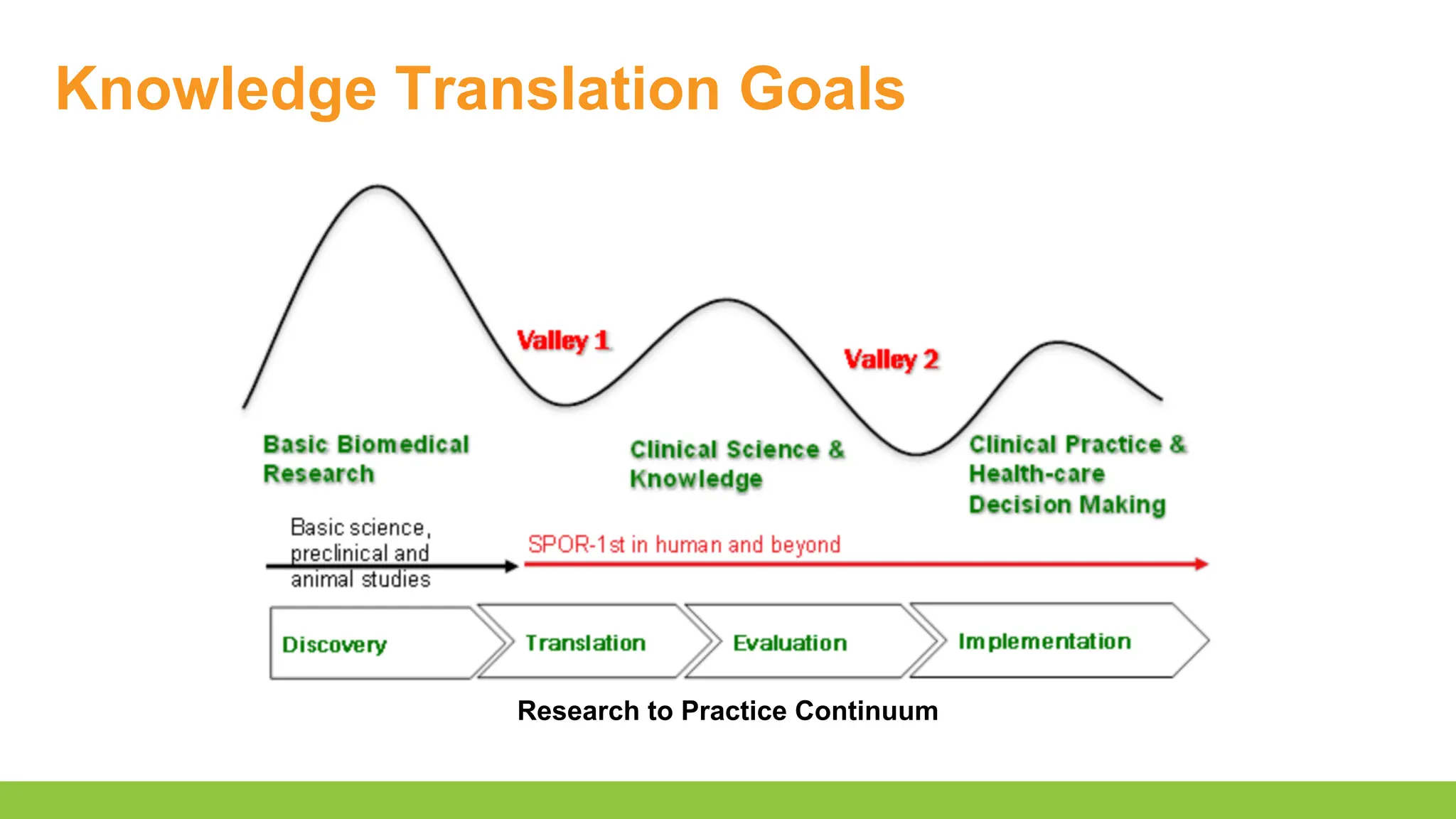
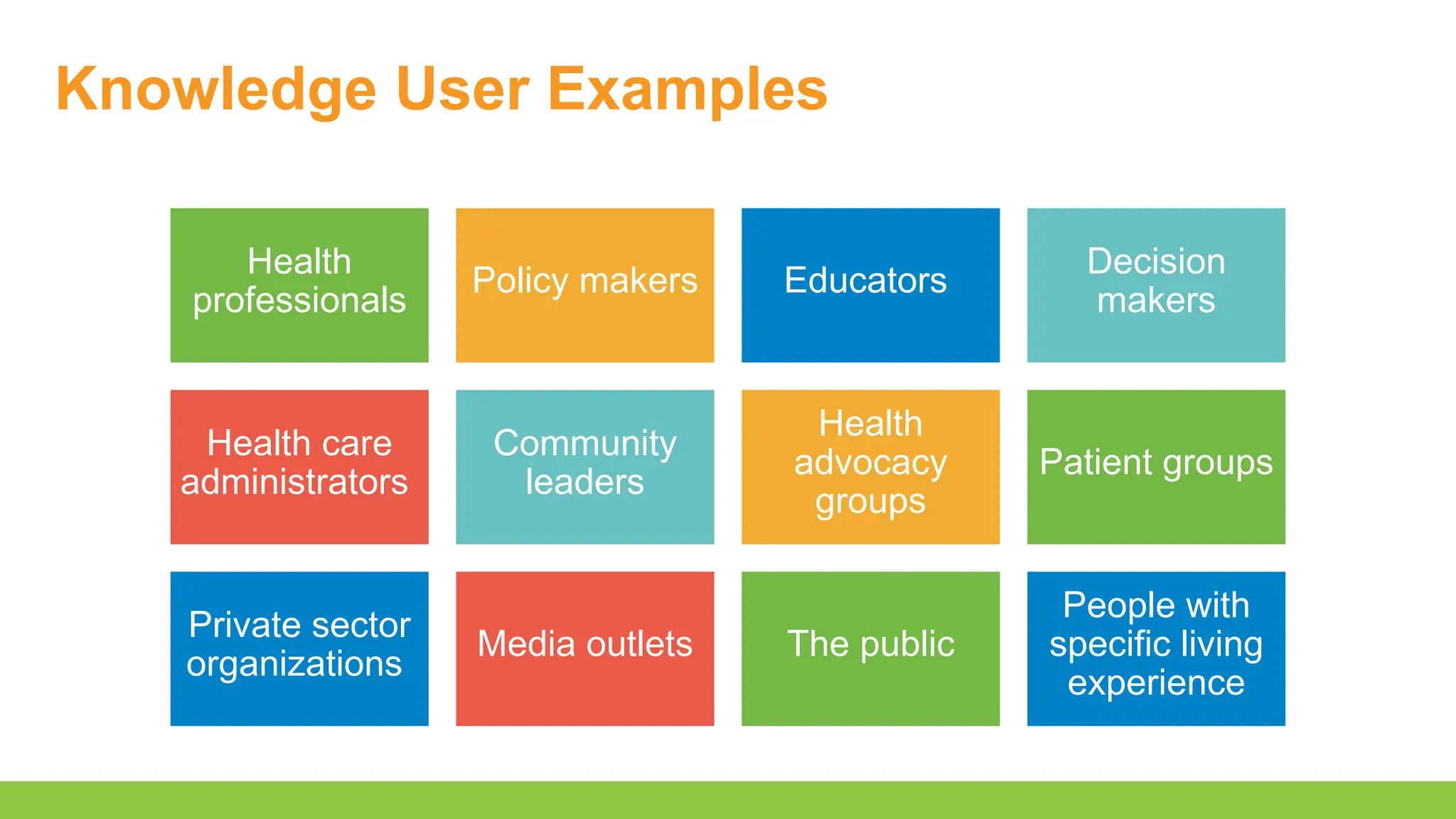
