This document discusses key concepts in the simple Keynesian theory of income determination, including:
1. Endogenous and exogenous variables - endogenous variables are explained by the theory, while exogenous variables are taken as given. Real output and consumption are initially treated as endogenous.
2. The consumption function - consumption is explained as autonomous consumption plus the marginal propensity to consume times disposable income. This can be shown graphically.
3. Induced saving and the marginal propensity to save - as disposable income increases, the remaining portion after consumption is induced saving. Actual U.S. data from 1929-2001 is presented to illustrate these concepts.



![t],)
An autonomous magni-
tude is independent of the
level of income.
The marginal propensity
to consume is the dollar
change in consumption
expenditures per dollar
change in disposable
income.
Induced consumption is
the portion of consump-
tion spending that
responds to changes in
income.
How do households divide their disposable income between consumption
and saving? Households consume a fixed amount that does not depend on their
disposable income, plus a fraction of each dollar of disposable income:
(,r'nr'r',il I int'.rr iorn
C: Co + ,U -;; (3.2)
The fixed amount is called autonomous consumption, abbreviated (Cr), and
this is completely independent of disposable income. The amount by which
consumption expenditures increase for each extra dollar of disposable income
is a fraction called the marginal propensity to consume, abbreviated (c). This
equation (3.2) says in words that consumption spending (C) equals autonomous
consumption (C) plus the marginal propensity to consume times disposable
income lc(Y - T)]. Another name for this last term is induced consumption.
The consumptionfunction is any relationship that describes the determinants
of consumption spending. This function can be written as a general expression,
as in equation (3.2), or as a numerical example. For instance, if we choose $500
billion to be the value of autonomous consumption and 0.75 to be the value of
the marginal propensity to consume, the consumption function can be written
ttrtrt't'ic,ti I r.trrr;,lt'
C:500+0.75(Y-T)
Either way of writing the consumption function, either in the general version of
equation (3.2) or in the specific numerical example, states that total consump-
tion is the sum of autonomous consumption and induced consumption.
The consumption function can also be shown graphically, as in Figure
3-1. The thick red line shows on the vertical axis the amount of consumption for
alternative values of disposable income (measured along the horizontal axis).
When disposable income is zero, total consumption consists just of the
autonomous component ($5OO billion). For each extra $1,000 billion of dispos-
able income, as we move to the right on the graph, the red consumption func-
tion line rises by $750 billion, since its slope (the marginal propensity to
consume) is 0.75. For instance, at point D disposable income is $8,000 billion and
total consumption is $6,500 billion (consisting of $6,000 billion of induced con-
sumption and $500 billion of autonomous consumption).
L. If a person's disposable income is zero, what is that person's level of con-
sumption spending in the general linear form of equation (3.2)? In the
numerical example?
2. How can that person consume a positive amount with a zero disposable
income? Think of yourself-what options are open to you to buy some-
thing even if you had no income?
Induced Saving and the Marginal Propensity to Save
The simplest way to show the amount of saving is to use a graph like Figure 3-1.
The thick black line shows the amount of disposable income in both a horizon-
tal and a vertical direction; this line is often called the "45-degree" line. Since the
thick red line shows the consumption function, the distance between the two
lines indicates the total amount of saving.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-4-320.jpg)
![64 (.}]APTF]R :J . TFIE SIIPL}.] KIIYNESIAN THEORY OF'INI]f)T{!] DETERNIINATIC)N
FIGURI' 3.1
A Simple Hypothesis Regarding
Consumption Behavior
The red line passing through F and D
illustrates the consumption function. It shows
that consumption is 75 percent of disposable
income pltrs an autonomous conlponent of
$500 billion that is spent regardless of the
lerrel of disposable income. The red sl-raded
area shows tire amount of positive saving that
occurs when income exceeds consumption;
the grav area shows the arnount of negative
saving (dissaving) that occurs when
consumption exceeds income.
HOW DISPOSABLE INCOME IS DIVIDED BETWEEN CONSUMPTION
AND SAVING
10,00t)
8,000
6,500
6,000
4,000
2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 I0,000
Real disposable income (Y-f)
U
q)
=.=
7,
c
o_
X
C
o.F
o_
E
f
C
o
G
CJ
u
I---l rotal
l----l total s.rving negative
Disposable income
To the right of point F, total saving is positive because disposable income
exceeds consumprtion; this is indicated by the red shading. To the left of point F,
total saving is negative because consumption exceeds disposable income; this is
indicated by the gray shading. How can sarring be negative? Individuals can
consume more tl-ran they earn, at least for a while, by withdrawing funds fron-r
a savings account, by selling stocks and bonds, or by borrowing. Negative sav-
ing is quite typical for many students who borrow to finance tl-reir education.
Figure 3-2 illustrates the relationship between induced saving, autono-
mous consumption, and total saving. The top frame duplicates Figure 3-1 but
highlights the division of disposable income between induced consumption
[0.75(Y - T)] and induced saving [0.25U - T)]. The bottom frame subtracts
induced consumption from the top frame and isolates the relationship between
autonomolrs consumption and induced saving.
The shaded rrertical distance between the black and red lines represents sav-
ing (S), that is, the difference between disposable income and consumption:
Ct,rrcr.rl Linear Frttrm
S: Y-T-C: Y-T-Cn-c(Y-T) 5
: -Cu + 0. - c)(Y -T) (3.3)
This sazring fiutction starts with the definition of saving as personal disposable
income minus consulnption; then it substitutes the consumptior-r function from
equatiorl (3.2). The last line simplifies the saving fur-rction, which now states that
N r,r nrt'ric.r I Era ur ple
- Y-T-C: Y-T-500 -0.75U-T)
: -500 + 0.25(y -T)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-5-320.jpg)
![PLANN]jD iiX PIN t)t'l't. titi 6ir
FIGURE 3.2
The Relation Between Induced
Consumption, Induced Saving, and
the Consumption Function
The upper frame duplicates Figure 3-1. The
thin black line shows the dividing line
between induced saving and induced
consumption. Starting at zero disposable
income, each dollar of disposabie income is
divided between 75 cents of induced
consumption and 25 cents of induced
saving. The lower frame subtracts induced
consumption from the upper frame. It
shows the relation between induced saving
and autonomous consumption. Total
saving in both parts of the diagram is
shown by the red and gray shading and
equals induced saving minus autonomous
consumption.
ANY CHANGE IN DISPOSABLE INCOME IS DIVIDED BETWEEN
INDUCED CONSUMPTION AND INDUCED SAVING
lnduced
savi ng
= 0.25 (Y-T)
lnduced
consumption
= 0.75 (Y_T)
2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000
Real disposable income (Y-f)
2,000 4,000 5,000 8,000 10,000
Real disposable income (Y-f)
Induced
saving
= 0.25 (Y-T)
Marginal propensity to
save is the change in
personal saving induced
by a $1 change in personal
disposable income.
personal saving equals minus the amount of autonomous consumption (-C,r)
plus the marginal propensity to save (7 - c) times disposable income U - T).
