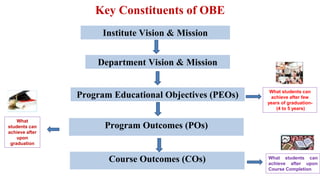
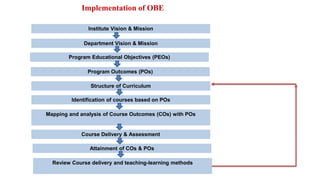
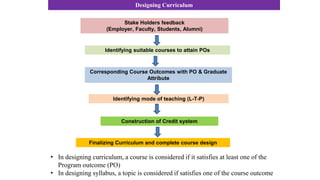
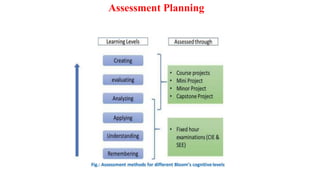
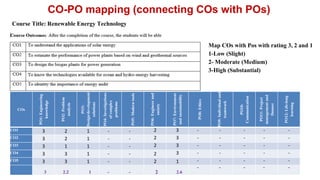
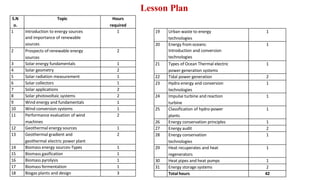
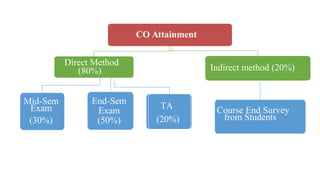
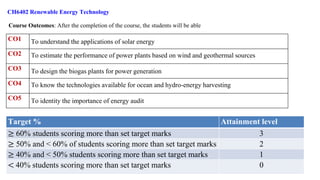
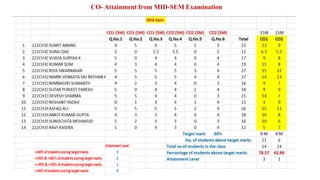
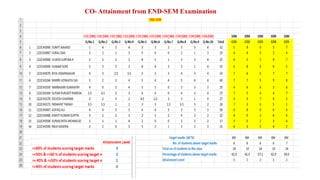
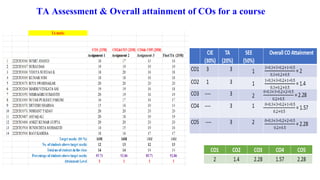
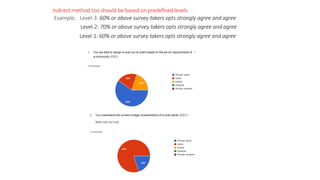
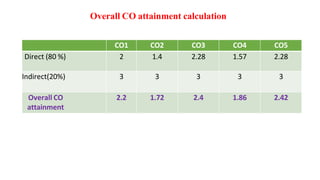
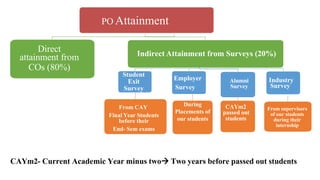
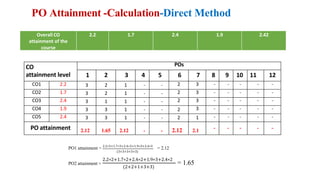
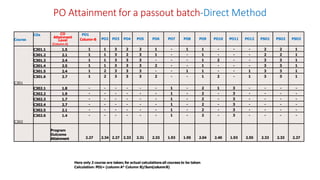
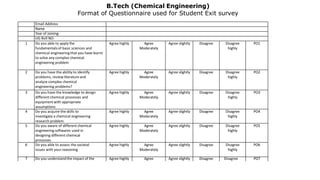
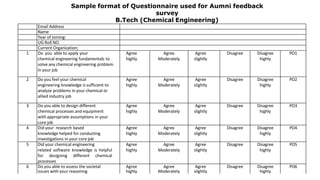
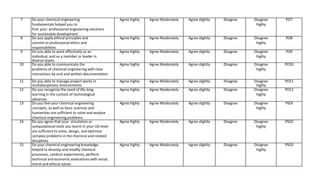
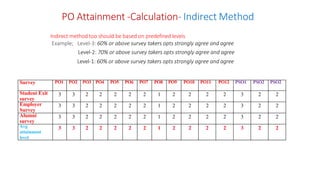
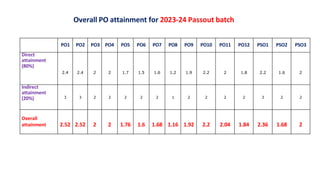
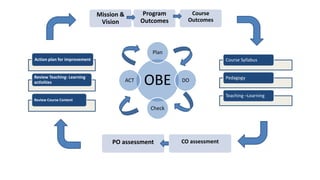
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) is an educational philosophy that prioritizes achieving specific, measurable competencies rather than merely covering content. It emphasizes student-centered instruction, flexible teaching methods, and assessments aligned with predefined outcomes to prepare students for real-world challenges. The document discusses the key principles of OBE, its significance in technical education, potential challenges, and a detailed framework for implementing and assessing educational programs.