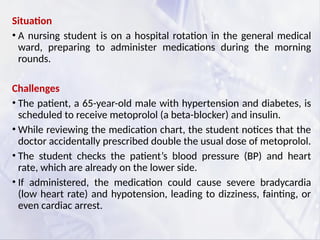
Nursing is both an art and a science, requiring technical expertise, critical thinking, and interpersonal skills. Professional nursing etiquette refers to the set of professional behaviors, ethical standards, and courteous interactions that guide nurses in their clinical practice. It ensures smooth communication, fosters trust with patients and colleagues, and enhances the overall healthcare experience.
Objectives
To understand the fundamental principles of professional nursing etiquette
To recognize the importance of etiquette in patient care and interdisciplinary collaboration
To develop appropriate communication skills and professional behaviors
To enhance the reputation of nursing as a disciplined and respected profession
To integrate ethical principles with professional decorum in daily practice.
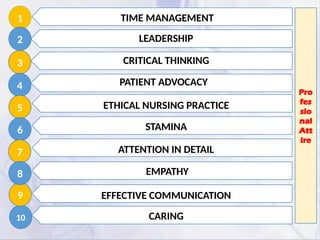
Professional nursing etiquette encompasses the values, attitudes, and behaviors that govern a nurse’s interactions with patients, families, and healthcare professionals. It includes courtesy, respect, effective communication, and adherence to ethical and professional standards.
Importance of Nursing Etiquette
Enhances Patient Trust and Comfort: Patients feel more secure and respected when nurses exhibit professionalism.
Fosters Effective Communication: Proper etiquette ensures clear and respectful interactions among healthcare team members.
Promotes Ethical Practice: Following etiquette guidelines aligns with ethical nursing principles.
Encourages Teamwork and Collaboration: Professionalism strengthens interdisciplinary relationships, leading to better patient care outcomes.
Maintains Workplace Harmony: A respectful work environment reduces conflicts and improves job satisfaction.