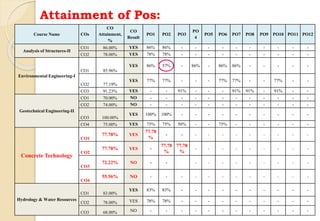
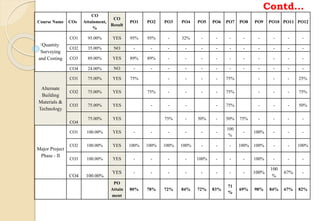
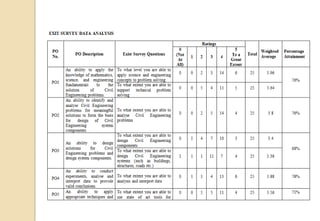
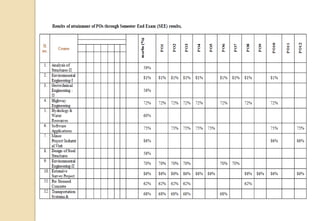
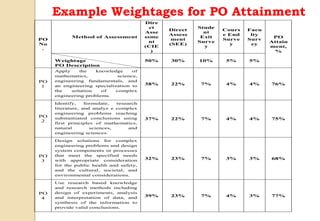
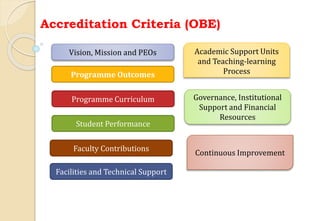
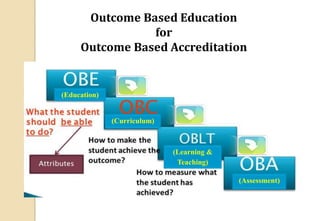
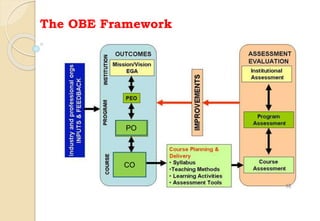
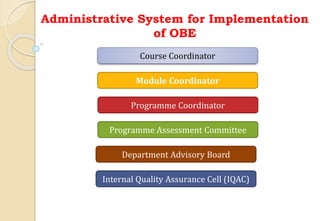
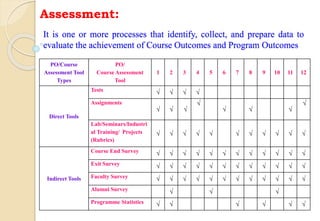
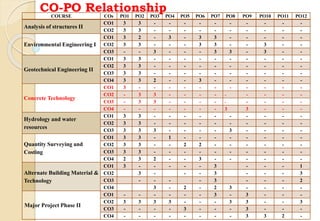
The document discusses key aspects of outcome-based education (OBE) and accreditation. It explains that OBE focuses on achieving high-order learning and mastery rather than just accumulating course credits. Globalization requires education to build learner competencies for a changing workplace. Accreditation criteria under OBE include vision, mission, program outcomes, student performance, curriculum, faculty contributions, facilities, academic support, governance and continuous improvement. Proper implementation of OBE requires defining program outcomes, course outcomes, assessment tools, and mapping the relationship between courses and outcomes.






































Q1.a, b,
Q2 a,b
- - - -
CO2
Compare behaviour of
concrete properties with
known materials for design
applications(PO2, PO3)
A1 - - -
CO3
Analyse characteristics of mix
constituents and design a
concrete mix for field
applications.
{ PO2, PO3)
Q1, Q2
-
A2
-
-
CO4
Prepare a comprehensive
report on new knowledge in any
one of the topic related to
concrete technology [K5] (PO8,
PO9)
- - lab-
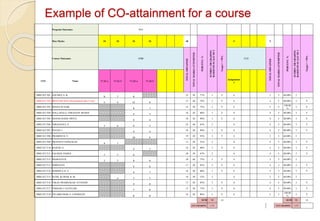
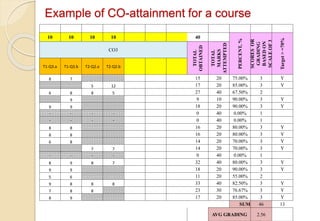
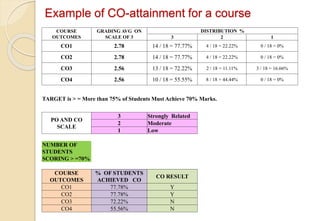
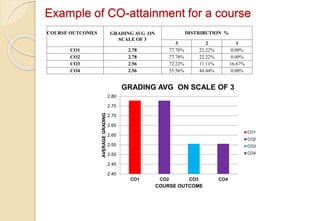
Example of CO-attainment for a course
Course Name
:
Concrete Technology
Course Code
:
CV 41
Session of
Course
Batch-2013, Sep-
Dec'2013
L : T : P -
Semester : I
Credits : 4
Batch : 2013
Faculty :R V Ranganath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/keycomponentsofobe-220829073817-c5e4c176/85/Key-Components-of-OBE-pptx-47-320.jpg)