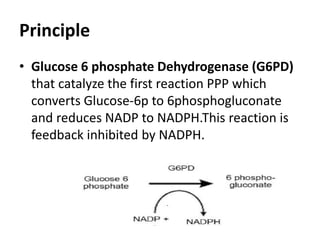
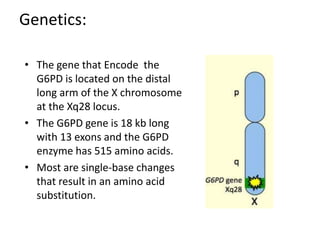
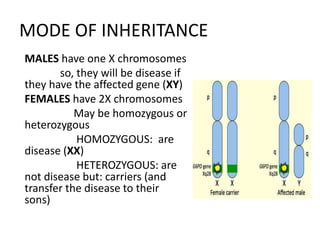
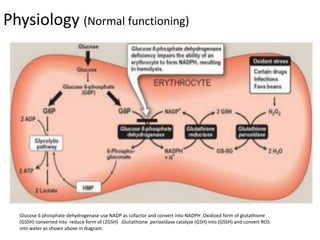
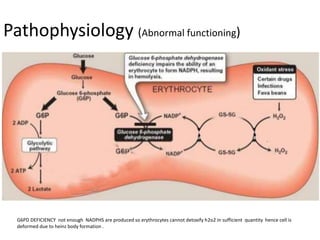
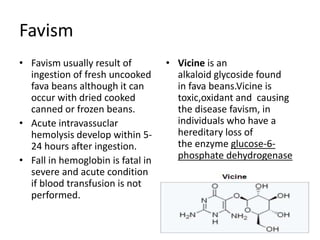
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD deficiency) is an inherited metabolic disorder that leads to hemolytic anemia due to the inability to detoxify reactive oxygen species, affecting over 400 million people globally. The condition is caused by mutations in the G6PD gene located on the X chromosome, with males being more severely affected due to having only one X chromosome. Diagnosis involves blood tests, and treatment may include blood transfusions, antioxidants, and avoidance of triggers such as fava beans and certain medications.