Notice the three points in both frames of Figure 3-2 marked with letters cor-
responding to different levels of disposable income. At H, disposable income is
zero, so consumption is C,,, or 500, and saving from equation (3.3) is -Cn, or
-500. AtF, disposable income and consumption are equal, so saving is zero. At
D, consumption of 6,500 is less than disposable income of 8,000, so saving is a
positive 1,500.
ffiN$ 1,.
2.
Can you derive a general expression showing how the level of consump-
tion and disposable income at point F depend on autonomous consump-
tion (Co) and the marginal propensity to consume (c)?
If disposable income is 5,000 rather than 8,000, the economy in Figure
3-2 will be at a point between points F and D. Calculate the values of con-
sumption (C) and saving (5) when disposable income is 5,000.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-6-320.jpg)
![(i6
Wuv Drn U"S. Savmc Alnnosr VaNrsH rN 2001?
Figure 3-3 is arranged exactly like Figure 3-1 and shows the actual values of dis-
posable income and consumption spending in the United States during the
years 7929-2001. As in Figure 3-1, the amount of personal saving' is shown by
the light red shaded area between the black and red lines.
Four major conclusions can be drawn from the evidence. First, consumption
increased as disposable income grew during the years since World War II.
Second, in the worst years of the Great Depression, in 7932 and 1933, house-
holds consumed more than their entire disposable incomes, so the fraction
saved was negative (-0.9 percent in7932 and -1.5 percent in 1933). Third, these
usual peacetime relationships were interrupted during World War II (794215),
when consumer goods were unavailable or rationed. In that period, households
F-[(;URII 3-:i
Consumption, Saving,
and Disposable
Income, 1929-2001
In 2001 saving was bareiy
positive and amounted to
a mere 1.6 percent of
disposable income. Saving
was unusualiy high cluring
World War II because
consumer goods were
rationed. During the four
decades before 2001,
personal saving as a
percentage of disposable
income ranged from 5.3 to
9.7 percent.
HOW ACTUAL U.S. DISPOSABLE INCOME HAS BEEN SPLIT
BETWEEN CONSUMPTION AND SAVING
8,000
=--o
O)
O)
o
C
::o
.F
o-
E
C
?
M.
7,OOO
6,000
5,000
4,0O0
3,000
2,O00
'1,000
0
[_-] Area inclicates disposable
income minus consumption,
or personal s.rving
t1929
1 933
1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 6,000 7 ,oo0 8,000
Real disposable income (billions of 1996 clollars)
World War ll
saving bulge
'Be careful to distinguish between "savings" (with a terminal "s"), which is the stock of assets that
households have in savings accounts or under the mattress, from "savrng" (rvithout a terminal "s"),
which is thefTozr per unit of time that leaks out of disposable income and is unavailable for pur-
clrases of consumption goods. It is the flow of sauittg that is designatecl by the symbol S.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-7-320.jpg)
![THE ECONON'IY IN AND OI,IT (X' EOIIII-IBRII]II 67
were forced to consume much less and save much more than is normal in peace-
time, fully 26 percent of disposable income tn7944. After the war, consumers
rushed out to spend their accumulated savings, helping to maintain prosperity.
The fourth conclusion is quite surprising. In the late 1980s and throughout
the 1990s, real personal saving decreased, from about 9447 billion in79}4,to$272
billion in7996, to a mere $121 billion in 2001. The gradual shrinking of saving in
the 1990s was generally attributed to the long stock market boom following 1982,
during which the average value of stock prices increased tenfold. Consumers
were able to raise their consumption relative to their disposable income by sell-
ing some of their stocks that had enjoyed large capital gains. Also, consumers
were able to boost their consumption by taking advantage of lower interest rates
and refinancing their home mortgages. In Chapters 4 and 15 we return to the
influence of interest rates and stock prices on consumption behavior.
3-4 The Economy In and Out of Equilibrium
Until now we have seen that the level of consumption spending depends on
disposable income. But so far we have no idea what the level of income will
actually be. $5,000 billion? $10,000 billion? We need an extra element, besides
the consumption function, to construct our theory of income determination.
This extra element is that expenditure is not always what is desired or
planned, and if some expenditure is unplanned, business firms will adjust pro-
duction until the unplanned component of expenditure is eliminated. The total
amount of spending that people want to do includes only the planned compo-
nent, called planned expenditure (Ep). The rest of expenditwe (E - Er,) is
unplanned and undesired. To simplify, we assume that investment (I) is the bnly
component of total expenditure that can contain an unplanned component,
whereas consumption (C), government spending (G), and net exports (I,JX) are
akuays equal to the planned ctmount.
Er:C+Ip+G+l/X
The four components of expenditure are exactly the same as in equation (3.1),
except that we use a subscript "p" for investment, since only for that component
of expenditure do we need to distinguish between the planned amount (lr,) and
the unplanned amount (1,,).
The next step is to combine the consumption function from equation (3.2)
with the definition of planned expenditure from equation (3.a):
Er,: Cn + c(Y - T) + It) + G +
^/x
(3.4)
(3.s)
A parameter is a value
taken as given or known
r.t'ithin a particular
analvsis.
In words, this states that planned expenditure equals autonomous consump-
tion, plus the part of consumption that depends on disposable income (induced
consumption), plus the fixed values of planned investment, government spend-
ing, and net exports.
The word parameter means something that is taken as given, including not
only exogenous variables but also fixed elements of a function. In the case of the
consumption function, there are two such fixed elements (Co and c), andwe will
take both as given. In addition, the three components of planned expenditure
other than consumption (1r,, G, and NX) can be considered as both exogenous
variables and parameters.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-8-320.jpg)



![72 C]HAP'fER I] . THE SI,{PLE K!]YNESIAN THEORY OF INCOIE DETERX'iINATION
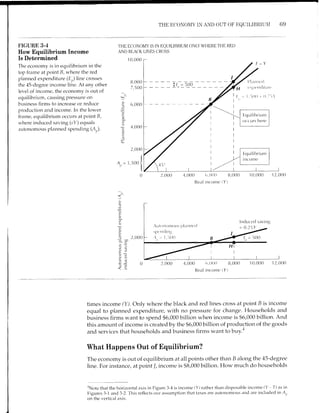
3-5 The Multiplier Effect
Our conclusion thus far that equilibrium income equals $6,000 billion is
absolutely dependent on our assumption that autonomous planned spending
(Ar,) equals $1,500 billion. Any change in autonomous planned spending will
cairse a change in equilibrium income. To illustrate the consequences of a change
in A., we shall assume that business firms become more optimistic, raising their
g.t"dr as to the likely profitability of new investment projects. They increase their
investment spending by $500 billion, boosting Ao from $1,500 billion to $2,000
billion. In each situation where a change is described, a numbered subscript is
used to distinguish the original from the new situation. Thus 4o6 denotes the orig-
inal level of A, ($1,500 billion), and A4 denotes the new level ($2,000 billion).
Calculating the Multiplier
We can use (3.12) to calculate the equilibrium level of income in the new and old
situations. Note that only A,, changes; there is no change in the marginal Propen-
sity to save (s).
