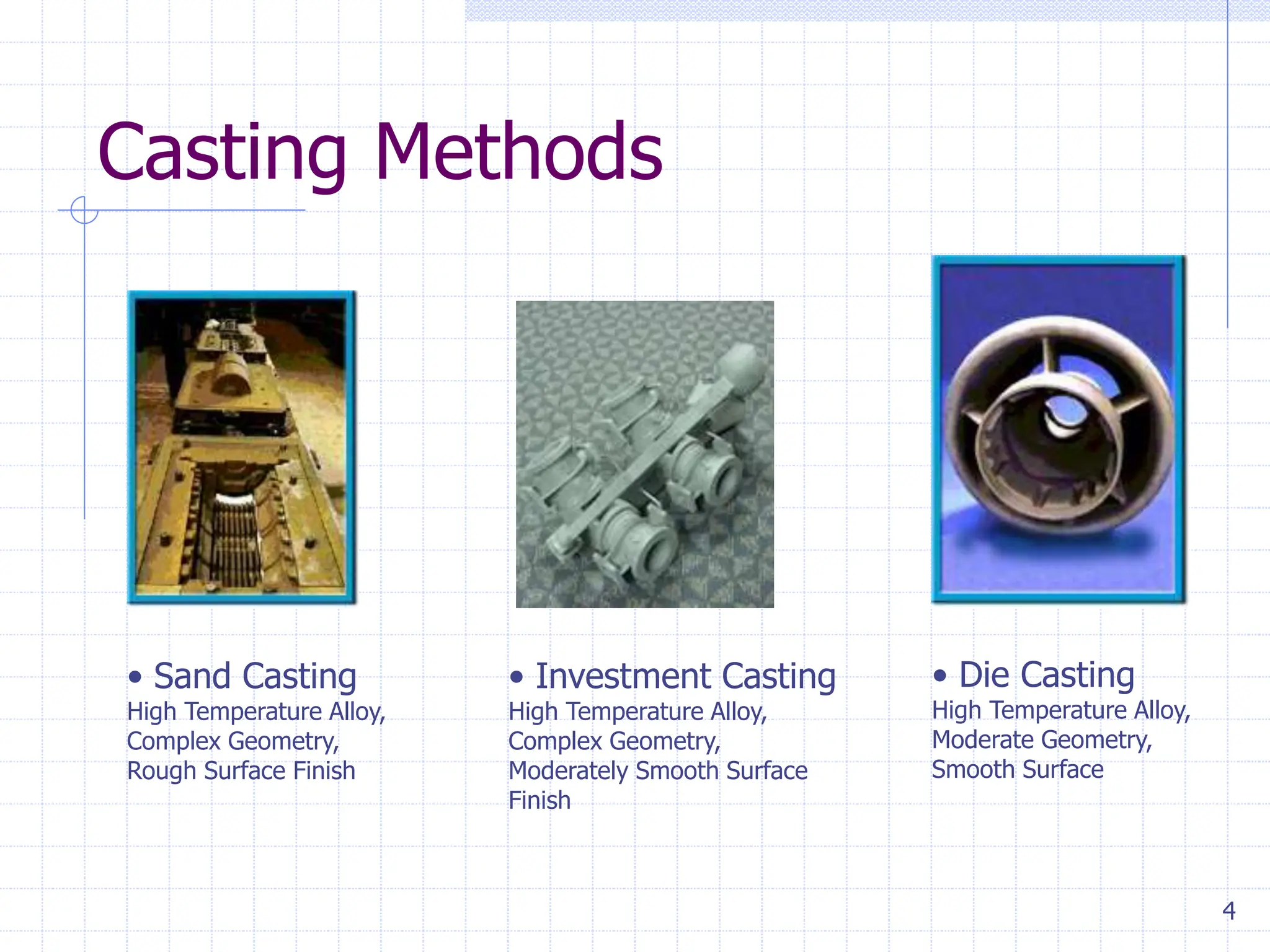
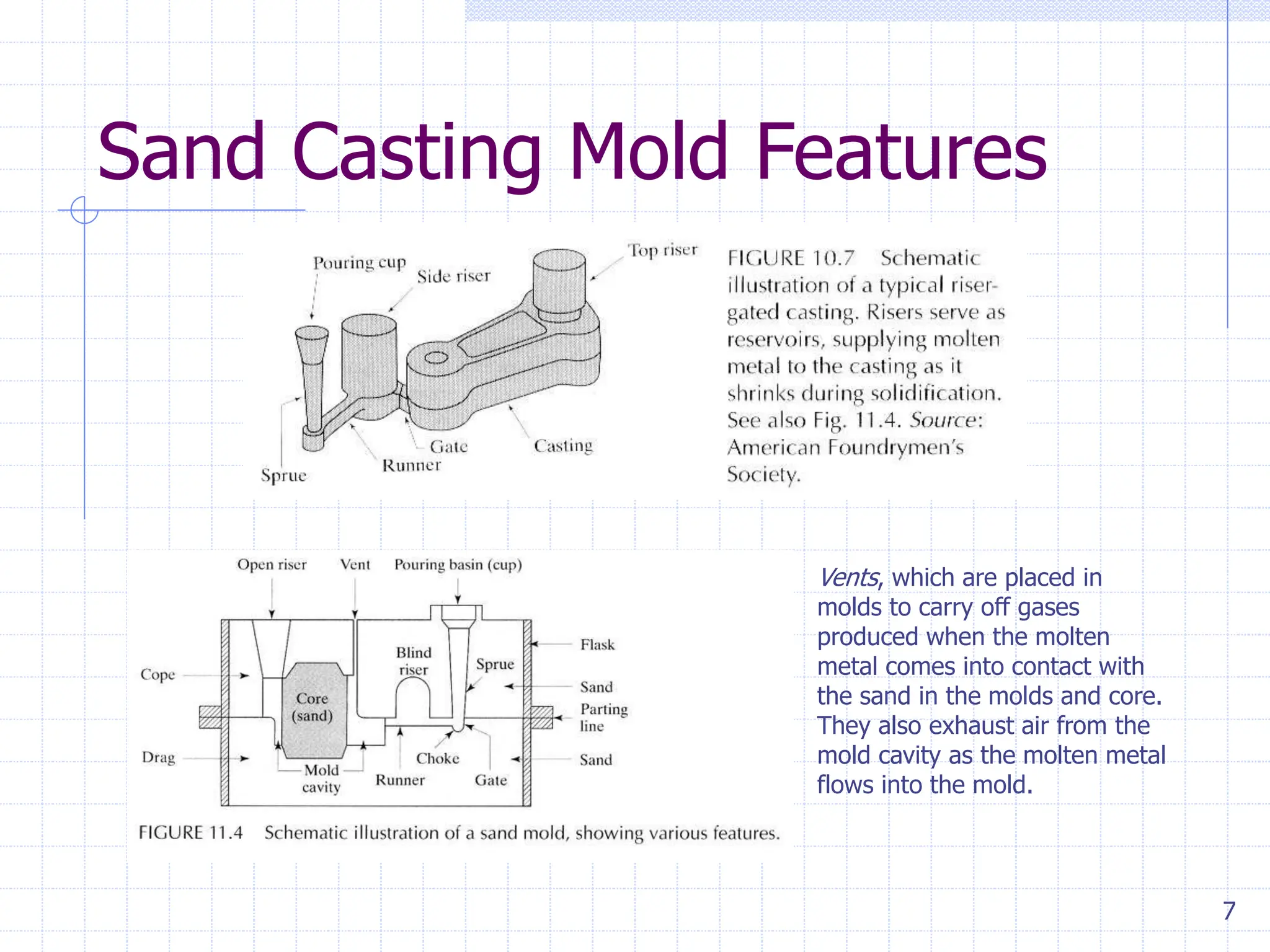
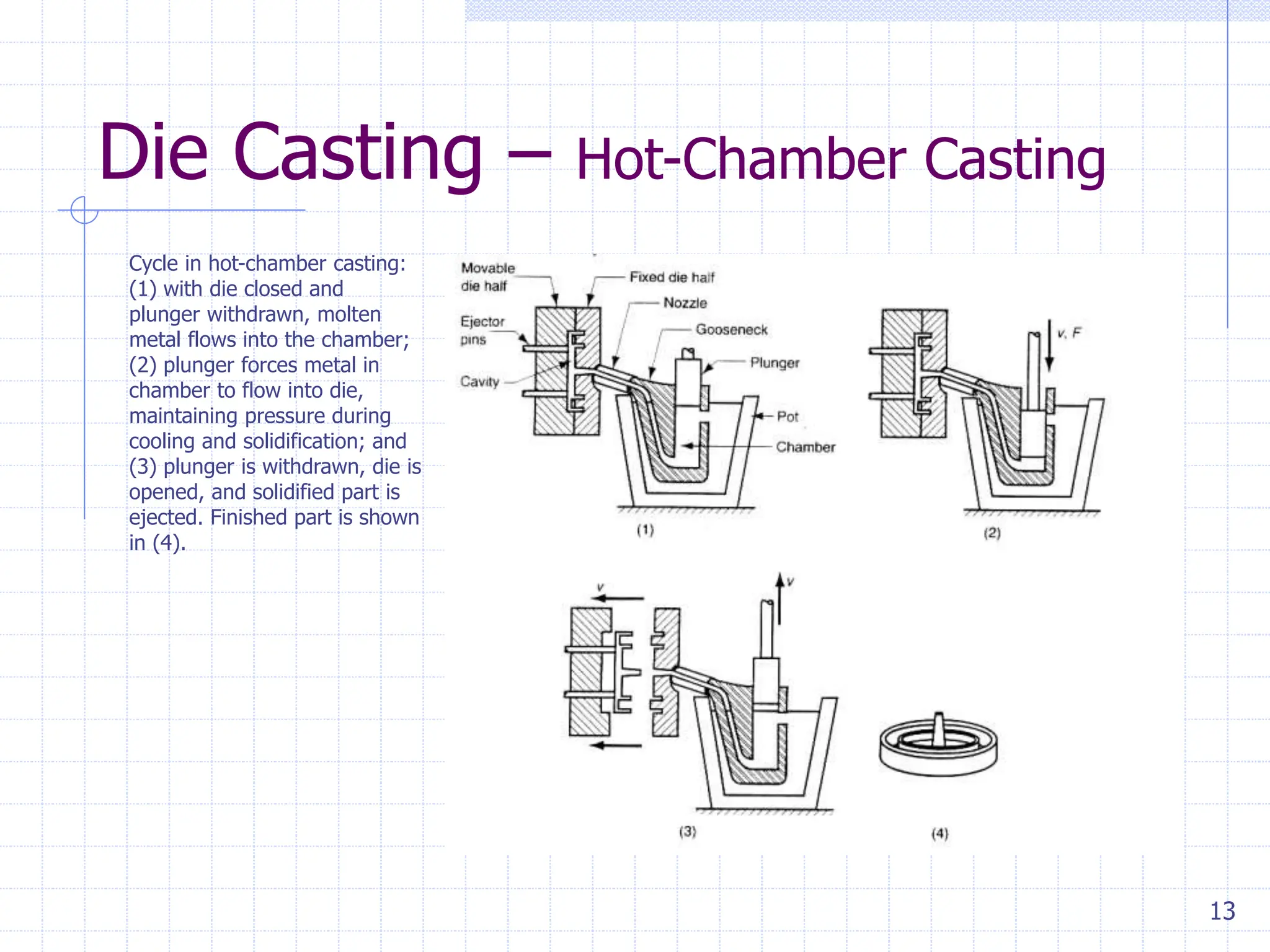
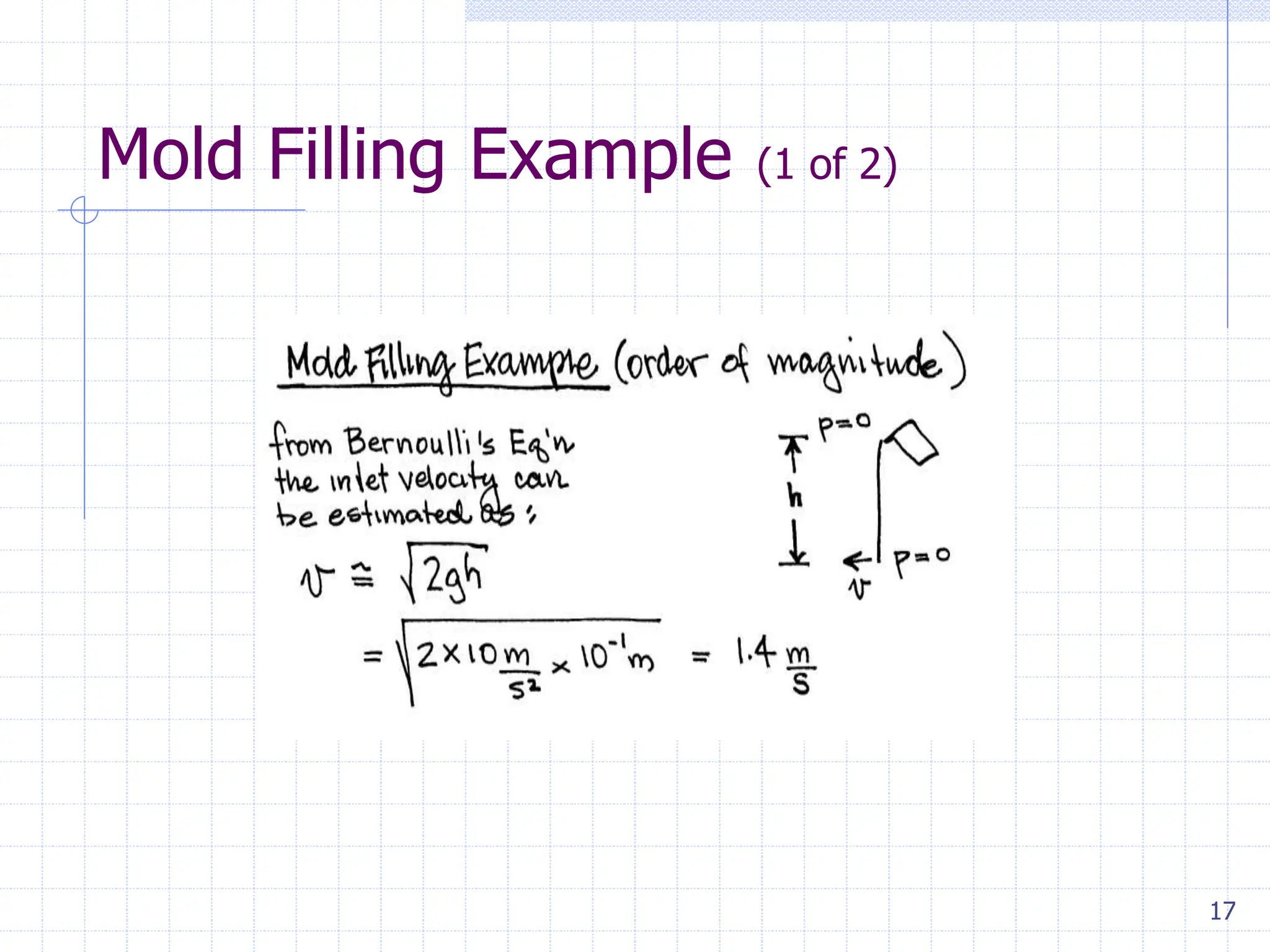