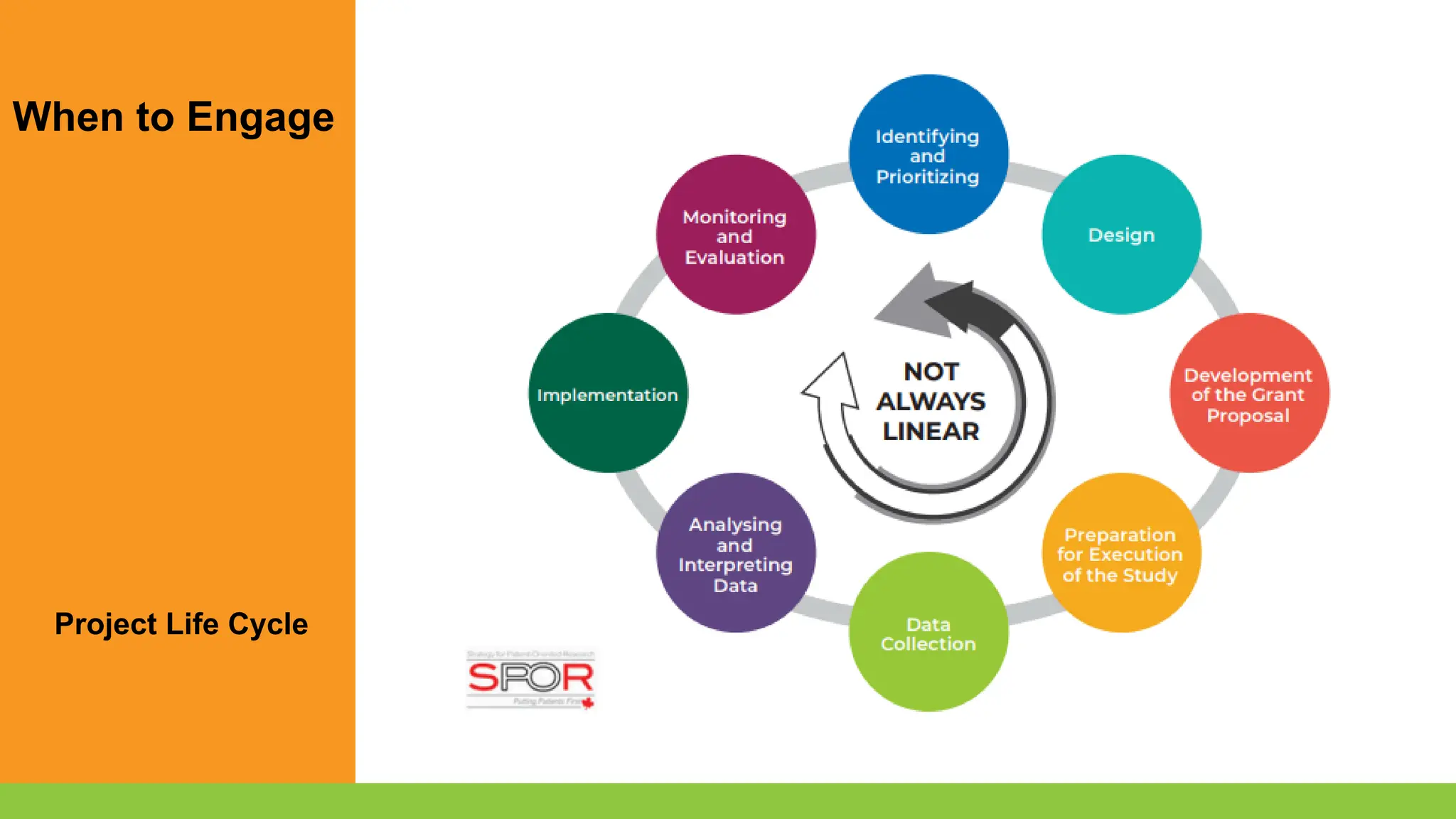
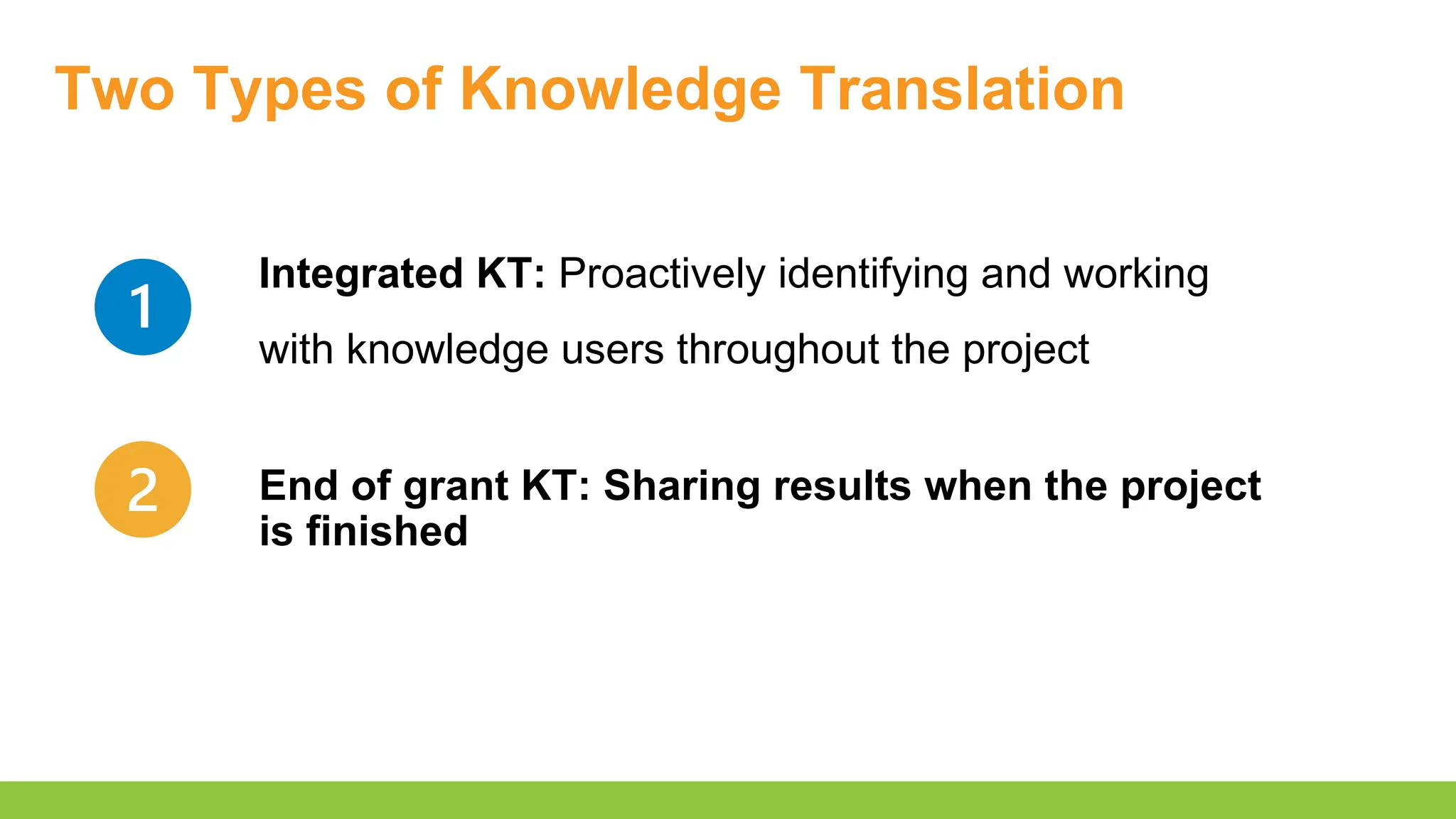
- Recognize