(,1'tl('l'.11 I itlt',ll Iittl'tll N r-r nrclic.r I F ra rtrp it'
2,000
Y,:; ^- : 8,000- u./-3
1,500
Y' : iru
: 6'ooo
Take new situation Y1 --
Subtract old situation Y,, :
A
^p7
s
4q
s
The multiplier is the ratio
of the change in output to
the change in autonomous
planned spending that
causes it. It is also 1.0
divided by the marginal
propensity to save.
(,t'rlet.ai I-tttc.lt' lrot rtt
AY 1
multiplier (k) : :
LAt, s
Equais change in income
multiplier (k)
AY:#:2,ooo (3.13)
AA,,
AY: -r
s
The top line of the table calculates the new level of income when A7,1rs at
the new value of 2,000. The second line calculates the original level of income
when,4,,,, is at the old value of 1,500. The change in income, abbreviated AY, is
simply the first line minus the second. The multiplier (k) is defined as the ratio
of the change in income (LY) to the change in planned autonomous spending
(LA) that causes it:
Lr nit't'ica I l:x.t rrr ;r ie
Ar: 1 :4.0
LAr, 0.25
In Figure 3-5 we can see why the multiplier (k) is 7f s, or 4.0. Figure 3-5
reproduces from Figure 3-4 the original situation, with A, at its original value of
$1,500 billion.
The 9500 billion increase in A,causes the A,, line to shift upward by $500 bil-
lion and to intersect the fixed induced saving line at point /. Because only 25 per-
cent of extra income is saved, income must rise by $2,000 billion to generate the
required $500 billion increase in induced saving. In terms of the line segments:
R/ 1.. RB,
RB: s(slnces: Rl)
Example of the Multiplier Effect in Action
How does the magic of the multiplier work? One answer is given by Figure
3-5, which is based on the idea that the economy can be in equilibrium only
(3.14)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-13-320.jpg)


![76 CHAPTER i] . THE SIMPLE KEYNESIAN THEORY OF INCOI'IE DETERNIINATION
defined in Section 2-4 as tax revenue minus government expenditure (T - G),
which in turn equals investment plus net exports minus private saving.'
T-C=1+l/X-S
Similarly, the change in the left side of the equation must balance the change in
the right side:
AT-AC-A/-Al/X-AS (3.16)
When the government boosts its spending by 500, the movement in Figure
3-5 from point B to point / assumes that autonomoLrs consumption, investment,
and net exports are fixed (ACu : A1 : Al/X : 0) and that tax revenue remains
at zero (AT : 0). Thus the only elements of (3.16) that are changing are AS and
AC. The value of AG is the fiscal stimulus of 500. But what is the value of AS?
Recall from the saving function shown in equation (3.3) that saving changes by
the marginal propensity to save times the change in disposable income,
AS : r^(AY - AT). Using this expression for saving, we can substitute the num-
bers for this example into equation (3.16) and obtain:
AT - AC : AI + Al/X - s(AY - LT)
0-AC:0+0-s(AY-0)
0 - 500 : 0 + 0 - 0.25(2,000) : -500
The $2,000 billion increase in output induces $500 billion of extra saving. Each
extra dollar of saving is available for households to purchase the $500 billion of
government bonds that the government must sell to finance its $500 billion gov-
ernment budget deficit. The payoff of this government deficit is the $2,000 boost
in income needed to raise income to its desired amount.
The Tax Multiplier
As an alternative to stimulating the economy by raising government spendir-rg
by $500 billion, it could choose to reduce autonomous taxes by $667 billion. As
we have seen, these two actions have exactly the same effect, which is to boost
autonomous planned spending by $500 billion and to raise income through the
multiplier effect by $2,000 billion.
How is the multiplier for a change in autonomous taxes stated? As before,
the change in income (AY) is equal to the change in autonomous planned spend-
ing (LA,,) divided by the marginal propensity to save (s):
C,t'ncr.r I L.it'tt'ir r Fonrr
A,,
-
LA,
- -cLTn_r : ' :
5S
NLrnrt'ricaI []r.trlplc
Ay : - (q4I 667) : :19 : 2,ooo (2.17)
0.25 0.25
Here we replace (LAr) by the effect of autonomous taxes on autonomous
planned spending (-cLT).
TSee
equation (2.5) on p. 36.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-17-320.jpg)
![The multiplier for an increase in taxes is
(3.17) divided by ATn.
Clcncrr-rl l.i rrt:a r []orrn
FISCAL POI,ICY 77
the income change in equation
NunrcricaI l:xitnrPlc
-g : 4!: -'L:, _ -c ^l : -gf!: _3.0 (3.18)
A4 sAL sAl] s 4L 0.25 J'v
Financing a Tax Cut
When the government decides to stimulate the economy with a tax cut, as did
the Bush administration in 2001, then the reduction in tax revenues raises the
government budget deficit. In fact, to achieve the same degree of stimulus,
enough to raise income by $2,000 billion, the government must cut taxes by $667
billion and run that amount of extra deficit, more than is needed when the econ-
omy is stimulated by the alternative method of boosting government spending
by $500 billion.
To see how this larger government budget deficit is financed, we use the
same equation (3.16) as before and substitute the example of a$667 billion tax cut:
AT - AG : AI + Al{X - s(AY - AT)
-667- 0 : 0 + 0 - 0.25[2,000 - (-667)l
-667 : -0.25(2,667) : -667
The $2,000 billion increase in output plus the fi667 billion tax cut boosts dispos-
able income by $2,667 billion, thus inducing 0.25 times 2,667 or $667 billion in
extra saving. Each extra dollar of saving is available for households to purchase
the $667 billion of government bonds that the government must sell to finance
its $667 billion government br"rdget deficit.
1. If govemment spending is reduced by $500 billion and the rest of the
example in the text is retained, how much does saving change?
2. What is the government doing when it runs a surplus, and how do private
savers react?
3. If taxes are raised by $667 billion and the rest of the example in the text is
retained, how much does saving change? How do private households pay
for the higher taxes?
The Balanced Budget Multiplier
In the previous example, the government could boost income by $2,000 billion
either by raising government spending by $500 billion or by cutting taxes by
$667 billion. Yet either method would create a large increase in the government
deficit, which may be undesirable. Yet, surprisingly, the government can stimu-
late the economy even if it needs to maintain a balanced budget. To see this, we
simply add the multipliers for government spending (k : 1/s) and that for a
change in taxes (tnx change multiplier : -c/s):
-c - c
: :1.0
ss
1
I
I
I
s
Balanced budget multiplier (3.1e)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-18-320.jpg)
![78 T]IIAT'TUR I] . THE SIXIPI,E KEYNESIAN TH!]ORY OF IN['[)NIE DETER'TINA'IION
II'{TERI{ATIOIAL
PERSPECTIVE
.-/ne method to stabilize the economy by reducing
the arnpiitude of business cycles is to ttse "counter-
cyclical" fiscal policy. Such a poiicy operates "counter"
or "against" the bttsiness cycle by using fiscal stimulus
(higher spending or lower taxes) when the economy is
weak and using the reverse when the economy is
strong. Hor.t,ever, fiscal policy in practice rtlns up
against major problerns. If government spending is
used, then government spending on what? If the gov-
ernment takes a long time to develop plans for projects
like highways, hospitals, or schools, the economy's
condition in the meantime may have changed from too
weak to too strong. If tax cuts are used, they may be
delayed by political debates, and households mav
decide to save the tax cut money rather than spending it.
