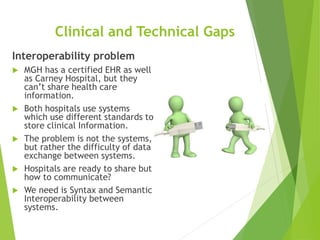
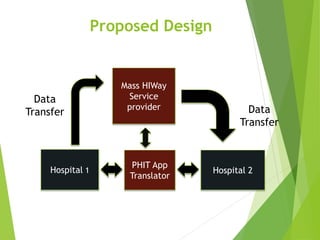
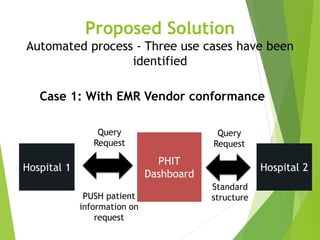
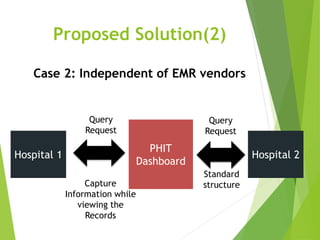
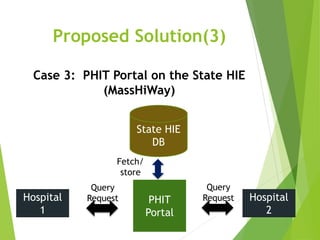
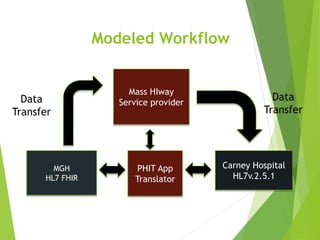
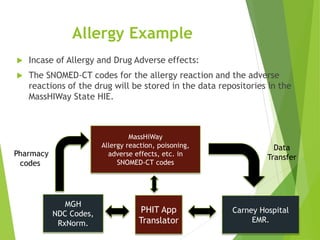
This document discusses key standards for health information exchange and interoperability. It describes three stages of meaningful use that aim to improve healthcare quality, safety, and privacy. The document also presents a case example where a patient's medical history from one hospital was unavailable during an emergency at another hospital due to lack of interoperability. It proposes a PHIT application that would enable data exchange between different electronic health record systems using standards like HL7, FHIR, and SNOMED to address this issue.