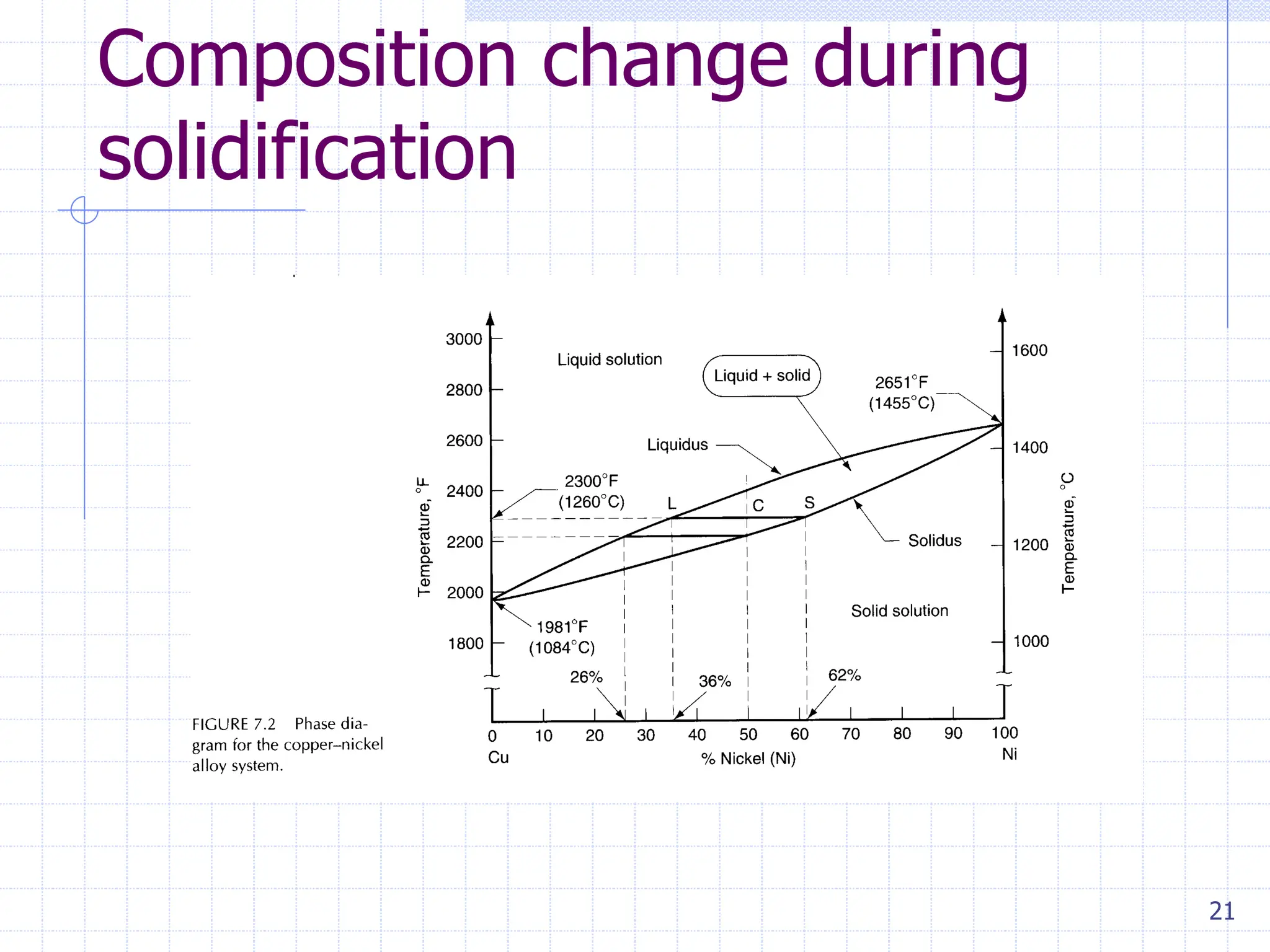
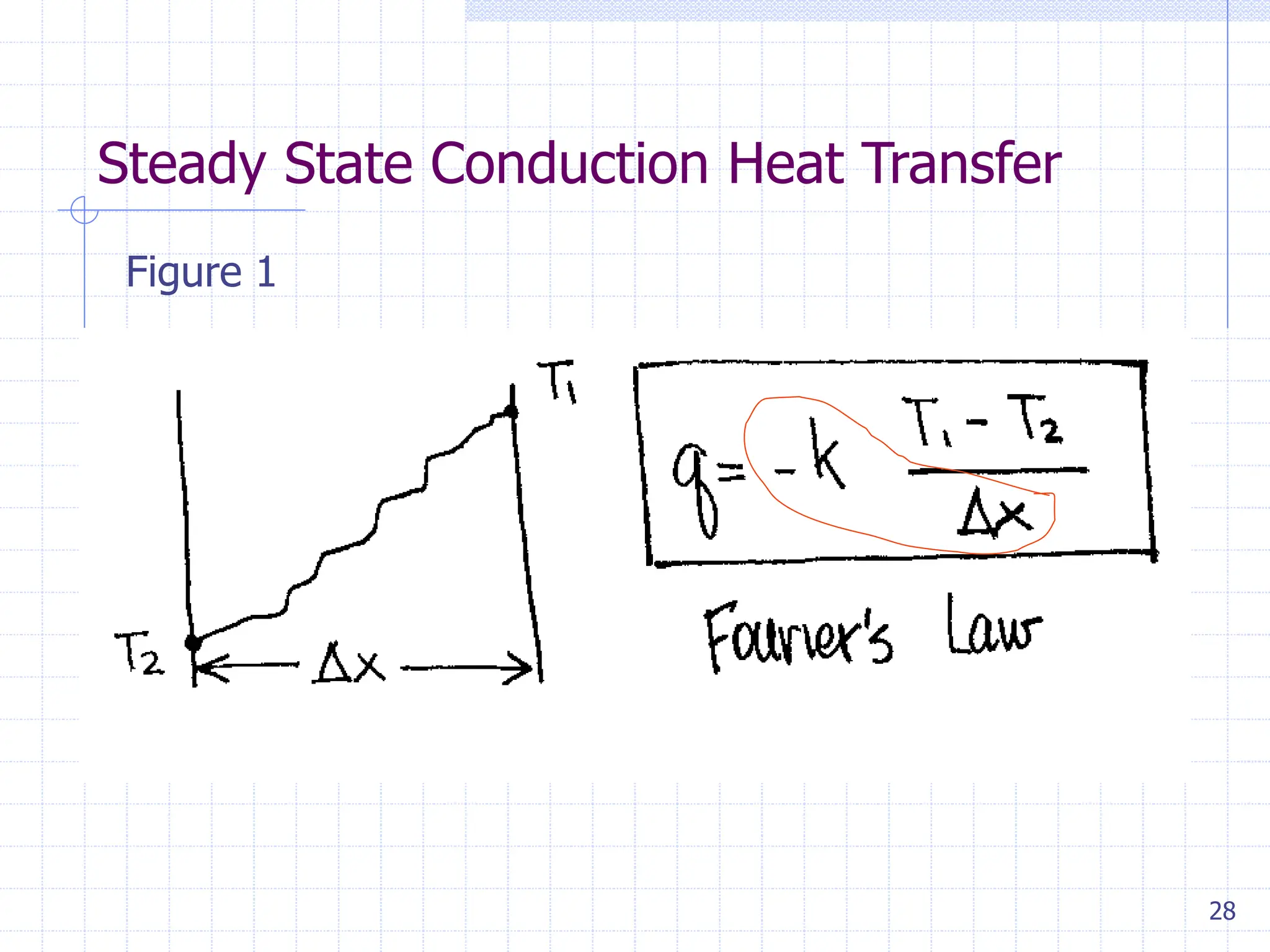
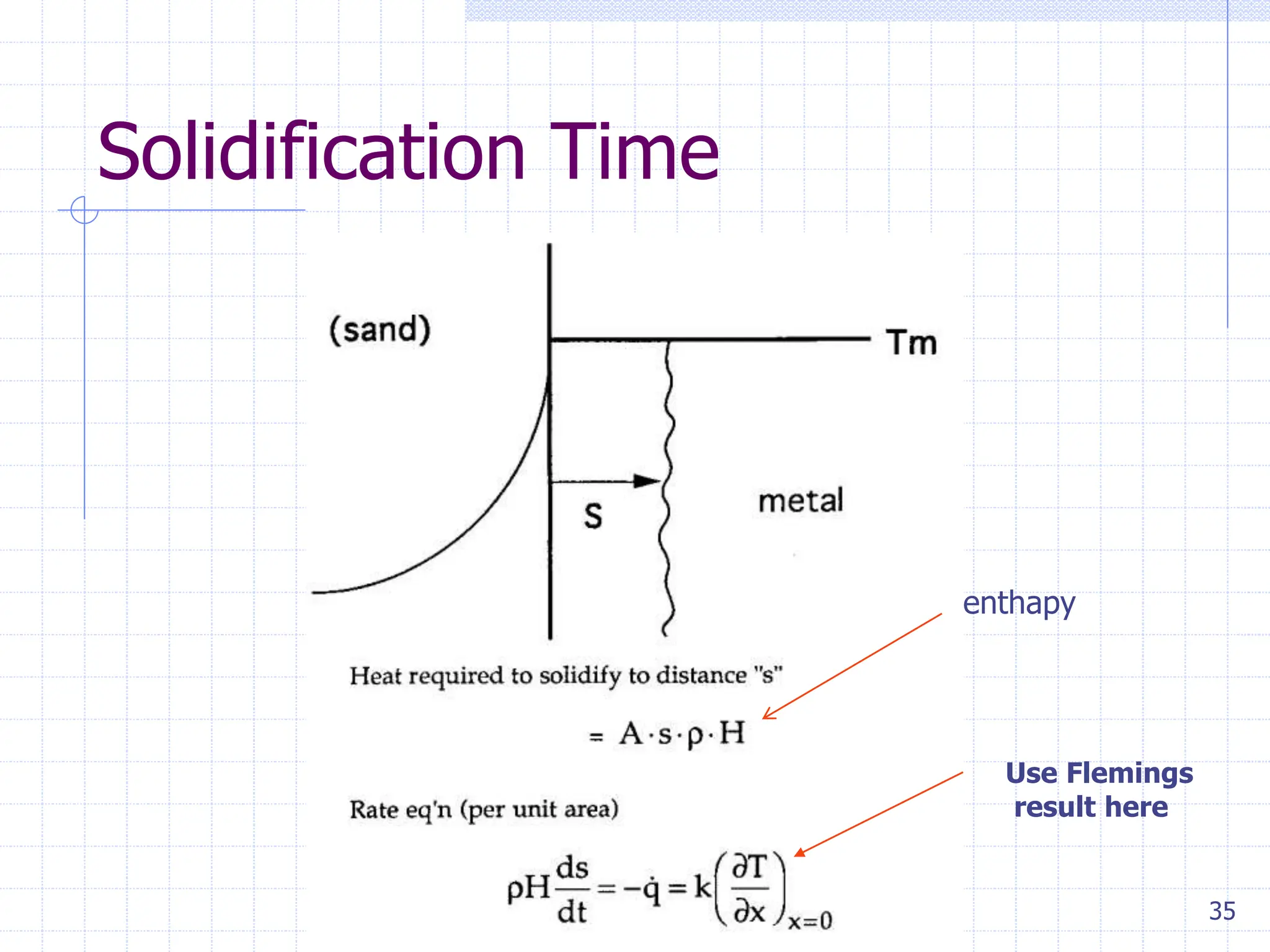
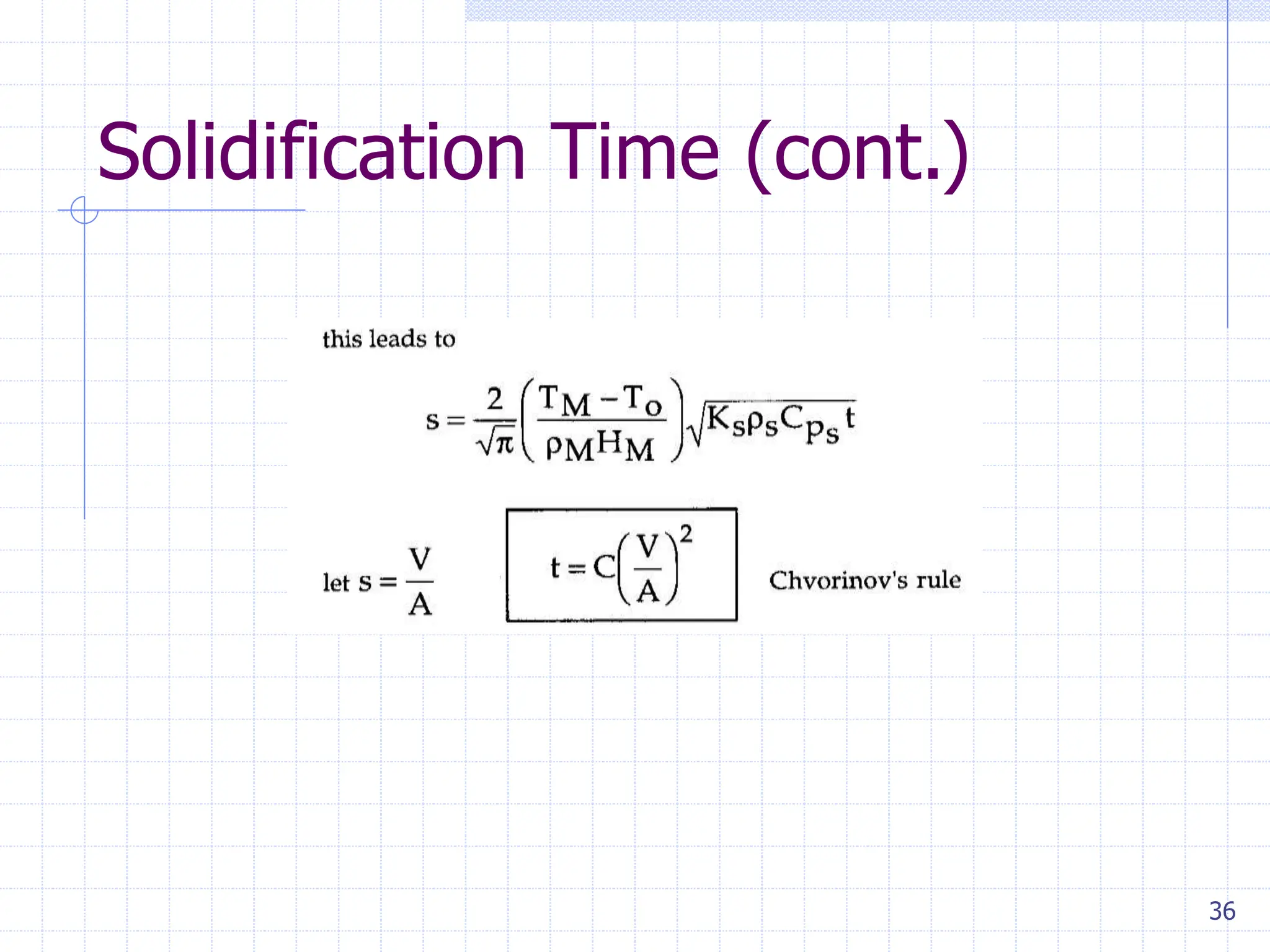