Cor-rntercyclical fiscal policy in the United States has
primarily used tax changes, and spending changes
have rarely been used since the New Deal era of the
1930s. Tax reductions were used to stimulate the econ-
orny in 1,964_-65, for restraint in 7968, and again for
stimulus in 7975 and 1981-83. However the tax cuts of
the early 1980s left the government budget mired in
persistent cleficits until the late 1990s, and this experi-
I ence gave fiscal policy a bad name.
I ttris changed in 2001 when Congress ratified the
] p,'.h .,-lminicfrqfinn'c nrnr-rnqnl fnt cionificenf nrfq ofBush ;rdministration's proposal for significant cuts of
How the United States and Japan Use
Fiscal Policy
income tax rates to be spread over the next half-decade,
starting with checks of $300 (for single filers) or $600
(for joint returns) sent in the mail to American taxpay-
ers in the sumrner of 2001. Skepticism seemed to be
warranted when the personal saving rate jumpecl, indi-
cating that a substantial fraction of the payments had
been saved rather than spent. A more novel use of fis-
cal policy n'as to help U.S. airlines with $5 billion in
emergency aid after the September 11, 2001, attacks
and to offer airlines up to an additional $10 billion in
loans, contingent on a complex set of criteria. Further
fiscal stimulus became caught in a political stalemate,
as Republicans and Democrats disagreed on the form
that the stimulus should take.
Since the early I990s, the Japanese econorny has
been depressed, aud numerous fortns of fiscal stimu-
lus have been employed as the Japanese government
struggles to find a route back to prosperity. In contrast
to the United States, the Japanese place much more
ernphasis on public works projects. To avoid time lags
in starting new projects, the Japanese have a set of
plans ready and vary fiscal expenditures to speed up
or slow down completion of particular projects. For
instance, the 115-mile Tokyo Coastal Bay Expressway
was under construction for two decades. Many
observers are skeptical of the usefulness of many of
Lll__
This states that the multiplier for a balanced-budget fiscal expansion is always
1.0, no matter what the value of c! Why? The positive multiplier occurs because
one dollar of government spending raises autonomous planned expenditure by
exactly one dollar, whereas the extra dollar of taxes only reduces autonomous
planned expenditure by c times one dollar, and c (the marginal propensity to con-
sume) is normally substantially less than unity. Thus, the government can achieve
any desired increase in income and real GDP by a sufficiently large increase in
governlnent spending accompanied by exactly the same increase in tax rates.b
Conclusion
This completes our analysis of the simple Keynesian model of income determi-
nation. As explained at the beginning of the chapter, we have maintained two
crucial assumptions-that both the interest rate and the price level are fixed. We
now turn in Chapter 4 to a more realistic model that builds on what you have
learned but allows the interest rate to vary and to influence the level of
autonomous planned spending. We retain the assumption of a fixed price level
throughout Chapters 4 and 5 before allowing the price level to be flexible, start-
ing in Chapters 6 and7.
8The app-,endix to this chapter shorvs that this simple expression for the balanced budget multiplier
does not apply to a more realistic world in which tax revenues and imports deper-rd on income.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-19-320.jpg)




![AI)PIINDIX T(] CHAPTER IJ E:]
Nlowing for Income Taxes and Income-
Dependent Net Exports
EFFECT OF II{COME TAXES
When the government raises some of its tax re/enue (T) 1'111l an income tax in addition
to the autonomous tax (7,), its total tax revenue is:
T:7,, ltY
The first component is the autonomous tax, for which we continue to use the symbol(7,,).
The second component is income tax rer.enue, the tax rate (f) times income (Y).
Disposable income (Y - T) is total income minus tax re.v'enue:
Yo: Y - T -
"
- r,,- tY :(1 - f)Y - Tn
Leakages from the Spending Stream
Following any change in total income (Y), disprosable income changes by only a fraction
(1 - f) as much. For iustance, if the tax rate ( t) is 0.2, then disposable incorne changes by
80 percent of the change irr total income. Any change in tcltal income (AY) is now divided
into induced consttmption, incluced saving, and induced income tax revenue. The frac-
tion of AY going into consumption is the marginal propensity to consume disposable
incotne (c) times the fraction of income going into clispctsable income (1 - 1). Thus the
change in total income is divided up as shown in the following table.
(1)
(2)
l"r'ltt'1 iotl goi tl!r tr):
1. Induced consumption
2. Induced savirrg
3. Induced tax revenue
Total
(]enerai Liuear F'ourr
c(1 -f)
s(1 - r)
t
+s)(1-t)+t
7-t+f:1.0
Numt'rical Exanrple
0.75(1 - 0.2): 0.6
0.25(1 0.21 - g.'
0.2
1.0
income equals
(3)
I
As in equation (3.9) on p.70,the economy is in equilibrir"rm rvhen
planrred expenditures :
Y:E,,
As before, we can subtract induced consumption from both sides of the equilibrium coll-
dition. According to the preceding table, income (Y) minus induced consumption is the
total of induced saving plus induced tax revenlte. Plernned expenditure (E,,,) minus
induced consumption is autonomous planned spencling(Ap). Thus the equilibrium con-
dition is
induced saving * inducecl tax revenue : autonomous planned spending (,4,,) (4)
From the table just given, equation (4) can be written in symbols as:
[s(1 - t) + tlY : A,, (5)
The term in brackets on the left-hand side is the fraction of a change in income that
does ruof go into induced consttmption-that is, the sum of the fraction going to induced
saving s(1 - f ) and the fraction going to the go/ernment as income tax revenr.re (f). The](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-24-320.jpg)
![84 (IHAPTFiR ll . 'fFIE SIIIPLE KEYNIISIANI THEORY OI" lN(lONIf DETIItriNI[N'TION
The marginal leakage rate
is the fraction of income
that is taxed or saved
rather than being spent on
consumption.
Automatic stabilization is
the effect of income taxes
in lowering the multiplier
effect of changes in
autonomous planned
spending.
sum of these two fractions within the brackets
equilibrium value for Y can be calculated when
the term in brackets:
is called the marginal leakage rate. The
we divide both sides of equation (5) by
rr rlcric.r I lrr.t Ittfrltr
2,000 2,000
- 5,000 (6)
0.25(0.8) r 0.2 0.4
Cle Ircr.rl l,irrcirr [rortrr
4,,
V_ r' Y:t-
s(1-t)+t
The numerical example shows that if autonomous planned spending (At,) is $2,000 bil-
lion, income will be only $5,000 billion, rather than $8,000 billion as in the example
used previously in Chapter 3. Why? A greater fraction of each dollar of income now
leaks out of the spending stream-0.4 in this numerical example-than occurred due
to the savinp; rate of 0.25 by itself. This allows the injection of autonomous planned
spending (Ar, 2,000) to be balancecl by leakages out of the spending stream at a lower
level of income.
