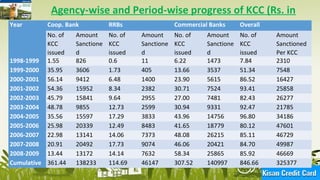
The document discusses the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme in India. KCC was introduced in 1998-99 by the Reserve Bank of India and NABARD to provide easy access to credit for farmers. It functions as a revolving cash credit facility with a limit set based on landholding and crops. Farmers can withdraw funds for agricultural inputs and household needs. Key features include flexibility in repayment if crops fail and insurance coverage. Over 750 million cards have been issued, aiming to improve farmers' access to formal credit sources.