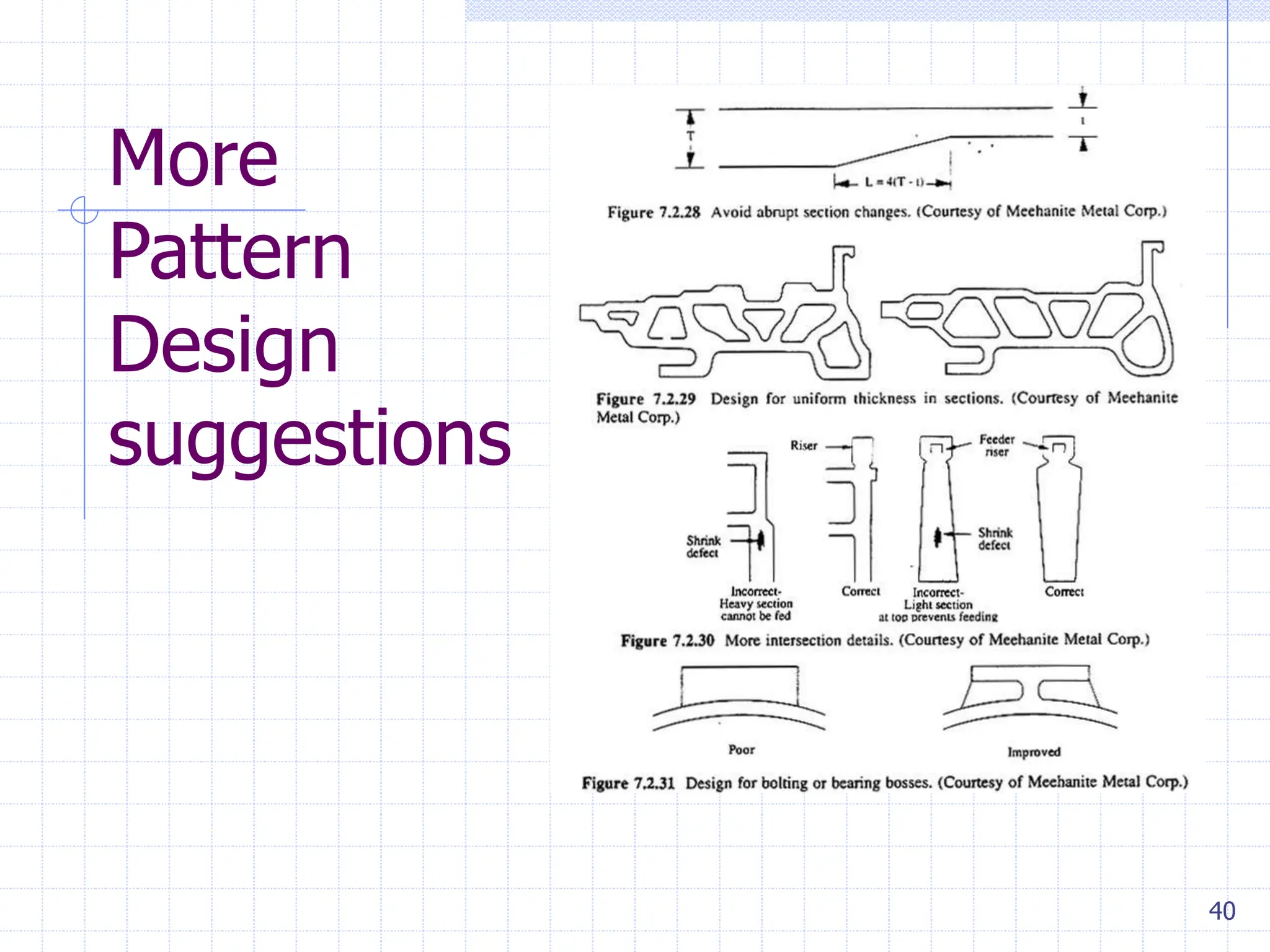
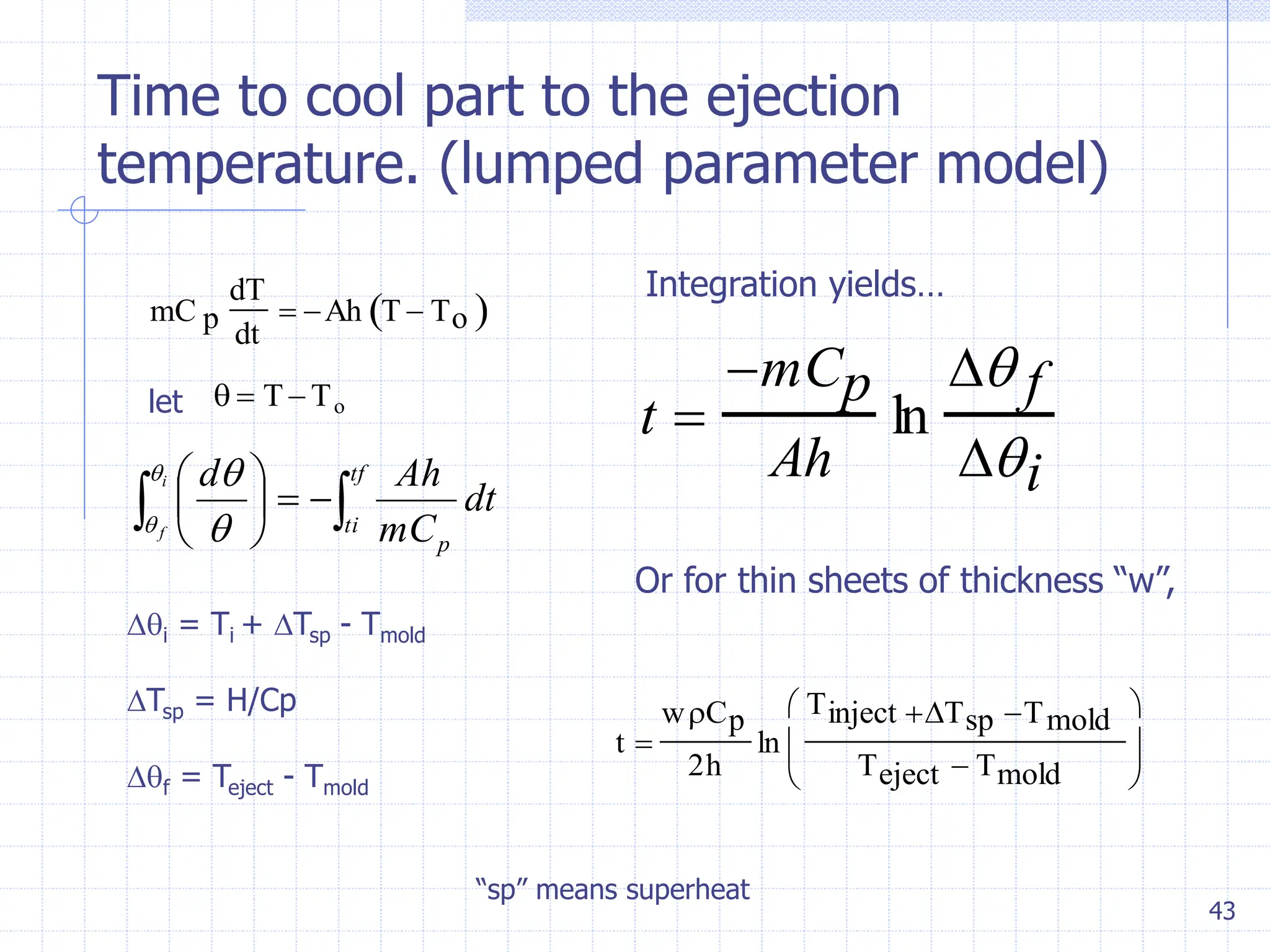
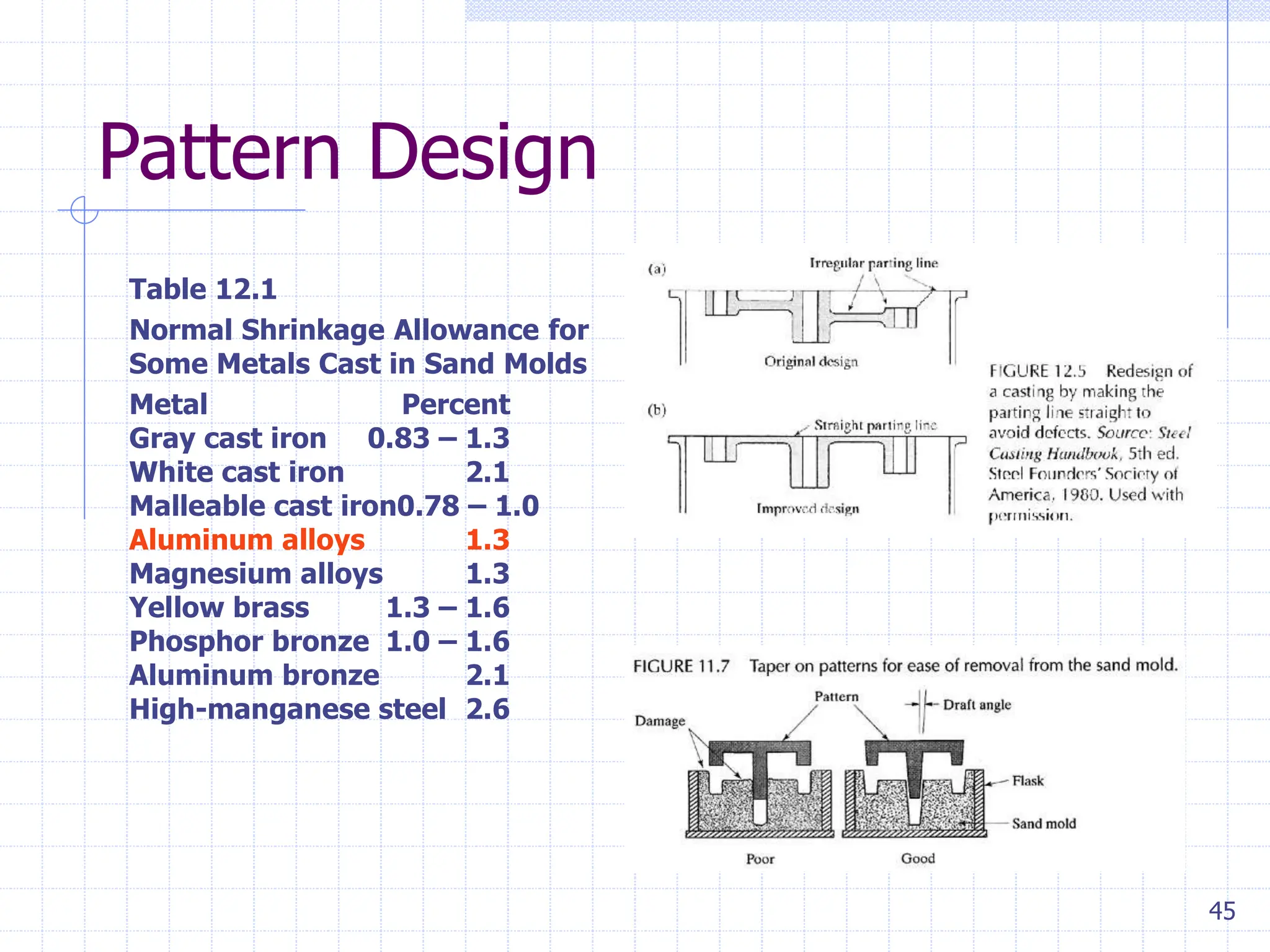