INCOME TAXES AND THE MULTIPLIER
The change in income (AY) is simply the change in autonomous planned spending(LA,,)
divided by the marginal leakage rate:
AY: ^ol.- (7)
s(1-t)+t
The multiplier (AYl AA,,) is simply 1.0 divided by the marginal leakage rate. The multi-
plier was 1/s when there was no income tax. Now, with an income tax:
11
mtrltiplier
marginal t"nt og*rate:s(1 -f) f f
(8)
In Chapter 3, where the income tax rate is assumed to be zero, the numerical exam-
ple of the multiplier was 4. This was a special case of equation (8), valid when f : 0, so
that the marginal leakage rate equals simply s, or 0.25.
Now that we have introduced an income tax rate of 0.2, the marginal leakage rate
is 0.4 [see equation (6)] and the multiplier is I /0.4 or 2.5. Thus raising the income tax
rate reduces the multiplier and vice versa. This gives the government a new tool for
stabilizing income. When the government wants to stimulate the economy and raise
income, it can raise income in equation (6) and the mr-rltiplier in equation (8)by cutting
income tax rates. This occurred most recently in 2001. And, when the government
It'ants to restrain the economy, it can raise income tax rates, as occurred most recently
in 7993.
THE GOVERNMENT BUDGET
The government budget surplus is defined as before; it equals tax revenue minus gov-
ernment spending;, T - G. Substituting the definition in equation (1), which expresses tax
revenue (T) as the sum of autonomous and induced tax revenue, we can write the gov-
ernment surplus as:
governmentbudgetsurplus -T - G:Tn+ tY - G (9)
Thus the government budget surplus automatically rises when the level of income
expands. This consequence of the income tax is sometimes called automatic stabiliza-
tion. This name reflects the automatic rise and fall of income tax rer.,enues as income rises](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-25-320.jpg)




![The rate of return on an
investment project is its
annual earnings divided
bv its total cost.
,ITlii RI|LATION OF'ALIT()NOtrTOLIS PLANI'IED SPEI{DING TO THF] INl'I'ItI'S'I'ITA'IIJ E9
4-3 The Relation of Autonomous Planned
Spending to the Interest Rate
We begin by asking why planned investment (a component of autonomous
planned spending) depends on the interest rate. Business firms attempt to profit
by borrowing funds to buy investment goods-office buildings, shopping cen-
ters, factories, machine tools, computers, airplanes. Obviously, firms can stay in
business only if the earnings of investment goods are at least enough to pay the
interest on the borrowed funds (or to attract enough investors to warrant a new
issue of stock).
Bxample of an Airline's Investment Decision
American Airlines calculates that it can earn $10 million per year from one addi-
tional Boeing 757 jet airliner after paying all expenses for employee salaries, fuel,
food, and airplane maintenance-that is, all expenses besides interest payments
on the borrowed funds. If the 757 costs $50 million, that level of earnings repre-
sents a 20 percent rate of return ($10,000,000/$50,000,000), defined as annual
earnings divided by the cost of the airplane. If American must pay 10 percent
interest to obtain the funds for the airplane, the 20 percent rate of return is more
than sufficient to pay the interest expense.
In the top frame of Figurc 4-7, point A shows that the 20 percent rate of
return on the ftrst 757 exceeds the 10 percent interest rate on borrowed funds.
The steplike red line in the top frame of Figure 4-1 shows the rate of return on
the first through fifth planes. The gray area between point A and the 10 percent
interest rate represents the annual profit rate made on the first plane. Point B for
the second plane also indicates a profit. Point C shows that purchase of a third
extra 757 earns only a 10 percent rate of return, or $5 million (10 percent of $50
million) in extra earnings after payment of all noninterest expenses.
Why do the second and third planes earn less than the first? The first plane
is operated on the most profitable routes; the second and third must fly on
routes that are less likely to yield full passenger loads. A fourth plane (at point
D) would have an even lower rate of return, insufficient to pay the interest cost
of borrowed funds. How many planes will be purchased? The third can pay its
interest expense and will be purchased, but the fourth will not. If the interest
cost of borrowed funds were to rise above 10 percent but remain below 15 per-
cent, American would purchase two planes instead of three. If the interest rate
were to fall to 5 percent or below, then American would purchase four planes.
The Interest Rate and the Rate-of-Return Line
The interest rate not only influences the level of business investment but also
affects the level of household consumption. For instance, households deciding
whether to purchase a dishwasher or a second automobile will consider the size
of the monthly payment, which depends on the interest rate. In the bottom
frame of Figure 4-, the rate-of-return line shows that the return on planned
investment and autonomous consumption spending (lr, + Co) declines as the
level of spending increases. As for American Airlines, each successive invest-
ment good purchased by business firms is less profitable than the last. Similarly,
each successive consumption good purchasedby households provides fewer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-30-320.jpg)
![1)i) ('l l l ''l'1._li I '
'fI IE /.s L 11 ]l( )l)Ei.
!'IGURI,i 4-l
The Pavoff to Investment for an Airline
and the Economy
The red steplike line in the top frame shows
the rate of return to American Airlines for
purchases of additionalTSTs.If the interest
rate is 10 percent, a profit is made by
purchasing the first two pianes, and the
company breaks even by buying the third
plane. Purchase of a fourth or fifth plane
would be a mistake, because the pianes would
not generate enough additional profit to pay
for the cost of borrowing the money to buy
them. The bottom frame shows the same
phenomenon for the economy as a whole.
AN ]NCREASE IN PLANNED PRIVATE SPENDING REDUCES THE RATE
OF RETURN
12345
Numlter of erlra 757s
ttttl
50 1 00 1 50 200 250 300
Cost ($ millions)
500 1,000 1,500 2,000 2,500 3,000
Real private autonomous planned spending (f * C,l
15
10
C
o-
-c=
Otr
cZ .=
20
15
10
c
o_
-c'.=
q)tr
cZ .=
Profit on first
and second planes
r'--t&*r
Loss made on fourth
and fifth planes
Interest rate
----
Loss area
services than the last (for instance, a family's second car is less important and
useful than its first car).
Determination of the level of It) + Cors a two-step process. First we plot the
rate-of-return line representing firms' and consumers' expectations of the bene-
fit of additional purchases. Second, we find the level of In + Co at the point
where the rate-of-return line crosses the interest rate level.
When the interest rate is 10 percent, as in Figure 4-1, autonomous planned
spending (1, + Cr) will be $1,500 billion at point C, as long as the level of busi-
ness and consumer optimism remains constant. A decrease in the interest rate
will increase purchases (10 + Co);for instance, a decrease from 10 percent to 5
percent moves autonomous planned spending from $1,500 billion at C to $2,000
billion at D.
Business and Consumer Optimism
Can purchases ever change when the interest rate is held constant at 10 percent?
