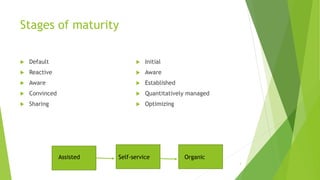
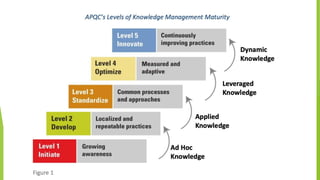
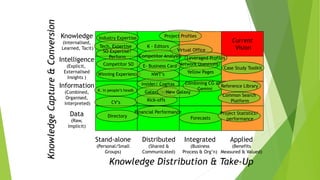
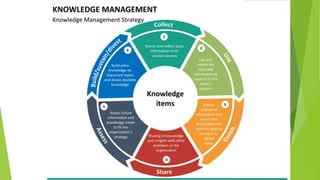
The document discusses various knowledge management (KM) maturity models including those developed by Carnegie Mellon, Fujitsu Consulting, and the KM Institute. It outlines the stages or levels of maturity in KM for each model from initial/chaotic to optimized/agile. The document also includes diagrams showing the progression from data to knowledge in stand-alone to integrated forms. It provides checklists for assessing KM capabilities and developing a KM business case.