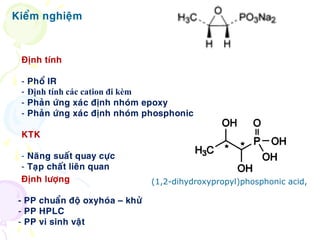
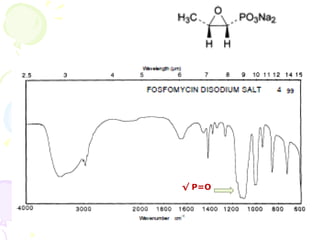
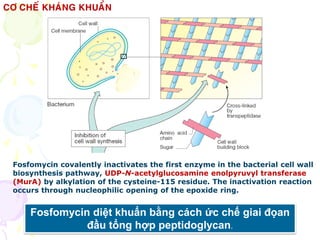
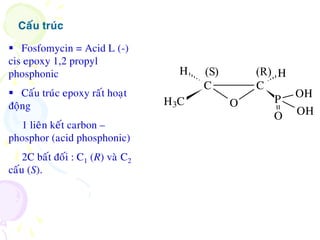
Fosfomycin is an antibiotic discovered in soil in 1966. It acts by inhibiting the first step of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis through covalent inactivation of the MurA enzyme. This occurs via nucleophilic opening of fosfomycin's epoxide ring. Fosfomycin shows activity against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria including E. coli. Resistance is rare but it is usually combined with other antibiotic classes like beta-lactams or aminoglycosides. It is indicated for severe hospital-acquired infections and those caused by multidrug-resistant organisms.

![Fosfomycin sodium
Fosfomycin trometamol
2-Amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol hydrogen
(2R,3S)-(3-methyloxiran-2-yl)phosphonate
Fosfomycin calcium
A white or almost white, very
hygroscopic powder, very soluble in
water, sparingly soluble in methanol,
practically insoluble in ethanol and in
methylene chloride.
Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per
cent) and in methanol, practically insoluble in acetone.
A white or almost white powder,
slightly soluble in water, practically
insoluble in acetone, in methanol and
in methylene chloride.
[gói bột uống , trị nhiễm trùng tiểu (E coli) liều duy nhất]
(Viên nang, hỗn
dịch uống)(Bột pha tiêm)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fosfomycinsv-190220044153/85/Khang-sinh-Fosfomycin-4-320.jpg)