Certainly-an increase in business and consumer optimism about the expected
payoff of additional purchases can shift the entire rate-of-return line to the right,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-31-320.jpg)
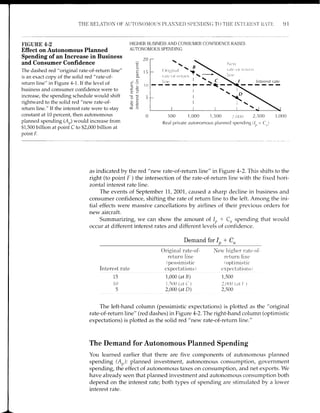





![98 CHAPTI]R ,1 . 'l'l{E IS-L,l,I lOD]ll,
HOW INCREASED CONFIDENCE SHIF'TS THE /S CURVE
2020
c
U
al
g
I rorE
q.)
C
c
6)
(J
o-
9 in
.tr
c
_+
--C I
t
t
l'
I
I
I
1
( )lri /.S,,
1 .-
l
It
0 2,000 4,000 0
Autonomous planned
spending (Ar)
FIGURE 4-5 Effect on the .[S Curve of a Rightward Shift in the
Demand for Autonomous Planned Spending
The "old" A,, demand schedule and IS curve are copied from Figure 4-4. Now we
assume that an increase in the level of business and consumer confidence shifts the Ai,
line $500 billion to the right, just as occurred in Figure 4-2. The 15 curve shifts to tl're
right by four times as much. Notice that the horizontal intercept of the new IS curve at
12,000 is four times the horizontal intercept of the A',,line-that is, A'yt : 3,000.
4-5 Why People Use Money
The second relationship between real income and the interest rate (in addition
to the IS curve) occLrrs in the "money market," a general expression for the
financial sector of the economy. In reality, the financial sector consists of many
assets in addition to money, including short-term debt of corporations and the
government, as well as bonds, stocks, and mutual funds of various types. In this
chapter we n'ill limit our attention to the segment of the financial sector gener-
ally referred to as "money."
The money supply (M') consists of two parts: currency and checking
accounts at banks and thrift institutions. At this stage in the book, the money
supply may be considered to be a policy instrument that the Federal Reserve
Board (the Fed) can set exactly at any desired value, just as we have been assum-
ing that the government can precisely set the level of its fiscal policy instru-
ments-that is, its purchases of goods and services and tax revenues. Later, in
Chapter 13, we will learn how the Fed achieves its control over the money sLrp-
ply in actual practice.
The theory developed in this chapter establishes a link between the rnoney
supply, income, and interest rates. In order to understand the hypothesis
6,000 8,000 10,000 12,000
Real income (Y)
The money supply
consists of currency and
transactions accounts,
including checking
accounts at banks and
thrift institutions.
[u'gf*',+; +rftr rS]
a - l curve to the right](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-39-320.jpg)



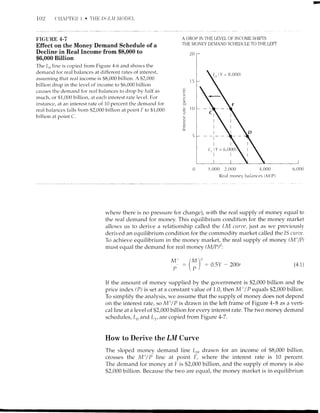
![10ll
A FIXED MONEY SUPPLY IS CONSISTENT WITH MANY DIFFERENT LEVELS OF'INCOME
0 2,000 4,000
Real money balances (MlP)
F'IGURE 4-8 Derivation of t}ne LM Curve
In the left frame the Ln and L., schedules are copied from the previous figure. The
vertical M' / P line shows the available supply of money provided by the government.
The money market is in equilibrium where the supply line (M'/P) ..om"s the demand
line (Lo or L1). When income is $8,000 billion, equilibrium occurs at point l, plotted
:.'iJl'#;:[:11TeH$,'ff :r,"Jt-if :fl ll*?i!:'iH:ffJil:'.il]"n"
shows all combinations of Y and r consistent with equilibrium in the money market.
20
C
I ls
_o_
P
3 io
c
0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 .l
0,000 12,000
Real income (Y)
I (V-Ll ' -
6,000)
when Y : 8,000 (assumed in drawing the Lo line) and r : 10 percent. This
equilibrium combination of values is plotted at point F in the right frame of
Figure 4-8.'
If income is $6,000 billion instead of $8,000 billion, the demand for money is
shown by schedule L, passing through points C and G in the left frame of Figure
4-8. Now the demand for real money balances can be equal to the
fixed real supply of money only at point G, where the interest rate is 5 percent.
Thus Y : 6,000 and r : 5 is another combination consistent with equilibriu.t-t il
the money market, and this is plotted at point G in the right frame of Figure 4-B.n
sThrs, in equation (4.1)
6Thus, in equation (4.1)
2,000 - 0.5(8,000) 200(10)
- 4,000 2,000
- 2,000
2,000 : 0.5(6,000) - 200(5)
: 3,000 - 1,000
: 2,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-44-320.jpg)


![-
106 ('l[APTI']R -l ' TIIFI IS'L]'I N'I()DEI.
HOW A HIGHER REAL MONEY SUPPLY CAN REDUCE THE INTEREST RATE
Higher money
supply shifts
LM curve to right
0 2,000 4,000
Real money balances WIP)
FIGURE 4-g The Effect on the LM Curve of an Increase in the Real Money Supply
from $2,000 Billion to $3,000 Billion
The dashe d LM'line in the figure is identical to LM in Figure 4-8. When the money
supply is increaied, the money available to support output increases and the LM curve
rnifir .ightwa.d by 2.0 dollars per dollar of extra money to the new LM, line.
20
c
9 1s
0.)
1
;O IU
C
0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 12,000
Real income (Y)
New lM, curve
(+ = 3,ooo)
1,, (Y= 8,000)
the LM curae. We must use both relations, the 1S curve and the LM curve, to
cletermine the two unknown variables-income and the interest rate' The next
section joins together the 15 and LM curves to determine the level of both
unknown variables.
4-8 The /S Curve Meets the LM Curve
Now we are ready to examine the economy's "general equilibrium," which
takes account of behavior in both the commodity and money markets. We do
this by bringing together the ISo curve from Figure 4-5 with the LMo curve from
Figure 4-9.
Equilibrium in the commodity market occurs only at points on the 1S curve'
Figure 4-10 copies the 1S,, schedule from Figure 4-5 drawn for a value of
Aiur: 2,500. Ai any point off tne ISo curve-, for instance G and l, the commod-
ity market is out of equilibrium. C, D, and E,, all represent different combina-
tions of income and the interest rate that are compatible with
commodity-market equilibrium. At which equilibrium point will the economv
come to rest? The single ISo schedule does not provide enough information to
cjetermin e both income and the interest rate. Truo schedules are needed to pin
down the equilibrium values of two unknown variables.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-47-320.jpg)
![NI0NETA1TY I)OI,I('' IN A(]'I-i0 107
FIGURE 4.10
The /S and, LM Schedules Cross
at Last
The 156 schedule is copied from Figure 4-5; the
LMo schedule is copied from Figure 4-9. Only
at the red point, E0, is the economy in "gen-
eral" equilibrium, with the conditions for equi-
librium attained in both the commodity market
(along 15) and the money market (along LM).