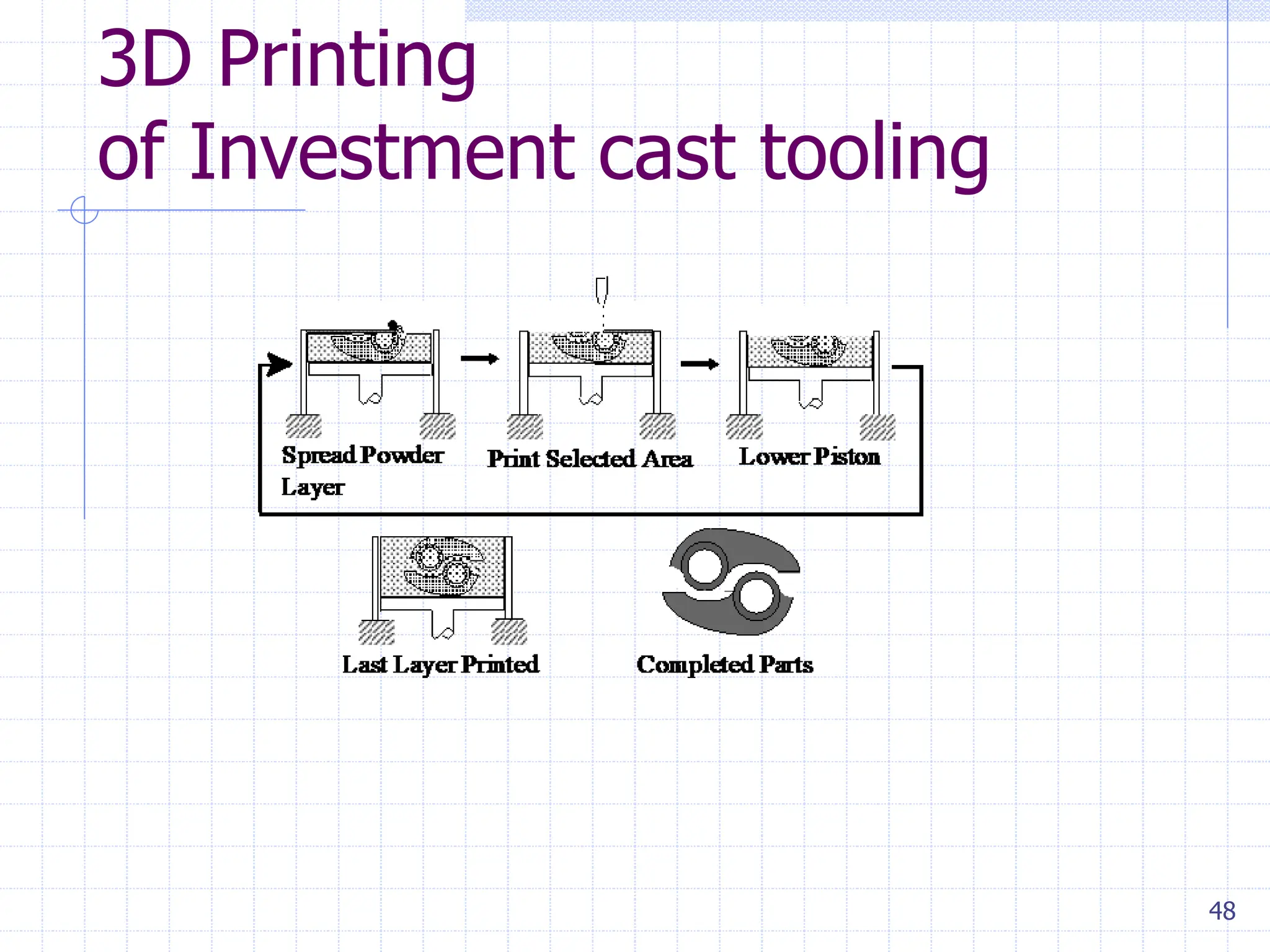
Sand casting, investment casting, and die casting are the three main casting methods discussed. Sand casting uses a sand mold and can produce parts in most metals with complex geometries but rough surfaces. Investment casting uses a wax mold and yields complex parts in high temperature alloys with smoother finishes. Die casting injects molten metal into steel dies under pressure for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys with smooth surfaces but moderate geometries. Key casting issues covered include phase change and shrinkage during solidification, heat transfer considerations, and pattern design guidelines. Variations like continuous casting and 3D printing of tooling were presented along with environmental impacts.