opportunities to involve knowledge users in knowledge translation to improve the integration of research results into clinical practice
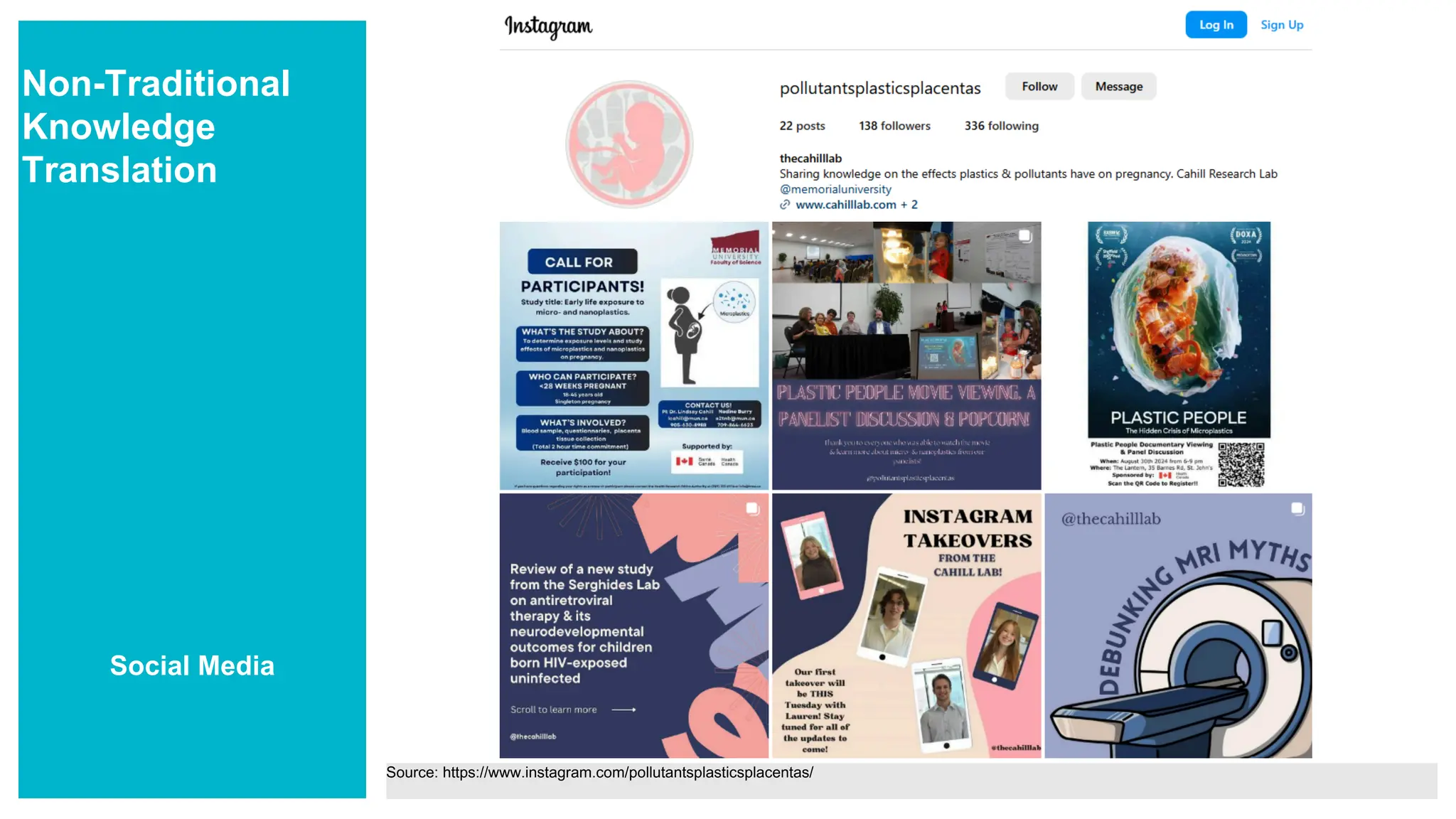