At points U, V, G, and E, the commodity mar-
ket is out of equilibrium. At points U, V, C, and
D, the money market is out of equilibrium.
THE ECONOMY'S "CENERAL" EQUTLTBRTUM
20
15
P
c
o_
.g 10
a)
c
4,000 6,000 - ,
( )( !0 8,000 1 0,000
Real income (Y)
2,55A, ft = 4,0)
General equilibrium is a
situation of simultaneous
eouilibrium in all the
mirkets of the economy.
The LM curve provides the necessary additional information, showing
all combinations of income and the interest rate at which the money market is
in equilibrium for a given real money supply-in this case, $2,000 billion. Figure
4-10 copies the LMo schedule from Figure 4-9 drawn for a value of Ms/P : 2,000.
At any point off the LMo curve, for instance points C and D, the money market
is out of equilibrium. At D income is too high and the real demand for money
exceeds the real supply. At C income is too low and the real demand for money
is below the real supply. Equilibrium in the money market occurs only at points
such as G, F, and Es, each representing combinations of income and the interest
rate at which the real demand for money is equal to a real money supply of
$2,000 billion.
How does the economy arrive at its general equilibrium at point E. if it
starts out at the wrong place, such as at points U or V ? If the commodity mar-
ket is out of equilibrium and involuntary inventory decumulation or accumula-
tion occurs, firms will step up or cut production, pushing the economy in the
direction needed to reach E0. If the money market is out of equilibrium, there
will be pressure to adjust interest rates, since people will have to sell stocks and
bonds if they cannot otherwise satisfy their demand for money. Either way the
economy arrives at En.
4-g Monetary Policy in Action
The IS-LM model uses two relations (or schedules) to determine the two
endogenous variables, real income and the interest rate. The exogenous vari-
ables, which the model does not explain, are the level of business and consumer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-48-320.jpg)

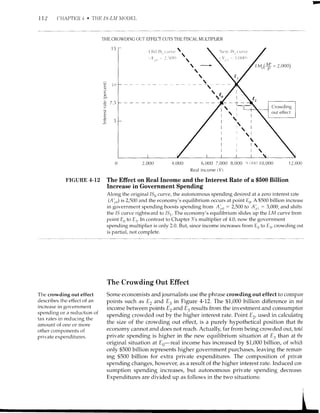
![HOV F'ISI]AL EXPANSION CAN "CROWD OUT'' I}.iVEST1I}'NT 109
FIGURE 4.11
The Effect of a $1,000 Billion
in the Money Supply with a
Normal LM Curve
fncrease 2o
We repeat the $1,000 billion increase in the
money supply that was shown in Figure 4-9.
In order to maintain equilibrium in both the
comrnodity and money markets here, two
effects occLrr: equilibrium income rises and the
interest rate declines, as indicated by the
movement from Eo to Er.
A HIGHER MONEY SUPPLY BOOSTS INCOME AND CUTS THE INTEREST RATE
c
o 10
o
CJ
c
2,OOO 4,000 6,000 7,000 ii,(xx) 10,000 12,000
Real income (Y)
Old lM,,curve /
(ry = 2.ooo) | P '/
New lM, curve
(+:3,ooo)
Equilibriunr
moves to nere
by reducing the real money supply from $3,000 billion
result, the LM, curve would shift leftwards to LMo, and
from $8.000 billion to $7,000 billion.
to $2,000 billion. As a
income would decline
4-10 How Fiscal Expansion Can "Crowd Out"
Investment
In the last section we exarnined the effects on real income and the interest rate
of changes in monetary policy by shifting the LM curve along a fixed 15 curve.
Now we shall do the reverse and shift the 15 curve along a fixed LM cun,e. The
original 15 curve is copied from Figure 4-10 and is labeled in Figure 4-12 (on
page 772) as the "old lSo curve " ; it is drawn on the assumption that the amount
of autonomous planned spending that would occur at a zero interest rate (Ai,o)
is equal to $2,500 billion.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy Shifts the /S Curve
An expansionary fiscal policy taking the form of a $500 billion increase in gov-
ernment purchases shifts the 1S curve to the right. Note that the horizontal dis-
tance between the old and new 15 curves is not $500 billion but $2,000 billion,
since the horizontal shift of 15 is $500 billion times the multiplier, still assumed
to be 4.0.
Figure 4-72 demonstrates that the effect of an expansionary fiscal policy on
real income is not indicated by our original Chapter 3 multiplier (k : 4.0) once](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-50-320.jpg)

![FIOV I'I S(]AL EXPANSION (]AN *CRO'D (]T]T" I N V I,] S1' N I E NT 111
the strong actions that many observers agreed were
needed. At the other extreme was France, where con-
sumer confidence hit all-time highs in late 2001 and
early 2002. The French economy was expected to con-
tinue growing at the most rapid rate of all the large
European countries, and French consumers reported a
record-high readiness to purchase cars and houses, as
well as optimism about the outlook for their own
household finances.
The ripple effects of the September 11 attacks
impacted the U.S. economy, and this amplified a sharp
decline in U.S. imports that was already underway and
that reduced net exports in many economies, particu-
larly in Asia. But, aside from the effect on foreign trade,
the attacks had virtually no separate impact on con-
sumer confidence in other countries, while even within
the United States, the slide in consumer confidence
was surprisingly small and short-lived.
.,1'
oL
1 9BB 1 989 1 990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1 995 1996 1997 ',r
998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003
Source: The Conference Board
taken into account. The increase in the interest rate from 7.5 to 10 percent cuts
private autonomous planned consumption and investment spending by $250
billion, fully half of the $500 billion increase in government spending. Thus fully
half of the original multiplier of 4.0 is "crowded out."
Comparison of Equilibrium Positions Eo and Eg
120
110
100
il90
x --
-o
c
70
Initial8,,
Interest rate (r) 7.5
Private autonomous spending Qp + C,,: 2,500 - 100r) 7,750
Government spending (C) 0
Total autonomous spending (A, : I, I C,? + C) 1,750
Income (Y : 4.04t)) 7,000
Ncu, E,
10.0
1,500
500
2,000
8,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-52-320.jpg)
![SL]NIIIARY
At O.,
500
1,500
6,000
8,000
113
Covernment purchases
Autonomous private spending (lp + Ca)
lndtrced consumption
Total real expenditures
At E0
0
7,750
5 ?50
z;,ntoo
Can Crowding Out Be Avoided?
The fundamental cause of crowding out is an increase in the interest rate that is
required whenever income rises and the supply of money is fixed while the
demand for money responds positively to an increase in income. To offset the
increase in the demand for money caused by higher income, it is necessary for
the interest rate to rise by enough to offset the effects of higher income on the
demand for money.