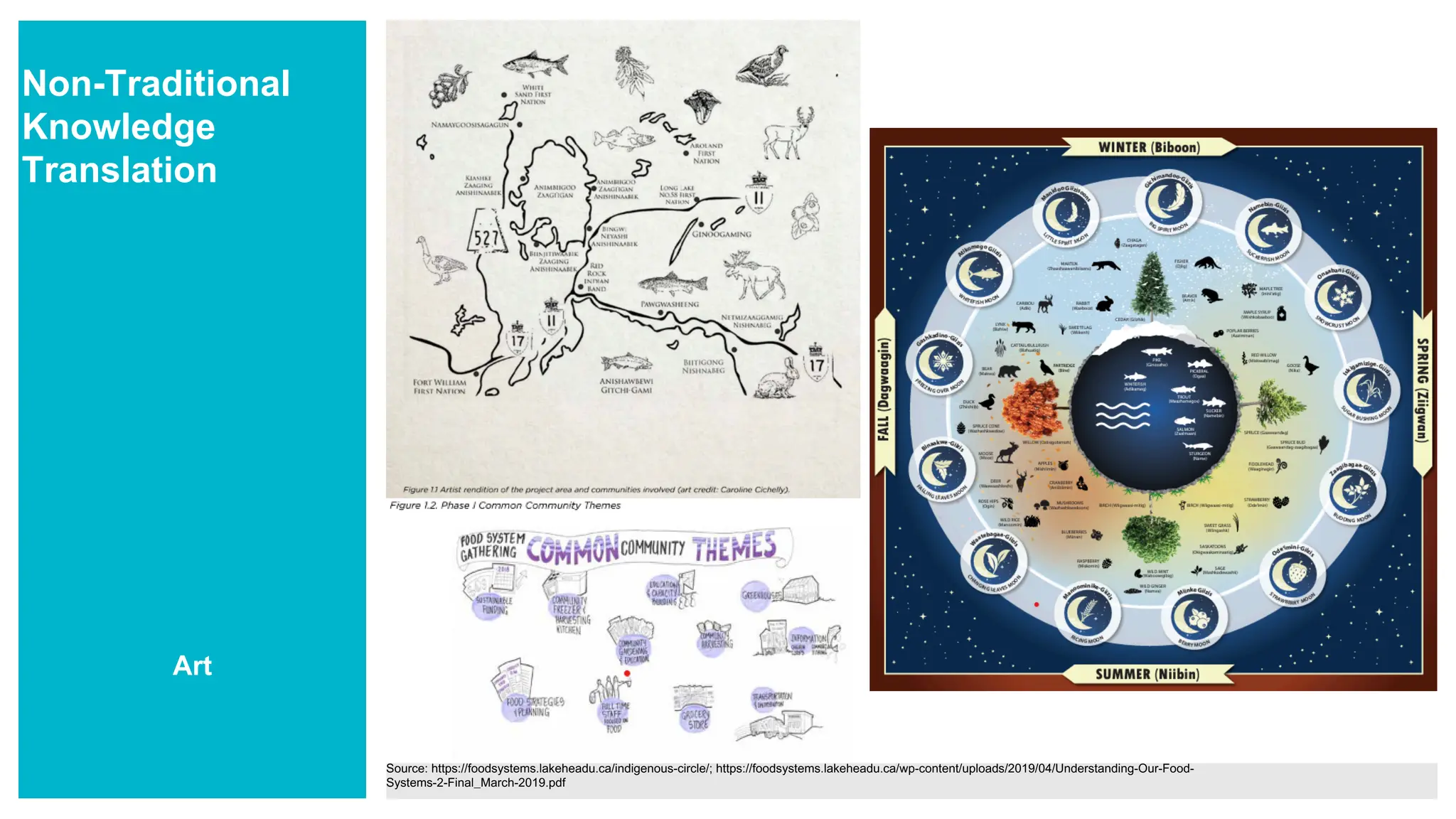
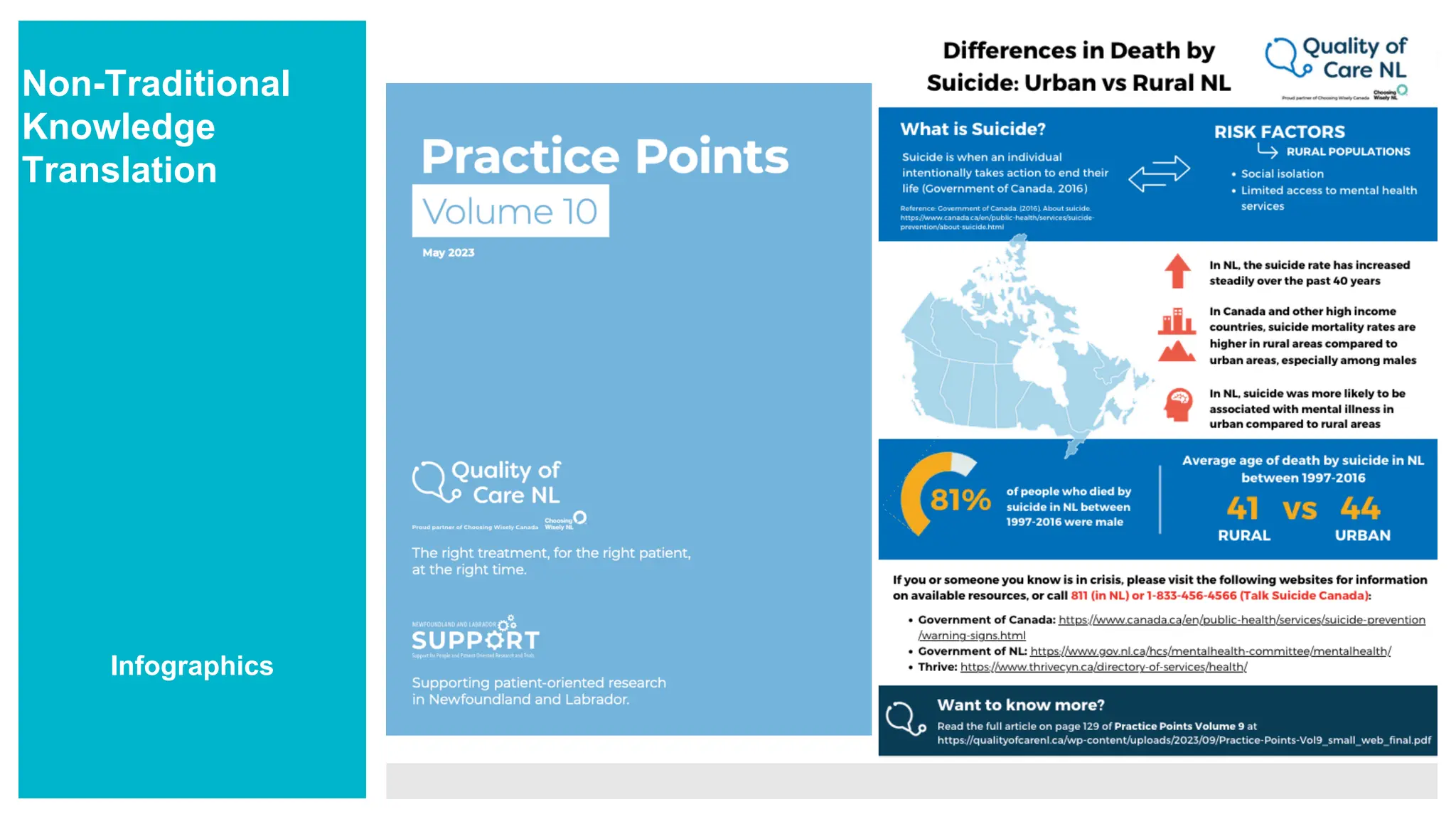
- List knowledge translation strategies beyond traditional dissemination methods (e.g. journal publications, conference presentations)
- Identify research supports available to them through SPOR