The simplest way to avoid crowding out would be for the Fed to increase the
money supply, thus allowing the LM curve to shift rightward by the same
amount as the /S curve. Another possible exception to crowding out would be if
the demand for money did not depend on income. Other hypothetical situations
in which crowding out would be avoided are when the 15 curve is vertical (that
is, the interest responsiveness of spending is zero) or when the LM curve is hor-
izontal (that is, the interest responsiveness of the demand for money is infinite).
In the next chapter we will begin by examining some of these situations in
which monetary policy and fiscal policy are unusually strong or weak, then study
interactions among monetary and fiscal policy, and finally learn about effects of
the government budget surplus or deficit on trade, investment, and growth.
1. Interest rates allocate the supply of funds available
from savers to alternative borrowers. Not only do pri-
vate households and firms borrow in order to buy
consumption and investment goods, but the govern-
ment also borrows to finance its budget deficit.
2. Private autonomous plannecl spending W) depends
partly on the interest rate. The higher the interest rate,
the lower is A,,.
3. Private autoiomous planned spending (Ar) also
depends on the optimism or pessimism of investors
and consumers about the future. An increase in optr-
mism tends to raise A, for any given level of the inter-
est rate.
4. The 1S curve indicates all the combinations of the
interest rate and real income at which the economy's
commodity market is in equilibrium. At any point
off the IS curve, the commoditv market is out of
equilibrium.
5. The main functions of money are its use as a medium
of exchange, a store of value, and a trnit of account.
6. The real quantity of money that people demand
depends both on real income and on the interest rate.
Equilibrium in the money market requires that the real
supply of money equal the demand for real money
balances.
7. The LM curve represents all the combinations of real
income and of the interest rate where the money mar-
ket is in equilibrium.
8. An increase in the money supply raises real income
and reduces the interest rate when the 15 curve has its
normal negative slope and the LM curve has its nor-
mal positive slope.
9. A fiscal expansion raises reai income and the interest
rate, causing crowding out if the money supply is held
constant and both the 15 and LM curves have their
normai slopes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-54-320.jpg)

![tz.
(c) responsiveness of the demand for money to
income
(d) business and consumer confidence
(e) interest rate (r)
(0 price level (P)
Suppose Congress raises autonomous taxes. How will
this tax hike affect real income? The interest rate?
Consumption? Planned investment?
13. If the A,, demand schedule shifts to the right, r.l'hat
happens to the real interest rate? Does the chan5;e in
real interest rate amplify or dampen the swings in
income that result from changes in,4,,?
14. You learned in Chapter 1 that infltrtion speeds up
when actual real GDP exceeds natural real GDP. If pol-
icymakers believe that actual real CDP is too high and
fear that inflation r.t,ill rise, how could they use lnone-
tary and fiscal policies to reduce actual real GDP?
Describe how each policy woulcl work ancl its effects
on the economy.
15. Evaluate the follou,ing argument trsing the 1S-LM
model: When consumer and business confidellce are
high and the economy is booming, the interest rate is
high. Therefore, cluring a recession the Fed could pro-
mote tr higher ler.el of income if it trsed monetary pol-
icv to raise the interest rate.
PR(}I]LEMS
*1. Let the structure of the commodity rnarket be repre-
sented by the following equations: C : Cu +
0.75(Y T), C,, : 200 70r, T : 200 + 0.2Y,
1,. : 300 - 3]r,ernd C : 400.
thl Wnat is the value of the multiplier (k)7
(b) What is the equation of the autonomous planned
expenditure iurrctir-rn? (Hirtt: Just substitute the
erluations given above for C,,, T, and 1,, .rnd the
value given above for G into the geueral formttla
for A,,: A,,: C,, - cTn + It, + G + NX,/. In this prob-
lem NX,, : 0.)
(Jlrt]sTloi{s rNI) f,R( )BLF}tS I 1 ir
and parameters /r and/in the LM curve: Mt /P = 300,
h:0.1, and/:50.
(a) What is the horizontal intercept of the LM curve?
(b) What is the slope (Lr / LY ) of the LM curve?
(c) What is the equtrtion of tlre LM cun,e?
(d) If the Fed increased the money supply by 100, at
r.vhart value on the horizontal axis r.r,ould the LM
curve intersect it? What happens to the slope of
the LM curve?
*3. Using the inforrntrtion contained in problems 1 and 2,
what is equilibrium real income (Y) and the interest
rate (r)
(a) in the inititil situation (i.e., G : 400, M' / P - 300)?
(b) if C increases to 450? What is the amount of
autonomous spending that is crolt'ded out irr this
situ.-rtion? What happens to velocitv?
(c) if M'/P increases to -100?
(d) if both C antl M'/P increase (i.e., C : 450 ancl
M' /P - 4oo)?
*4. Assume that the economv is initially in equilibriunr at
a ler..el of real output (Y) oi $5,000 ancl an interest rate
(r) ctf 5 perccnt. If as a result of an incrcase in govern-
ment spending of $500, the economy rrloves to a new
eqr-rilibritrm at Y : $5,750 trncl r : 6.5 percent (.rud
given that k : 3), how much Y woulcl be crowded ottt
due to the increasc in the interest rate? How much
autonor-rrous spencling r,t,oulc1 be cror,r,ded out? What
is the value of the cocfficient for intercst-rate r€'spon-
o siveness of the 15 curve? Of the A,, dernand schcdule?
*5. Assume that the following ecl,rations summarize. the
structnre of an ecolromy.
C: C,, + 0.8(Y - T);
C,,: 700 - 15r;
T :200 + 0.2Y;
(M/P|l : 0.7Y - 70r; M'/P: -1.10;
/,, : 500 25r;
i - 1,100;
NX: 100 - 0.04Y.
Answer the follovviug questions:
(a) What is the ecluation of the 15 cun,e?
(b) Whtrt is the eclttation of the LM cun,e?
(c) What is the equilibritrm retrl output?
(d) What is the erprilibrium interest rate?
(e) What is the level of saving at equilibrium?
(f) What is the level of planned investment at eqr.ri-
libriurn?
(g) Determine r.t,hether leakages equ;rl injectiorrs at
equilibrium.
(h) Assr.rme that r : 4 arrcl Y : 5,t100. Is there an
excess denrtrnd for money or cxcess suprply of
money in this situatictrr? Hort, mttch? Is there
unplanned inventory change? If so, what is the
vahre of the urrplannerl irrventory change?
What is the equation of the IS curr.e? (Hirrf: The
general equation for tht. 15 curve is Y : kA,,.)
Wlrat is the slope of the /S curve (r / LY )?
If government spencling increased by 50, zrt what
value on the horizontal axis would the new 1S
cllrve intersect it? What would happen to the
slope of the 15 cun'e?
*2. The equation of the LM ctrrve is given by the follow-
ing formula: Y : l(M'/P) + frl/lt, where M'/P is the
real money sr-rpply, /r is the response of money
derr-rand to a $1 change in income at a fixecl interest
rate, and/ is the response of money demand to a one
percentage point change in the interest rate. Assume
the folkrvving values for the exogenous yariable M'/P
(c)
/.-t
Ll/
(e)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gordonmacro-140722094513-phpapp01/85/Keynesian-Income-Determination-56-320.jpg)
